Accounting account 62 is a special analytical account that is used to reflect the supplier’s transactions with the buyer and customer. This article will give you an idea of the main transactions on account 62, which is reflected in the debit and credit of account 62, as well as the documents that are the basis for their implementation.
Account 62 - can reflect both our debt to the buyer (credit) and the buyer's debt (debit). Therefore, this account is considered active-passive - it can be included in the balance sheet as a Liability or an Asset.
What transactions are reflected in account 62 in accounting?
According to the recommended Chart of Accounts, a business entity must use account 62 to record transactions with buyers and customers.
The law establishes that two types of debts must be kept in the account:
- To the company for goods sold, or work and services performed;
- To buyers for advances received from them.
When selling products or performing work, it must be immediately shown in the debit of the account. At the same time, the same amount is indicated on the sales accounts (90, 91) or the gradual execution of work. After receiving payment from the counterparty, it should be reflected on the credit of the account, simultaneously with the debit of the cash settlement accounts.
If the buyer makes payment before actually receiving goods or work, then this receipt is reflected in account 62 as an advance received. Since this amount is accounts payable, it must be recorded in separate accounts. It is not possible to show both debts collapsed.
Also, the buyer may not repay the debt, but issue his own bill. This paper will act as a deferment of payment and a guarantee of further repayment of the debt.
Attention! This kind of payment must be taken into account in account 62, but separately from simple debt. However, if the buyer issues a third party’s bill of exchange as payment, then such a step is already recognized as a financial investment and is subject to accounting on account 58.
Results
For different types of debt, the chart of accounts provides for special accounts. One of them is account 62, which can be either active or passive, since it is used to account for both debt from buyers and customers, and creditors in the form of advances and prepayments received.
Read about accounting for accounts receivable in the article “Keeping records of accounts receivable and accounts payable.”
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Characteristics of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
The adopted chart of accounts establishes that account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is active-passive. This means that he can have two balances at the same time - both debit and credit.
This means that this account can immediately show both the company’s receivables and payables:
- A balance in the debit of the account means that buyers have an unpaid debt to the company for work performed or goods shipped.
- The loan balance shows that the organization has received an advance payment for future deliveries of goods or performance of work, but has not yet fulfilled its obligations to buyers or customers.
What does the debit and credit of the account reflect:
- The debit of account 62 shows the amounts of work performed or goods shipped, for which documents for payment were issued to counterparties. In addition, debit can also take into account the amounts of payments that were returned to customers due to failure to fulfill obligations to them.
- Credit 62 of the account takes into account the amounts of money that were transferred by buyers of goods or customers of work for received goods and materials. The amounts that were received as an advance payment for future work or shipment of goods are also indicated here.
The process of determining the balance at the end of the period under review depends on what exactly the balance was at the beginning. If it was debit, then you need to add the debit turnover to it and subtract the credit turnover. If the result is positive, then this balance is entered as a debit at the end of the period. If it turns out to be negative, then it is transferred to credit, but without the minus sign.
You might be interested in:
08 accounting account - “Investments in non-current assets”
If at the beginning of the period under consideration the balance was in credit, then you must first add the credit turnover to it, and then subtract the debit turnover. When determining which part of the balance sheet to record the final balance in, a similar rule applies - if it turns out to be positive, then in credit, otherwise - in debit.
Attention! The balances of account 62 must be shown when preparing the balance sheet, but in different sections. The debit balance is accounted for in accounts receivable and recorded as an asset. At the same time, it is shown minus the reserve for doubtful debts (if it was created). The credit balance constitutes accounts payable and is reflected in liabilities.
What subaccounts are used?
On account 62, it is necessary to record both the process of shipping products to customers or providing services to consumers, and the receipt of payment from them.
To do this, the following subaccounts can be opened on the account:
- Account 62.01 - to reflect the payment that was transferred under normal conditions;
- Account 62.02 - to account for advances received from buyers for future supplies of products;
- account 62.03 - for accounting for bills received from buyers.
Additional accounts may also be opened for each of these sub-accounts, depending on the payment currency. In addition, for his convenience, an accountant can organize analytical accounting for each counterparty or concluded agreement.
In addition, it is allowed to keep records in the following context:
- According to the actual payment method (advance payment, payment upon delivery, etc.);
- By the deadline for payment for the supply (whether there was a delay or the repayment period did not occur);
- By the presence of the bill (whether it was presented, whether the maturity date has arrived, etc.).
Attention! The accountant has the right to independently decide how to build accounting for customers in the enterprise. Analytics should allow you to check account balances for overdue debts.
Which accounts does it correspond with?
