Employment contract form
Art.
67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates that all labor relations between the management of the company and the employee must be documented in writing. The employment agreement must contain reliable information about the parties, the terms of execution of the agreement, indicating details and other required information. In its form, an employment agreement, as a rule, should contain the following structure:
- Document title “Employment contract”
- Place and date of his imprisonment.
- Preamble, which displays the details of the parties.
- Subject of the agreement.
- Rights and obligations of the parties.
- Opening hours and weekends.
- Validity period of the document.
- Conditions of remuneration of the employee.
- Conditions for termination of the agreement.
- Addresses and signatures of the parties.
The employment agreement is drawn up in 2 copies and personally signed by the parties.
Documentation
When concluding an employment agreement, the following documents are required:
- Civil passport of the applicant for employment.
- Labor book
- SNILS certificate.
- Military ID (for those liable for military service).
If a candidate for a vacancy does not have a work record book due to his first employment, the employer is obliged to create one himself.
Persons who apply for remote work prepare the necessary documents themselves, and then send them to the employer.
In addition to the basic mandatory documents, additional ones may be required:
- Application for a job.
- Educational documents (diploma, certificate, certificate of advanced training, etc.).
- TIN
- Certificates of marriage and presence of children.
- Certificate 2-NDFL (for tax deductions for children)
- Certificate of income for the last 2 years (for accrual of sick leave)
- International passport.
- Permit for employment (for migrants).
- Certificate of income of the spouse.
- Medical book (for some vacancies), certificate of absence of diseases that prevent work.
- Certificate of no criminal record.
Note: The last 3 points apply to municipal and government employees and to employees of education, health care and law enforcement systems.
Contents of the employment contract
The content of the employment agreement is regulated by Article 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, reflecting mandatory, additional, derivative and indicative conditions that must be included in the contract.
Mandatory conditions include:
- Place of work
- Labor obligations.
- Date of starting work and its completion.
- Payment for work activities.
- Nature of work.
- Social insurance.
The mandatory conditions of the TD are open. There are several types of mandatory conditions:
- The conditions noted in Part 2 of Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Conditions displayed for individual TD types (duration in fixed-term agreement).
- Conditions relating to rights and obligations that are binding.
- Place of work is the company with which the employee signs an employment agreement to carry out his work activities.
- Labor obligations are work in accordance with the staffing table, profession, specialty, and displaying qualifications.
The content and scope of responsibilities is determined by the job description, which should be based on the principles:
- Freedom of labor agreement.
- Job stability.
- The principle of certainty.
A change in work activity is possible only by agreement of the parties, drawn up in writing.
- Date of starting work and its completion. The employment agreement begins to be valid from the moment it is signed, or from the date of actual start of work. The employee is obliged to return to work from the date specified in the employment agreement. If the start date of work is not specified in the TD, then the employee must go to work the next day after the start of the TD. Within a 3-day period, an order for employment must be issued, and within a 5-day period, an entry in the work book must be made.
When concluding an urgent TD, it must display the duration of validity or a specific date or period (for example, 1 year, for the period of maintenance of the baby, for the period of the employee’s illness). If the specified periods are not displayed, the TD will be indefinite.
- Payment for work activities. The TD must display the salary amount, indicating incentive and compensation payments (additional payments, interest, etc.).
- Nature of work. In this section of the TD it is required to display the daily routine at the company, indicating working hours, rest time, including:
- Duration of basic paid leave.
- Duration of additional paid leave.
- The principle of dividing vacation days into parts.
- Duration and types of breaks (break for lunch and rest, ranging from 30 minutes to 2 hours)
- Presence of technical and technological interruptions.
- Social insurance. This condition obliges the management of the company to insure the employee in the Pension Fund, Social Insurance Fund, and Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund.
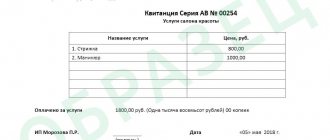
3.1. A milker of the 4th category is obliged to:
— carry out manual milking of cows with a productivity of up to 3.5 thousand kg.
milk per year; hand milking of mares, sheep and goats;
- perform massage, washing the udder and other operations on
influence on the speed and completeness of milk production and milk purity;
— carry out veterinary and sanitary work to care for the udder;
— prepare and distribute feed; cleaning animals, stalls and
— carry out measures to improve animal welfare,
feeding nutritionally balanced feeds to
increasing the milk productivity of animals, obtaining high milk
quality and increase in calf yield;
- identify animals in heat and prepare them for artificial
insemination or mating;
— carry out the transfer of deep-calving cows and heifers to
certain dates in the maternity ward;
— assist veterinary workers in carrying out
preventive measures, treatment and artificial insemination
— carry out preventive measures together with veterinary personnel
measures to prevent animal diseases;
— perform primary milk processing;
- wash and clean dairy utensils. 4. Rights
How to draw up an employment contract with an employee in 2021
Evasion from concluding a TD or drawing up such an agreement with errors threatens the head of the company with administrative fines.
