Receiving and issuing interest-free loans is not uncommon, especially during the formation of a company or in unforeseen force majeure circumstances. In cases where the company’s reserves are not enough to repay obligatory payments, the founder has the right to help it by arranging and providing such a loan. In turn, the company, if necessary, can lend the founder or employee an agreed amount in money (in kind) without charging interest for their use. Let's talk about how this happens in practice.
Interest-free loan from the LLC founder
According to legislative standards, a citizen who is the founder of an organization is obliged to replenish its current account with an amount equal to the authorized capital of the LLC within 4 months. Its value is determined by the company’s constituent documentation.
If the activity of a business entity has recently begun, then the funds in the account may be needed for settlement transactions. For example, transferring earnings to employees, fulfilling financial obligations to contractors, paying obligatory payments, purchasing raw materials and equipment, and so on. A business entity may not have enough available money to cover all expenses. In this case, the founder can provide a loan to his company without charging interest.
The founders can deposit the required amount of money into the company's current account. To do this, you will need to draw up an agreement for an interest-free loan and provide it to the employees of the banking organization where the account is opened. There is also the possibility of depositing the required amount into the cash desk of a business entity. In the future, when the financial situation improves, the loan amount can be repaid.
Legal basis
The fundamental parameters of the operation of an LLC are determined by the provisions of the country’s civil legislation and the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On LLC”.
Issues related to the opening and constituent documentation are regulated by federal legislation on state registration of legal entities and individuals.
The rules of civil law define the concept of a loan agreement, the rules for its execution, the powers and obligations of the parties. The rules, goals, and methods of accounting are determined by the Federal Law of the Russian Federation “On Accounting”.
Loan taxes
When determining the amount of tax, a loan without interest is not considered either in income or in expenses. Such a loan is considered a benefit in accordance with Art. 41 tax legislation. A benefit of this nature cannot be considered income according to Art. 25 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If the founder does not claim to repay the loan, then it is classified as non-operating income. In this case, income tax will have to be transferred to the state treasury. But if the founder who provided the loan owns more than half of the authorized capital, then you will not have to pay income tax. Such receipt of funds will not be considered income.
What's better?
As mentioned earlier, the founder can help his company with money. However, the methods of such support may vary.
Most often, options are considered such as non-repayable financial assistance, implemented through a gift transaction, and repayable assistance, usually formalized in an interest agreement or an interest-free loan agreement.
To choose the most suitable option for financial support, you need to know the characteristic features of each of them, taking into account the specifics of the relationship between the shareholder providing the funds and his company accepting this assistance.
Non-repayable financial assistance to society
Registration of a deed of gift is considered the simplest option for providing financial assistance.
A shareholder who wants to support his company donates appropriate funds to it (money or other property), and the company, in turn, accepts this gift.
To comply with the legality of this procedure, the parties draw up a formal gift agreement.
An important nuance - the donor in this situation can only be an individual.
The norm of the Civil Code (clause one of Article 575) establishes that legal entities do not have the right to enter into gift transactions with each other for amounts exceeding 3,000 rubles.
Thus, a shareholder of a business company who has the status of a legal entity and at the same time is a parent organization cannot act as a donor in relation to his company.
Violation of this prohibition by the parties may lead to the recognition of the gift transaction as void if the dispute that arises is resolved in court.
Another aspect is taxation. If the participant who acted as the donor has a share in the donee company of a maximum of 50%, the business company that accepted this gift will be obliged to pay income tax on the funds received, since for the donee company the money received will be considered non-operating income.
If the founder, who is the donor, owns a share in the recipient company that exceeds 50%, the business company that accepted this gift would have the right not to include the funds received in the tax base.
Thus, non-repayable financial assistance to a business company in the form of a gift may make sense if the donor participant is an individual and his share in the recipient company exceeds 50%.
Is it possible to provide an interest-free loan to an LLC?
Many founders who want to provide financial support to their companies prefer to formalize it through a loan agreement.
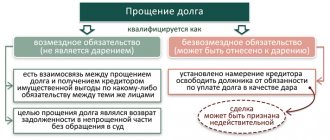
An important feature of this option is the repayment of the funds provided. However, even in this case, the shareholder-creditor has the opportunity to maneuver - he has the right to forgive the borrower company the debt that has arisen.
The procedure for loan forgiveness by the founder.
