The organization can outsource materials for further processing and manufacturing of products. Such materials are called toll materials. How the process works:
- one organization (customer) transfers materials, while remaining the owner;
- another organization (processor) manufactures the product and transfers it to the customer along with the remaining materials;
- The processor receives remuneration for his services.
In the 1C 8.3 Accounting program, accounting is automated both on the customer’s side and on the processor’s side. The functionality is located in the “Production” section.
Let's take a closer look at the procedure.
Documenting
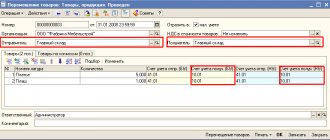
When transferring materials for processing to the contractor, issue an invoice in form No. M-15. In the documents, indicate that the materials were transferred for processing on a toll basis.
After processing the materials, the performing organization must submit the following documents:
- invoice in form No. M-15;
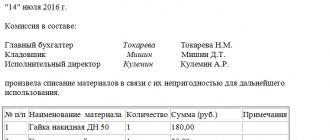
- report on the consumption of materials (clause 1 of article 713 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This document must contain information about materials received and not used for production, the quantity and range of materials (products) received. It also indicates how much waste was received, including returnable waste. The surplus must be returned to the seller, unless otherwise provided by the contract;
- act of acceptance and transfer of work for the cost of processing work (Article 720 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
When receiving materials from processing, the customer must issue a receipt order (Form No. M-4). If finished products are obtained as a result of processing materials, issue an invoice for the transfer of finished products to storage locations (Form No. MX-18).
Question:
Hello Elena Pavlovna!
My name is Valentina, I attended your lecture at the advanced training courses. I have a huge request to you, if possible, help me figure out how to implement the write-off of spare parts in 1C, taking into account the requirements of our auditors. The situation is like this:
We are a budget organization and buy spare parts.
to account 105.36 under KFO 4, then
we transfer them to the organization with which an agreement was concluded for the provision of vehicle repair services
- in 2013, the write-off of spare parts was formalized by an act on the write-off of inventories (form 0504230) drawn up on the basis of the acceptance certificate, posting 4.401.20.272 * 4.105.36.440.
The “auditors” pointed out to us that this is incorrect and all this should be drawn up as an invoice for the transfer of materials to the third party since 2014. parts were carried out in 1C (inventory-disposal - transfer of materials to the outside - operation “free transfer to organizations” posting 4.401.20.242 + 4.105.36.440, which is also not correct.
How can you implement the write-off of spare parts in such a way as to take into account the requirements of the inspectors and formalize everything correctly?
Can write off from 105.36.440 to 401.20.272 at the request of an invoice (form 0315006) (but better, of course, an invoice for the transfer of materials to the outside (form 0315007) to the off-balance sheet account "09" debit and immediately write off from the credit 09 account with the preparation of an ACT write-off of inventories (form 0504230) ???!!!
THANK YOU IN ADVANCE FOR YOUR UNDERSTANDING AND HELP. Best regards, Valentina.
Accounting: transfer and processing results
When materials are transferred for processing on a toll basis, sales do not occur, since ownership remains with the organization that ordered the work (Clause 1, Article 220 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, do not write off the cost of materials from the balance sheet of the customer organization, but take them into account in a separate subaccount 10-7 “Materials transferred for external processing” (clause 157 of the Methodological Instructions approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n):
Debit 10-7 Credit 10
– materials were transferred for processing.
Further accounting of materials sent for processing depends on the result of processing. Accounting rules vary depending on the following cases:
- the result of processing is a finished product;
- recycling only prepares the material for use;
- recycled materials are used in the manufacture (creation) of fixed assets.
If, as a result of processing, a finished product is obtained, then the processing costs form the cost of the finished product (clause 5 of PBU 10/99). Reflect this operation like this:
Debit 20 (23...) Credit 10-7
– materials from processing are returned and they are taken into account in the cost of finished products;
Debit 20 (23…) Credit 60
– the cost of processing work is taken into account in the cost of finished products.
If materials are prepared for use, processing costs increase the cost of these materials (clauses 68, 71 of the Methodological Instructions approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n). Reflect this operation like this:
Debit 10 Credit 10-7
– materials from processing were returned;
Debit 10 Credit 60
– the cost of processing work is taken into account in the cost of materials.
If materials obtained from processing are used in the creation (manufacturing) of fixed assets, processing costs form the initial cost of these fixed assets (clause 8 of PBU 6/01). Reflect this operation like this:
Debit 08 Credit 10-7
– materials from processing are returned and they are taken into account in the initial cost of fixed assets;
Debit 08 Credit 60
– the cost of processing work is taken into account in the initial cost of fixed assets.
