From July 1, 2021 and January 1, 2021, the Russian Federation will introduce a list of important changes to the tax legislation of the Russian Federation. Who will be affected by the planned innovations and what their essence is, read below.
From January 1, 2021, companies and entrepreneurs in 11 regions of Russia will be exempt from paying several taxes and fees at once: the corresponding provision is reflected in bill No. 886255-7.
Businesses will have the opportunity to save on VAT, income tax, mineral extraction tax, and water tax. Companies and entrepreneurs may not pay excise taxes, state duties and fees for the use of wildlife and for the use of aquatic biological resources.
Reserve for future expenses for payment of bonuses
Companies have the right to create reserves in tax accounting for future expenses for the payment of bonuses.
We are talking about bonuses for length of service and based on the results of work for the year. Article 324.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is devoted to such reserves. But this article talks about reserves not only for the payment of bonuses, but also for upcoming vacations. Moreover, all the rules apply specifically to vacations. The procedure for calculation, inventory and write-off is given for them. And only in paragraph 6 of this article there is a short mention: a similar procedure applies to bonuses.
Calculate salaries and bonuses with all taxes and contributions in an understandable service for small businesses Calculate for free
However, as practice has shown, it is difficult to use the same rules for vacations and bonuses. After all, vacation pay is paid in the same year in which the vacation was granted. And bonuses for the year - next year (for more details, see “Reserves for the payment of remuneration at the end of the year: deceptive simplicity”).
Lawmakers have made things easier for accountants. From January 2021, a new paragraph 7 of Article 324.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation will come into force. It sets out a clear algorithm for reserves for the payment of remuneration. According to the amendments, an inventory of this reserve will need to be carried out before submitting an interim or annual income tax return.
REFERENCE
Let us remind you that the interim profit declaration is submitted no later than the 28th day of the month following the reporting period. Annual declaration - no later than March 28 of the next year (Article 289 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Fill out and submit a current income tax return via the Internet Submit for free
Next, you need to compare the two values. The first is the amount of bonuses accrued before the inventory date (this does not include bonuses that were written off from the reserve created in the previous tax period). The second is the amount of the reserve as of the end of the reporting or tax period. Then you need to act according to the circumstances:
- if the first value is greater than the second, then the excess must be included in the expenses of the reporting (tax) period;
- if the second value is greater than the first, then the excess must be included in the income of the reporting (tax) period.
Let us add that in accounting (as well as in tax) accounting, the creation of a reserve for the payment of bonuses is a right, not an obligation of the company. Therefore, organizations usually do this: either they form such reserves both in OU and in BU, or they do not form them anywhere. Either option is correct. The main thing is to reflect it in the accounting policies. For information on how to compile it, see “Accounting policies of the organization: samples for 2021, how to compile, examples.”
Get a sample accounting policy for a small LLC Get it for free
Information in the Pension Fund
In connection with the transition to electronic work books, from 01/01/2020 it is planned to introduce a new form for employers - SZV-TD on dismissed and hired employees, as well as on personnel changes (draft Law No. 748684-7 of 07/08/2019). Reporting is monthly - the form will need to be submitted to the Pension Fund by the 15th day of the month following the reporting month, and, with a staff of 25 or more people, only in electronic form.
To reflect the employee’s work activity in the company, the Pension Fund plans to introduce a new form of SZI-TD. It will be provided upon request by the employee.
Residual value of an intangible asset
Before the adoption of the commented amendments, the Tax Code determined only the initial cost of an intangible asset. From January 2021, there will be a definition of residual value. This is the difference between the original cost and the amount of depreciation accrued during the period of operation (new edition of clause 3 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Plus, it will be clearly stated that when selling intangible assets, proceeds from the sale can be reduced by the residual value. If an investment deduction has been applied to such an asset sold before the expiration of its useful life, you must proceed as follows. First, restore the corresponding part of the income tax. And only after that, reduce the income from the sale of intangible assets by its original cost (new editions of subparagraph 1 and subparagraph 4, paragraph 1, article 268 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Negative changes in legislation
1. The procedure for distributing profits between separate divisions
The Tax Code will establish the procedure for distributing profits between separate divisions when applying different income tax rates, which is currently recommended by the Ministry of Finance (letter dated May 14, 2020 No. 03-03-07/39124).
