For accounting of travel expenses and settlements with the posted employee, account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” is used. The debit of the account reflects the amounts given to the employee, and the credit reflects all expenses incurred by him on a business trip.
When sent on a business trip, an employee is given a certain amount of money for reporting; upon return, the employee is obliged to submit a completed advance report, form AO-1, and a travel certificate, form T-10, within three days; all documents confirming expenses incurred (travel cards) must be attached to these documents , tickets, checks, transport rental agreement, housing rental agreement, etc.).
Changes in 2015: The Government of the Russian Federation, by its Resolution dated December 29, 2014, abolished the mandatory issuance of a travel certificate and official assignment. Details in this article.
If upon return the employee still has part of the issued advance, then he returns the remaining funds to the enterprise to the cash desk with the execution of a cash receipt order.
If the advance payment issued to the employee was not enough and his own funds were spent, then the organization reimburses the expenses incurred in excess of the advance payment issued, and an expense cash order is issued.
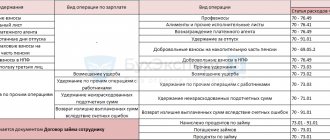
Postings for expenses in excess of the advance payment issued
| Debit | Credit | Operation name |
| 71 | 50 | Funds issued on account |
| 50 | 71 | Unspent funds were returned to the company's cash register |
| 71 | 50 | The employee was given the amount spent by him in excess of the advance payment issued |
Travel expenses, depending on the purpose of the trip, are charged to the appropriate accounting accounts. Costs associated with cultural and entertainment events are recorded as non-operating expenses.
If VAT is allocated for expenses incurred and there are supporting documents with VAT highlighted in a separate line (invoices, strict reporting forms), then this VAT can be attributed to account 19 and then sent for deduction (provided that these expenses relate to expenses , reducing the tax base when calculating income tax).
Travel accounting: basic procedures
Participation of an employee on a business trip is a process that consists of the following basic procedures:
1. Issuance of advances and daily allowances to the employee.
The exact deadline for issuing advance funds, as well as the procedure for their calculation, is not established by law. But in any case, they are issued before a business trip. If the advance is not issued, the employee has the right to refuse the trip, and this will not be a violation of work duties.
2. Checking the advance report and establishing specific items of travel expenses.
This procedure is carried out after a business trip upon submission of an advance report by the employee. Depending on the results of the audit, amounts of money are classified into certain categories (we will study how exactly later).
3. Reimbursement of overexpenditures made at the expense of the employee’s personal funds, or, conversely, deduction of the shortfall from him (if there is an overexpenditure or shortage).
Unconfirmed expenses, as well as expenses exceeding the daily allowance limit, are subject to return to the company. In turn, if an employee makes any expenses on a business trip at his own expense, the company must reimburse them.
ConsultantPlus experts tell you in detail how to prepare and submit an advance report for a business trip. Get free demo access to K+ and go to the Ready Solution to find out all the details of this procedure.
4. Payment of wages to an employee on a business trip.
During a business trip, the employee continues to be on the company’s staff and receives a salary. But it is accrued according to a special scheme (we will consider its features below).
Now let’s study in more detail the specifics of these accounting transactions, as well as what accounting entries are used to reflect these transactions in the accounting registers.
Legally established daily payment limits
The legislation establishes fixed amounts of daily allowance that are not subject to taxation:
- 700 rubles – for trips within the territory of the Russian Federation;
- 2,500 rubles – trips abroad.
Amounts in excess of the limits established by the state are subject to personal income tax and insurance contributions (with the exception of contributions for injuries), as they are recognized as the employee’s income. Taxes and contributions are calculated upon presentation of the advance report.
Addition! When making a work trip outside the territory of the Russian Federation: crossing the Russian border with a foreign state is paid in foreign currency, and when traveling within Russia - in rubles. Border crossing dates are determined based on the stamps in the employee’s foreign passport.
Accounting for business trips: issuing advances and daily allowances
Before leaving on a business trip, an employee receives:
1. Advance.
The traveler uses this amount to cover planned, most probable (and most often well-calculated) expenses, for example: travel, accommodation. Calculation of advance amounts to be issued is carried out on the basis of the manager’s order to send him on a business trip.
2. Daily allowance.
An employee receives a daily allowance to cover everyday, not always planned and calculated expenses. One way or another, the employee spends the daily allowance in any case at his own discretion, and he is not obliged to report on it.