It should be noted that the loan agreement can be either interest-free or paid (interest-bearing).
It is noteworthy that any loan agreement is considered paid (paid, interest-bearing) by default if the text of the relevant agreement does not mention interest or the absence thereof at all.
As a result, the borrowing company has an obligation to accrue and pay credit interest in accordance with the base rate, which is provided for by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (clause one of Article 809).
If the founder-lender intends to provide his company with an interest-free loan, he must include a specific no-interest clause in the relevant agreement.
Unlike non-repayable financial assistance, receiving funds under a loan agreement does not lead to an increase in tax liabilities for the borrowing company.
If borrowed funds are used by a business company on an interest-free basis, it also does not receive additional material benefits in this case.
Therefore, providing an interest-free loan is the most convenient option for a shareholder who wants to help his own company solve the problem of cash shortages.
Interest-bearing loan to a company
The specificity of a paid loan is that, under the relevant agreement, the borrower company undertakes to pay the agreed interest to the lender-investor for the use of the funds provided.
The payment of credit interest, which has a proper economic justification, is a cost for the borrowing company, which, of course, is reflected in the taxable profit of the business company using borrowed funds.
However, there is one caveat in the tax legislation of the Russian Federation.
If a loan provided to a company by a shareholder is rightfully considered a controlled transaction, interest costs are included in the reduction of the borrower’s taxable profit not in full, but in a limited amount.
Another nuance is that the borrowing company will have to withhold and transfer personal income tax from the interest paid if the shareholder-creditor is an individual, since such interest is taxable income for the shareholder-citizen.
Loan accounting
Legislative standards require mandatory recording of the movement of funds within a business entity. To do this, the accountant must create the appropriate entries.
Registration of a loan also requires recording in accounting, and it does not matter who the creditor is: the founder or the financial structure. It is necessary to record accounting entries for any loan, both with and without interest.
To fix a loan for a period of up to 1 year, account 66 “Short-term loans” is used. If funds are provided for a period of more than a year, then account 67 “Long-term loan” is used.
If the founder provides money to his company, this will be accompanied by an increase in accounts payable in the legal entity’s liability. Forgiveness or return of funds is accompanied by a decrease in accounts payable by a certain amount.
Depending on the operations carried out, borrowed funds are recorded using the transactions described in Table 1.
| Operation | Dt | CT |
| If borrowed funds are deposited by the founder into the current account of a legal entity | 51 | 66 (or 67) |
| Money can be processed using other transactions | 52 “Currency account” 10 "Materials" 41 "Products" | 66 (or 67) |
| When depositing borrowed money into the organization's cash desk | 50 | 66 (or 67) |
| Subsequently, borrowed funds are transferred from the cash desk to the current account | 51 | 50 |
| When returning borrowed funds | 66, 67 | 50 (51, 52, 10, 41 and so on) |
How to take into account a loan issued from the founder, watch the video:
Requirements
A loan from the founder is an extremely unprofitable event for the lender. Firstly, the director usually chooses an interest-free transaction, which means he does not receive income from the use of money.
Secondly, he is authorized to “forgive the debt.”
Thirdly, you will need to pay taxes:
| situation | Tax consequences | Link to normative act |
| Lender with a share in the authorized capital of less than 50 percent | Non-operating income, the amount of which depends on the amount of unreturned finances. The tax rate is 20 percent. | |
| A lender with a share in the authorized capital of more than 50 percent | Taxes are not paid on the amount of debt | Art. 251 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
Postings of an issued interest-free loan from the founder and to the founder
If the founders of a business entity do not have the opportunity to draw up a loan agreement at a banking institution, you can borrow money from your own company. To do this, one of the founders will need to draw up an agreement for the provision of borrowed funds.
If the other founders at the meeting determined that the lender should make a profit from the funds issued, then its amount may increase monthly.
The decision on the procedure for repaying the debt by one of the founders is determined at the meeting. Borrowed funds can be provided at a certain percentage or without it. In this case, the amount of money received from one of the founders is not income and is not subject to taxation.