To correctly prepare a TD, you need to read Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which displays a list of mandatory data that must be displayed in the employment agreement. The document must include:
- FULL NAME. employee and company name.
- Details of documents confirming the identity of the applicant for the vacancy and the employer, if he is an individual.
- Employee TIN.
- Information about the company representative authorized to sign the TD. It is important to follow the rule that the one who is written in the preamble of the TD is also obliged to sign at the end of the document.
- Place and date of registration of the TD.
According to Part 3 of Art. 57 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the missing data can be entered manually directly into the text of the TD.
- Labor activity. Lawyers do not have a single interpretation of what work means, so it is advisable to display the position, profession, specialty in the document and specify the implied obligations, for example: accounting, communication with clients, etc. You can display job obligations in the TD text or attach a job description, displaying the conditions of the nature of the work (mobile, traveling, on the road, etc.).
- Work start date. The date of arrival at the company may not coincide with the time of registration of the TD. If a specialist went to work by verbal agreement with the company’s management, then the boss is obliged to issue a TD within 3 days.
- Terms of remuneration. In this section, the head of the company must display the specialist’s tariff rate or salary, allowances and bonuses and other financial incentives. It is also necessary to familiarize the specialist with internal departmental regulations, daily routines, collective agreements, regulations on bonuses and other compensatory and incentive payments (additional payment for night work, for length of service, bonus based on annual work results, etc.).
Note. The employment agreement cannot indicate that “the specialist may be accrued other additional payments...”, since this is considered a violation of Art. 57 Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
- Condition for mandatory insurance of a specialist. Here, the management of the company can limit itself to the phrase that the specialist is included in the compulsory social insurance program, in accordance with this legislation.
At the end of the document, the parties sign. The employment agreement is drawn up in 2 copies, each having equal legal force. One copy is given to the employee, the second, with the employee’s signature confirming receipt of the first copy, is sent to the company’s human resources department.
IT terms using the example of the process of growing potatoes
Recently I was talking with a colleague about the topic of personnel selection in IT, and I remembered Alexander Krakovetsky’s sketch on this topic. Easy, fun and straightforward :) I decided to share it with everyone. The link to the original article is provided at the end. Krakovetsky Alexander Recently. In this article we will highlight the role of video content in personnel selection. So, HR department and video. You can’t immediately come up with a direct connection, except perhaps video presentations of yourself that are relevant today. That is, in essence, casting. To the office. For any position. In turn, for the new.
The procedure for terminating an employment contract with an employee
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of terminating an employment agreement at the initiative of any party.
The general procedure for terminating an employment relationship is as follows:
- Regardless of the circumstances and the initiator of the severance of the relationship, the termination of a trade union is accompanied by the issuance of an order on the expulsion of the working person, with whom he must be familiarized with signature.
- If the expelled specialist refuses to sign the order, this will be shown in the presence of at least two witnesses.
- Then the employer is obliged to make a corresponding entry in the work book and issue it, along with the final payment, to the dismissed person on the final date of his work.
The following types of severance of employment relations are distinguished:
- Termination of TD at the initiative of the employee.
- Termination of TD by agreement of the parties.
- Completion of urgent TD.
- Severance of labor relations at the initiative of the administration.
Termination of TD at the initiative of the employee
In other words, this is leaving work at will, when the employee submits an application and works for a 2-week period before actual dismissal (if the manager leaves work, the work is one month).
At the same time, an employee can leave the company without working on the following grounds:
- Violation of TD by the management of the company.
- Moving to another region.
- Upon retirement.
- Upon enrollment in an educational institution.
- Due to deteriorating health
During the service period, the employee has the right to change his mind and withdraw his resignation letter.
Termination of TD by agreement of the parties
In this option, an agreement to terminate the labor contract is drawn up and, if there are no claims from the parties, the application is signed by a personnel employee and the further procedure is carried out in accordance with the general procedure for terminating employment relationships.
Completion of urgent TD
The management of the institution must notify employees of the termination of a fixed-term employment agreement 3 days before the expiration of the TD. However, the boss can fire a pregnant employee only after completing her maternity leave.
