All enterprises operating as legal entities must pay property tax. This type of taxation is regional, that is, local governments can regulate certain standards, providing property tax benefits for organizations. But at the same time they must be guided by federal laws.
Organizations in this case have certain protection from the state, in the sense that it is at the level of government that the possibilities of obtaining benefits and discounts for certain types of enterprises are determined.
Real estate
The level of rates is specified in the Tax Code and should not be higher than the maximum limit specified by law. Property duty is paid by companies at these rates. And the size of the rates is completely determined by the regional authorities. For different real estate, different rates are provided, depending on the region where the business is conducted and the organization operates.
| For what | How many |
| Real estate in Moscow | 1,4% |
| Real estate in other cities | 2% |
Who plays favorites with the law?
Not all companies are required to pay tax duty. An interesting article of the Tax Code No. 381 lists the lucky subjects who received freedom “from the hands” of the law:
Do not pay any property tax:
- Lawyers (colleges)
- Legal advisors (bureau)
- Participants of the Skolkovo project
Certain types of property are not subject to tax:
- Property base of criminal enforcement authorities
- Church and monastery property
- Pharmaceutical equipment
- Basic funds on the balance sheet of organizations – residents of free and special economic zones
Important! Zero tax does not serve as an exemption from filing a property tax return. It still must be submitted, indicating all fixed assets, without exception, that are not taxed.
Updated declaration
Starting from 2021, the tax duty for legal entities is calculated based on the cadastral price. The price at the time the property is entered into the state real estate register is taken.
Note! Since 2021, an updated sample property tax return for legal entities has been introduced. For the convenience of accountants, some data and OKVED codes have been removed from the declaration.
In the new sample declaration there is a column to be filled out, numbered 2.1 , where the following is entered:
- Numbering according to the cadastre with coding designation
- Encoding according to OKOF.
- The volume of the price of all property on the balance sheet.
Federal benefits
No. 381 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation , does not expire . The effect of this article does not depend on the wishes of regional authorities.
There are two main categories of federal benefits:
- Relaxations that completely exempt the company from taxes.
- Exempting only from payments on certain types of property.
The following are completely exempt from property taxes:
| Type of company activity | Characteristics of preferential property |
| Religion | Has a purpose |
| Criminal - executive | Used in the work of the institution |
| Medical | Owned by prosthetic and orthopedic companies |
| Scientific | Is the property of companies recognized at the federal level as scientific centers |
Also, companies that are organizations of residents limited in their capabilities due to health conditions (disability) are completely exempt from the tax burden if their number in the company is at least 80% of the entire team.
Partially exempt from the tax burden:
- Penal organizations.
- Churches and parishes.
Attention! Federal relaxations on these points can only be obtained if there is approval from regional authorities.
Federal benefits are completely tax exempt. There are two options when it comes to delivery:
- temporary (for 3.5 or 5 years);
- unlimited
We remind you that even if you thoroughly study all the data that is in the public domain, this will not replace the experience of professional lawyers! To get a detailed free consultation and resolve your issue as reliably as possible, you can contact specialists through the online form .
Registration of federal benefits
To receive a property tax benefit, an organization must contact the Federal Tax Service with the appropriate application and declaration, indicating the preferential coding.
Important information! The amount of tax duty in the declaration is based on accounting indicators with a mandatory indication of the base - the average annual cost of fixed assets.
The accountant (accounting) of the company is required to pay the tax. Therefore, the use of benefits is also relevant to accounting.
The “start” for obtaining benefits is the submission of the organization’s reports to the tax office. To this end, a number of actions must be taken:
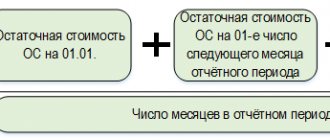
- The tax base from which the duty is calculated and paid is determined: this is the average annual or cadastral price of the property. With an annual average, the valuation is carried out at the residual value, namely: the difference between the original price of the property and its price after depreciation.
- The duty rate established by the subject of the Russian Federation is determined. Its size depends on the property type and nature of the company’s activities.
- The calculation is carried out using the formula: tax base x tax rate/100.
The tax base
This is the amount on which tax is calculated. According to Art. 375 is used as the OS tax base:
- average annual cost (ACV) - the difference between the price of the asset at the start of the payment period and depreciation at the end of the NP. The rules for calculating the base for the SSg are established in Art. 376 NK;
- cadastral value (CV) – assessment recorded in Rosreestr. The payment is calculated by multiplying the KS parameter by the regional rate for the property category. The nuances of applying the tax mechanism are set out in Art. 378.2 NK.
The most important requirement for the second option is that the property must be listed in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. The cadastre assessment is endorsed at the regional level, and only then the new taxation scheme is applied.
Regional benefits
The local authorities of each region have the legislative right to introduce other tax deductions under certain conditions for their compliance. Let's take the Moscow region as an example: here they use the funds saved from paying taxes to carry out social projects.
Local authorities cannot change or set restrictions on the time frame of benefits, since the deadlines are set in accordance with a letter from the Ministry of Finance.
Regional relaxations usually concern such objects as:
- Organizations receiving government funding.
- Institutions of power and management.
- Companies that carry out: social activities, sports, educational and medical.
- Firms that own property of special importance.
