If inventory or other work supplies have lost their functions or for some other reason they cannot be used, then such objects are written off. Inventory in agriculture is written off by filling out an act for writing off inventory and household supplies. It has the form 421-APK. Let's look at the features of filling it out.
- Form and sample
- Free download
- Online viewing
- Expert tested
FILES
Inventory write-off act
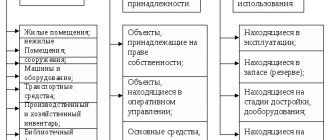
In accordance with OK 013-2014, inventory is part of fixed assets, which includes:
- household equipment, i.e. items not directly used in the production process;
- production equipment, i.e., technical items that are involved in the production process, but cannot be classified as either equipment or structures (Order of Rosstandart dated December 12, 2014 No. 2018-st).
Inventory includes, for example, containers for storing liquids, devices and containers for bulk, piece and packaged materials, work tables, racks, clocks, cleaning carts, cleaning material, mops, brushes, fire-fighting equipment (fire cabinets, panels , buckets, barrels for water, boxes for sand, cabinets for placing fire extinguishers, etc.), sports equipment.
Industrial and business inventory generally refers to types of property that meet the criteria of fixed assets, along with buildings and structures, machinery and equipment, computer equipment and vehicles (clause 5 of PBU 6/01). However, taking into account that the cost of a unit of inventory, as a rule, does not exceed 40,000 rubles, inventory is usually taken into account not as part of fixed assets, but as part of inventories. It is no coincidence that the Chart of Accounts provides for the opening of subaccount 10-9 “Inventory and household supplies” to account 10 “Materials”. As noted, this sub-account takes into account the presence and movement of inventory, tools, household supplies and other means of labor, which are included in the funds in circulation (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
How to draw up an inventory write-off act?
Features of accounting in a budgetary institution
The legislation does not clearly define what kind of property can be classified as inventory and household supplies (IHP). In accordance with established practice, IHP in budgetary institutions consists of:
- office furniture (cabinets, chairs, tables, bedside tables);
- electronic equipment (voice recorders and tablets, video cameras and cameras);
- devices for keeping rooms, workplaces and surrounding areas clean (mops, brooms, brooms, buckets);
- devices intended for lighting;
- things for toilet procedures (towels, soap, fresheners, sprays and gels);
- fire extinguishing equipment (fire cabinets, stands, fire extinguishers, shovels, hooks);
- household and kitchen appliances (refrigerators, coffee makers, microwave ovens, coolers);
- stationery
The criteria for classification as OS or materials are standard. The main one is SPI (useful life). When it is greater than 12 months, these non-financial assets are correctly reflected among fixed assets. Accordingly, those household supplies that will be written off in less than a year are inventories.
Activating inventory write-off
Write-off of inventory means the transfer of its value from the credit of account 10 to the debit of the corresponding accounts (mainly costs) in the case of the use of inventory for production and management purposes, its disposal due to unusability after expiration of the storage period, as well as obsolescence, disposal when shortages are identified, theft or damage. There is no mandatory form for the inventory write-off act. Therefore, for an act on the write-off of production equipment, as well as for an act on the write-off of business equipment, the organization develops a sample independently. At the same time, regardless of the type of inventory, a single sample form can be developed in compliance with the requirements for the presence in it of the mandatory details of the primary accounting document (Part 2 of Article 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
Unified forms approved by the State Statistics Committee can be used as an act for writing off inventory when released into production. For example, form No. M-11 “Demand-invoice” or form No. M-8 “Limit-fence card” (approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of October 30, 1997 No. 71a).
To write off unusable equipment, an organization can develop an act form, for example, similar to the act for writing off workwear, the form of which we have given. Or turn to industry forms specifically approved for recording inventory write-offs and, based on them, develop your own forms. For example, form No. 421-APK “Act on write-off of inventory and household supplies” (approved by Order of the Ministry of Agriculture dated May 16, 2003 No. 750) or form according to OKUD 0504143 “Act on write-off of soft and household equipment.” An organization approves a sample of the developed form of an inventory write-off act in its Accounting Policy for accounting purposes.
