What is the penalty for violating the payment limit?
Violation of the payment limit can result in a fine for entrepreneurs and companies (Article 15.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation):
- for individual entrepreneurs - from 4,000 to 5,000 rubles;
- for LLC - from 40,000 to 50,000 rubles.
The tax inspectorate can impose a fine only within months from the date of calculation in excess of the limit (Part 1 of Article 4.5 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation). Both parties can be fined: the one who pays and the one who accepts the payment.
For example, your individual entrepreneur wants to supply equipment for your office. You cannot accept more than 100,000 rubles from him. for one operation due to restrictions in the law, otherwise both you and him will be fined.
The restrictions in the new rules still apply to settlements between organizations and organizations, organizations and individual entrepreneurs, individual entrepreneurs and individual entrepreneurs within the framework of one agreement - they are limited to the amount of 100,000 rubles. or equivalent in currency at the official rate of the Bank of Russia. This applies to settlements not only under current contracts, but also under expired ones, under which the counterparty will have to repay the debt.
The calculation cannot be exceeded even by 1 ruble. For 100,001 rubles. the manager and the payer will be fined.
To avoid a fine, the contract can be divided into several - each within 100,000 rubles.
Settlements with individuals and self-employed people without individual entrepreneur status and withdrawal of money for personal purposes are not limited.
Entrepreneurs can use cash that they:
- received through the sale of goods;
- received for performing work or providing services;
- received as insurance premiums;
- received a loan under a loan agreement from a microfinance organization, a pawnshop, a credit agricultural cooperative and a consumer cooperative;
- received as share contributions from consumer cooperatives;
- returned as the amount of debt under agreements with credit institutions.
Control your business remotely: check how much money is in the cash register and in the current account, see when cashiers open and close shifts.
To learn more
Cash payments between legal entities and individual entrepreneurs are carried out using money received at the cash desk from a bank account.
Cash payment: how to keep money in the cash register
All receipts and withdrawals of funds from the cash register must be recorded as receipts and expenditures cash orders. In this case, it is allowed to store small amounts of money in the cash register within the limit, the amount of which is determined independently by the head of the organization in accordance with clause 2 of the Bank of Russia instruction “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions...” dated March 11, 2014 No. 3210-U (hereinafter referred to as instruction No. 3210-U ). It is possible to exceed the limit, for example, during the payroll period.
The receipt order must be signed by the chief accountant, and the expenditure order - by the manager, chief accountant or other authorized person. Documents must be written in clear handwriting or using technical means.
If a power of attorney was used for cash payments, this must be indicated in the expense documents. The original power of attorney remains at the company's cash desk.
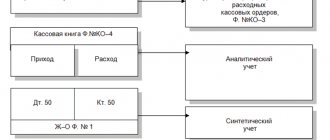
All transactions at the cash desk must be recorded in the cash book (clause 4.6 of instruction No. 3210-U), which is laced, numbered and sealed with the organization’s seal. At the end of the working day, the cashier must summarize the transactions performed and write down how much cash is left in the cash register. At the same time, the legislator allows for maintaining the book in an automated way (clause 4.7 of Directive No. 3210-U).
What can individual entrepreneurs and organizations spend cash on?
They can spend it for several purposes:
- salary fund and social benefits for employees;
- payment of insurance amounts to individuals who paid insurance premiums in cash;
- payment of cash for personal needs of individual entrepreneurs not related to business activities;
- payment for goods, works and services (except for shares and other securities);
- issuing cash to employees on account;
- refund for goods, works, services previously paid in cash for which the buyer wants to issue a refund;
- issuing cash for transactions as a bank payment agent.
Payment methods for goods and services
The priority is to use non-cash payment. Cash circulation is gradually fading into the background: in retail outlets, grocery chains, public transport, and in state and municipal authorities, non-cash payments are increasingly used.
Cashless payment is convenient because it does not require the payer to perform any actions: in a few clicks the amount is transferred in the required direction. Service about payment methods in more detail.
Rules for microfinance organizations, pawnshops and credit cooperatives
They can direct cash from the treasury to make loans and repay the loans received with interest.
- For MFOs and pawnshops, the issuance and repayment of loans, payment of interest, fines, penalties and penalties on loans attracted by MFOs and pawnshops are limited to 50,000 per agreement and 1 million rubles. per day for a separate office of the organization.
