Characteristics of account 62
Accounting account 62 is an analytical account that summarizes information on all customers of an organization, including legal entities and individuals.
Using the account 62 the accountant of an enterprise at any time and on the required reporting date can, on the one hand, formulate the amount of debt for sold products and services, and on the other hand, determine the amount of planned shipments. Thus, we can say that account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is a mirror copy of the account. 60. And the turnover and balance generated by the seller duplicate the buyer’s data. The information obtained is clearly used by the parties to the transaction when conducting reconciliations by drawing up reports.
- By payment method - upon shipment, prepayment, mutual settlement, etc.
- According to the timing of settlements - whether the debt is overdue or not.
- According to the presence of the bill - discounted (discounted) at the bank, overdue or the maturity date has not yet arrived.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0GzYgLnYMX4
The accounting service of the organization has the right to decide independently how to use account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”, taking into account the legislative norms of Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000. The main thing is to provide external and internal users with reliable and timely information. If the activity is carried out by a group of interconnected enterprises account 62, the postings are given below and are carried out separately in relation to such operations.
Account 51 in accounting: meaning, postings and examples
51 “Current account” is used by organizations and individual entrepreneurs to display transactions on mutual settlements with counterparties - individuals and legal entities in the currency of the Russian Federation using company current accounts opened in credit institutions.
51 accounts in accounting is the collection of information about non-cash payments made with counterparties - individuals and legal entities through bank accounts. The following basic operations are displayed here:
- Receipt of funds - payments from buyers and customers for goods provided or services provided;
- Depositing trading proceeds in excess of established cash limits;
- Payment to suppliers for raw materials, materials, goods
- Payroll calculations
- Calculations with budgets (transfer of contributions, taxes, penalties), etc.
Attention! Account 51 displays information about settlements only in the currency of the Russian Federation.
Account 51 in accounting is active, that is, the debit shows non-cash receipts of funds (payments from customers, deposits of revenue, returns from suppliers) in correspondence with the corresponding accounts (62, 50, etc.), and the credit shows the expenditure of funds ( bank commissions, payments to suppliers, repayment of loans and borrowings, payment of taxes, etc.)
Basic Accounting Principles
3. instructions, recommendations, etc., methodological guidelines for accounting, which are adopted by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and federal executive authorities.
1. federal law, government regulations, presidential decrees, which directly or indirectly regulate accounting in organizations.
2. accounting provisions (standards), which set out the principles and basic rules of accounting.
- instructions, recommendations, etc., methodological guidelines for accounting, which are adopted by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation and federal executive authorities.
The main account that appears in settlements with counterparties is account 62 of the same name. It reflects payments for shipped goods and ordered services. The score will be synthetic. In most cases it is active. DT account 62 reflects the formed receivables arising from the shipment of goods, and CT account records the repayment of debt.
Account 62 will be passive when the company received an advance payment under an agreement on services provided. To summarize information about settlements, a subaccount “Advances received” is opened. When shipping products, this wiring is used: DT62 KT90. When the buyer's debt is paid, it will be written off from KT62 to DT50-52.
The company may enter into agreements with customers or counterparties that require prepayment. If a company has received an advance, it must provide settlement documentation for the full cost of products or services. The advance payment is used to reduce the debt of the buyer/counterparty. Accounts payable for advances are repaid after the sale of goods, when the company presents settlement papers to customers. Let's look at the postings that are used when shipping goods:
- DT51 KT62. Acceptance of accounts payable.
- DT62 KT90. Repayment of accounts payable.
The amount is indicated for each transaction. For example, this could be the size of the accounts payable.
Common business transactions and postings for them
- Transfer of funds to suppliers - payment for equipment, materials, goods, etc.
