Simplified reporting can be submitted by small businesses, non-profit organizations and participants in the Skolkovo project that are not subject to the restrictions established by clause 5 of Art. 6 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ. Simplified reporting forms used for the 2021 report are contained in Appendix No. 5 of Order No. 66n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 2, 2010 (as amended on April 19, 2019). Line codes in the simplified financial statements of the company are indicated independently. We will tell you what is included in each indicator and how to choose the necessary encoding for it.
Targeted financing on balance sheet
A selection of the most important documents on request Targeted financing in the balance sheet (regulatory acts, forms, articles, expert consultations and much more).
Regulatory acts: Targeted financing on the balance sheet
Reference information: “Forms of accounting statements” (Material prepared by ConsultantPlus specialists) - prepare financial statements in a reduced volume (balance sheet and income statement - for a commercial organization; balance sheet and report on the intended use of funds - for a non-profit organization). In particular, the decision to include in the financial statements a statement of changes in capital and a statement of cash flows is determined by the need to provide the most important information in appendices to the balance sheet, statement of financial results, report on the intended use of funds, without which it is impossible to assess the financial position organization or financial results of its activities (clause “b”, clause 6 of the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 07/02/2010 N 66n, clause 26 of the Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 06/29/2016 N PZ-3/2016);
Articles, comments, answers to questions: Targeted financing on the balance sheet
A Guide to Corporate Litigation. Issues of judicial practice: Withdrawal of a participant from a limited liability company In accordance with the expert opinion of Yulex Audit LLC No. 1 dated March 12, 2012, information in the balance sheet of the developer about the amount of target funds received from participants in shared construction is disclosed in the balance sheet as of 09/30/2010 in line 640 “Deferred income” is incorrect. In the 4th quarter of 2010, the company disclosed this information in line 660 “Other short-term liabilities” correctly. Taking this into account, the value of the company's net assets as of December 31, 2010 is RUB 6,471,000. Tax Guide. Practical guide for filling out the Report on the targeted use of funds. For this line, non-profit organizations reflect information about the funds of targeted financing used for the acquisition of non-current assets, the amount of which increased the indicator of line 1360 “Real estate and especially valuable movable property fund” in section. III “Targeted financing” of the Balance Sheet (note 4 in Appendix No. 4 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 2, 2010 N 66n, clause 35 of Information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia PZ-1/2015).
Article provided by specialists of the Avtor24 service
Author24 is a community of teachers and professors who you can turn to for help with your school work.
Section III “Capital and Reserves”: line 1310, 1320, 1340, 1350, 1360, 1370
Section III of the balance sheet consists of seven lines. They, in particular, reflect the amount of the organization’s authorized capital, the value of its own shares purchased from shareholders, the amount of additional and reserve capital, the amount of retained earnings or uncovered losses.
Let's look at the order in which each of these lines is filled out.
line 1310, line 1320, line 1340, line 1350, line 1360, line 1370
Line 1310 “Authorized capital”
Line 1310 is filled in by all companies. It reflects the amount of the organization’s authorized capital. Moreover, you need to write in line 1310 exactly the amount that is recorded in the constituent documents. It does not matter if one of the founders paid his share partially.
Or has not yet made a contribution to the authorized capital. That is, the fact of payment of the authorized capital does not play any role in determining the indicator of line 1310, which accountants sometimes forget about. The debt of the founders is reflected as receivables on line 1230 of the balance sheet asset.
The credit balance of account 80 “Authorized capital” is transferred to line 1310.
Line 1320 “Own shares...”
Line 1320 can be filled in by both joint stock companies and limited liability companies (if the company buys out shares from retiring founders). Joint-stock companies on line 1320 show their own shares purchased from shareholders, and limited liability companies reflect the value of shares in the authorized capital purchased from the participants (founders) of the company.
The debit balance of account 81 “Own shares (shares)” is transferred to this line. Be careful: the indicator in line 1320 is shown in parentheses. This means that the value is negative - it will need to be subtracted from the total liabilities of the balance sheet.