Severance of labor relations at the initiative of the administration
The company's management has the right to break off relations with an employee, both on general and additional grounds.
General reasons include:
- Liquidation of the institution.
- Reduction in numbers.
- Inconsistency of the employed person with the vacancy.
- Failure of an employee to fulfill labor obligations.
- Waste of company property.
- Forgery of documents, etc.
All of the above facts must be documented. At the same time, the manager does not have the right to terminate the TD when the employee is on vacation or sick leave.
Additional grounds include the conditions for severing labor relations, enshrined in intradepartmental regulatory documents.
Note. It is impossible to terminate a TD at the initiative of the company’s management if the employee is pregnant, is a mother supporting an infant under 3 years of age, is a single mother supporting a child under 14 years of age, or a disabled child under 18 years of age.
In addition to the listed grounds for termination of a trade union, the relationship can be terminated by transfer if there is an application from the employee and confirmation from another company, when there is a change in management, etc.
The basis for deduction may also be circumstances beyond the control of the parties.
This may include:
- Call for military service
- Recognition of a worker as disabled
- When reinstating a former employee
- Death or unknown absence of an employee, etc.
In such cases, supporting documents are required as a basis for deduction.
Also, a TD can be terminated if it is declared invalid, that is, it was concluded in violation of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In any case of severance of relations, the expulsion procedure is carried out in accordance with the general procedure for terminating a TD, starting with the order of expulsion.
Job description for machine milking operator
1.1. The machine milking operator is a worker and reports directly to ………….. (name of position/profession of the manager) 1.2. To work as a machine milking operator, a person with secondary vocational education is accepted - training programs for qualified workers (employees). 1.3. To the work specified in paragraph 1.
2 of this instruction, a person is allowed: 1) who has passed in accordance with the Procedure for training on labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations (Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia and the Ministry of Education of Russia dated 13.01.
2003 N 1/29) training in safe methods and techniques for performing work, instruction on labor protection (introductory and in the workplace), on-the-job training and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements; 2) have undergone mandatory preliminary (upon employment) and periodic medical examinations (examinations), as well as extraordinary medical examinations (examinations) in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. 1.4. The machine milking operator must know: 1) the structure and principle of operation of the assembly units of milking machines; 2) design, principle of operation and technical characteristics of milking equipment; 3) rules for the preparation and operation of milking machines; 4) machine milking technology; 5) design, principle of operation and technical characteristics of equipment for primary processing of milk; 6) rules for the preparation and operation of equipment for primary milk processing; 7) technological schemes for primary milk processing; location and fastening of working parts of milking equipment;
2) have undergone mandatory preliminary (upon employment) and periodic medical examinations (examinations), as well as extraordinary medical examinations (examinations) in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation. 1.4. The machine milking operator must know: 1) the structure and principle of operation of the assembly units of milking machines; 2) design, principle of operation and technical characteristics of milking equipment; 3) rules for the preparation and operation of milking machines; 4) machine milking technology; 5) design, principle of operation and technical characteristics of equipment for primary processing of milk; 6) rules for the preparation and operation of equipment for primary milk processing; 7) technological schemes for primary milk processing; location and fastening of working parts of milking equipment; 9) schematic diagrams of individual working bodies and milking equipment as a whole; 10) rules for preparing for work and operating milking equipment; 11) operating modes of milking equipment; 12) rules for maintaining primary documentation; 13) design and rules of operation of devices, tools, equipment, personal protective equipment; 14) rules for udder care and signs of the most common animal diseases; 15) technology for keeping animals and producing milk on farms and complexes; 16) basics of behavior of dairy animals (ethology); 17) physiological, anatomical and economic characteristics of dairy animals; 18) a list of approved disinfectants used in livestock farming and the rules for their use; 19) labor protection rules when working with milking machines and installations; 20) labor protection rules when working with farm animals; 21) means and methods of disinfection used when working with milking machines; 22) means and methods