- Funds for mutual settlements with customers for goods or services provided
Dt51 Kt62 – making paymentDt62 Kt51 – return of excess amounts transferred
- Settlements with employees
Dt70 Kt51 – transfers of wages to employeesDt71 Kt51 – issuance of accountable amounts
Dt69 Kt51 – payment of contributions
- Transfer of taxes, fines, penalties to the budget of the Russian Federation
- Depositing cash proceeds into a credit institution in excess of established cash limits
- Transfers of funds to repay loans and borrowings, payment of interest on them
- Bank commissions for servicing the company and conducting operations
Natalya Vasilyeva, 2017-02-13
Features of accounting for settlements with customers (account 62)
Debit account 62 reflects the cost of shipped inventory items, that is, the buyer’s receivables to the organization are formed here (proceeds from the sale).
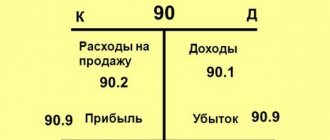
The debit of account 62 corresponds with the credit of accounts for sales or other income and expenses. Account 90 “Sales” is used when selling goods or products to the buyer, when this is a normal activity of the organization. Account 91 “Other income and expenses” is used for one-time sales of assets: fixed assets, materials, intangible assets, when this is not a normal activity of the enterprise - postings D62 K90/1 or D62 K91/1.
Credit account 62 reflects receipt of payment from the buyer, that is, repayment of existing debt. The credit to account 62 corresponds with the debit of cash accounting accounts (accounts 50, 51, 52, 55) - postings D50 (51, 52, 55) K62.
The cost of sold inventory items is reflected in the debit of account 62, taking into account VAT.
If an organization is a payer of this tax, then it must be calculated in accordance with the applicable rate and paid to the budget. The accrual of value added tax is reflected using entry D90/3 (91/2) K68/VAT (depending on what is sold). Tax payment is reflected using entry D68/VAT K51.
These postings are reflected during a regular sale, when the organization ships inventory items, and the buyer then pays for them.
In this case, account 62 behaves as active: the debit reflects the receivables (asset), and the credit reflects the repayment of debt (reduction of the asset).
| Debit | Credit | the name of the operation |
| 62 | 90/1 | Revenue from the sale of finished products and goods is reflected |
| 90/3 | 68/VAT | Tax payable on goods sold |
| 62 | 91/1 | The cost of sold fixed assets, intangible assets, materials is reflected |
| 91/2 | 68/VAT | Tax accrued on sold assets |
| 51 (50) | 62 | Payment received from buyer |
Another option for settlements with customers is possible, when the organization first receives an advance payment from the buyer (advance payment), after which it makes the shipment. Accounting for settlements will be conducted slightly differently.
First of all, an additional subaccount 2 “Advances received” is opened. In this case, the first subaccount records calculations in the general case.
Receipt of an advance payment is reflected using posting D51 K62/2, and the seller’s accounts payable to the buyer is formed.
If an organization is a VAT payer, then it must allocate tax from the advance received to pay it to the budget. To do this, you can use additional account 76, on which a sub-account “VAT on advances received” is opened. The posting for calculating tax payable on an advance received has the form: D76/VAT on advances K68/VAT, posting is made on the day the advance is received.
Next, the seller organization ships goods, products, assets, repaying this debt - posting D62/1 K90/1 (91/1).
On goods sold, VAT must also be charged for payment by posting D90/3 K68.VAT, posting is carried out on the day of shipment.
After the shipment has been made, it is necessary to offset the advance received as payment for the shipped valuables using posting D62/2 K62/1.
As for VAT, we see that the tax is assessed for payment twice: on the advance payment and on the sale. Of course, the organization will not pay it in double amount, so it is necessary to deduct VAT from the advance payment; for this purpose, posting D68/VAT K76/VAT from advances is performed.
If an advance payment is received from the buyer, account 62 will behave as a passive account: accounts payable (liability) are formed on the loan, and debt is repaid on the debit (reduction of liability).