An inventory write-off act is usually drawn up by a commission specially created for this purpose, certified by the signatures of its members and approved by the head of the organization.
Here is a sample of filling out an act for writing off soft equipment, drawn up according to the form for state (municipal) institutions. Soft equipment includes, for example, bed linen and bedding (mattresses, pillows, blankets, sheets, duvet covers, pillowcases, bedspreads, sleeping bags, etc.) (Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated December 1, 2010 No. 157n). Let us assume that an act is drawn up to write off soft inventory from off-balance sheet accounting, the cost of which was already included in expenses when it was transferred to its intended purpose, but which continued to be registered for control purposes.
Providing soft equipment: norms for issuing and service life of soft equipment.
The standards for the provision of soft equipment and the terms of their operation are regulated by various regulatory documents depending on the profile of the institution, for example:
– Order of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated November 13, 2018 No. 203 established the norms and procedure for providing, at the expense of the federal budget, a free set of clothing, shoes and soft equipment for minors and persons over the age of 18 years, studying and being brought up in educational organizations for students with deviant (socially dangerous) ) behavior that requires special conditions of education, training and requires a special pedagogical approach (special educational institutions of open and closed types); – Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated September 18, 2017 No. 1117 approved the norms and rules for providing, at the expense of the federal budget, a free set of clothes, shoes and soft equipment for orphans and children without parental care; – Letter of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation dated September 22, 1993 No. 164-M provided recommendations for the provision of soft equipment to kindergartens, institutions of secondary vocational education, pupils of general education boarding schools of a general type and boarding schools for children with disabilities in physical or mental development, orphanages , as well as students in boarding schools at full state support; – Order of the State Sports Committee of the Russian Federation dated 03.03.2004 No. 190/l established the procedure for providing participants in the educational process with sportswear, shoes and personal equipment, as well as rules for recording and writing off items of sports equipment; – Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated June 1, 2009 No. 290n approved the rules for providing workers with special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment; – Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 1997 No. 66 regulates, among other things, the procedure for the free issuance of special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment to employees of higher educational institutions.
Act on write-off of soft and household equipment. Form 0504143
The act on writing off soft and household equipment (form 0504143) is used to write off soft equipment, dishes and household equipment. The act is drawn up by a commission and approved by the head of the enterprise. The form is filled out in two copies (the first is sent to the accounting department, the second remains with the financially responsible person).
The form can be filled out by hand or in a machine-readable manner. This is determined by the accounting policy of the enterprise. When registering, the date and number of the document, the name of the organization (institution) and department, the composition of the commission (positions and names), and the details of the legal document (order, regulation) are indicated.
The form consists of two tables and eight columns each. You must provide information such as:
- serial number;
- name of inventory;
- period of operation;
- quantity;
- price;
- sum;
- accounting record accounts.
The final indicators for the quantity and amount of inventory to be disposed of are calculated, and a commission conclusion is drawn up. Next, you need to fill out a table about materials that were received as a result of write-off and are subject to delivery to a warehouse or storeroom. The names of materials, code, unit of measurement, quantity, price per unit and amount are recorded. The last column indicates the purpose of use.
The act is signed by the chairman and members of the commission. At the end of the form, a link is made to the primary document according to which all materials were posted to the warehouse (invoice number and date, total amount).
Disposal of dishes is completed additionally on the basis of the tableware damage registration book. The act serves as the basis for reflecting in the accounting records of the enterprise the disposal of all accounting objects listed in the document.
Ensuring the safety of soft equipment.
In order to ensure the safety of soft equipment items, the institution appoints a financially responsible person (supply manager, warehouse manager, storekeeper, etc.), with whom an agreement on full financial responsibility is concluded.
Before they are put into operation, purchased items and linen are delivered to a warehouse (another special room) and stored there under the supervision of the specified person.