Line 1340 “Revaluation of non-current assets”
Line 1340 is filled in by those companies that revaluate fixed assets and intangible assets. In line 1340 it is necessary to show the amount of increase in the value of non-current assets established during revaluation. That is, it is necessary to transfer to this line of the balance sheet the credit balance of account 83 “Additional capital” in terms of subaccounts that reflect the additional valuation of property.
Line 1350 “Additional capital (without revaluation)”
Note that additional capital can be formed both through the additional valuation of non-current assets and through share premium. Such income arises, for example, from joint-stock companies if the organization’s own shares are placed at a price higher than their par value.
In addition, additional capital can be formed when the founders make contributions to the property of the LLC or take into account the amount of VAT recovered by the participant when transferring the property as a contribution to the authorized capital and transferred to the established organization. To fill out line 1350, take the credit balance of account 83 “Additional capital” and from it subtract the amounts of additional valuation of fixed assets and intangible assets.
Line 1360 “Reserve capital”
Line 1360 is filled out by organizations that create a reserve fund. It must be formed only by joint stock companies (Article 35 of the Federal Law of December 26, 1995 No. 208-FZ “On Joint Stock Companies”).
According to this article, joint stock companies must annually contribute at least 5 percent of net profit to the reserve fund. These deductions stop when the reserve fund reaches the size provided for by the charter.
In this case, the size of the fund cannot be less than 5 percent of the authorized capital.
Limited liability companies can also create a reserve fund. At the same time, they determine its size and order of formation independently.
The credit balance of account 82 “Reserve capital” is transferred to line 1360 of the balance sheet.
Line 1370 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”
Line 1370 is filled in by all organizations. After all, it is in this line that the retained profit or uncovered loss of the company is shown. Agree, it is unlikely that the company will break even. There will still be at least a minimum profit or a minimum loss.
Filling out line 1370 is easy. To do this, from account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss”), transfer to line 1370:
- debit balance (indicate it in parentheses, that is, when calculating the value of the final line 1300, this amount will be subtracted);
- credit balance (if there is retained earnings).
In order to determine the annual financial result and fill out line 1370 of Form 1, the organization must reform its balance sheet. This must be done on December 31 of the reporting year. Balance sheet reformation means closing accounts:
– 90 “Sales”; – 91 “Other income and expenses”;
– 99 “Profits and losses.”
The balance on them as of January 1 of the year following the reporting year should be equal to zero.
Source: https://www.glavbukh.ru/art/21593-razdel-iii-kapital-i-rezervy-balansa
The concept of targeted financing
Definition 1
Targeted financing is a type of assistance to an enterprise that is provided by various organizations or the state at the expense of budget funds for the implementation of certain programs.
Targeted financing programs can be of various types:
- Social development of a region or an individual enterprise.
- Programs that promote economic growth.
- Innovative development programs.
- Investment programs.
- Environmental conservation programs.
- Programs for the development of foreign economic activity.
- Programs to eliminate the consequences of natural disasters.
When preparing a target program, the essence and nature of the problem for the solution of which targeted funding is allocated are taken into account. The programs also indicate the timing of the program, the stages of its implementation and a list of all necessary resources to fulfill the program’s objectives (monetary, labor, material). If the implementation of the program requires the participation of third-party organizations, then such target program must indicate such participants and the degree of their participation in the implementation of the project.
Can not understand anything?
Try asking your teachers for help
Balance lines 2021: decoding
Descriptive pages of financial statements. Drawing up a balance sheet under the simplified tax system for 2021 implies only 5 types of assets and 8 types of liabilities (Fig. 1). Passive accounts have been detailed compared to the previous form.
Two added items “target funds” and “fund of real estate and especially valuable movable property” are necessary to detail the organization’s assets. They must indicate data on targeted funds aimed at major repairs, modernization of fixed assets or innovation.
In addition, many organizations will be required to record the value of real estate or vehicles on their balance sheet. Please note: the line code corresponds to the account that has the greatest share of it. For example, an enterprise has intangible assets worth 100 thousand rubles. (code 1110) and financial investments worth 50 thousand rubles. (code 1170).