That is why account 62 is active-passive, since it can behave as a passive and as an active account.
| Debit | Credit | the name of the operation |
| 51 | 62/2 | Advance payment received from the buyer (including VAT) |
| 76/VAT on advances | 68/VAT | Advance tax charged |
| 62/1 | 90/1 | Revenue from the sale of finished products and goods is reflected |
| 90/3 | 68/VAT | Tax accrued on goods sold |
| 62/2 | 62/1 | Advance credited towards debt repayment |
| 68/VAT | 76/VAT on advances | Accepted for deduction of VAT in connection with the sale of goods paid in advance |
Home{amp}gt; accounting {amp}gt; Features of accounting for settlements with customers (account 62)
Settlements with customers are carried out on accounting account 62. What are the features of accounting for settlements with customers, accounting entries for account 62 will be discussed in this article. We will also consider how bills and advances received from the buyer are accounted for?
| Dear readers! The article describes typical situations, but each case is unique. If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, use the online consultant form in the lower right corner of the site or call direct numbers ext. 445 - Moscow - CALL 7 (812) 426-14 -07 ext.394 - St. Petersburg - CALL here - if you live in another region. It's fast and free! |
The shipment of goods to the buyer, the provision of services or the performance of work forms a receivable from the buyer to the organization by the seller. The debit of account 62 shows exactly the amount of this debt. The debt arises due to the fact that the shipment to the buyer occurs before payment for it is received.
Accounting on account 62
Revenue received by the organization by the seller from the sale of goods and finished products is recognized as the organization’s income from ordinary activities and is reflected by entry D62 K90/1. This posting is made for the cost of shipped products, goods, indicated in the attached primary documents.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ng4Ifp0Mgog
Revenue received by the organization by the seller from the sale of fixed assets, materials and other assets, in the case where this sale is of a one-time nature and does not relate to the main activities of the organization, is recognized as other income of the enterprise and is reflected by entry D62 K91/1. Read more about the sale of fixed assets in this article.
If the seller is a VAT payer, then the sales price includes a tax that is applied to the cost of goods, products, assets sold and is payable to the budget.
If goods or products are sold, then VAT is charged by posting D90/3 K68.VAT.
If assets are sold, and this is not the usual type of activity of the enterprise, then posting D91/3 K68.VAT is performed.
August 28, 2014 Accounting for settlements
In the previous article we dealt with suppliers, now let's move on to buyers. How is customer accounting kept, what are the features of settlements with them, what entries in account 62 reflect mutual settlements with customers in the general case, when receiving advances or bills from them.
Buyers are individuals or legal entities to whom an organization sells goods, products and other tangible assets and assets. Accounting for settlements with customers is kept on account 62. On account 62, analytical accounting can be kept for each individual buyer. The same account may reflect services provided and work performed.
Account 62 is active-passive, that is, it records assets and liabilities. This account was analyzed in more detail in this article, read it.
Several sub-accounts can be opened on account 62:
- Subaccount 1 – for accounting for calculations in the general case;
- Subaccount 2 – for accounting for advances received;
- Subaccount 3 – for accounting for bills received.
VAT on advance payment issued from the buyer
After transferring the prepayment, you will receive an “advance” invoice from the supplier. Based on it, you have the right to deduct tax. But follow the conditions from clause 12 of Art. 171 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- the invoice is issued in accordance with the requirements;
- there is a document confirming payment;
- There is a condition for prepayment in the contract.
When transferring the advance payment, the buyer should have the following entries in his accounting:
Dt 60 Kt 51 - advance payment transferred to the supplier;
Dt 68 Kt 76 - VAT on the “issued” advance is accepted for deduction.
Record the received “advance” invoice in the purchase book. Indicate VAT on the advance payment in line 130 of section 3 of the tax return.
You can accept an “advance” invoice for deduction only in the quarter in which it was received. It cannot be transferred to the future. The rule on transferring deductions for a period of up to 3 years does not apply to advances (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-11/67480 dated October 17, 2017).
How to improve accounting calculations
Organizing accounting with buyers/customers is not without its drawbacks. However, this area can and should be improved. Let's look at the shortcomings that are typical for the operations under consideration:
- Insufficient control of the accountant's work by the management team. If the manager does not neglect control, there is a greater chance that the accountant will comply with regulations.
- The invoice must be issued within 5 days after shipment of the products. After this period expires, the document is considered invalid. However, very often a company issues an invoice later than this period.
- Errors in crediting funds sent to the company.