To avoid difficulties with the fiscal authority, the loan agreement must include the following provisions:
- provision of borrowed funds without paying interest
- if interest is accrued, then its amount must be reflected
- if a business entity has only 1 founder, then the agreement is drawn up individually
- the currency of the agreement must be the ruble
If a business entity lacks its own funds to develop a business, then one of the solutions is to receive borrowed funds from its founder. This loan has a number of positive aspects:
- no interest, fines or penalties
- the founder's interest in the successful activities of the organization
The founder can deposit the required amount of money to the current account or to the cash desk of the business entity. In the future, the creditor may refuse to demand the return of the loaned funds. But such a clause cannot be indicated in the agreement, since the loan provides for the return of money.
If the funds do not need to be returned, then one of the following procedures must be carried out:
- execution of the corresponding agreement between the lender and the borrower
- the lender can send the recipient of the funds a notice of loan forgiveness
In each document, the lender will need to indicate:
- fact of termination of the borrower's obligations
- details of the parties to the agreement
- details of the agreement itself
- amount of debt and interest accrued on it (if any)
But if the debt is forgiven, then the business entity must transfer a tax to the state treasury, since the amount received will be considered profit. The amount of the fee will depend on the tax regime used by the enterprise.
Obligations to pay tax do not arise if the founder’s share in the authorized capital exceeds half.
Key points of the borrowing agreement
There are a number of points that are of particular importance for the tax consequences of a loan agreement with the founder. Among them is the ability to make an agreement:
- Provides for the payment of interest at a frequency convenient for its parties. The absence of reservations in this regard will require monthly interest accrual (clause 3 of Article 809 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Interest-free (in the case of loaning things, the absence of interest becomes mandatory - clause 4 of Article 809 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In order for an agreement to be considered interest-free, the condition of non-accrual of interest must be fixed in the text of the document, since the absence of such a condition will entail the need to calculate interest on the key rate of the Bank of Russia (clause 1 of Article 809 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
- Targeted. For this situation, the contract will have to provide for a procedure for monitoring the use of what was loaned and a procedure for returning it if misuse is identified (Article 814 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Accordingly, interest accrued on borrowed funds used for other purposes will not be taken into account to reduce the tax base for profits or the simplified tax system; It will also be impossible to take into account the negative exchange rate difference on a loan issued by a foreign founder in foreign currency.
- Does not contain an indication of the repayment period or makes it dependent on the moment of reclaiming the loan from the lender. Under such conditions, the debt must be repaid no later than the 30th day from the date of the demand from the lender, unless a different period is specified in the text of the agreement (clause 1 of Article 810 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Moreover, the date of return (unless otherwise provided by the agreement) will be considered the day of actual receipt of the debt by the lender (clause 3 of Article 810 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In order to avoid undesirable consequences, it is recommended to stipulate each of the listed points in detail in the text of the loan agreement.
From the founder to the employee
An economic entity has the right to issue loans to its employees. To record the transaction, account 73-1 “Settlements on submitted loans” is used. The issuance of funds affects the debit of the account, the return affects the credit. The accumulated interest is taken into account in the same account.
Accounting records each loan issued to employees of the enterprise. The operation is accompanied by the following transactions:
- transfer of money to the worker: Dt 73.1 – Kt 50 (or 51)
- accrual of interest under the agreement: Dt 73.1 – Kt 91.1
In the absence of interest on the loan, as well as if their value is less than 2/3 of the refinancing rate, the borrower generates a profit. In this case, the business entity must transfer personal income tax to the treasury.
Currently, the refinancing rate is equal to the key rate. The value of the latter is 7.75%. Then we get:
7,75 * 2/3 = 5,17
If the accrued interest is less than the result obtained, then personal income tax will need to be transferred to the state. The amount of profit received is subject to taxation.
When providing a cash loan at 4%, the profit received will be:
5,17 – 4 = 1,17%
From the amount of interest received, the accountant should withhold personal income tax at a rate of 35%.
From the founder of another organization
The details of providing borrowed funds from the founder of another business entity must be specified in the loan agreement. It can be provided with or without interest. If there is interest under the terms of the agreement, it must be reflected in financial investments.
The operation is accompanied by the creation of the following transactions:
- issuance of borrowed funds: Dt 58.3 – Kt 51
- accrual of interest for using a loan: Dt 76 – Kt 91.1
- transfer of interest for using the loan is recorded as: Dt 50 – Kt 76
Postings of the received loan from the founder
The situation when the founder provides funds as a loan with interest is recorded by the following entry: Dt 66 (67) – Kt 50 (51).
The percentages are recorded by posting: Dt 91.2 – Kt 66 (67).
