Description of the types of activities that give the right to benefits
Reduced tariffs when calculating contributions for employee insurance under the simplified tax system do not apply to all OKVED groups. The list of types giving the right to benefits is given in paragraph 5 of paragraph 1 of Art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The list contains mainly types aimed at creating material wealth, including production:
- Food products, soft drinks, textiles, leather, wood, pulp, paper.
- Machinery, equipment, vehicles, rolled metal, steel profiles,
- Household products, toys, sports equipment, furniture and other types of products not listed in the list.
The benefit is also provided for enterprises operating in the field of construction, healthcare, cultural activities, provision of household services, processing of recyclable materials, retail trade in pharmaceutical goods, and sports activities.
Enterprises carrying out the specified activities, but applying other taxation regimes, cannot exercise the right to apply reduced tariffs (
What types of activities are considered preferential under the simplified tax system?
One way to reduce the amount of mandatory payments for taxpayers is the ability to pay insurance premiums at reduced rates. Let's try to figure out who can take advantage of this advantage.
As you know, “simplified” tax regimes are one of the most loyal to entrepreneurs. By choosing a simplified system, a taxpayer receives a number of advantages, which include a simpler procedure for maintaining accounting records, a reduction in the number of fees, and eliminating the need to submit monthly returns. Moreover, for taxpayers who have registered for the first time, there is a preferential tax regime, the so-called tax holiday. The duration of this benefit, as well as what type of activity it is, are determined by regional authorities. So, for example, for entrepreneurs whose place of work is the Moscow region and they were registered after 04/13/2015, the tax rate will be 0%. For entrepreneurs - residents of the Moscow region, who have chosen this type of payment of fees as “income minus expenses”, the tax rate will be 10%.
However, in addition to the single tax, entrepreneurs operating under the simplified tax system are responsible for paying insurance contributions to the Pension Insurance Funds, as well as social and medical funds.
Moreover, in addition to insurance premiums paid by organizations and individual entrepreneurs for their employees, individual entrepreneurs are also required to pay contributions for themselves.
Let us note that from January 1, 2021, Chapter 34 of the Tax Code “Insurance Contributions” became fully legal, according to which the functions of collecting and accounting for insurance premiums are assigned to the powers of the Federal Tax Service (previously this was handled by extra-budgetary funds). Payments should now be made to the tax authorities' details. Therefore, it is worth remembering that in 2021, budget classification codes were also changed, according to which it is necessary to make payments at a preferential rate.
As before, insurance premiums calculated from employees are transferred by organizations to the budget every month before the 15th.
As for the insurance fees that individual entrepreneurs pay for themselves, they are fixed and can be transferred throughout the year (and they can be paid in installments). In addition, it is necessary to take into account that if the income of an individual entrepreneur exceeds 300 thousand rubles, extraordinary pension investments “for oneself” should be transferred before April 1 of the next year.
Insureds working under the “simplified” system can significantly reduce the burden of insurance obligations for themselves with the help of reduced tariffs. This opportunity is provided by Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which contains a list of types of activities carried out on preferential terms.
Additional conditions for receiving benefits
The benefit is provided to enterprises engaged in social and industrial activities (Article 427 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) in the amount of more than 70% of the total. To be able to apply reduced rates, the specified OKVED must be declared by the enterprise in the constituent documents and register as the main one. If the preferential type of activity is not recognized as the main one in the documents of the enterprise, the organization or individual entrepreneur using the simplified tax system will lose the right to reduced rates.
Let's name the main requirements for receiving benefits: (click to expand)
| Required condition for the benefit | Criterion |
| Type of activity carried out by the enterprise | Established for the main type of OKVED and coincides with the list of paragraph 5 of paragraph 1 of Art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. |
| Revenue from the main activity | 70% of total revenues |
| Enterprise's marginal income | The annual income of the enterprise should not exceed 79 million rubles |
To determine the indicator of priority receipts for the main type of activity, it is allowed to add up revenues for one OKVED class. In the absence of revenue or other income, there is no way to determine the right to a reduced tariff. Companies using the simplified tax system determine income without taking into account the company's expenses.
To apply the benefit, enterprises do not have to submit an application and supporting documents. Taxpayers using the simplified tax system fill out Appendix 6 of Section 1 of the calculation of contributions. When filling out the data, it is necessary to ensure compliance with the information on the OKVED title and the income indicated in the application for the main type. In the calculation, you must correctly indicate the payer code depending on the benefit applied. If the right to a reduced tariff is lost and adjustment calculations with additional payment are submitted, Appendix 6 is not submitted.
How to determine the main activity
To receive benefits, only one type of activity can be the main one for the simplified person. The summing of income from different types of activities (that is, those belonging to different classes of OKVED) is not provided for by law (letters of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated September 29, 2015 No. 17-4/10/OOG-1357, dated September 18, 2014 No. 17-4 /B-442).