- Untimely or simply lack of inventory of calculations. This results in overdue debts being discovered very late. That is, no measures are being taken to repay the debt.
- Overload of accountants, which leads to confusion.
- Accounting rules that can be interpreted in two ways.
- Constant changes in documents governing accounting rules.
- There is no established system for document verification.
- Uncoordinated work of departments. For example, documents from the sales department arrive late in the accounting department.
Identifying shortcomings is the first and main step towards an established payment system. The second step is to eliminate them. That is, the manager needs to devote more time to monitoring the accounting department. It is important to ensure that documents are prepared on time. It is important to draw up your accounting policy correctly and not change it constantly.
IMPORTANT! The standard direction for improving accounting is automation. It will help reduce the number of errors.
Account 51 “Current accounts” corresponds with the following Plan accounts:
by debit
- 50 "Cashier"
- 51 “Current accounts”
- 52 “Currency accounts”
- 55 “Special bank accounts”
- 57 “Translations on the way”
- 58 “Financial investments”
- 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
- 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”
- 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings”
- 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”
- 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security”
- 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”
- 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations”
- 75 “Settlements with founders”
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
- 79 “Intra-economic settlements”
- 80 “Authorized capital”
- 86 “Targeted financing”
- 90 "Sales"
- 91 “Other income and expenses”
- 98 “Deferred income”
- 99 "Profits and losses"
on loan
- 04 "Intangible assets"
- 50 "Cashier"
- 51 “Current accounts”
- 52 “Currency accounts”
- 55 “Special bank accounts”
- 57 “Translations on the way”
- 58 “Financial investments”
- 60 “Settlements with suppliers and contractors”
- 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
- 66 “Settlements for short-term loans and borrowings”
- 67 “Calculations for long-term loans and borrowings”
- 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees”
- 69 “Calculations for social insurance and security”
- 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”
- 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”
- 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations”
- 75 “Settlements with founders”
- 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors”
- 79 “Intra-economic settlements”
- 80 “Authorized capital”
- 81 “Own shares (shares)”
- 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)”
- 96 “Reserves for future expenses”
- 99 "Profits and losses"
Feedback
COGNITIVE
Willpower leads to action, and positive actions create a positive attitude.
How to Determine Your Vocal Range - Your Vocals
How your target knows what you want before you act. How companies predict habits and manipulate them
Healing Habit
How to get rid of resentment yourself
Conflicting views on the qualities inherent in men
Self Confidence Training
Delicious “Beet Salad with Garlic”
Still life and its visual possibilities
Application, how to take mumiyo? Shilajit for hair, face, fractures, bleeding, etc.
How to learn to take responsibility
Why are boundaries needed in relationships with children?
Reflective elements on children's clothing
How to beat your age? Eight unique ways to help achieve longevity
How to Hear God's Voice
Classification of obesity by BMI (WHO)
Chapter 3. Covenant of a man with a woman
Axes and planes of the human body - The human body consists of certain topographic parts and areas in which organs, muscles, vessels, nerves, etc. are located.
Chiselling of walls and cutting of jambs - When there are not enough windows and doors on the house, a beautiful high porch is only in the imagination, you have to climb from the street into the house along a ladder.
Second-order differential equations (market model with predictable prices) - In simple market models, supply and demand are usually assumed to depend only on the current price of the product.
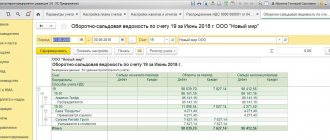
Turnover balance sheet for account 62 using an example
In addition, there is a sub-account for separate accounting of bills received (62.03). If the supplier receives a bill of exchange from the buyer providing for the payment of interest, the amount of interest is reflected in accounting account 91 “Other income and expenses.” Repayment of the principal amount of the debt is reflected by posting Dt account 51 (for foreign currency accounts DT 52) and Kt 62.
For the convenience of the accountant, analytics for account 62 are carried out in the context of each invoice sent to the buyer, as well as separately for each counterparty and agreement with him. In addition, operations can be classified according to the following criteria:
- payment method (availability of advance payment or payment upon shipment, provision of services);
- payment deadline (payment is overdue or not due);
- presence of a bill of exchange (the bill of exchange has been accounted for in the bank, its maturity has not yet come, or payment on the bill of exchange is overdue).