The minimum and maximum daily allowance (the limit of expenses that the traveler makes at the expense of the enterprise) are established by the employer in local regulations. A daily allowance of 700 rubles per day for business trips in Russia and 2,500 rubles per day for trips abroad is not subject to personal income tax and social contributions.
Despite the fact that advance payment and daily allowance are essentially different payments from the point of view of tax accounting, in the accounting registers their issuance is recorded using the same entry:
- Dt 71 Kt 50 - if the advance and daily allowance are issued from the cash register;
- Dt 71 Kt 51 - if payments are transferred to the employee’s card.
The employee thus receives in his hands or in his bank account the amount for which he is obliged to report with documents attached. The accounting department, having studied the report and documents, will make a decision on whether to reimburse the employee for certain amounts or, conversely, to claim the shortfall from him.
Setting the rules
Setting limits and deadlines is not a mandatory circumstance, since the legislator does not stipulate this anywhere. However, many companies stipulate all the conditions, and they must be followed.
In any case, the rules for working with cash approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation must apply, that is, settlements with legal entities cannot exceed 100,000 rubles.
To appoint accountable persons, a special order must be issued, which each named employee must read and sign.
Often, enterprises also develop their own format for a reportable application.
Postings for travel expenses: return of unspent amounts and reimbursement of overexpenses
Within 3 working days after the end of the business trip, the employee sends the employer an advance report and supporting documents, against which the expenses issued to the employee as part of the advance will be verified (clause 26 of the Regulations on Business Travel, approved by Decree of the Government of Russia dated October 13, 2008 No. 749).
Based on the results of studying the report and the documents submitted with it, the accounting department will determine 3 types of monetary amounts:
1. Spent by the employee and confirmed by the advance report and supporting documents.
2. Amounts corresponding to daily allowance limits.
3. The amount initially given to the employee before the business trip.
Next, the sum of the indicators for points 1 and 2 is subtracted from the indicator for point 3.
If the result is positive, then the employee will have to return the corresponding amount to the company’s cash desk.
The following entries are recorded in the accounting registers:
- Dt 50 Kt 71 - when returning funds to the cash desk; or
- Dt 51 Kt 71 - when returning funds to the company’s bank account.
If the result is negative, the company must reimburse this amount, since the employee will be considered to have spent his money.
In this case, the transaction will be classified as travel expenses - the entries for it are the same as in the case of payment of advances and daily allowances: Dt 71 Kt 50.
How to set up the 1C program
To avoid doubling the amount, you need to set the settings correctly in the 1C: Salary and HR Management program. It's easy to do.
It is necessary to create a separate accrual type with which you will reflect the employee’s similar income. When setting up this type of accrual, there should be a checkmark in the “Is income in kind” field. Then the amount for this calculation will not be taken into account by the program for payment to the employee and will not generate a posting.
This amount will be used only for calculating personal income tax (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1
On the “Taxes” tab there should be a personal income tax code (Fig. 2 on p. 50).
Rice. 2
Amounts in excess of the excess daily allowance are registered in “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” using the document “Registration of one-time accruals for employees of organizations.”
In this case, the mentioned excess amount in mutual settlements with the employee for payment of wages will not be registered.
This type of accrual will only register income for calculating personal income tax, which will be taken into account when calculating wages using the document “Payroll for employees of organizations” (Fig.
Checking the expense report: expense entries
The procedure discussed above (when an accountant determines whether an employee should return something to the company or, conversely, whether the company is obliged to pay him compensation) is closely related to determining the amounts corresponding to specific types of expenses of the traveler. For these purposes, the same expense report and supporting documents are used.
Main types of travel expenses:
1. Daily allowance.
To write them off as travel expenses, the following entry is used:
- Dt 26 Kt 71.
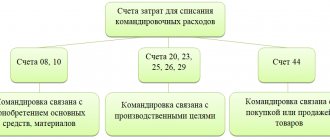
In this case, depending on the purpose of the trip, the operation can be carried out by debiting such accounts as:
- 20 (23, 25, 28) - if the employee is sent on a business trip for operational reasons;
- 08 - if the trip is related to the acquisition of fixed assets;
- 44 - if the business trip was carried out in connection with the purchase/sale of goods.