Reflection of targeted financing in the accounting and balance sheet of the enterprise
The enterprise to which targeted financial assistance was sent must, in a certain order, reflect all transactions for receiving and spending funds in the appropriate accounts.
The procedure for recording targeted financing transactions is contained in:
- For tax accounting - in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- For accounting – in PBU 13/2000 “Accounting for state aid”
Note 1
In addition, certain elements of accounting for funds from targeted financing are taken into account by separate regulations. For example, the procedure for reflecting targeted financing in reporting is regulated by PBU 4/99 “Accounting statements of an organization.”
First of all, to take into account targeted financing, the organization needs to determine the classification of such financing according to the areas of financing. For example, this could be a classification in the context of:
- areas of financing (social, economic, innovative, to cover losses, to eliminate consequences, etc.)
- deadlines for the implementation of target programs (short-term, long-term).
- other signs of using targeted financing
Sources of targeted financing are also subject to classification. For example:
- state at the expense of budgetary funds;
- various foundations or public organizations4
- private individuals;
- foreign investors;
- etc.
This classification of elements and objects of targeted financing must be approved in the accounting policy of the enterprise, since it directly affects the formation of the enterprise’s balance sheet.
Note 2
The balance sheet of an enterprise reflects the balances of property, liabilities and equity of the enterprise as of a certain reporting date. Targeted financing is reflected in the balance sheet of the enterprise, taking into account a number of features. Despite the fact that the chart of accounts for accounting for targeted financing provides for account 86 from the “Capital and Reserves” section, such financing is reflected as liabilities in the organization’s balance sheet.
When concluding an agreement for targeted financing, the following entry is generated in the company’s accounting:
D-t 76 K-t 86
When using targeted financing funds, from the credit of account 86, these funds are written off to the debit of the corresponding accounts. Thus, when forming the balance sheet of an enterprise, the funds received for targeted financing are reflected in the income of future periods on the liability side of the balance sheet.
It is important that the costs of targeted financing are identical to the costs stated in the estimates drawn up for target programs.
Previous article Postings of target financing
]]>]]>
Section I of the balance sheet “Non-current assets”
Intangible assets.
Their residual value is reflected on line 1110.
Results of research and development.
Research and development expenses recorded on account 04 “Intangible assets” are entered on line 1120 of the balance sheet.
Intangible and tangible search assets.
These two indicators are given in lines 1130 and 1140. The data reflects organizations that are users of subsoil. Here they provide information on the costs of developing natural resources (PBU 24/2011 “Accounting for costs of developing natural resources”, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 6, 2011 No. 125n).
Fixed assets.
For depreciable objects, the residual value of fixed assets is recorded in line 1150. For property that is not subject to depreciation, its original cost is indicated. The cost of unfinished work is also reflected here - clause 20 of PBU 4/99. To do this, you can add the decoding line “Unfinished construction” to line 1150.
Profitable investments in material assets.
The data is reflected on line 1160. This is the residual value of property for rent (leasing), which is accounted for in account 03. If the property was first used in production and management, but was later leased out, it must be reflected in a separate subaccount of account 01. Then the information will be reflected on line 1150.
Financial investments.
For long-term financial investments (with a maturity of more than a year), line 1170 is intended (short-term financial investments - line 1240). Investments in subsidiaries, affiliates and other companies are also shown here.
Deferred tax assets.
Line 1180 is filled in by income tax payers.
Other noncurrent assets.
Line 1190 shows data on non-current assets that are not reflected in other lines of Section I of the balance sheet.
Account 86 in balance
The answer to the question whether account 86 is active or passive depends on the pre-agreed conditions of the subject of financing. The chart of accounts considers account 86 as active-passive. Although most often the balance of the record is of a credit nature. If the allocated funds are overspent, the account may also have a debit balance.
Unspent funds 86 account in the balance sheet will be reflected in the passive part on lines 1450 and 1550. In case of overexpenditure of allocated target funds, asset line 1190 is used, which includes other non-current assets.
Records of the movement of received amounts depend on the nature of the activity of the economic entity.