For example, the preferential types of activities of a “simplified” worker belong to different classes of OKVED, but the income for none of them separately exceeds 70% of the total income. In this case, reduced contribution rates cannot be applied.
But if the types of activities belong to the same OKVED class, the “simplified” can summarize the income received. And if it turns out that the total income from activities combined into one class according to OKVED exceeds the 70% barrier, the company has the right to apply a reduced tariff (letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated April 3, 2013 No. 17-4/551).
Benefits for non-profit enterprises on the simplified tax system
In addition to commercial companies, non-profit enterprises, with the exception of state and municipal institutions, are entitled to reduced tariffs. The opportunity to use the benefit arises if the following conditions are met:
- An NPO must be registered with the Ministry of Justice. When reorganizing and transforming a company into a commercial organization, the right to benefits for non-commercial organizations on the simplified tax system on this basis is lost.
- Conduct activities in the areas of healthcare, education, culture, scientific development, social services and others specified in paragraphs. 7 clause 1 art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- Have income from carrying out the named types of activities in the amount of at least 70% of total income. NPO enterprises have the opportunity to conduct commercial activities, unless otherwise stated in the statutory documents. The fulfillment of the requirement to comply with the income threshold must be met based on the income results of the year preceding the transition.
- The amounts of income include targeted income - grants, subsidies and other funds used to run NPOs.
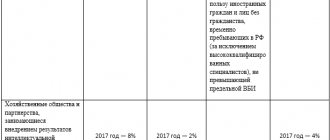
In order to receive benefits, NPO enterprises must comply with the requirements for maintaining the simplified tax system regarding general indicators. The system obliges to take into account indicators of the number, residual value of property, and criteria for the categories of founders. If the conditions are met, the tariff for deductions for compulsory health insurance in the amount of 20%, for compulsory medical insurance and compulsory social insurance - 0% is applied.
USN - what is it?
The abbreviation USN stands for “simplified taxation system”.
This system is easy to use, its use reduces tax payments, facilitates the accounting of business transactions and the reporting process. When applying the simplified tax system, the payer is exempt (with rare exceptions) from paying taxes such as:
- VAT;
- income tax (and individual entrepreneurs - from personal income tax);
- property tax (except for that calculated from the cadastral value).
Benefit for charitable organizations
Along with non-profit organizations of other directions, charitable organizations are entitled to benefits if their statutory documents indicate this type of activity. If the conditions are met, contributions to the income of the organization's employees are calculated at reduced rates equal to the tariffs of other types of non-profit organizations.
Example of application of reduced rates
The NPO Solidarity, a charitable organization, has 2 employees who receive a remuneration of 10,000 rubles per month. In January 2021, the organization accrued:
- Pension insurance contributions: C1 = 20,000 x 20% = 4,000 rubles;
- There are no contributions for compulsory medical insurance or compulsory social insurance.
Additionally, organizations must comply with the requirements applicable to non-commercial organizations under the simplified tax system (
Determining the compliance of types of activities with those established for the OKVED benefit
There is a peculiarity in determining the types of activities approved in the constituent documents of the enterprise specified in the list of Art. 427 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. When developing the types, the OKVED1 qualification guide, valid until 2021, was used. After the OKVED2 directory was put into effect, a contradiction arose in the exact formulation of types of activities.
Confirmation of the contradiction that has arisen and ways to resolve disputes are indicated in the letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-15-06/2197 dated January 19, 2017. Enterprises are invited to use transition keys to obtain data on the compliance of codes specified in the classifiers. Direct and reverse keys are posted on the official portal of the Ministry of Economic Development of the Russian Federation. This method of identifying preferential activities is used for a transition period with the subsequent elimination of inconsistencies in the data.
On November 27, 2021, Federal Law No. 335-FZ came into force, clarifying the inconsistencies between the OKVED reference books. Enterprises with an unclear question about the application of a reduced tariff, which received the right in connection with the innovation, can submit adjustment calculations from the beginning of the 2017 tax period.
Restrictions associated with the use of simplified taxation system
The simplified tax system cannot be used simultaneously with other taxation systems, such as OSNO and Unified Agricultural Tax.
There is also a limitation regarding the organizational structure of the enterprise. If an enterprise has branches in its structure, it cannot apply the simplified tax system (clause 3 of article 346 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Please note that separate divisions that are not branches are not deprived of the right to use the simplified tax system for permitted types of activities in 2021.
A limitation for the application of the simplified tax system is also the share of participation in the organization of other legal entities, which should not exceed 25%.
The number of employees should be no more than 100 people, the value of fixed assets should not be more than 150 million rubles, income (from sales plus non-sales) for the year of application of the simplified tax system should be no more than 150 million rubles. And in order to take advantage of the opportunity to switch to the simplified tax system from next year, you must have an income of no more than 112.5 million rubles for 9 months of the current tax period.