To calculate advance payments and taxes payable to the budget of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation at the location of the separate division, the tax base is determined based on the share of profit attributable to this separate division, defined as the arithmetic average of the share of the average number of employees (labor costs) and the share of the residual value of depreciable property of this separate division, respectively, in the average number of employees (labor costs) and the residual value of depreciable property, determined in accordance with paragraph 1 of Article 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, for the taxpayer as a whole.
At the same time, paragraph 2 of Article 274 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the tax base for profits taxed at a rate different from the rate specified in paragraph 1 of Article 284 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is determined by the taxpayer separately. The taxpayer maintains separate accounting of income (expenses) for transactions for which, in accordance with Chapter 25 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, a different procedure for accounting for profit and loss is provided for.
The problems lie in the lack of a clear methodology for distributing profits between separate structural divisions, and we understand that there is no clarity of regulation, there may be abuses by inspectors and, consequently, penalties.
2. New types of tax audits are being introduced: operational audits that relate to cash discipline
Operational audits are a type of tax audits, the purpose of which is to verify the correctness and completeness of recording calculations made using cash register systems. As part of the operational audit, a period not exceeding 3 calendar years will be inspected.
It is clear that any tax audits are aimed at assessing additional taxes, and therefore taxpayers will face new types of risks. In addition, additional charges are possible not only during the period of an error or violation of cash discipline, but also over the past years. That is, the tax authority will interrogate, for example, former employees to assess additional taxes for past periods.
Also, negative consequences include an increase in penalties. Controllers plan to fine people for recording imaginary or feigned payments. It is proposed to enshrine these concepts in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Fine amount:
- for individual entrepreneurs - 50% of the amount of the recorded imaginary or feigned payment, but not less than 10 thousand rubles;
- for an organization - the amount of the recorded imaginary or feigned payment, but not less than 30 thousand rubles.
They plan to impose a large fine for the absence of the name of a labeled product in a fiscal document or the indication of such a name in a distorted form:
- they want to collect 50 thousand rubles from individual entrepreneurs,
- from the organization - 100 thousand rubles.
3. Cancellation of UTII
UTII is cancelled. By default, from 01/01/2021, companies and individual entrepreneurs will be transferred to the general taxation regime: organizations will have to pay VAT and income tax, and individual entrepreneurs will have to pay VAT and personal income tax (Federal Tax Information).
The abolition of UTII includes micro and small enterprises, individual entrepreneurs selling socially significant goods and services: small retail stores, veterinary clinics, cafes and restaurants, hotels, personal services.
As a result of the abolition of the single tax on imputed income, entrepreneurs will be faced with a choice: change the taxation regime to the OSN, simplified tax system, patent system, or move into the category of self-employed, or close the enterprise and enter the labor exchange or go into the shadows.
Each of the above options may lead to the fact that the budget may not receive the funds that the Government of the Russian Federation is counting on (about 60 billion rubles), and the consequences of such cancellation will be much more severe: about 1.1 million enterprises on UTII may close, resulting in 1.7 million people. will become unemployed.
How to stop tax accrual if an individual’s property or transport is destroyed
A number of amendments are devoted to the calculation of transport tax, as well as property tax for individuals in the situation of death or destruction of taxable objects.
Transport tax
Previously, the Tax Code did not have special rules for the case when a vehicle is destroyed.
Explanations on this matter were given by Federal Tax Service specialists in a letter dated October 25, 2019 No. BS-4-21 / [email protected] Officials said: when a car is destroyed, its owner must submit an application to the inspectorate and attach supporting documents to it. Then the accrual of transport tax will be stopped (see “The car is destroyed or seized: how to pay transport tax?”). The recommended application form is given in the letter of the Federal Tax Service dated March 18, 2020 No. BS-4-21 / [email protected] (see “The Federal Tax Service approved the application form for the death of a taxable object for transport tax”).
Fill out waybills indicating the route and mandatory details in a special service
Starting in January 2021, the Tax Code will include provisions that deal with the loss or destruction of vehicles. New paragraph 3.1 of Article 362 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states: taxation ceases on the 1st day of the month of destruction (destruction) of transport. The owner of the lost vehicle submits an application to any Federal Tax Service of his choice. Individuals can also transfer it through the multifunctional public services center. The form and electronic format of the application, as well as the procedure for filling it out, will be approved by the Federal Tax Service. Until this happens, you can submit an application in free form indicating the month of death or destruction of the transport (Clause 16, Article 9 of Law No. 374-FZ).