Account 86 “Targeted financing” posting (example of records of a commercial organization):
- Dt 76 - Kt 86 - an agreement arose on the need to use targeted assets;
- Dt 10, 50, 51 - Kt 76 - materials, cash resources and other assets were capitalized as target accounting;
- Kt 20, 26 - Kt 10 - received materials are taken into account as part of other expenses.
Funds received from the budget can be immediately recorded in accounts with the appearance of appropriate entries, for example:
- Dt 50, 51 - Kt 86 - monetary assistance credited.
celevoe_finansirovanie_v_buhgalterskom_balanse0.jpg
Related publications
Targeted financing is funds directed to a company from budgets of various levels, from legal entities and private investors for pre-agreed and strictly defined purposes. Their expenditure must be carried out in strict accordance with the approved budget and for the purpose established by the source of funding.
If the conditions set are strictly fulfilled, the received investments become the company’s own, and failure to fulfill them will entail their return. Let's talk about the features of accounting and reflection of target allocations in the company's reporting.
How to close an 86 account?
The result of the use of targeted funds is reflected in the debit of account 86. The generated entries will depend on the nature of the transactions and the current accounting policy. The posting of property and materials that were received within the specified conditions in commercial enterprises is reflected by the following entries:
- Dt 86 - Kt 98 - assets received are considered as deferred income;
- Dt 60 - Kt 51 - allocated amounts were spent as repayment from suppliers for the valuables provided;
- Dt 10 - Kt 60 - materials delivered to the arrival;
- Dt 20 - Kt 10 - writing off materials as expenses;
- Dt 91 - Kt 20 - closing an expense account.
- Dt 98 - Kt 91 - target assets received are reflected as other income.
Using targeted funds, non-profit organizations can cover their costs directly:
- Dt 86 - Kt 20, 26 - receipts are directed to the expenses of the organization.
In addition, the acquired assets can increase additional capital:
- Dt 86 - Kt 83 - use of invested funds by a non-profit entity.
How is account 86 closed at the end of the year? If the received assets cannot be used in full, the balance of the targeted financing will be taken into account as a liability on the balance sheet. In a situation where less funds were required to complete a task than were allocated, the organization takes into account the remaining money as other income: Dt 86 - Kt 91. Depending on the current terms of the contract, a refund may be made: Dt 86 - Kt 51.
Analytical accounting of assets, the receipt of which is associated with targeted financing, must be maintained for each source of income. If necessary, subaccounts are opened for account 86.
Section II of the balance sheet “Current assets”
Inventories.
The cost of inventories is reflected on line 1210. The indicator must be deciphered if it is significant. In this case, you should add decryption strings, for example:
- raw materials and materials;
- costs in work in progress;
- finished products and goods for resale;
- goods shipped.
Value added tax on purchased assets.
Line 1220 reflects the debit balance of account 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets.” This is input VAT, which was not deducted.
Accounts receivable.
Line 1230 provides information about short-term receivables - when payments are expected within 12 months after the reporting date.
Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents).
For these assets, line 1240 is provided, which, in particular, shows loans provided by the organization for a period of less than 12 months.
Cash and cash equivalents.
To fill out line 1250, you need to sum up the cost of cash equivalents (balances of the corresponding subaccounts of account 58) and the balances of accounts in which cash is accounted for (50 “Cash”, 51 “Settlement accounts”, 52 “Currency accounts”, 55 “Special accounts in banks " and 57 "Translations on the way").
Other current assets.
Here (line 1260) shows data on current assets that are not reflected in other lines of section II of the balance sheet.
Postings to account 86 using an example
Let’s say that Stromex LLC received subventions in March 2021 in the amount of:
- 1,200,000 rub. — for the purchase of production equipment;
- 2,000,000 rub. — for current expenses (targeted work according to the approved estimate).
Until the end of 2021, funds from the state budget went to:
- equipment, RUB 1,500,000, useful life 10 years;
- purchase of materials, 250,000 rubles;
- remuneration for employees involved in targeted activities, RUB 150,000;
- social insurance, 39,000 rubles;
- materials released into production (in fact), 170,000 rubles.