Accounting account 62 can correspond with the following accounts.
From the debit of account 62 to the credit of the following accounts:
- account 46 - when writing off the cost of the next stage of work;
- account 50 - when returning from the cash register previously deposited funds to the buyer;
- account 51 - when returning funds previously deposited by the buyer from the current account;
- account 52 – when making a return from a foreign currency account of funds previously deposited by the buyer;
- account 55 - when performing a return from a special account of funds previously deposited by the buyer;
- account 57 - when making a refund by postal order or similar method;
- account 62 - when offsetting a previously received advance to repay the buyer’s debt;
- account 76 - when conducting mutual offsets;
- account 79 - when conducting a sale through the head office or branch;
- account 90 - when reflecting the shipment of main products;
- account 91 - when reflecting other sales (fixed assets, materials, etc.).
On the credit of account 62, entries can be made to the debit of the following accounts:
- Account 50 - when reflecting payment for delivered goods to the cash register;
- account 51 - when reflecting payment for delivered goods to the current account;
- account 52 – when reflecting payment for goods delivered to a foreign currency account;
- account 55 – when reflecting payment for goods delivered to a special account;
- account 57 - when reflecting payment by the buyer through a savings account, postal order, etc.
- count 60 - when carrying out mutual offsets;
- account 62 – when offsetting a previously received advance to repay the buyer’s debt;
- Account 63 - when writing off a bad debt using a pre-formed reserve;
- account 66 - when offsetting the supply of products against a short-term loan;
- account 67 - when offsetting the supply of products against a long-term loan;
- account 73 - when selling products to company employees;
- account 75 - when conducting mutual offsets according to the requirements of the founders;
- account 76 - when conducting mutual offsets;
- account 79 - when conducting a sale through the head office or branch;
You might be interested in:
Account 19 in accounting: what is it used for, subaccounts, characteristics, postings
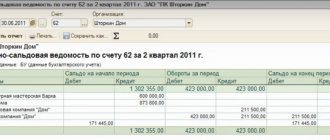
Balance sheet for account 62
By its structure, count 62 is active-passive. This means that it can contain both a debit and a credit balance. In order to calculate them correctly, it is necessary to record transactions for each customer.
Modern computer programs for accounting, for example, 1C, allow you to automatically carry out this kind of accounting, as well as create not only general registers for synthetic and analytical accounts, but also build a balance sheet for each customer.
The balance sheet is a special accounting register. The law does not define strict conditions for how it should look, but it does establish mandatory details for use in it.
These include:
- Name of company and register;
- Start and end days of the register formation, as well as the period;
- In what monetary values is it compiled?
- Indication of responsible persons.
If you are preparing a balance sheet document for account 62, you must adhere to the following rules:
- When compiling debit turnover, it is necessary to reflect all operations of the sale of inventory items to customers. In this case, it is necessary to enter information about the document on the basis of which the sale is made - delivery notes, invoices, UPD, etc. In addition, the debit turnover must reflect the return of funds to the buyer if the delivery of goods or provision of services was not made .
- When registering a credit turnover, it is necessary to include the repayment of the buyer’s debt for the products sold, or the crediting of an advance payment. Here you must also indicate the details of the documents for which the payment was made - PKO, payment orders, etc.
Tax accounting when exporting goods
VAT
Operations for the sale of goods for export are subject to VAT at a rate of 0% (clause 1 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). To apply a zero rate, you need to confirm the fact of export of goods outside the Russian Federation. The list of supporting documents is given in Art. 165 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. It depends on where the goods are exported: to the EAEU countries or outside the EAEU territory.
When exporting outside the territory of the EAEU, the following documents will be required.
- Copy or original of the export contract (agreement). If the contract provides for several deliveries with the execution of separate documents, then it is not necessary to submit it for each shipment. It is enough to attach a notification with the details of the document with which you previously sent the contract.
- Customs declarations (their copies or registers) with marks from Russian customs.
They must be submitted to the tax office along with VAT returns no later than 180 calendar days from the date of registration by customs.
If tax authorities see inconsistencies in the main documents, they may request additional ones - transport, shipping documents and others. They must be submitted within 30 calendar days of the request.
When exporting to the EAEU countries, the following documents will be required.
- Copy or original of the export contract (agreement).
- Application for import of goods and payment of indirect taxes from your foreign buyer (copy or electronic register).
The deadline for submission to the Federal Tax Service is no later than 180 calendar days from the date of shipment of goods.
If you are late with export confirmation, you must pay VAT at general rates. To do this, follow these steps:
- Issue an invoice with VAT of 10 or 20%.