of disinfection used when working with equipment for primary milk processing; 23) requirements for personal hygiene and industrial sanitation; 24) requirements for the quality of work performed; 25) types of defects and ways to prevent and eliminate them; 26) the procedure for notifying the manager of all deficiencies discovered during work; 27) rules for providing first (pre-medical) aid to victims of injury, poisoning and sudden illness; 28) Internal labor regulations; 29) rules of labor protection, industrial sanitation and personal hygiene, fire safety; 30) ………….. (other requirements for necessary knowledge) 1.5. A machine milking operator must be able to: 1) master the following techniques: – preparing the milking machine for work, starting it up and shutting it down; – safe inspection and treatment of the animal’s udder; – preparing milking equipment for operation, the procedure for starting and stopping it; 2) perform adjustment work; 3) prepare cleaning and disinfecting solutions; 4) work with milking equipment and inventory; 5) identify sick animals; 6) manage the milking process using hardware and software systems; 7) use control devices and automation equipment during the operation of equipment for the primary processing of milk; ensure uniform supply of milk during primary processing; 9) prepare cleaning and disinfecting solutions; 10) know how to prepare a machine for work, the procedure for starting and stopping it; 11) identify deviations from the specified operating standards of milking equipment; 12) have the skills to adjust milking and milk equipment; 13) use technical means, instruments, equipment and diagnostic tools to carry out maintenance operations of milking and dairy equipment; 14) use personal protective equipment; 15) ………………. (other requirements for necessary skills) 1.6. ………………. (other general provisions)
9) schematic diagrams of individual working bodies and milking equipment as a whole; 10) rules for preparing for work and operating milking equipment; 11) operating modes of milking equipment; 12) rules for maintaining primary documentation; 13) design and rules of operation of devices, tools, equipment, personal protective equipment; 14) rules for udder care and signs of the most common animal diseases; 15) technology for keeping animals and producing milk on farms and complexes; 16) basics of behavior of dairy animals (ethology); 17) physiological, anatomical and economic characteristics of dairy animals; 18) a list of approved disinfectants used in livestock farming and the rules for their use; 19) labor protection rules when working with milking machines and installations; 20) labor protection rules when working with farm animals; 21) means and methods of disinfection used when working with milking machines; 22) means and methods of disinfection used when working with equipment for primary milk processing; 23) requirements for personal hygiene and industrial sanitation; 24) requirements for the quality of work performed; 25) types of defects and ways to prevent and eliminate them; 26) the procedure for notifying the manager of all deficiencies discovered during work; 27) rules for providing first (pre-medical) aid to victims of injury, poisoning and sudden illness; 28) Internal labor regulations; 29) rules of labor protection, industrial sanitation and personal hygiene, fire safety; 30) ………….. (other requirements for necessary knowledge) 1.5. A machine milking operator must be able to: 1) master the following techniques: – preparing the milking machine for work, starting it up and shutting it down; – safe inspection and treatment of the animal’s udder; – preparing milking equipment for operation, the procedure for starting and stopping it; 2) perform adjustment work; 3) prepare cleaning and disinfecting solutions; 4) work with milking equipment and inventory; 5) identify sick animals; 6) manage the milking process using hardware and software systems; 7) use control devices and automation equipment during the operation of equipment for the primary processing of milk; ensure uniform supply of milk during primary processing; 9) prepare cleaning and disinfecting solutions; 10) know how to prepare a machine for work, the procedure for starting and stopping it; 11) identify deviations from the specified operating standards of milking equipment; 12) have the skills to adjust milking and milk equipment; 13) use technical means, instruments, equipment and diagnostic tools to carry out maintenance operations of milking and dairy equipment; 14) use personal protective equipment; 15) ………………. (other requirements for necessary skills) 1.6. ………………. (other general provisions)
2.1. The labor functions of a machine milking operator are: 2.1.1. Milking animals using milking equipment: 1) preparing milking equipment for work; 2) preparing the animal for milking; 3) milking; 4) primary processing of milk; 5) maintenance of milking equipment. 2.2. ……………… (other functions)
Responsibilities
3.1. Before the start of the working day (shift), the machine milking operator: 1) undergoes a pre-shift (preventive) medical examination in accordance with the established procedure; 2) receives a production task; 3) if necessary, undergoes training on labor protection; 4) takes over the shift; 5) checks the serviceability of devices, tools, inventory, etc.
, personal protective equipment; 6)………………. (other responsibilities) 3.2.