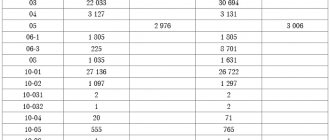
Table of entries for accounting for subventions in account 86:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 76 | 86 | 3 200 000 | Subventions are recognized in accounting (as approved in budget expenditures) | Targeted financing agreement |
| 51 | 76 | 3 200 000 | Subventions received are recognized in accounting | Bank statement |
| 08.04 | 60 | 1 500 000 | Equipment (cost) included | Packing list |
| 01 | 08.04 | 1 500 000 | Equipment put into operation | OS commissioning certificate |
| 86 | 98 | 1 000 000 | The amount of the subvention is recognized as part of deferred income (upon commissioning of equipment) | Targeted financing agreement, Consignment note, OS commissioning certificate |
| 20,23,25,26,44 | 02 | 12 500 | Depreciation reflected (monthly deduction) | Depreciation statement |
| 98 | 91.01 | 12 500 | Recognition of other income from the received subvention | |
| 10 | 60 | 250 000 | Materials (cost) included | Receipt order (Form No. M-4)/Act of acceptance of materials (Form No. M-7) |
| 86 | 98 | 250 000 | The amount of the subvention is recognized as part of deferred income | Targeted financing agreement, Consignment note, M-4/M-7 |
| 20,23,25,26,44 | 70 | 150 000 | Payments have been accrued to employees of Stromex LLC | Certificate-calculation/ Salary slip (form No. T-53) |
| 20,23,25,26,44 | 69 | 39 000 | Social insurance contributions (including accidents and occupational diseases) | Payroll (form T-51) |
| 86 | 98 | 189 000,00 | The amount of the subvention is recognized as part of deferred income | Targeted financing agreement, certificate of calculation, T-53 and T-51 |
| 98 | 91.01 | 189 000 | Recognition of a subvention as part of the income of the reporting period of Stromex LLC | Targeted financing agreement, certificate of calculation |
| 20,23,25,26 | 10 | 170 000 | Materials released into production (cost) are taken into account | Packing list |
| 98 | 91.01 | 170 000 | Recognition of a subvention as part of the income of the reporting period of Stromex LLC | Targeted financing agreement, Consignment note |
Explanation of balance sheet asset lines
| Indicator name | Code | Algorithm for calculating the indicator | |
| Intangible assets | 1110 | 04 “Intangible assets”, 05 “Amortization of intangible assets” | D04 (excluding R&D expenses) - K05 |
| Research and development results | 1120 | 04 | D04 (in terms of R&D expenses) |
| Intangible search assets | 1130 | 08 “Investments in non-current assets”, 05 | D08 - K05 (all regarding intangible exploration assets) |
| Material prospecting assets | 1140 | 08, 02 “Depreciation of fixed assets” | D08 - K02 (all regarding material exploration assets) |
| Fixed assets | 01 “Fixed assets”, 02 | D01 - K02 (except for depreciation of fixed assets accounted for in account 03 “Income-generating investments in tangible assets” | |
| Profitable investments in material assets | 1160 | 03, 02 | D03 - K02 (except for depreciation of fixed assets accounted for on account 01) |
| Financial investments | 1170 | 58 “Financial investments”, 55-3 “Deposit accounts”, 59 “Provisions for impairment of financial investments”, 73-1 “Settlements on loans provided” | D58 - K59 (in terms of long-term financial investments) + D73-1 (in terms of long-term interest-bearing loans) |
| Deferred tax assets | 1180 | 09 “Deferred tax assets” | D09 |
| Other noncurrent assets | 1190 | 07 “Equipment for installation”, 08, 97 “Deferred expenses” | D07 + D08 (except for exploration assets) + D97 (in terms of expenses with a write-off period of more than 12 months after the reporting date) |
| Reserves | 10 “Materials”, 11 “Animals for growing and fattening”, 14 “Reserves for reducing the cost of material assets”, 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”, 16 “Deviation in the cost of material assets”, 20 “Main production”, 21 “Semi-finished products own production”, 23 “Auxiliary production”, 28 “Defects in production”, 29 “Service production and facilities”, 41 “Goods”, 42 “Trade margin”, 43 “Finished products”, 44 “Sales expenses”, 45 “Goods shipped”, 97 | D10 + D11 - K14 + D15 + D16 + D20 + D21 + D23 + D28 + D29 + D41 - K42 + D43 + D44 + D45 + D97 (for expenses with a write-off period of no more than 12 months after the reporting date) | |
| Value added tax on purchased assets | 1220 | 19 “Value added tax on acquired assets” | D19 |