Interest is accounted for in the subaccount for accounts 66 (or 67).
If the founder has drawn up a loan agreement to pay the debt of a legal entity, then the following accounting entries are formed: Dt 60 – Kt 66. This procedure does not contradict legal norms, but contributes to the emergence of problems when paying VAT.
If the money lent is not subject to interest, then the entries in the accounting system remain the same. But the absence of interest is necessarily indicated in the agreement for the provision of borrowed funds.
A business entity can pay off existing debt with money or goods produced. In this case, the proceeds from the sale of goods to pay off the debt are recorded: Dt 76 – Kt 91. The sale of goods is accompanied by the accrual of VAT: Dt 90.3 – Kt 68.02. To offset the debt, a posting is created: Dt 66 – Kt 76.
How to apply for a loan
The replenishment of the RS by the founder is reflected in a written agreement. The document indicates the information of each party, information about the transferred amount or property, and the conditions for the use of money (material assets). The procedure for transfer and payment, rights and obligations, liability, regulation of controversial issues and other points characteristic of contracts are also reflected.
Other documents are also prepared:
- cash deposit - cash order (it specifies the terms of the transaction);
- in the case of a non-cash transfer, a record is made of the order regarding the transfer and the Internet banking system.
When drawing up a contract, attention is paid to the following points:
- The period for which funds are issued. It is necessary to indicate the day of return of funds from the current account. If this parameter is not specified, the money must be returned before the 30th day from the date when the founder requests a refund.
- Features and terms of interest transfer. If the participant plans to make a profit, a payment schedule is specified in the agreement. In the absence of it, interest is accrued every month.
- When issuing an interest-free loan, this fact is reflected in the agreement. If there is no clause, interest is calculated at the rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
- If money is given to solve specific problems, it is reflected in the agreement of the parties.
Example of transactions for an interest-free loan
For example, we can consider the case of lending money in the amount of 180 thousand rubles. the sole founder of the company for a period of 9 months at 1.5%.
Postings for an interest-free loan from the founder will have the following form (Table 2).
| Dt | CT | Operation | Transaction amount | Supporting document |
| 51 | 66 | receiving money from the founder | 180,000 rub. | Bank statement |
| 91,1 | 66 (percent) | accrual of interest for the use of borrowed funds | 2,700 rub. | accounting certificate |
| 66 | 51 | funds were returned to the founder | 180,000 rub. | outgoing payment order |
| 66 | 51 | transfer of interest to the founder's account | 2,700 rub. | outgoing payment order |
If funds are lent by a business entity to the founder, then the procedure is formalized with the following entries (Table 3).
| Dt | CT | Operation |
| 76/73 | 50/51 | The borrower must pay personal income tax on the amount received, but due to the lack of interest, the founder will be able to save a certain amount of money. |
| 58/73 | 50/51 | If the terms of the agreement provide for the accrual of interest on the loan. |
| 58/73 | 01/41 and more | If the loan was of a property nature. |
| 76 (or 58, 73) | 91,1 | Calculation of interest on the loan. |
Loan forgiveness: postings
For example, we can consider a situation where the founder in June 2018 loaned his company funds in the amount of 380,000 rubles. Due to financial problems that arose, the lender decided to forgive the debt in January 2021. Such an operation is accompanied by the following accounting entries:
- Upon receipt of funds: Dt 51 – Kt 66. Cash in the amount of 380,000 rubles. received from the founder.
- In January 2021, the fact of debt forgiveness is accompanied by the following entry: Dt 66 – Kt 91. The entire amount provided by the founder as a loan relates to non-operating income of the business entity.
As another example, we can consider a situation where the founder of a business entity purchased its bill of exchange worth 95,000 rubles. After 1 month, the acquirer decided to return the security to the legal entity free of charge. This situation should be accompanied by the formation of the following entry: Dt 66 – Kt 91, transaction amount 95,000 rubles. – the emergence of non-operating income from the return of one’s own security.
But do not forget that the legal entity will have to pay tax to the state treasury on the income received.
conclusions
If a shareholder wants to help his own company with money, the best option for him is to enter into an interest-free loan agreement with it.
For a business company acting as a borrower, this method can also be considered optimal. The return of the funds provided guarantees the founder financial peace of mind.
We should not forget that the shareholder-creditor has the right to refuse the loan issued by forgiving his business company for this debt.