The application must be accompanied by documents confirming the fact of the destruction of the object. If they are missing, no problem. The inspectors themselves will make a request to the relevant departments or contact persons who have information.
Tax authorities are given 30 working days from the date of receipt to consider the application. If you had to request information about the destruction of a vehicle, the period is allowed to be extended for another 30 days. Next, employees of the Federal Tax Service are required to notify the taxpayer of their decision: to terminate the accrual of transport tax, or to refuse.
Fill out and submit via the Internet in 2021 a message about the availability of transport and land Submit for free
Property tax for individuals
There are already rules in force that the accrual of property taxes on individuals stops on the 1st day of the month of the destruction of the property. And that the owner must write a statement and attach supporting documents to it. If they are absent, the inspection itself will request the missing information (clause 2.1 of Article 408 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The form and format of the application were approved by order of the Federal Tax Service dated May 24, 2019 No. ММВ-7-21/ [email protected] (see “Application for the destruction of an individual’s real estate property can now be submitted in electronic form”).
But until now, the time frame within which the inspectorate is obliged to consider the application has not been specified. In January 2021, a new version of paragraph 2.1 of Article 408 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation will come into force. According to the amendments, tax authorities are given 30 working days to review this document. And if you have to request information about the destruction of real estate, this period can be extended by 30 days. Then employees of the Federal Tax Service will notify the taxpayer of the results of consideration of the application: termination of tax accrual, or refusal.
RSV
The updated RSV form has been adopted. The changes are minor, some have already been applied during 2021.
The “Average Headcount” field has been added to the title page. At the same time, the separate document “Information on the average number of employees for the previous calendar year” KND 1110018 is abolished from 01/01/2021. Those. for the tax period 2021 it is no longer necessary to transfer it to the Federal Tax Service. The specified information will be transmitted in the form of DAM.
Instead of Appendix 5 to Section 1, Appendix 5.1 (conditions for applying the reduced tariff) is introduced. It will indicate payer code 1 or 2 - for IT companies and organizations designing and developing electronic components and electronic products, respectively. This 5.1 application will be available in the Balance-2W and Balance-2N programs from 2021.
In Section 1, tariff codes have been added - already used in 2021 with the support of small and medium-sized businesses and enterprises according to the approved list - 20 and 21, and 22 - for organizations designing and developing electronic component base products and electronic products - from 2021.
The new tariff codes will correspond to the new codes of the category of insured persons:
20 – MS, VZhMS, VPMS,
21 – KV, VZhKV, VPKV,
22 – EKB, VZhEK, VPEC.
New base limits have been approved from 01/01/2021:
- for calculating insurance premiums for compulsory health insurance - 1,465,000 rubles;
- for calculating insurance premiums for the Social Insurance Fund - 966,000 rubles.
Recalculation of “property” taxes when the value of an object changes
The Tax Code establishes algorithms for the recalculation of corporate property tax, personal property tax and land tax. Recalculation is done if the cadastral value of the property has changed. For different cases, different scenarios are provided (see table; for more details, see “Amendments to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation: what has changed in the calculation of property tax for organizations, property tax for individuals and land tax”).
Table
Rules for recalculation of “property” taxes due to changes in cadastral value (valid in 2020)
| Situation | How to calculate taxes | Tax Code norms |
| In the middle of the year, the quantitative and (or) qualitative characteristics of the object changed | Separately for each of two periods of time: before and after the change | Clause 5.1 art. 382 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 5.1 art. 408 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 7.1 art. 396 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
| The cadastral value has been revised by a court or commission decision | Recalculated retroactively for all periods in which the disputed cadastral value was applied | Clause 15 Art. 378.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 2 art. 403 Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 1.1 art. 391 Tax Code of the Russian Federation |
Fill out and submit land, transport and “property” tax declarations online for free
From January 2021, the recalculation rules will change. There will be two cases when it is necessary to recalculate the tax due to adjustment of the cadastral value.