Moreover, if the daily allowance limit approved by the employer exceeds the norms established in the Tax Code, then the excess amounts are subject to personal income tax and contributions. The fact of their accrual is reflected by the following entries:
- Dt 70 Kt 68;
- Dt (08, 20, 23, etc.) Kt 69.
2. Travel, accommodation, etc.
For relevant travel expenses, postings are applied according to the same principle as in the case of per diem expenses:
- Dt 26 Kt 71 (in general) or correspondence on the debit of accounts 08, 20, 23, etc.
If expenses are confirmed by primary documents and an invoice, then input VAT is accepted for deduction, which is recorded by the following entries:
- Dt 19 Kt 71 - incoming VAT is recorded;
- Dt 68 Kt 19 - input VAT is accepted for deduction.
Find out what is included in travel expenses with the help of explanations from ConsultantPlus experts. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Let's study the procedure for accounting the salary of a posted employee.
What happens when data is uploaded
So, on the day the advance report is approved, the excess daily allowance must be registered in the employee’s personal income tax base in the 1C: Salary and Personnel Management program.
The program must calculate the tax and generate transactions.
At the same time, if in the payroll calculation program, in addition to transactions for withholding personal income tax, transactions are generated for accrual of the amounts of excess daily allowances themselves, when uploading data from this program to the 1C: Accounting program, the amount of daily allowance will be doubled precisely in terms of accrual of daily allowances exceeding the limit ( that is, the excess amount will double).
In addition, the amount of daily allowance payable to the employee will double (since the posting will be unloaded, which will turn out to be superfluous).
Salary on a business trip: postings
While on a business trip, the employee also receives a salary. True, it is calculated not as usual, but according to average earnings (clause 9 of the Regulations). In addition, weekends while a person is on a business trip are paid double or single when subsequent time off is granted, provided that the accounting documents are correctly filled out (clause 5 of the Regulations, Article 153 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Find out about the nuances of paying for a business trip on weekends here.
Payroll for a posted employee is calculated using the following entries:
- Dt (08, 20, 23, etc.) Kt 70 - calculation of wages calculated based on average earnings;
- Dt 70 Kt 68 - personal income tax withholding;
- Dt (08, 20, 23, etc.) Kt 69 - calculation of insurance premiums.
The transfer of wages to the employee is made using correspondence accounts:
- Dt 70 Kt 50 - if the employee receives his salary at the cash desk;
- Dt 70 Kt 51 - if the salary is transferred to the card.
Read more about the nuances of accounting for travel expenses in the article “Procedure for accounting for travel expenses.”
Results
Accounting for transactions that characterize sending an employee on a business trip is carried out in several stages. First, the employee is given an advance amount and daily allowance, and after his return from a business trip, the mutual financial obligations of the employee and the employer are determined - based on the report and supporting documents. Any cash movements between the cash desk (current account) of the enterprise and the employee (his bank account) are recorded in transactions, the content of which is determined by the purpose of the business trip.
You can learn more about the procedure for maintaining accounting and tax records when traveling on business trips in the following articles:
- “A business trip ticket includes meals - should an employee be paid daily allowance for days on the road?”;
- “We pay personal income tax on travel expenses in 2020”.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Are excess daily allowances subject to insurance premiums?
3).
Rice. 3
In the payslip, accruals with the established attribute “Is income in kind” will be displayed in a separate section (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4
O.Ya.Leonova
Head of Department
automation of personnel records
and payroll
The preparation of accounting entries for daily payments to employees for business trips is carried out in the following sequence:
— calculation of daily allowances based on the amounts of payments established at the enterprise in rubles and foreign currency (based on a management order to send an employee on a business trip, which can be drawn up on the basis of the unified T-9 form); — payment of funds to an employee in cash or by bank transfer; — calculation of personal income tax and calculation of insurance premiums on amounts exceeding the limit established by law (regardless of the established limit at the enterprise); — transfer of taxes and contributions to regulatory authorities (IFTS of Russia).
There are often situations when, by order of management, an employee is sent on work trips on company issues - business trips. The current legislation of the Russian Federation provides for the obligation of organizations to repay employee expenses for:
- living in a territory other than your permanent place of residence;
- employee food;
- additional expenses - daily allowance;
- other costs as agreed with the management of the organization.
Note from the author! Payment of daily allowances is made in advance the day before the business trip based on the order of the manager.