How to write off materials in “1C 8 3”: table of entries
The responsible person of the organization will have to establish in the accounting policy a suitable method of working on write-offs (both for accounting and tax). To simplify your task, choose the same method for both situations. Accountants often use this option as average cost. The methodology for cost estimation per unit is relevant for those enterprises where the items produced are unique (like jewelry).
| Check | What postings are presented? | |
| Debit | Credit | |
| 20 | 10 | removal of positions from main production |
| 23 | for additional production needs | |
| 25 | for general production expenses | |
| 26 | for general economic use | |
| 44 | on costs for selling finished products | |
| 91.2 | disposal on a gift basis | |
| 94 | in case of damage, theft, etc. Inventory | |
| 99 | in case of their loss due to natural disasters | |
It cannot be said that all the described operations are identical in the frequency of their execution. But in order to carry out any of them, you should pay attention to the issue described below.
Do you want to implement “Store 15”? Get all the necessary information from a specialist.
Thank you!
Thank you, your application has been accepted.
BASIC: income tax
The procedure for accounting for the costs of processing materials on a toll basis for taxation depends on whether they form the initial cost of fixed assets or not.
If the cost of processing costs forms the initial cost of fixed assets, write off expenses (in the form of the cost of processing work and in the form of the cost of the materials themselves) through depreciation. For more information, see How to calculate depreciation in tax accounting.
If processing costs do not participate in the formation of the initial cost of fixed assets, apply the following rules. When calculating profit tax, an organization can take into account in material expenses the costs of processing materials (performing part of the production processes) by another organization (subclause 6, clause 1, article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The date of recognition of expenses in the form of the cost of processing work will be:
- with the accrual method, the date of signing the acceptance certificate for the work performed (paragraph 2, paragraph 2, article 272 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- with the cash method, the date of repayment of the debt to the executing organization (subclause 1, clause 3, article 273 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The date of recognition of expenses in the form of the cost of materials transferred for processing also depends on which method of calculating income tax the organization uses:
- accrual method;
- cash method.
Recognition of expenses using the accrual method
When calculating income taxes using the accrual method, apply the following rules. The cost of materials transferred for processing on a toll basis can be taken into account in expenses at the time they are written off for production in the part used in it at the end of the month (clause 2 of Article 272, clause 5 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the moment of transfer for processing is equivalent to the transfer of materials into production, since processing is one of the stages of production.
If processing costs are classified as direct, then they can be taken into account only after the work is completed (accepted by the customer). Such rules are established by paragraph 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Situation: should materials transferred for processing be taken into account as part of work in progress when calculating income tax?
Answer: yes, it is necessary.
This is due to the fact that the obligation to distribute direct expenses on a monthly basis is established for all production organizations (paragraph 3, paragraph 1, article 319 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And no exceptions are provided for organizations that transfer materials for recycling.
Documentation of the amount of processed materials and unprocessed residue can be done with a report from the recycler. Such reports must contain data in quantitative terms on the consumption of raw materials and materials, on the availability of products that are partially ready.
This point of view is also shared by the tax department (see, for example, letter of the Department of Tax Administration of Russia for Moscow dated August 17, 2004 No. 26-12/54019).
Advice: include in the agreement on the transfer of raw materials to be supplied a condition on the submission by the processing organization of monthly reports on the balances of work in progress. Such reports must contain data on the consumption of raw materials and materials, on the availability of products that are partially ready. The submission of reports by the processor will allow the seller to confirm the validity of writing off direct expenses during a tax audit.
Sales of finished products
In our example, the enterprise produced products with the help of a third-party processor, to whom it transferred raw materials.
The next step is the sale of the produced goods. In “1C: Trade Management + Production” in the “Sales” section we create the document “Sales of goods and services”, fill in all the basic details of the document header. In the tabular part of the document “Sales of goods and services”, select our product and indicate the quantity of 100 pieces at 5 rubles per piece. Total 500 rub.
We carry out the document “Sales of goods and services”.
BASIS: VAT
When transferring materials for processing on a toll basis, ownership of them does not pass, therefore this operation is not considered a sale (Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, paragraph 1 of Article 220 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). This means that it is not subject to VAT (Article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, VAT paid for the processing of materials can be deducted if the conditions for its reimbursement are met.
The transfer of inventory items (work, services) to pay for the processing of materials is subject to VAT (subclause 1, clause 1, article 146 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Registration of SF supplier
Register the invoice using the Register at the bottom of the document.
If the document has the Reflect VAT deduction in the purchase book by date of receipt checkbox , then when it is posted, entries will be made to accept VAT for deduction.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 68.02 Kt 19.04 - acceptance of VAT for deduction.
Purchase Book report can be generated from the Reports - VAT - Purchase Book section. PDF
simplified tax system
If an organization applies a simplification and pays a single tax on the difference between income and expenses, take into account the costs of processing raw materials on a toll basis as part of material expenses (subclause 5, clause 1, clause 2, article 346.16, subclause 6, clause 1, art. 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Work on processing materials must be taken into account if two conditions are met: they are paid for and accepted from the contractor. Please include the cost of recyclable materials in your expenses at the time of payment. Such rules are established by subparagraph 1 of paragraph 2 of Article 346.17, paragraph 2 of Article 346.16 and paragraph 5 of Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If processing costs form the initial cost of fixed assets, the organization can also take them into account when taxing. For more information about this, see How to use the simplified tax system to take into account the receipt of fixed assets and intangible assets.
Organizations that use simplification for the object do not take into account income and expenses for processing materials (Article 346.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).