The first case: the cadastral value of the object changes due to the fact that its market value has been established. Then it is necessary to recalculate the tax retroactively for all periods during which the variable cadastral value was applied (new editions of clause 15 of article 378.2, clause 2 of article 403, clause 1.1 of article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The second case: the cadastral value changes due to changes in the characteristics of the object. The calculation algorithm is as follows (new editions of clause 5.1 of Article 382, clause 5.1 of Article 408, clause 7.1 of Article 396 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- for the period from January 1 to the date of change, the tax amount is calculated based on the previous cadastral value, taking into account the coefficient. It is equal to the number of full months that have passed from January 1 to the specified date, divided by the number of calendar months in the tax period. If the change occurred after the 15th day, the current month is considered a full month;
- for the period from the date of change to December 31, the tax amount is calculated based on the changed cadastral value taking into account the coefficient. It is equal to the number of full months that have passed from the specified date to the end of the tax period, divided by the number of calendar months in the tax period. If the change occurs on or before the 15th, the current month is counted as a full month.
Changes in the minimum wage and the maximum contribution base
From 2021, a new minimum wage has been established throughout Russia in the amount of 12,792 rubles
. This means that no one working full time will receive less than this amount (minus personal income tax, of course). In addition, regional authorities have the right to set their own minimum wage, which must also be at least 12,792 rubles.
Currently, the State Duma of the Russian Federation is considering Draft Law No. 1027749-7, which provides for changes to the methodology for calculating and annual indexation of the minimum wage. The bill has already passed the first reading, and if it is finally adopted, then by 2023 the minimum wage will increase to approximately 14,200 rubles
.
In connection with the increase in the minimum wage, new contribution limits have been approved for 2021:
- 1,465,000 rubles – compulsory pension insurance;
- 966,000 rubles – temporary disability and maternity.
Other amendments to “property” taxes (come into force on January 1, 2021)
1. A new section will appear in the corporate property tax return. It will need to indicate the average annual value of movable property (new edition of paragraph 1 of Article 386 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This norm should be applied when filling out the declaration for 2021 (Clause 13, Article 9 of Law No. 374-FZ). Let us remind you that movable objects are not subject to property tax. Therefore, information about them will obviously be for reference only.
2. A period has been established during which the Federal Tax Service has the right to consider a notice of submission of a unified report on the property tax of organizations in relation to several objects. A company has the right to submit it if its real estate is located in different places, but on the territory of one subject of the Russian Federation. You can submit a single declaration if the tax for all objects is calculated at the average annual cost and is fully credited to the regional budget without deductions to local budgets (for more details, see “The form of notification on the submission of general property tax reporting for an organization and its branches has been approved”) .
Inspectors are given 30 working days from the date of receipt to review the notification. In some cases, it is allowed to extend the period for another 30 days (new edition of clause 1.1 of Article 386 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Fill out and submit a notice of submission of unified property tax reporting online
3. A period has been established during which the Federal Tax Service has the right to consider the notification of the selected land plot. It is submitted by individuals from preferential categories (pensioners, heroes of Russia, etc.) who own several plots of land. Such persons have the right to receive a land tax benefit for one of the plots. The size of the benefit is equal to the cadastral value of 600 square meters. m. area of land. You must inform the inspectorate about which site has been selected as a preferential site by submitting a notification (see “Deduction for land tax: the notification form for the selected site has been approved”).
Federal Tax Service employees are given 30 working days from the date of its receipt to review the notification. Under certain circumstances, it is permissible to extend the period for another 30 days (new edition of clause 6.1 of Article 391 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
4. A period has been established during which the inspectorate can consider a notification of selected objects for applying the property tax benefit for individuals. It is submitted by persons from preferential categories (heroes of Russia, disabled people since childhood, etc.) who own several properties. Such persons have the right to receive benefits for one of the objects. You should inform the Federal Tax Service about your choice by submitting a notification.
Inspectors must review the notice within 30 working days from the date of receipt. Under certain circumstances, it is permissible to extend the period for another 30 days (new edition of paragraph 7 of Article 407 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
5. Another transition period rule has been introduced for the property tax of individuals. It is intended for objects formed starting from the fourth tax period after the relevant locality switched to calculating tax based on cadastral value. For such objects, the tax for the first tax period in the general case should be calculated taking into account the coefficient of 0.6 (new clause 8.2 of Article 408 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This norm applies to legal relations that arose from the beginning of 2021 (clause 14 of Article 9 of Law No. 374-FZ).