| Accounts receivable | 1230 | 46 “Completed stages of work in progress”, 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”, 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, 63 “Provisions for doubtful debts”, 68 “Settlements for taxes and duties”, 69 “Settlements for social insurance and security", 70 "Settlements with personnel for wages", 71 "Settlements with accountable persons", 73 "Settlements with personnel for other operations", 75 "Settlements with founders", 76 "Settlements with various debtors and creditors" | D46 + D60 + D62 - K63 + D68 + D69 + D70 + D71 + D73 (except for interest-bearing loans accounted for in subaccount 73-1) + D75 + D76 (minus VAT calculations reflected in the accounts on advances issued and received) |
| Financial investments (excluding cash equivalents) | 1240 | 58, 55-3, 59, 73-1 | D58 - K59 (in terms of short-term financial investments) + D55-3 + D73-1 (in terms of short-term interest-bearing loans) |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 50 “Cash”, 51 “Current accounts”, 52 “Currency accounts”, 55 “Special bank accounts”, 57 “Transfers in transit”, | D50 (except for subaccount 50-3) + D51 + D52 + D55 (except for the balance of subaccount 55-3) + D57 | |
| Other current assets | 1260 | 50-3 “Money documents”, 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables” | D50-3 + D94 |
Assignment of codes and numbers
Codes for certain lines must be indicated in a certain column. It is worth noting that codes are needed mainly so that statistical authorities can combine information presented in different types of balance sheets into one whole. The codes are mandatory to fill out when the balance sheet being compiled must be transferred to state executive structures with further use of information on them.
In a situation where the balance sheet is prepared for a quarter or other reporting period, in order for it to be considered at internal meetings for the purpose of introducing the state of affairs or analyzing the company’s activities, it is not necessary to fill in the code lines, since they do not carry any responsibility in this case no functions.
Line coding is performed only if this reporting documentation is submitted to government agencies and is not an obligation for the internal preparation of reporting balances. Since financial statements are submitted to the tax authorities only once a year, the coding applies only to annual balance sheets.
Useful video about filling out your balance from scratch:
An example of filling out a simplified balance sheet for a simplified tax system
We talked about the content and structure of the balance sheet in our consultation. Let us remind you that the current form of the balance sheet submitted to the tax inspectorate and statistical authorities was approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated July 2, 2010 No. 66n. We showed how to draw up a balance sheet using an example in a separate material. We noted that drawing up a balance sheet is essentially transferring the balances of the accounting accounts to the lines provided for them. Therefore, to correctly draw up a balance sheet, you need not only to keep accounting records correctly and in full, but also to know which accounting accounts are reflected in which line of the balance sheet. In our consultation we will provide a breakdown of all the lines of the balance sheet.
In this case, we will detail the balance sheet lines according to the most typical accounts, which are reflected on such lines.
How to decrypt strings
In order to understand how the process of deciphering codes line by line is carried out, it is worth understanding that not a single code is a simple set of numbers. This is a code for a certain type of information.
- The first value confirms the fact that this line relates specifically to the main type of accounting statements, or rather, to the balance sheet, and not to another type of reporting documents.
- The second digit indicates which section of the asset the amount belongs to. For example, a unit indicates that the amount belongs to non-current assets.
- The third figure serves as a certain indicator of the liquidity of this resource.
- The fourth digit is initially equal to zero, adopted in order to provide some detailing of the items according to their materiality.
For example, deciphering line 1230 of the balance sheet is accounts receivable.
For a liability, decoding occurs according to the same principle as in the situation with an asset:
- The first digit indicates that it belongs specifically to the balance sheet for the year.