- For credit cooperatives, the issuance and repayment of loans under agreements for the transfer of personal savings, payment of interest, penalties, penalties and fines, payment of share savings by a consumer cooperative cannot exceed 100,000 rubles. under one contract and 2 million rubles. per day in one department.
Cash register
The main condition when working with cash is proper fiscalization. That is, it is important for the state and the tax inspectorate that the organization pays taxes on all funds received at the cash desk. If payments are made in non-cash form, tracking the movement of funds is very simple - through the databases of credit institutions. And for cash payments, information about revenue must be reflected using cash documents. That is why all organizations must use cash registers when carrying out their activities. But there are exceptions. The legislation allows not to use cash registers in the following cases:
- The company is on UTII (at the same time it issues analogues of checks to customers, which reflects the fact of payment);
- If it is possible to issue strict reporting forms instead of cash receipts;
- When providing various services to the population;
- If business entities are located in remote locations;
- When carrying out certain types of activities, such as selling magazine products, etc.
Organizations and entrepreneurs with cash register equipment must have documents such as special reports, a cash register and a contract with the technical center. service.
In some cases there are no restrictions
There are no restrictions for:
- cash payments between individuals;
- banking operations;
- customs duties and taxes.
Ordinary entrepreneurs and organizations cannot issue and repay loans using cash. First, they must deposit money into a current account and withdraw it again.
Cash that is returned to the cash desk as the balance of an advance that has not been spent cannot be used for settlements. First, they need to be returned to the bank and deposited into a current account (Letter of the Bank of Russia dated July 9, 2020 No. 29-1-1-OE/10561).
conclusions
Conducting non-cash and cash payments requires the presence of 2 counterparties. Conducting cash payments between individuals who do not carry out entrepreneurial activities occurs without any restrictions. Cash payments from legal entities and individual entrepreneurs are carried out in compliance with cash discipline.
You will learn about how important it is to maintain cash discipline in our article “Is your cash discipline in order?”.
Non-cash payments are carried out with the participation of banking institutions that execute their client’s order to write off funds from his current account in favor of another person to his current account opened in the same or another bank with which the bank executing the payment order has established correspondent relations.
To display cash and non-cash payments in accounting, active synthetic accounts 50 and 51 are used. These accounts may have a balance at the end of the reporting period, which indicates the availability of funds from the organization or entrepreneur.
For those who, by law, can conduct simplified accounting, it will be useful to read our article “The list of organizations that can use simplified accounting methods has been clarified .
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
How to issue an invoice correctly
An invoice is a piece of paper issued by a company that provides a product or service.
For individual entrepreneurs and LLCs there is no single sample document and no specific regulations. However, when issuing an invoice, the following information must be included:
- data of the parties
- list and name of goods or services
- unit price
- total amount
- conditions for returning goods
- details of the parties
- payment method
When creating paper, it is advisable to use a proven sample to avoid mistakes.
Errors when preparing an invoice for payment
Common mistakes include:
lack of transcripts of signatures- violation of the five-day invoice deadline
- indication of different dates on copies of the seller’s and buyer’s invoices
When paying by bank transfer, the total amount is inclusive of VAT. The invoice for a service or product indicates the exact details of the seller, to whom the required amount of money is transferred after fulfillment of obligations.
Using non-cash allows you to make and receive payments without restrictions in a short time. After studying the regulations, problems with the use and reporting of non-cash payments in the organization will not arise.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Using payment orders
When you use this payment method, an account is created at the bank. As necessary, a paper called a payment order is created. It specifies to whom and how much the bank should transfer. As a result, the banking institution, after receiving the order, performs the necessary actions by making the transfer.
This method is used for settlements with suppliers or contractors, payment of taxes and wages to employees. The bank accepts the order only if the required amount is available in the account.
Why do we need a payment system?
The need to pay by bank transfer at one time led to the emergence of a system of settlements between banks with each other, since payers and recipients were serviced by different financial organizations. In Russia, the Russian Federation payment system was developed for transfers between banks. Each country organizes its own structures to ensure safe and fast circulation of funds within the state. Together they form international payment systems. Thanks to this, trade relations are possible between different countries, sometimes located on different continents.
Using check books
The method is a calculation by issuing a special check. The recipient of the check can subsequently cash the check at the bank, provided that there is sufficient money in the account of the person who issued the check. Both individuals and legal entities can use checks. Payment through this type is widely used in the West.
Money is written off only after checking the authenticity of the check and confirming your identity.
What it is
A wire transfer is a payment that is made without the use of cash.