For more information about the restrictions affecting the possibility of using the simplified tax system, read the article “Revenue restrictions under the simplified tax system in 2019 - 2021.”
V.V. Gorbunova, 2nd class State Civil Service Advisor, answered individual questions from taxpayers about the application of the simplified tax system.
Get trial access to ConsultantPlus and find out the official’s opinion for free.
Preferential rates for simplified taxation system payers
Enterprises using the simplified tax system have the right in 2021 to apply reduced rates for deductions for compulsory insurance of employees. Lower rates have been established for all types of contributions.
| Type of contribution | Regular rate | Reduced rate |
| OPS | 22% | 20% |
| Compulsory medical insurance | 5,1% | 0% |
| OSS | 2,9% | 0% |
Preferential rates are provided only for employers in terms of contributions to employee insurance. Individual entrepreneurs who pay insurance premiums for personal pension and health care do not have the opportunity to reduce the amount of contributions. Fixed contributions are set at the government level and are paid regardless of the regime applied by entrepreneurs.
Insurance premium rates for LLCs using the simplified tax system in 2021
When calculating insurance premiums for employees in 2021, simplified organizations use basic rates:
| No. | Insurance premiums | Tax limit | Basic tariff | Additional tariff for income above the tax limit |
| 1 | For compulsory pension insurance | 1,150,000 rub. | 22% | 10% |
| 2 | For compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity | 865,000 rub. | 2,9% | 0% |
| 3 | For compulsory health insurance | – | 5,1% | 5,1% |
Payment of insurance premiums for “simplified” residents is also carried out in the general manner - before the 15th day of the month following the reporting month.
Let's look at an example . Based on a fixed-term employment contract, the director of Vector LLC Timofeev was given a salary of 300,000 rubles per month.
During the period from January to September 2021, Timofeev was paid a salary in accordance with his salary; bonuses and allowances were not accrued.
When calculating insurance premiums in the period from January to March 2021, the Vector accountant used base rates (PFR - 22%, Social Insurance Fund - 2.9%, Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund - 5.1%).
In March 2021, Timofeev’s income reached the maximum tax limit for FSS insurance premiums (RUB 865,000). In this regard, the calculation of insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund for March is carried out partially at a rate of 2.9%:
865,000 rub. – 600,000 rub. * 2.9% = 7.685 rub.
The balance of income for March 2021 was not subject to contributions to the Social Insurance Fund (0% tariff). Until the end of 2021, Timofeev’s income is exempt from taxation on insurance premiums.
In April 2021, Timofeev’s income reached the maximum tax limit for PFR insurance premiums (RUB 1,150,000). In this regard, the calculation of insurance premiums to the Pension Fund for April is carried out partially at a rate of 22%, and partially at an additional rate of 10%:
- calculation at the base rate of 22% (RUB 1,150,000 – RUB 900,000) * 22% = RUB 55,000;
- calculation at an additional tariff of 10% (300,000 rub. – (1,150,000 rub. – 900,000 rub.) * 10% = 5,000 rub.
An additional tariff (10%) was used to calculate Timofeev’s insurance contributions to the Pension Fund until the end of 2021.
The calculation of Timofeev's insurance premiums for the period from March to September 2021 is presented in the table below:
| Reporting period | Salary accrued | Amount of taxation (cumulative total) | Pension Fund | FSS | Compulsory medical insurance 5.9% | ||
| within the limit (22%) | over limit (10%) | within the limit (2.9%) | over limit (0%) | ||||
| January 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 300,000 rub. | 66,000 rub. | – | 8,700 rub. | – | 17,700 rub. |
| February 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 600,000 rub. | 66,000 rub. | – | 8,700 rub. | – | 17,700 rub. |
| March 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 900,000 rub. | 66,000 rub. | – | RUR 7,685 | – | 17,700 rub. |
| April 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 1,200,000 rub. | 55,000 rub. | 5,000 rub. | – | – | 17,700 rub. |
| May 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 1,500,000 rub. | – | 30,000 rub. | – | – | 17,700 rub. |
| June 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 1,800,000 rub. | – | 30,000 rub. | – | – | 17,700 rub. |
| July 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 2,100,000 rub. | – | 30,000 rub. | – | – | 17,700 rub. |
| August 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 2,400,000 rub. | – | 30,000 rub. | – | – | 17,700 rub. |
| September 2021 | 300,000 rub. | 2,700,000 rub. | – | 30,000 rub. | – | – | 17,700 rub. |
| TOTAL | 2.700.000 rub. | 2.700.000 rub. | 253.000 rub. | 155.000 rub. | 25.085 rub. | – | 159.300 rub. |
Timofeev's insurance premiums were paid monthly by the 15th day of the month following the reporting month.