- The second figure demonstrates that this amount belongs to a separate section of the liability column.
- The third number indicates the urgency of the obligation.
- The fourth value is adopted for detailed perception of information.
The total liability is line 1700, which is the sum of line 1300 of the balance sheet, 1400 and 1500.
So, the process of deciphering the codes line by line in the balance sheet occurs on the basis of Appendix No. 4 to 66 Order of the Ministry of Finance. The structure of the codes themselves has a certain meaning. It is important to navigate the very structure of the balance sheet, or rather, its sections and articles.
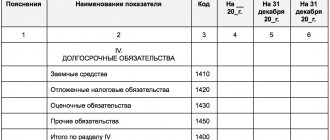
Section IV of the balance sheet “Long-term liabilities”
Borrowed funds.
Line 1410 is reserved for the debt of the organization itself on long-term (with a repayment period of more than 12 months) loans and credits.
Deferred tax liabilities.
Line 1420 is filled in by income tax payers.
Estimated liabilities.
Line 1430 is filled out if the organization recognizes estimated liabilities in accounting in accordance with PBU 8/2010 “Estimated liabilities, contingent liabilities and contingent assets.”
Other obligations.
Other long-term liabilities that were not reflected in other lines of Section IV of the balance sheet. Enter on line 1450.
Reflection of targeted financing in financial statements
The Appendix to the Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 22, 2003 No. 67n “On Forms of Accounting Reports of Organizations” provides samples of accounting reporting forms, including a sample balance sheet form. At the same time, the balance sheet form does not provide a special line for targeted financing.
According to Order No. 67n, organizations can take these samples into account when developing and adopting (approving by administrative document) their forms of accounting statements based on the specifics of their activities.
The procedure for reflecting targeted financing in financial reporting forms is different for commercial and non-profit organizations.
Commercial organizations, according to paragraph 20 of PBU 13/2000, show received budget funds in the Balance Sheet in Section V “Short-term liabilities” on line 640 “Deferred income” or they can be shown as a separate line. Other targeted funds are also shown by commercial organizations in sections IV or V of the balance sheet as long-term or short-term liabilities.
A non-profit organization must be guided by paragraph 13 of the Instructions on the procedure for drawing up and submitting financial statements, approved by Order No. 67n. Instead of the groups of items “Authorized capital”, “Reserve capital” and “Retained earnings” given in the sample forms, a non-profit organization should include the item “Targeted financing” in the balance sheet.
Income from the use of targeted financing funds, recognized in accounting account 91 “Other income and expenses” in accordance with this provision, is reflected in non-operating income of the Profit and Loss Statement (Form No. 2) as assets received free of charge.
Amounts of targeted financing recognized in accounting in previous years as income, but subject to return, are reflected in non-operating expenses of the income statement (Form No. 2) and decoding of individual profits and losses as losses of previous years recognized in the reporting period. year.
In the report on changes in capital (form No. 3), data on the balances of targeted financing and revenues (from the budget, extra-budgetary funds, from other organizations and citizens), their use and balances at the end of the reporting period can be given in the Certificate after the section “Changes in capital” . To do this, the corresponding columns are added to the Help.
The cash flow statement (Form No. 4) reflects the funds received for targeted financing received in cash.
To form the “State Aid” section of the Appendix to the Balance Sheet (Form No. 5), information on budget funds received in the reporting year by type of revenue is used.
The report on the targeted use of funds received (Form No. 6) reflects information on the balances of target funds at the beginning of the reporting year, the receipt of funds by type of income and their expenditure by areas of expenditure for the reporting year and the previous year.
The explanatory note must disclose at least the following information regarding targeted budget financing:
· the nature and amount of budget funds recognized in accounting in the reporting year;
· purpose and amount of budget loans;
· the nature of other forms of government assistance from which economic benefits are directly obtained.
Other forms of government assistance include benefits provided that cannot be reasonably assessed (providing consulting services free of charge, providing guarantees, interest-free loans or loans with a reduced interest rate, etc.), and also cannot be separated from normal business activities (for example , state procurements). Other forms of state assistance are subject to disclosure in the financial statements in an explanatory note if they are significant for characterizing the financial position and financial results of operations (clause 18 of PBU 13/2000).