The accountant has the right to independently choose the criteria on which the analytical accounting of account 62 at the enterprise will be based.
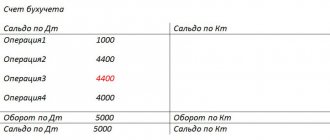
What do we see from this SALT?
For example, the counterparty LLC Horns and Hooves made a payment in our favor for 2021 in the amount of 61,114.56 rubles, and we shipped him goods or provided services in the amount of 27,110.68 rubles. The final accounts payable to the buyer is 34,004.88 rubles.
On account 62, analytical accounting should be provided according to the following parameters:
- According to issued invoices.
- For each counterparty.
- By groups of affiliated persons (with whom consolidated reporting should then be prepared).
- By payment characteristics (received prepayments, postpayments).
These tasks are solved, among other things, through the opening of sub-accounts to account 62.
Subaccounts are usually identified by an additional numeric coding of one or two characters added to the main account code. In the original chart of accounts, a unified standard for creating subaccounts for account 62 is not provided. But as a result of the widespread use of computer programs, assigning a subaccount code in practice is approximately the same.
For example:
- Account 62.1 (or 62.01 in most current versions of accounting programs) is assigned to account for postpaid settlements. When the goods have been shipped (services have been provided) but payment has not yet been received. The balance according to 62.1 is debit and means that the buyer (customer) owes the organization for the part of the transaction that it has already completed.
- Account 62.2 (or 62.02) is used to record received payments against future shipments (performance of work, provision of services). The balance is a credit balance and characterizes the size of the organization’s obligations to counterparties who have made prepayments for transactions.
Read more about accounting automation in the material “Review of programs for accounting expenses and income of an organization.”
- Invoice 62.01 – payment received in accordance with the general procedure;
- Account 62.02 – advances from buyers.
Account 51 “Current accounts”
Account 51 “Current accounts” is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of funds in the currency of the Russian Federation on the organization’s current accounts opened with credit institutions.
The debit of account 51 “Settlement accounts” reflects the receipt of funds to the organization’s settlement accounts. The credit of account 51 “Current accounts” reflects the write-off of funds from the organization’s current accounts. Amounts erroneously credited or debited to the organization's current account and discovered when checking statements of a credit institution are reflected in account 76 “Settlements with various debtors and creditors” (sub-account “Settlements for claims”).
Transactions on the current account are reflected in accounting on the basis of the credit institution's statements on the current account and the monetary settlement documents attached to them.
Analytical accounting for account 51 “Current accounts” is maintained for each current account.
Analytical accounting on account 62 and its subaccounts
Analytical accounting involves the use of personal and material accounts. They bring together detailed information about operations. Let's consider the postings within the framework of analytical accounting:
- DT62 KT90/1. Debt on goods that have been shipped.
- DT62 KT90/1. Reversal of the amount of shortages detected upon acceptance of goods.
- DT62 KT76/2. Collection by the client of the shortfall amounts.
- DT62 KT91/1. Buyers' debt for materials, fixed assets, securities, etc.
- DT62 KT90/1. Calculation of lease payments.
- DT50-52 KT62. Receipt of money from counterparties.
- DT50, 51 KT62. Advance payment against future delivery of goods.
- DT52 KT62. Advance in foreign currency against future delivery.
- DT62 KT68. Accrual of VAT on advance payment.
- DT68 KT62. Crediting VAT on advance payment upon release of goods that have been paid for.
- DT51 KT62. Receipt of money as payment for goods sold.
- DT52 KT62. Receipt of currency for goods sold.
- DT62 KT50, 51. Refund from clients of funds paid in excess.
- DT62 KT50, 51. Refund of advance payment to clients.
- DT62 KT90/1. Accrual of commissions.
- DT76 KT62. Settlement of remuneration.
- DT62 KT62. Assignment of claims.