Payment can be made in several ways. By using non-cash payments, organizations can simplify their activities.
Non-cash can be used to pay for goods or services by both companies and ordinary people. The method can be used as a full or partial alternative to cash. The payment procedure in this way is much faster and easier, allowing organizations to accelerate cash turnover.
Advantages and disadvantages
Organizations and individuals who choose this type of payment are able to obtain the following benefits:
- ease of operation
- small transfer commission or no commission at all
- instant transfer
- simple control over completed operations
Specific benefits depend on the form of payment. For small and large organizations, using this method allows you to save money by reducing maintenance costs.
Among the disadvantages are:
- complexity of organizing a settlement and payment system
- possibility of failures and delays in payment (depending on the specific bank)
- occurrence of risks when making transfers
Non-cash payments are strictly controlled by supervisory authorities, so when switching to non-cash payments, you need to prepare for the creation of detailed reporting.
Funds control
In organizations, control over funds is exercised through the use of a ledger of expenses and income. All transactions are recorded. Extracts allow you to keep records. Depending on the form of non-cash payment used, statements of deposits, letters of credit, etc. are used.
Individuals need to use bank statements to control their funds. When using electronic money, certain statistics are maintained by the bank itself or the electronic payment service.
Refund
When using cashless payment, a refund is provided under certain circumstances. Refunds by bank transfer are made to a bank account. Individuals can expect a refund if their rights under the PLA are violated. Refunds between two legal entities are carried out in accordance with the standards specified in the Civil Code.
Quite often, a dispute can only be resolved in court, if an agreement has not previously been concluded regulating the return of funds. It is worth noting that it is extremely difficult to return money for goods of proper quality. You can count on a refund if the other party provided a product or service of inadequate quality or not in accordance with the agreements.
What challenges do payment systems face?
Payment systems perform a number of tasks:
- Safety and efficient operation.
- Reliability, which guarantees the absence of any disruptions in the operation of payment systems.
- Process workflows quickly and cost-effectively.
- An honest approach that meets all the necessary criteria.
In general, for any such system the main function is to ensure dynamic economic turnover.
The individual elements of payment systems are very closely related to each other. Their relationship is carried out according to certain rules that are included in state regulations. The work of the Russian payment system is built on legal documents, thanks to which its functioning occurs. They regulate a set of procedures that are necessary for the operation of this structure and the transfer of funds from one counterparty to another.
The procedures of the payment system include forms of non-cash payments, norms of payment documents and all means used for communication (software, Internet, telephone lines, hardware).
Using plastic cards
Plastic cards for payment are issued by banking organizations, after which the card holder can carry out transactions to pay or receive cash. Debit and credit cards are popular among individuals.
Any payment by card is carried out taking into account the conditions stipulated in the agreement between the holder and the bank. The terms and conditions reflect the capabilities of the card (can you pay worldwide, is there a percentage when withdrawing cash, etc.).
By letter of credit
The letter of credit method is often used when paying for the supply of goods and similar services. It represents the creation of a letter of credit by the party who will pay for the goods or services. The letter of credit itself is an order that the bank must carry out after the payer confirms that the other party has fulfilled its obligations to it, or the seller provides the necessary accounting papers.
It is worth noting that a letter of credit is created in advance as confirmation that the payer is able to pay for the service or product provided. The method is very popular because it is highly secure. Without receiving the necessary reports, the bank will not transfer money.
What can and cannot replace cash receipts?
- Instead of a check, you cannot use invoices, since they have different purposes. The invoice can only confirm that the products were transferred, and the receipt can only confirm that the products were paid for. The invoice can be provided along with the check, but not without it.
- Sales receipts also cannot replace cash receipts. They can only be a complement to each other. There are only two situations where a sales receipt can be provided without a cash receipt - when it is on UTII or on a patent tax system.
- The use of receipt and expense orders instead of checks is also prohibited. In most cases, orders are only used internally. The receipt can serve as an addition to the check if the client is a company or entrepreneur.
- If products are sent by mail, you do not need to use a cash receipt. It is not needed due to the fact that the client does not provide cash directly to the seller. The payment is accepted by postal employees who transfer the funds to the organization's account.
Most common form
Among legal entities, non-cash payments using payment orders are the most popular. Using this method, companies manage to carry out a huge number of operations. By order, settlements are carried out within the organization. Payments are also made for services provided by other companies or individuals. The order sent to the bank contains detailed information about the recipient and the payment deadline.