Capitalized soft equipment is subject to marking (clause 118 of Instruction No. 157n). This procedure is carried out by the financially responsible person in the presence of the head of the institution (his deputy) and an accounting employee. Items are marked with a special stamp with indelible paint without damaging their appearance, indicating the name of the institution. And when they are put into operation, additional marking is carried out reflecting the year and month of issue from the warehouse.
For your information:
Marking stamps must be kept by the head of the institution or his deputy.
Some things don't need to be labeled. These include clothing and footwear for all groups of pupils of organizations for orphans and children without parental care (clause 118 of Instruction No. 157n).
However, you should not completely abandon this procedure. The Ministry of Finance in Letter No. 02-06-05/7872 dated February 15, 2016 indicated that the procedure for marking soft equipment provided for in Instruction No. 157n is an established practice and allows us to ensure:
– safety of objects, their quantitative accounting; – compliance with the established wearing (operation) periods; – assigning specific subjects to each pupil of organizations for orphans and children left without parental care.
Therefore, the abolition of the procedure in question regarding all soft equipment and all age groups of pupils of the relevant organizations is inappropriate. In this case, financiers propose to mark clothes and shoes (including sports shoes) of the older age group of pupils (graduates) without damaging their appearance by attaching (sewing on) fabric tokens with a special marking stamp applied with indelible paint.
In addition, the Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 27, 2016 No. 02-07-10/43970 states that, as part of the formation of an accounting policy, an institution has the right, based on the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation, to develop and approve in its structural divisions rules for accounting for soft inventory, including labeling rules.
Equipment write-off act
In production, it is necessary to timely update production capacities. This is necessary to increase labor productivity; in addition, the accumulation of outdated and irreparable mechanisms is prohibited by occupational safety and health regulations.
The form for the equipment decommissioning act has a uniform form, however, in the description of the technical characteristics of the mechanisms, a free detailed description is allowed.
The main points of the content of the act on write-off of mechanisms:
- details of approval by the head of the enterprise (signature, date);
- document's name;
- date of drawing up the act;
- composition of the commission that makes the decision;
- number of the order (instruction) for the enterprise on write-off;
- list of mechanisms that cannot be repaired or are outdated (unit of measurement, quantity, service life, time of entry into operation);
- condition of the equipment at the time of write-off;
- final conclusions about the condition of the equipment;
- signature of the chairman and members of the commission.
After the manager approves this act (his signature is certified by a seal), the act is subject to execution.
The act, signed and approved, is the basis for the accounting department to remove this equipment from the balance sheet as fit for use. All three copies of the text of the act are stored in the accounting department for reporting.
General information
Timely decommissioning of equipment is a necessary requirement for establishing normal accounting. As soon as the devices are documented by the relevant act, they are considered to be written off from the balance sheet of the enterprise.
The act of writing off office equipment assumes that there will be three copies. They must be signed by the management of the enterprise. Every year, managers have the responsibility to draw up an order, on the basis of which a special commission responsible for the equipment is assembled.
When working with the following objects, execution of accompanying acts is mandatory:
- With existing damage.
- When completely worn out.
- Morally obsolete.
- Missing based on inventory results.
- If they cannot be used in the future due to unsuitability.
The act itself must contain the following information:
- Title of the document.
- Date of compilation, approval.
- Name of company.
- The write-off object in number and letter designation.
- List of defects.
- Exact characteristics of flaws.
- Positions of commission members.
- Signatures of each of them.
- The main thing is to accurately indicate the date on which the document was drawn up.
- If the inventory is carried out before the paperwork is completed, this is indicated separately.
- The title is in the prepositional or genitive case.
They begin the text part by indicating the reasons why drawing up the act became necessary. Usually the director's order is indicated as the basis. A certain procedure must be followed when the equipment itself is written off.
Determining the cost of objects deserves special consideration. Indicators of cost for the period of acquisition, transportation costs, fees for consultations, and customs expenses are subject to accounting.
When a document is drawn up, the following regulations are taken as a basis:
- Reporting on manufactured goods for a certain time.