Taking out an interest-free loan does not cause any tax consequences for either the lender or the borrowing company.
List of required documents
The procedure for obtaining a loan between the founder and the business entity must be accompanied by the following documentation:
- agreement for the provision of borrowed funds
- documentation certifying the receipt of the amount of money specified in the agreement from the lender to the borrower
The loan agreement does not require notarization. To formalize the agreement, the following documents are required:
- civil passports of the founders and director
- statutory documentation
- OGRN, INN
- information from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities
- If there is collateral, you will need documentation for it
If an agreement is concluded between an individual and a business entity, then it must contain the following information:
- loan amount in rubles
- purpose of providing funds
- order and parameters of its return
- accrued interest
- presence of penalties
The agreement must indicate the procedure for calculating interest or the fact of its absence. Today the following methods of debt repayment are used:
- One-time deposit of funds before the day specified by the concluded agreement. If there is interest, the borrower must pay the principal amount and interest on it.
- Debt repayment is carried out in accordance with the schedule determined by the terms of the agreement (once a week, month, quarter).
- The debt is returned upon presentation of a claim from the lender.
Due to the fact that funds are used to develop their own business, collateral is usually not issued. For the founders, the order in which the funds lent are spent is of great importance. Each of the participants can exercise control over the use of money without being part of the company's management.
List of documents on video:
If the borrower does not comply with the terms of the agreement, the lender may go to court. In this case, the borrower will have to not only repay the existing debt and interest on it, but also reimburse legal costs and pay fines to the creditor.
Thus, the procedures for providing and receiving borrowed funds require mandatory recording in the accounting system. If there is interest for using the loan, their accrual is recorded in separate transactions.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Interest-bearing loan: tax implications
Quite often, a loan agreement, even one concluded with the founder, provides for the payment of interest on it. What tax consequences will an interest-bearing loan from the founder bring in 2021?
The interest amounts received by the lender will become his taxable income. The founder-individual (both Russian and foreigner) will have to pay personal income tax from them at a rate of 13% (clause 1 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or 30% (clause 3 of Article 224 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), respectively, and withholding tax on income will be carried out by the borrower (clause 1 of Article 209 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). And the founder - a legal entity of Russian origin, upon receipt of interest, will be the payer of income tax (clause 6 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or the simplified tax system (clause 1 of Article 346.15 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) at rates of 20% (clause 1 of Article 284 Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and 15% or 6% (clause 1 of Article 346.20 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), respectively. On the income of the founder, who is a foreign organization, when paying interest to him, the borrower will also have to withhold tax himself (clause 1 of Article 310 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) at a rate of 20% (subclause 1 of clause 2 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Under certain conditions, part of the interest accrued in favor of a foreign founder is equated to dividends (clause 6 of Article 269 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and is taxed at the corresponding rate of 15% (clause 3 of Article 224 and clause 3 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) .
From what base will the tax be calculated: from interest, the amount of which is provided for in the borrowing agreement, or from those that correspond to the real market level of such income? This question arises because the parties to the loan agreement may be mutually dependent. Let us recall that the interdependence between the founder and the legal entity in which he participates is directly related to the share of such participation (both direct and taking into account indirect contribution). For a dependence to arise, it is enough for the share to slightly exceed 25% (subclauses 1, 2, clause 2, article 105.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Thus, in relation to an interest-bearing borrowing agreement, the following situations are possible:
- There is no dependency. Then the prices agreed upon by the parties to the transaction are considered market prices (clause 1 of Article 105.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and there is no need to revise them.
- There is a dependence. Its consequences will be different for resident founders and non-resident founders. In the first case, transaction prices will be controlled only when the amount of all transactions between the parties for a calendar year exceeds 1 billion rubles. (Subclause 1, Clause 2, Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In the second case (with a non-resident), the transaction will always be controlled.
The recipient of the loan has the right to accept interest accrued in accordance with the terms of the agreement as a reduction in the profit base (subclause 2, clause 1, article 265 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or the simplified tax system, the base of which is determined taking into account expenses (subclause 9, clause 1, article 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation). However, in relation to a controlled transaction with a foreign founder, the determination of the amount of interest included in expenses occurs in a special order (Article 269 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), and it is here that, if the maximum permissible amount is exceeded, the question arises of equating interest to dividends for tax purposes .