The basis for postings is an accounting statement, a commission agent's report, etc.
VAT on advances received from the supplier
Let's consider the situation with VAT, when the buyer made an advance payment to the supplier. Within 5 days from the date of receipt of the prepayment, issue an invoice for the advance payment in two copies (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Give the first one to the client, register the second one in the sales book.
Please indicate VAT on the invoice. To calculate it, use the formula:
VAT = Advance × 20/120
The rate of 20/120 is changed to 10/110 if goods are sold with VAT of 10% (for the list see clause 2 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). If an advance is received for the supply of goods with different VAT rates, then calculate the tax at the general rate of 20/120.
Calculate VAT on advance payment for the transfer of property rights using the formula:
VAT = (Advance Costs for the acquisition of rights) × 20/120
Charge VAT on the day you receive the advance. This day will be the moment of determining the base for calculating the tax.
The advance amount from the invoice falls into column 3 of line 070 of section 3 of the VAT return. The amount of VAT on the advance payment falls into column 5 of the same line.
In addition, we create the following entries in accounting:
Dt 51 Kt 62 - the buyer made an advance payment;
Dt 76/62 Kt 68 - VAT was charged on the advance payment.
Debit 91.2 Credit 62
Other expenses. Settlements with buyers and customers
- Write-off of receivables in favor of the financial agent (factor), when transferring to the factor debt rights (monetary claims) in relation to buyers or customers: The amount of factoring due to be received is reflected, i.e. transferred/sold receivables. The factor's client reflects the factoring interest using the same posting. It is carried out on the basis of the factoring agreement and invoices.
Factors (financial agents) are usually banks, investment companies and other credit organizations.
Scheme of transactions reflecting the transfer/sale of debt rights to the factor:
- Dt 91.2 Kt 62 - for the amount of factoring due to be received (i.e. minus the funds allocated for the payment of interest on factoring and funds reserved by the factor in case of bad faith of the debtor);
- Dt 76 Kt 62 – for the amount of factoring funds reserved by the factor;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 62 – for the amount of interest on factoring;
- Dt 51 Kt 66 - for the amount of funds received from the factor; further, as notifications are received from the factor:
- Dt 66 Kt 91.1 - reflects the repayment of debts by debtors as notifications are received;
- Dt 91.2 Kt 76 – costs are charged for paying for the factor’s services for maintaining a register of buyers’ accounts (from funds previously reserved by the factor), excluding VAT;
- Dt 19 Kt 76 – VAT on the volume of factor services;
- Dt 68 Kt 19 – VAT refundable;
- Dt 51 Kt 76 - the amount of the reserve unused by the factor is credited to the account.
In the event of only partial fulfillment by the debtor of its obligations, the amount of the outstanding debt is retained by the factor at the expense of the reserve (see above Prov. Dt 76 Kt 62) and, accordingly, is reflected in the client’s accounting using the same entry as the cost of payment for the factor’s services:
- Dt 91.2 Kt 76, after which the remaining amount from the reserve funds is credited to the account: Dt 51 Kt 76, or, if this turned out to be insufficient, the corresponding factoring amount, by way of recourse, is written off in favor of the factor: Dt 66 Kt 51.
Factoring with recourse essentially means providing a loan to a client (although it is not formally recognized as a loan - see Chapter 43 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), and factoring without recourse means purchasing debt rights from the client. In both cases, the factor receives investment income - interest/remuneration on factoring.
In the Instructions to the current Chart of Accounts (No. 94n), this posting (Dt 91 Kt 62) is not indicated among the correspondence.
Posting Dt 62 Kt 62 always means making changes according to calculations. There are three possible options:
- Debit 62 Credit 62 between subaccounts.
Example
is part of a group of companies preparing consolidated financial statements. Technotrade accounts for settlements with companies in its group in account 62.4. The company has a counterparty, LLC "Zapchasti", which has a credit balance of 62.2. received information that Zapchasti LLC was included in the same group on the date the balance was formed.
- Debit 62 Credit 62 between counterparties.