Exemption of citizens from property tax: legal norms
Like organizations, individuals also pay a property tax on real estate assets. However, the tax transferred by citizens from their own property is considered a mandatory payment (fee) at the local level. Paragraph 2 of paragraph 2 of Article 399 of the Tax Code stipulates that preferences for this tax can be established not only by general federal regulations, but also by legal acts of the relevant municipalities.
Reducing the tax base
In order to partially or completely avoid paying a property tax, an individual can use deductions when determining the tax base for this payment. This possibility is stipulated by paragraphs 3-6 of Article 403 of the Tax Code. When calculating the tax base, a citizen has the right to reduce the cadastral value of a real estate property of a particular type by the following amounts, also assessed at the cadastral value:
- 20 square meters - for part of a residential building or an entire apartment;
- 10 square meters – for part of an apartment or an entire room;
- 50 square meters - for an entire residential building;
- 1 million rubles – for a single real estate complex, including at least one residential building.
Clause 6.1 of Article 403 of the Tax Code stipulates an additional reduction (deduction) of the tax base for one real estate asset of a certain type. This deduction is 5-7 square meters per each minor child. It can be used by a citizen who has at least 3 such children.
Who has the right not to pay local property tax?
Certain categories of citizens may not transfer the property tax for one real estate asset of each type. The following groups of individuals can use this preference (clause 1 of Article 407 of the Tax Code):
- Heroes of the Russian Federation;
- Heroes of the USSR;
- holders of the Order of Glory of three degrees;
- disabled children;
- citizens who have had disabilities since childhood;
- persons with disabilities (groups 1, 2);
- participants of the Second World War and other military operations (military operations) listed in subparagraphs 4-5 of paragraph 1 of Article 407 of the Tax Code;
- people affected by radiation due to nuclear disasters, accidents and tests (subparagraphs 6 and 8 of paragraph 1 of Article 407 of the Tax Code);
- military personnel, as well as individuals who left the army for valid reasons (health status, age limit, organizational and staffing measures), having at least 20 years of total military service;
- family members of deceased (dead) military personnel;
- age pensioners;
- citizens with the status of an internationalist warrior;
- people with radiation diseases, as well as individuals who have become disabled from working with nuclear installations;
- spouses and parents of citizens who died while performing military or other public service;
- this tax is not charged on premises professionally used by individuals for creative activities;
- Outbuildings (maximum 50 square meters) located on land used for its intended purpose are exempt from property taxes.
Movable property
When property is easily moved without compromising its integrity or changing its purpose, it is considered “movable” property.
According to the letter of the law, movable property is not only transport, but also all other things:
- money supply,
- securities of different values and assets,
- cars for various purposes;
- communication lines, etc.
Important! Regulation in matters of benefits for organizations has been transferred to regional authorities. Only local managers at the regional level can decide who should pay property tax and who should receive benefits.
“Simplified” is a priority
Small business structures are exempt from tax on movable property, subject to the use of a “simplified tax” and a single tax on imputed income.
The “simplified” people have a significant privilege given by law - this is the absence of the obligation to pay tax on movable objects. Simply put, they are obliged to do only one thing - to pay real estate taxes to the state treasury, the base of which is determined by the market value of the property.
Benefit for movable property
The whole point of this tax break is contained in Article 381 of the tax code: tax duty can be avoided in the case when movable property is registered by the owner strictly after the end of 2012. The exception is movable property received during the liquidation procedure in relation to a legal entity.
The tax rate, if movable property does not fall into the category of beneficiaries, in 2021 cannot exceed 1.1%. Meanwhile, it is quite possible to increase this tax rate next year to 2.2%.
Legal payers and tax entities
Payers of property taxes are Russian organizations that have movable and immovable property on their balance sheet (Article 373 of the Tax Code). And it is not always property. The accounting databases may contain objects:
- in temporary possession;
- in trust management;
- classified as joint activities.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 374 tax objects of an enterprise must be accounted for as fixed assets (fixed assets). According to the law, only such property has the status of an object of taxation.
Features of enterprise OS categories
When grading fixed assets, they are guided by the definitions of the categories of Art. 130 Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
Real estate
inseparable from the land plot. It is impossible to move such objects without structural changes and violation of integrity. State registration is mandatory.
The categories include:
- industrial and administrative buildings;
- residential buildings and premises;
- unfinished construction;
- garage blocks, hangars for storing vehicles;
- natural resources, subsoil;
- aircraft, water or sea vessels subject to registration;
- space objects.
Movable property
freely changes location and spatial position and is subject to state registration only in special cases. accounting.
The category of movable assets of an enterprise includes:
- transport (except for those included in the real estate category);
- cash;
- equipment not registered in Rosreestr;
- business shares;
- shares and other securities;
- farm animals, seed fund;
- computers and servers;
- inventory.
Enterprises and tax authorities often interpret the categories of balance sheet property differently, which leads to disputes in matters of property taxation. Thus, the Federal Tax Service can classify company equipment that is not registered in this status as real estate. This is especially true for large enterprises in the oil and gas sector, energy, and metalworking.
In order to eliminate contradictions, in 2021 the Ministry of Economic Development plans to introduce a new gradation of movable/immovable property. Proposals have already been prepared to specify the concepts in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. In particular, the definition of real estate will be supplemented by the need to be taken into account as a capital construction object.