· conditions for the provision of budgetary funds that were not fulfilled as of the reporting date and the associated contingent liabilities and contingent assets (link to the provision).
You can find out more about issues related to budgetary and targeted financing in the book of JSC “BKR Intercom-Audit” “Budget and targeted financing”.
Targeted financing is funds directed to a company from budgets of various levels, from legal entities and private investors for pre-agreed and strictly defined purposes. Their expenditure must be carried out in strict accordance with the approved budget and for the purpose established by the source of funding.
If the conditions set are strictly fulfilled, the received investments become the company’s own, and failure to fulfill them will entail their return. Let's talk about the features of accounting and reflection of target allocations in the company's reporting.
An example of filling out a balance sheet for 2016 using a general form
The general form of the balance sheet is given in Appendix No. 1 to Order No. 66n. You cannot delete any lines from the approved form, but you can enter additional ones if desired. For example, if an organization wants to separately show deferred expenses in the balance sheet, then you can independently add a special line to section "Current assets".
The balance sheet in its general form has columns in which the following indicators are given for each item:
- as of December 31 of the year preceding the previous one (when filling out the balance sheet for 2014 - as of December 31, 2014).
- as of the reporting date (when filling out the balance sheet for 2021 - as of December 31, 2021);
- as of December 31 of the previous year (when filling out the balance sheet for 2016 - as of December 31, 2015);
Column 1 of the balance sheet is intended to indicate the number of the corresponding explanation to the balance sheet (if an explanatory note is drawn up). Column 3 of the organization is added
Targeted financing in accounting
Usually the following are financed in a targeted manner:
- Design, survey and research work;
- Capital construction;
- Various special campaigns or ongoing activities (for example, repayment of debts to creditors);
- Technical re-equipment of production;
- Reimbursement of expenses incurred.
Investment of targeted funds from any sources is formalized by an agreement that reflects all the conditions that are mandatory for receiving and using financing, as well as defining a clear project framework and methods for controlling spending. These circumstances dictate separate accounting (analytical and synthetic) for each funded project.
Operations on targeted financing and its expenditure are combined on account 86 “Targeted financing” (TF). The credit of account 86 from the debit of account 76 records the receipt of funds, and the debit records their use in connection with the accounts:
- Production (accounts 20, 26) - with funding from NPOs;
- Additional capital (account 83) - with TF in the form of financial investments;
- Deferred income (FPI) on the account. 98 - when financing the acquisition of assets or current costs. Upon expenditure of these funds, the TF amounts attributable to them are transferred to the company’s income (accounts 90/1, 91/1).
Those. The credit balance of account 86 indicates the balance of unused target funds, the credit turnover records the volume of such receipts, and the debit balance indicates their use for planned needs. Basic operations are recorded by records:
| Operations | D/t | K/t |
| Receipt of targeted funding | ||
| Use of funds from the Central Fund for the purchase of fixed assets, intangible assets, goods and materials, payment of bills, payment of salaries | 08,10,60,70 | 60, 51 |
| Entering fixed assets or intangible assets acquired at the expense of the Central Fund into the corresponding assets | 01,04 | |
| The use of financial funds in the form of financial investments is reflected | ||
| When financing current expenses, funds are accumulated in the account. 98, and as they are used, the amounts are transferred to the company’s income | ||
| Return of unused funds |
Withdrawal of financing is recognized as the formation of accounts payable subject to repayment. In this case, previously recognized income from targeted assistance should be written off as expenses. The amount of repaid financing is credited to the settlement accounts (account 76), and its excess over the balance of the unused amount becomes an expense and is included in losses.
How to fill out a simplified form of a report on the intended use of funds
Important
Online cash register: who can take the time to buy a cash register Individual business representatives may not use online cash register until 07/01/2019.
However, for the application of this deferment there are a number of conditions (tax regime, type of activity, presence/absence of employees). So who has the right to work without a cash register until the middle of next year?
Info
If an employee has worked for the company for less than a year, compensation is calculated based on the number of months actually worked.