Example
Stroymontazh LLC performed repair work for the customer 1 per 100,000 rubles. and customer 2 for 80,000 rubles. The customers are affiliated persons, resulting in payment under both contracts in the amount of 180,000 rubles. received from customer 1. Stroymontazh LLC accepted this payment, securing its terms in an additional agreement with customers. To correctly reflect the calculations, the accountant of Stroymontazh LLC made a posting of Dt 62 / customer 1 Kt 62 / customer 2 for 80,000 rubles.
- Debit 62 Credit 62 for two transactions.
Example
Stroymontazh LLC contracted to perform work at several sites of one customer. At site 1, the work has been completed, but not all of it has been paid for. An advance payment has been received for object 2, but work is still underway. The customer proposed to offset part of the prepayment for object 2 to pay off his debt for object 1. According to the corresponding additional agreement, Stroymontazh LLC will make an entry in its accounting Dt 62 / customer / object 2 Kt 62 / customer / object 1 for the balance of the customer’s debt for the object 1.
Refund of advance payment to buyer
The seller can return the advance to the buyer. The reasons for this are different - from an agreement of the parties to a court decision. VAT on the returned advance can be deducted after the return is reflected in accounting and the contract is terminated.
Confirm the advance refund with documents, for example, a payment order with allocated VAT for transferring money to the buyer. Register the payment in column 7 of the purchase book.
In accounting, make the following entries:
Dt 62 Kt 51 - return of advance payment to the buyer;
Dt 68 Kt 76 - accepted for VAT deduction.
You can use the deduction within a year; the right to a tax refund for three years does not apply.
Enter VAT for deduction in line 120 of section 3 of the declaration.
Synthetic accounting
When shipping goods by the seller and presenting payment documents, these postings are used:
- DT62 KT90. Recognition of income from sale.
- DT90/3 KT68. VAT accrual.
- DT51, 50, 52 KT62. Receipt of payment.
Other entries will be used if the transfer of ownership is completed on the date the funds are received by the company:
- DT51, 50, 52 KT62. Receipt of funds to the account of the seller company.
- DT62 KT90/1. Recognition of firm income.
- DT90/3 KT68. VAT accrual.
Posting DT50 KT90/1 is used only within retail trade, when the transaction agreement and the transaction are concluded simultaneously.
Accounting stages
Accounting is a multi-part operation that involves drawing up documents and making entries.
The shipment of goods is carried out on the basis of an order sent to the warehouse and an invoice for the release of products. The last document is drawn up in two copies. Based on the invoice, the accounting department issues a payment request for settlements. Invoices are issued by any company, regardless of whether the products are taxable. VAT is calculated based on the invoice. However, the buyer also needs this document. It is required for VAT refund.
If goods are accounted for as payments are received, the following postings are made:
- DT43 KT20. Capitalization of goods at actual cost.
- DT45 KT43. Shipment of goods to the buyer.
- DT62 KT90. Receiving proceeds from sales.
- DT90 KT68. VAT accrual on revenue.
- DT51 KT62. Receipt of payment from the buyer.
- DT 90 KT45. Write-off of the actual cost of the goods that were shipped.
If accounting is carried out as shipment occurs, these postings are made:
- DT43 KT20. Receipt of goods to the warehouse.
- DT62 KT90. Shipment and presentation of settlement papers.
- DT90 KT68. VAT accrual.
- DT90 KT43. Write-off of actual cost.
- DT51 KT62. Payment for shipped goods.
When concluding agreements, a free place is established. It involves identifying the person who will pay the costs of transporting the products.
Analytical monitoring
According to current legislation, legal entities have the right to open any number of accounts necessary to carry out their activities, both in Russian and foreign currency. Data on the opening are automatically transmitted to the Federal Tax Service inspection where the company is registered.
Analysis of incoming and outgoing non-cash funds is carried out in the context of each individual current account opened by the organization.
In order to verify the correctness of mutual settlements and filling in information in the company’s accounting records, an extract is requested from the credit institution (through the Bank-client system or in person through the branch operator). The statement displays all performed transactions and payment documents for them. Balances at the beginning and end of the period, as well as all turnover in accounting, must be identical to information from the bank.