Plastic cards are the most popular among individuals.
What forms are there?
There are the following forms of non-cash payment:
money orders- checks
- electronic money
- collection orders
- plastic cards
- letters of credit
Individuals often use cards to pay and receive cash. Legal entities often opt for payment orders.
Article 861 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Cash and non-cash payments (current edition)
1. Payments on the territory of the Russian Federation are made by cash and non-cash payments.
Cash payments are payments made using cash means of payment. Legal tender, obligatory for acceptance at face value throughout the Russian Federation, is the ruble.
Legislation limits settlements between subjects of civil law in cash. Payment in cash is allowed without taking into account the maximum amount if two conditions are met:
- if at least one of the subjects of legal relations is a citizen;
- if the settlements are not related to business activities.
In such circumstances, cash payments can be made without any limitation on the amount.
Settlements between legal entities, as well as settlements with the participation of citizens related to their business activities, can also be made in cash in an amount not exceeding 100 thousand rubles.
The procedure for legal entities to make cash payments is strictly regulated by law and is necessarily reflected in the organization’s accounting records.
A legal entity (individual entrepreneur) is required to keep money in bank accounts. Cash in the organization's cash desk should not exceed 100 thousand rubles. The established limit may be exceeded on salary payment days, on weekends, non-working holidays if a legal entity or individual entrepreneur conducts cash transactions on these days and in other cases provided for by law.
2. According to the general rules of settlements between legal entities, a non-cash procedure is provided for their implementation; cash settlements can also take place, unless otherwise provided by law. The establishment of a maximum amount of cash payments between legal entities, being one of the mechanisms for organizing cash circulation, is not in itself an obstacle to the free movement of financial resources, since it does not deprive legal entities of the opportunity to make non-cash payments among themselves without limiting amounts and in any from the forms provided by law.
Settlements between legal entities, as well as settlements with the participation of citizens related to the implementation of their business activities, are made by bank transfer.
Transfer of funds is carried out within the framework of the following forms of non-cash payments:
— settlements by payment orders;
— settlements under a letter of credit;
— settlements by collection orders;
- payments by checks;
— settlements in the form of transfer of funds at the request of the recipient of funds (direct debit);
— settlements in the form of electronic money transfer.
Forms of non-cash payments are chosen by payers and recipients of funds independently and may be provided for in agreements concluded by them with their counterparties.
To carry out non-cash payments, a third party - a bank or other credit organization - participates in civil legal relations. In this case, the credit institution is not a party to the transaction for which settlements are made. Banks do not interfere in the contractual relations of clients.
The means of making non-cash payments is an account opened by the payer (recipient) with the relevant credit institution (unless otherwise follows from the law and is not stipulated by the form of payment used).
3. Applicable law:
— Federal Law dated June 27, 2011 N 161-FZ “On the National Payment System”;
— Federal Law dated June 3, 2009 N 103-FZ “On the activities of accepting payments from individuals carried out by payment agents”;
— Federal Law of May 22, 2003 N 54-FZ “On the use of cash register equipment when making cash payments and (or) payments using payment cards”;
— Federal Law of December 2, 1990 N 395-1 “On banks and banking activities”;
— Instruction of the Bank of Russia dated May 30, 2014 N 153-I;
— Directive of the Bank of Russia dated October 7, 2013 N 3073-U;
— Directive of the Bank of Russia dated December 24, 2012 N 2945-U;
— Regulation of the Bank of Russia dated June 19, 2012 N 383-P;
— Regulation of the Bank of Russia dated December 24, 2004 N 266-P.
4. Judicial practice:
— Determination of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation dated April 13, 2000 N 164-O;
— decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated June 28, 2010 N GKPI10-497;
— Determination of the RF Armed Forces dated April 29, 2003 N KAS03-160;
— Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District dated November 30, 2010 in case No. A28-2959/2010;
— Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga-Vyatka District dated February 18, 2010 in case No. A28-16681/2009.
Comment source:
“COMMENTARY ON THE CIVIL CODE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION. PART TWO OF JANUARY 26, 1996 No. 14-FZ"
ON THE. Barinov, S.A. Baryshev, E.A. Bevzyuk, M.A. Belyaev, T.A. Biryukova, Yu.N. Vakhrusheva, R.R. Dolotina, N.V. Elizarova, R.Yu. Zakirov, N.A. Zakharova, P.Z. Ivanishin, S.Yu. Morozov, T.N. Mikhaleva, 2014