- Register it in the additional list of the sales book for the quarter in which the goods were shipped.
- During the same period, submit an updated declaration.
In addition to VAT, you will have to pay a penalty, which will arise due to the fact that you calculated the tax after the goods were shipped.
The right to confirm export will remain with you for three years from the end of the quarter in which the goods were shipped.
If you do not want to collect a package of documents, you can refuse the preferential rate of 0% and apply the general rate of 10% or 20%. To do this, submit a free form application to the tax office. The deadline for submission is until the 1st day of the quarter from which you plan to abandon the zero rate . After refusal, it cannot be used for at least 12 months .
But when exporting goods to the EAEU countries, you will not be able to refuse the zero rate, since in this case you need to be guided by the Treaty on the Eurasian Economic Union. It, unlike the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, does not provide for refusal.
The tax that you paid when purchasing exported goods (input VAT) can be taken as a deduction (clause 3 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The procedure for deducting VAT depends on the applicable tax rate and the type of goods exported. Thus, paid VAT amounts can be reimbursed in the usual manner prescribed in Art. 176 and art. 176.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, if you:
- refused the 0% rate;
- export non-commodity goods registered on July 1, 2016;
- export goods that are considered raw materials, but are not included in the List, approved. By Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 466 of April 18, 2021
In this case, all the conditions necessary for the deduction must be met - the tax is presented by the supplier, the goods are used for activities subject to VAT, are accepted for registration, and a correctly executed invoice or universal transfer document is received.
For the export of primary goods, the right to deduct VAT arises in one of two moments.
- On the last day of the quarter in which documents were collected to confirm the preferential rate of 0%.
- On the day of shipment of the goods, if the fact of export of goods from Russia has not been confirmed. In this case, you need to apply the general VAT rates - 10% or 20%.
Legal entities and individual entrepreneurs who work in special modes or have received an exemption from VAT under Art. 145-145.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, do not charge VAT and do not apply a 0% rate.
Typical entries for accounting account 62 for dummies
Let's look at typical transactions for account 62:
| Debit | Credit | Description |
| Selling goods to a buyer | ||
| 62/1 | 90/1 | Goods shipped to buyer |
| 90/2 | 41, 43 | The cost of goods sold is written off |
| 90/3 | 68 | VAT charged on sales |
| 50, 51 | 62/1 | The goods are paid for by the buyer |
| 90/9 | 99 | The financial result from the sale was calculated |
| Purchasing goods with prepayment | ||
| 50, 51 | 62/2 | Received advance payment for goods |
| 76 | 68 | VAT has been charged on the advance payment |
| 62/1 | 90 | The shipment has been made to the buyer |
| 90/3 | 68 | VAT has been charged on the sale |
| 62/2 | 62/1 | The prepayment has been offset |
| 68 | 76 | VAT has been deducted from the advance payment |
| Payment for goods by bill of exchange | ||
| 62/1 | 90/1 | The goods have been shipped to the buyer |
| 90/3 | 68 | VAT charged on the sale amount |
| 62/3 | 62/1 | A promissory note was received as payment |
| 50, 51 | 62/3 | The buyer has made payment |
| Postings for writing off debt on account 62 | ||
| 91 | 62 | Debt was written off for expenses if no reserve was created, or for the amount of debt not covered by the reserve |
| 63 | 62 | The debt was written off within the created reserve |
| 007 | – | The written-off debt was taken into account in the off-balance sheet account |
| Other postings to account 62 | ||
| 62 | 50, 51 | Refund of advance payment for undelivered products |
| 62 | 76 | Settlement has been made |
| 62 | 91 | Sales of non-core products were made |
| 60 | 62 | Settlement has been made |
Example of writing off accounts receivable
| Chief accountant On June 15, 2012, Alpha LLC reflected the receivables of Beta LLC on the basis of a product supply agreement in the amount of 100,000 rubles. On August 20, 2013, Beta LLC transferred part of the funds stated in the agreement in the amount of 50,000 rub. How and when can an accountant write off a debt? To write off receivables, the statute of limitations must expire - 3 years from the date of violation of payments. Accounts receivable were formed on June 15, 2012 and are confirmed by a reconciliation report. On August 20, 2013, part of the borrower’s debt in the amount of RUB 50,000 was received, which is reflected in the following entries. Since the borrower acknowledged part of the debt, the claim period is interrupted (Article 203 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) and a new claim period of three years begins. If after three years Alpha LLC has not filed a claim for reimbursement of the debt and Beta LLC has not recognized the remaining debt, then the receivables can be written off after August 20, 2021. Write-off receivables are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 007 for 5 years - “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss.” |