Attention! Credit organizations set their own additional tariffs for servicing the company; amounts are debited automatically on the first or last day of the month, depending on the bank’s policy - these amounts are displayed in accounting as expenses for banking services in correspondence with account 91.02.
Main entries for account 62
- In accounting, fixed assets are reflected:
at original cost;
- at market value;
- at residual value;
- according to the degree of liquidity.
- Fixed assets are reflected in the balance sheet:
- at original cost;
- at market value;
- at residual value;
- according to the degree of liquidity.
Fixed assets include assets of an organization if they:
The main operations on account 62 are the reflection of settlements with customers in the general manner, based on the prepayment received, as well as in the presence of a bill of exchange. Let's look at each of these cases with an example.
Let’s say that an agreement was concluded between Faktotum LLC and Vestra LLC for the supply of goods and materials in the amount of 34,000 rubles, VAT 5186 rubles. The cost of the goods is 23,000 rubles. The contract stipulates that the buyer, Vestra LLC, pays for goods and materials after shipment.
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 62/1 | 90/1 | Reflected revenue from the sale of inventory items | 34,000 rub. | Packing list |
| 90/2 | 41 | The cost of inventory items is written off | 23,000 rub. | Costing |
| 90/3 | 68 VAT | VAT charged 18% | 5186 rub. | Packing list |
| 51 | 62 | Payment for the shipped goods was received from Vestra LLC | 34,000 rub. | Bank statement |
| 90/9 | 99 | Profit from the supply of goods and materials is reflected | 5814 rub. | Bill of lading, costing |
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 51 | 62/2 | An advance payment was received from Gamma LLC under the supply agreement | 36,000 rub. | Bank statement |
| 76 Advances received | 68 VAT | VAT charged on advance payment 18% | 5492 rub. | Bank statement |
| 68 VAT | 76 Advances received | VAT 18% accrued on advance payment has been restored | 5492 rub. | Bank statement, delivery note |
| 62/1 | 90/1 | Reflected revenue from the supply of stationery | 36,000 rub. | Packing list |
| 62/2 | 62/1 | The advance received from Gamma LLC is credited | 36,000 rub. | Bank statement, delivery note |
| 90/3 | 68 VAT | VAT charged at 18% for transfer to the budget | 5492 rub. | Bank statement, delivery note |
If the buyer does not agree to make an advance payment, and also does not have the opportunity to pay for the goods upon shipment, then in this case the supplier receives a bill of exchange from the customer, which acts as security for the receivables.
| Dt | CT | Description | Sum | Document |
| 62 | 90/1 | Reflected revenue from the sale of furniture | 114,000 rub. | Packing list |
| 90/3 | 68 VAT | VAT charged 18% of revenue | RUB 17,390 | Packing list |
| 62/3 | 62/1 | A promissory note was received from Antika LLC | 114,000 rub. | Simple bill of exchange |
| 51 | 62/3 | Payment for furniture was received from Antika LLC | 114,000 rub. | Bank statement |
Analytical accounting of account 62, organized taking into account all the necessary criteria, will ensure accurate and transparent maintenance of account 62.
When VAT is not charged on advances
VAT is not charged on advances in the cases listed in paragraph 1 of Art. 154 Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- the organization that received the advance payment is not a VAT payer;
- goods sold are exempt from VAT;
- goods sold are subject to VAT at a rate of 0% (for export);
- the duration of the production cycle of the goods sold is more than 6 months (the duration of the cycle must be confirmed by a certificate from the Ministry of Industry and Trade of the Russian Federation, and the product itself must be included in the List from the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 468 of July 28, 2006);
- place of sale of goods outside the Russian Federation.
With Kontur.Accounting, VAT accounting becomes easier. Keep records of advances received and issued, calculate VAT, issue deductions and offsets. Regularly enter transactions into the system to receive an automatically generated tax return at the end of the quarter. It can be submitted to the tax office for free directly from the service. Also in the Accounting Department you can conduct employee payments and accounting, generate reports, check counterparties and receive expert advice. New users receive 14 days of service as a gift.