During the work process, the machine milking operator: 1) performs the work for which he has been instructed and authorized to work; 2) uses special clothing, safety shoes and other personal protective equipment; 3) receives instructions from the immediate supervisor on the performance of the task, safe techniques and methods of work; 4) complies with the rules for using technological equipment, devices and tools, methods and techniques for performing work safely; 5) immediately notify the immediate supervisor of all deficiencies discovered during work; 6) complies with the requirements of personal hygiene and industrial sanitation; 7)………………. (other responsibilities) 3.3. During the working day (shift), the machine milking operator performs the following duties as part of his job functions: 3.3.1. Within the framework of the labor function specified in paragraphs. 1 clause 2.1.1 of these instructions: 1) checks: – the correct assembly of milking machines; – correct operation of pulsators, collectors, tightness of all connections; – pulsation frequency of milking machines; 2) carries out adjustment work; 3) washes milking machines before milking; 4) connects the milking machine to the vacuum line. 3.3.2. Within the framework of the labor function specified in paragraphs. 2 clause 2.1.1 of these instructions: 1) inspects the animal’s udder before milking; 2) washes the animal’s udder; 3) wipes the animal’s udder with a clean, dry towel or paper napkin soaked in a disinfectant solution; 4) performs a massage of the animal’s udder; 5) carries out preliminary milking of milk into special containers; 6) draws up primary documentation. 3.3.3. Within the framework of the labor function specified in paragraphs. 3 clause 2.1.1 of these instructions: 1) puts the milking machine into operation; 2) puts the teat cups on the udder nipples; 3) monitors milk yield and operating mode of the milking machine; 4) performs machine milking; 5) turns off the milking machine; 6) removes the milking cups from the animal’s udder teats; 7) treats the animal’s udder teats after milking with special disinfectant solutions. 3.3.4. Within the framework of the labor function specified in paragraphs. 4 clause 2.1.1 of this instruction: 1) monitors the technical condition and serviceability of equipment for the primary processing of milk; 2) carries out preparation, startup and control of equipment operation: – for milk purification; – for pasteurization of milk; – for cooling milk; – for storing and dispensing milk; 3) performs adjustment work; 4) stops and washes equipment for primary milk processing. 3.3.5. Within the framework of the labor function specified in paragraphs. 5 clause 2.1.1 of this instruction: 1) carries out visual control of the level of technical and technological parameters of milking equipment; 2) cleans the working surfaces of the equipment and its components from contaminants and residues of the processed product; 3) monitors the condition of protective barriers, safety devices and protection devices, the reliability of fastening of equipment components, grounding conductors, the presence of leaks and the level of lubrication; 4) checks and evaluates the technical condition of equipment according to controlled parameters; 5) checks the performance of the equipment and its components by sequentially putting it into operation; 6) lubricates equipment. 3.4. At the end of the working day (shift), the machine milking operator: 1) puts devices and tools in proper condition and transfers them for storage; 2) removes dirt from workwear and safety shoes, if necessary, places them for drying and storage; 3) submits established reports; 4) performs an inspection (self-examination); 5) turns over a shift; 6) ……………… (other duties) 3.5. As part of the performance of his labor functions, the machine milking operator: 1) carries out instructions from his immediate supervisor; 2) undergoes periodic medical examinations (examinations), as well as extraordinary medical examinations (examinations) in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation; 3) performs work under the supervision of an employee with a higher qualification level; 4) …………….. (other duties) 3.6. ……………… (other provisions on responsibilities)
Rights
4.1.
When performing his labor functions and duties, the machine milking operator has labor rights provided for by the employment contract concluded with the employee, the Internal Labor Regulations, local regulations, the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and other acts of labor legislation. 4.2. …………… (other provisions on employee rights)
Responsibility
5.1. The machine milking operator is subject to disciplinary liability in accordance with Art. 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation for improper performance through his fault of the duties listed in this instruction. 5.2.
The machine milking operator bears financial responsibility for ensuring the safety of the inventory items entrusted to him. 5.3.
The machine milking operator for committing offenses in the course of his activities, depending on their nature and consequences, is subject to civil, administrative and criminal liability in the manner prescribed by law. 5.4. ………………. (other liability provisions)
Final provisions
6.1. This instruction has been developed on the basis of the Professional Standard “Machine Milking Operator”, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation dated May 19, 2014 N 324n, taking into account …………. (details of local regulations of the organization) 6.2.
The employee is familiarized with these instructions upon hiring (before signing the employment contract). The fact that the employee has read these instructions is confirmed by………………..
(signed on the familiarization sheet, which is an integral part of these instructions (in the log of familiarization with the instructions); in a copy of the instructions stored by the employer; in another way) 6.3. ………………..
Sample employment contract with an employee in 2021
Form of employment contract with employee
Employer's liability
An employment contract is a basic document of labor legislation. It is designed to protect the rights of workers, and this is the very first “goal” of the inspection of the State Labor Inspectorate. Above we wrote about what must be included in it. Now let us briefly list the amount of fines that the director and the company will have to pay for violations in the execution of employment contracts. According to Article 5.27 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, for violations in the field of labor relations, the amounts of fines are:
- for the head of the enterprise - 10,000–20,000 rubles;
- for a legal entity - 50,000–100,000 rubles;
- for individual entrepreneurs - 5,000–10,000 rubles.