- Planned costing containing information about expenses.
- Reports compiled by financially responsible persons.
Organizations keep documents for no more than a decade and a half. The write-off rules also have the following description:
- At the first stage, objects are examined for technical condition.
- Next, documentation is drawn up listing the resources that have failed.
- Registration of the act.
- Obtaining permission from the director for the actual write-off.
- Dismantling, disposal.
- The write-off procedure itself.
Additional information on the document
Act on write-off of fixed resources - the name of the document that becomes the basis for writing off certain material assets from the register. Mandatory applications include a technical report for decommissioning a computer; a sample is usually easy to find in the public domain.
Signing the act
Mandatory points for such documents are the presentation of the results of examinations and measurements taken. It is impossible to do without a detailed description of the current equipment, existing shortcomings, and possible elimination methods.
Among other things, the act must contain the following information:
- Signatures of each participant.
- List of applicable documentation.
- Troubleshooting tips.
- Final conclusions on the work performed.
- The opinion of each participant.
- The conditions for the inspection are to indicate the exact time along with the equipment used.
- Description of the operation of the equipment being tested.
- Location of equipment.
- The name of what is to be checked, indicating the markings, exact models, and so on.
- Information about everyone present and participating in the procedure.
- Data on experts.
- Place of inspection, date.
Purpose and role of the document
Using the equipment in the future or carrying out disposal are two main situations when the preparation of such documents is required. You cannot do without acts in the following circumstances:
- The need to obtain data regarding the cost of manufactured goods. For example, when a further price is formed.
- Justification, documentary evidence of taxation costs.
- Confirmation of the performance of an asset transferred for use by other enterprises.
- Assessing the condition of warehouse inventory.
Write-off must be carried out in relation to assets that become unsuitable for further use. For example, in case of damage or loss of original qualities.
The document helps confirm the fact that the product was withdrawn from circulation for one reason or another. Thanks to the act, the procedure becomes more formal and official. This is the main document against which equipment is subsequently checked for unsuitability and malfunctions.
About legal regulation
A typical form for a write-off act is established in Government Decree No. 7, which was issued on January 21, 2003. We must also rely on Federal Law No. 402 FZ. He says that companies have the right to develop their own forms to complete the relevant procedure.
Recommendations for filling
One copy of the act remains with the financially responsible person, the other is transferred to the accounting staff. When compiling it will be useful to adhere to the following rules:
- The day the equipment is written off will be considered the date of registration and signing of the act.
- It is acceptable to draw up a document for an entire group of products. It is enough to correctly indicate all the characteristics used.
- Valuables must be named in accordance with the receipt documentation.
- The form must contain a link to the document that served as the basis for the write-off procedure.
- The use of a written form for the act also applies to mandatory requirements.
- It is permissible to use the TORG-16 form as a basis. The name of the document with the place and time of preparation are indicated in the part called the header.
- The main part should be devoted to a description of the equipment and the reasons for write-off.
- The final decision is made by the commission during the last stage of the inspection. The form ends with the initials of the commission members, with signatures.
When filling out there are additional nuances:
- The invoice will help you decide on the names that should be used in a particular case.
- You can separately indicate the time and reason for accepting equipment to be written off.
- The total cost of funds debited is indicated in capital letters.
What to do with the reason
If the equipment is completely worn out, then it can no longer be used for the further activities of the enterprise. Therefore, there is a need to write off. One of the mandatory items in the relevant act is to indicate the reason.
Worn out equipment
There are different circumstances that can be specified:
- Partial liquidation during reconstruction.
- Damage to property.
- Drawing up an agreement for exchange, donation.
- The equipment is transferred as part of the capital to another enterprise.
- An emergency situation that causes liquidation to take place.
- Wear and tear on physical indicators, moral character.
- The need to sell an asset.
Disposal and liquidation are two main groups, one of which can be attributed to each reason.
In case of obsolescence
In practice, wear and tear often remains physical. This means that the equipment is aging “materially”. Because of this, the original value is lost. Wear is associated with the continuous process of operation or emergency incidents.
Obsolescence means obsolescence due to more advanced versions of equipment being introduced. Write-off in this case becomes a mandatory procedure. The main thing is to justify the process and use documentary evidence.
A special commission is appointed to decide whether the equipment can be used in the future. First, the products are inspected, then the reason for write-off is determined.
The special act contains the following information:
- The date when the equipment was accepted for accounting in the accounting department.
- Date of manufacture, together with useful life.
- Initial cost plus accrued depreciation.
- Number of repairs performed.
- Description of the reason that led to the write-off.
- Condition of all main parts and assemblies.
If the procedure is carried out for computer equipment
Many enterprises use electronic equipment, which can also become obsolete over time. From this moment on, the need to register a write-off arises. First, a commission is formed that takes upon itself the responsibility of carrying out the procedure. The main requirement is the availability of special education and appropriate skills in working with equipment.
- The head of the organization himself decides who will be part of such a commission.
- The decision is confirmed by an appropriate order.
- After inspecting equipment that has become unusable, a corresponding report is drawn up, where all conclusions are written. It is necessary to separately determine the cost of computer parts, the use of which is still possible in the future. After this, a statement in form M-4 is filled out so that the office equipment is accepted for accounting.
- The form of the act itself is OS-4.
Regarding objects that have fallen into disrepair
Equipment with material or obsolescence is considered unusable. This often happens for technical reasons when the defects that appear do not allow further repairs. After the manager has issued the order, they begin to draw up the act.
And here you cannot do without a commission responsible for control. The inventory card, which is kept at the enterprise for a maximum of five years, is used when storing disposal data.
Accounting for inventory and household supplies as part of the inventory
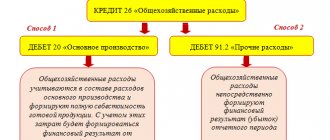
ICP with a useful life of up to a year should be correctly considered as one of the components of the MPZ. For these purposes, the account is used. 10.9. The purchase of household equipment is formalized and reflected in accounting in the same way as it is provided for materials. Read also the article: → “Accounting for goods and products in the warehouse”
The main wiring used in the company:
| Debit | Credit | Explanation |
| 10.9 | 15, 23, 60 | IHPs are accepted for accounting at discount prices |
| 68, 70, 71 ,69 | Reflected the costs of purchasing IHP | |
| 20, 23, 29, 44 | 10.9 | Write-off of the full cost of industrial equipment that has been put into operation |
Example 1. I purchased household gloves from Rostok LLC in the amount of 58 thousand rubles. VAT – 10,440. Accessories were delivered by our own transport.
Subject to write-off:
- The cost of transport services is 8 thousand rubles;
- Travel allowances paid to the forwarder – 2.8 thousand rubles.
The following entries appear in the accounting:
| Debit | Credit | Explanation | Amount, rub. |
| 10 (11) | 60 | Gloves purchased from supplier | 58 000,00 |
| 19 (3) | 60 | VAT reflection | 10 440,00 |
| 10 (11) | 23 (3) | Write-off of transportation expenses | 8 000,00 |
| 10 (11) | 71 | Write-off of travel expenses | 2 800,00 |
| 60 | 51 | The debt to the supplier has been paid | 68 440,000 |
Write-off from fixed assets
OS-4 is a standard form used when fixed assets are written off. A specially created commission is also responsible for drawing up the document. A document is issued if the main resources can no longer be used.
Disposal of obsolete office equipment
The document must reflect the following indicators:
- The relationship between costs and revenue during liquidation.
- Results of the liquidation.
- Expenses during the liquidation process.
- Amount of wear and tear during use.
- The initial value of the object.
- Reason for liquidation.
- The state of the resource in technical terms at the time of document execution.
When the write-off procedure is completed, the object falls off the balance sheet of the enterprise. It is possible for enterprises to store an object; the law does not oblige them to get rid of it. It’s just that another asset is considered the main resource.
Technical report: features
The conclusion of a competent expert, papers on the inspection performed are mandatory attachments for the write-off act. Conclusions can only be drawn up by specialists with appropriate experience and education.
Drawing up a document involves following the established order and using numbering. It is necessary to write about a general assessment of the condition and possible ways to resolve the problem. The management of the organization is separately informed if a problem is found that cannot be eliminated. An employee who is a member of the audit commission cannot independently formulate such acts.
Accounting for inventory and household supplies as part of the operating system
Those types of household equipment that are expected to be used for more than 12 months should be accounted for as part of fixed assets. When developing accounting policies, you should not miss the limitation of their cost. Within its boundaries, operating systems with a period of use of more than a year are taken into account among the inventories. The upper limit is 40 thousand rubles.
You can view the inventory card.
About defective statements
There are several reasons why defective statements are issued when writing off:
- The need to provide a reason why an OS object is being written off. The issue of use and operation is considered from an economic point of view.
- To use the information to analyze the reasons why equipment in an enterprise fails. In the future, this information is used to save on costs and avoid new troubles.
- If necessary, defective statements can be requested by shareholders or partners, customers. Then they can easily be convinced that the write-off procedure was legal.
Indication of the facts due to which the use of the device became impossible is a mandatory part of any such document. It consists of almost the same points as the write-off act. The main thing is to describe the equipment and the identified faults.
What else needs to be considered
The invoice is the basis for the capitalization of valuables, the source of which was the write-off. It is also called the act of acceptance of material assets. The cost of materials is determined on the basis of market prices valid for a particular segment. Actual wear and tear must be taken into account. The assessment results are documented in the appropriate act.
Subaccount 238 is used to account for parts and assemblies if the enterprise allows the use of equipment in the future. In the case of unusable parts, it is recommended to give preference to subaccount 239.
Capitalization and preliminary withdrawal of suitable parts is mandatory if unusable parts of equipment are handed over to special enterprises for further processing and obtaining additional benefits.
At the same time, part of the funds received from scrap processing should go to the state budget.
Managers have the right to freely dispose of the other part of the money. Funds can be used for the economic needs of the enterprise and its further modernization.
Only after signing the act are material assets disposed of in an appropriate way. D94K10 and D20K94 are mandatory accounts that the accountant must use after the transaction. The book value must be indicated in one of the entries. This information is easy to find in the act drawn up earlier.
The amount of the shortage is also indicated separately, if such a phenomenon occurs. Here it is also necessary to rely on the act of writing off material assets. If the shortage occurs due to the fault of the employees, then the citizen responsible for this must reimburse the amount in full. Otherwise, he faces additional fines and penalties.
Tax consequences of writing off equipment that has not been put into operation - on video:
The procedure for writing off materials
To write off material assets, the creation of a special commission is required. It consists of financially responsible persons, as a rule, from different structural divisions of the enterprise. It is their responsibility to identify and examine damage, defects or malfunctions of equipment, machinery, furniture, household equipment, tools and other valuables contained on the organization’s balance sheet.
After recording such facts, they are authorized to draw up an act of write-off of materials. As a rule, in large organizations there are specially developed clear instructions for such actions.
To write off materials, there must be compelling reasons with documentary evidence.
Write-off of materials cannot occur without compelling reasons, confirmed by a certain evidence base. In particular, during the procedure for writing off materials, supporting documents can be used.
So this is:
- reports on products produced over a certain period (its volume, names, etc.);
- reports from financially responsible persons on the material assets used;
- written documents on the consumption of materials in excess of established standards (with justification for these facts);
- approved calculation according to material cost standards for the manufacture of a unit of goods;
- other financial and accounting documents.
Before writing off material assets, the enterprise must conduct an inventory of property and enter its results into the relevant documents.
What applies to inventory items?
The inventory category includes all objects that a company uses during the production process. This group includes various types of consumables, raw materials and work in progress products . It is important to note that even unsold items are inventories owned by companies. It is necessary to write off such objects if it is impossible to use them further or transfer them to third parties. In the case of consumables and raw materials, a write-off act is issued during the transfer of objects to production.
All objects owned by the company must be reflected in the financial statements. This means that tools that have become unusable cannot be disposed of without the appropriate document. Otherwise, during the inventory the fact of a shortage may be revealed. In such a situation, the company’s accountant may be presented with a claim that financial documents do not correspond to real circumstances. Before disposing of an object, responsible persons must carry out a write-off procedure that allows the assets to be removed from the balance sheet . It is important to note that the current legislation provides strict regulations for this procedure.
Strict adherence to the regulations reduces the likelihood of making mistakes that will lead to negative consequences.
It is very important for the management of each company to prevent possible theft of objects. That is why a whole group of specialists takes part in the procedure under consideration. Responsible persons are appointed by order of management. The responsibilities of the company administration include not only selecting the workers who will take part in this process, but also appointing the chairman of the commission. The task of the commission members is to thoroughly analyze the facilities for the possibility of further exploitation. In the event that an object that has fallen into disrepair cannot be repaired, the commission writes off the asset.
How to correctly draw up an act of write-off of materials
This document must necessarily contain information about the enterprise and the members of the write-off commission: their positions, surnames, first names, patronymics, as well as a detailed list of materials being written off, including their quantity and cost (piece and total), the reason for write-off. The commission is appointed by a separate order of the head of the organization, and the chairman of the commission is also prescribed in it. After entering all the data into the write-off act, each member of the commission must sign the document, thereby certifying that all the information was entered correctly. Also, upon completion of the procedure, the report must be certified by the head of the organization.
The act of writing off materials has a legal status, since on the basis of it the specialists of the accounting departments reflect the book value of the written-off material assets, as well as the direct loss of the enterprise due to their loss. In turn, this information is reflected in the tax records of the legal entity.
The act does not have a unified, standard template, so it can be drawn up in free form or according to a template developed within the organization, in accordance with the characteristics of its activities and needs. The document can be drawn up on a regular A4 sheet or on the organization’s letterhead in a single copy intended for the accounting department of the enterprise (however, if necessary, members of the commission, as materially responsible persons, can request a copy of the act). It is not necessary to certify it with a seal, since it relates to internal document flow and is recorded in a special journal.
Basis for compilation
The basis for compilation may be:
- an inventory was carried out, during which it became clear that some of the accounting objects needed to be disposed of;
- initiative of persons responsible for the use of values (PRO).
The reason for writing off materials in the write-off act depends on what kind of material assets are supposed to be written off. For example, the disposal of soft equipment may be due to the wear and tear of the item, stationery must be transferred according to a statement from the MOL to the direct user (statement for issuing valuables for the needs of the institution according to form 0504210), dishes are entered according to the tableware breakage registration book (form code 0504044). In case of destruction of inventory items, approved documents must be attached.
Responsible persons are members of the commission for the receipt and disposal of assets. They are appointed by order of the head of the institution.
Instructions for filling out the Material Write-off Certificate
- In the upper right corner of the document we enter the name of the enterprise, as well as the position, surname, first name, patronymic of the manager, who, after drawing up the act, will approve it.
- Then we fill in the title of the document, and also briefly convey its essence (in this case, “about the write-off of materials”), put the date: day, month (in words), year.
- Next, we move on to the composition of the write-off commission: the position of each employee, last name, first name, patronymic, as well as record the fact of writing off material assets and indicate the reasons for their write-off (unsuitability for use, identified defects, completed depreciation period, obsolescence, etc.) .
In the second part of the act, you need to include a table that lists in detail all the materials that have been written off, their name, quantity, price of one piece and the total cost of the written-off values as a whole. If there are any notes on the materials being written off, they also need to be indicated in the table. Under the table you need to indicate the total cost of written-off materials (in numbers and in words), and after entering all the necessary information into the document, each member of the commission signs it, and the document is submitted to the head of the organization for signature.