6. A clarification has appeared regarding real estate (offices, shopping centers, etc.) included in the regional list of objects for which corporate property tax is calculated based on cadastral value. Previously, it was not clear how to calculate the tax if the cadastral value was established in the middle of the year. The Ministry of Finance believed that in this case there is no need to pay tax at all (letter dated September 27, 2017 No. 03-05-04-01/62799). Since January 2021, the rule has been in force: in such circumstances, the tax should be calculated at the average annual cost (new editions of paragraph 2 and paragraph 12 of Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Income tax return
By Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated September 11, 2020 No. ED-7-3 / [email protected] the following changes were made.
New taxpayer characteristics are being introduced 15 - 19:
15 - organizations that apply a reduced tax rate and own licenses to use subsoil plots.
16 - organizations applying a reduced tax rate, carrying out activities in the production of liquefied natural gas and (or) processing of hydrocarbon raw materials.
17 - an organization operating in the field of information technology.
18 - resident of the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation.
19 - an organization carrying out activities in the design and development of electronic component base products and electronic (radio-electronic) products.
New fields in Sheet 02 and in some appendices to it will have to be filled in, including by participants in special investment contracts and residents of priority development territories.
In Sheet 04, Type of Income “9” has been added - income received by a shareholder of a Russian organization when distributing the property of a liquidated organization between its shareholders
(the tax on it is reflected in Section 1.3 with the payment type code “1”).
In Sheet 08 it will be possible to reflect another type of adjustment - based on the results of the mutual agreement procedure.
Appendix No. 2 to the declaration. Previously, it provided information on the income of individuals from transactions with securities. Instead, the new Appendix No. 2 will have to be completed by taxpayers who have entered into an investment protection and promotion agreement (IPA) and are included in the relevant register.
The new form will be applied starting with reporting for 2021 .
Amendments to the first part of the Tax Code (came into force on December 23, 2021)
1. Individuals have the obligation to report to the Federal Tax Service about the presence of objects subject to property tax, transport and land taxes. It arises if a person has never received tax payment notices during the entire period of ownership of the property. And, as a result, he did not pay them. Now this information can be provided through the multifunctional center of public services (new edition of clause 2.1 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
2. Individual entrepreneurs received the right to issue a power of attorney to their authorized representative in the form of an electronic document signed with an electronic signature (new edition of clause 3 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For information about the electronic signature of an individual entrepreneur, see the article "".
Order an electronic signature certificate according to the new GOST
3. The amount of debt of an individual (without individual entrepreneur status) has been increased, the excess of which gives tax authorities the right to go to court to collect it. Previously it was 3,000 rubles, but now it is 10,000 rubles. The deadline for filing an application depends on how much debt has accrued within three years from the date on which the taxpayer was due to comply with the earliest requirement. If it amounted to 10,000 rubles. or more, tax authorities will go to court within six months from the moment this limit was exceeded, if less - within six months from the date of expiration of the three-year period (new editions of clauses 1 and 2 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation; see “ The amount of arrears that tax authorities will be able to recover from individuals through the court has been increased."
4. It follows from the amendments that a “paper” tax notice will be issued to the taxpayer (his representative) at the inspectorate or at the MFC after submitting an application (it must indicate the method of obtaining the document). The Federal Tax Service has 5 working days from the date the application is received to prepare the notification. If an application has not been received from an individual, the notification will be posted in the taxpayer’s personal account on the Federal Tax Service website, or sent by mail (new edition of clause 4 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
IMPORTANT
You can find out about tax debts and pay them through the taxpayer’s personal account on the Federal Tax Service website.
Obtain an electronic signature to log into the taxpayer’s personal account on the Federal Tax Service website
5. Previously, the period for submitting a demand for payment of arrears was one year from the moment it was identified, if the amount of tax debt (penalties, fines) was equal to: for individuals - less than 500 rubles, for legal entities and individual entrepreneurs - less than 3,000 rubles. Thanks to the amendments, the specified value for everyone, including individuals, will be 3,000 rubles. (new edition of clause 1 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
6. A period has been established during which the Federal Tax Service has the right to send a demand for payment of the debt for penalties accrued on the arrears after the day the demand for payment of such arrears was formed. The period is equal to one year from the date of payment of the arrears, or from the day when the amount of penalties exceeded 3,000 rubles. (new edition of clause 1 of Art. Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
7. It is stipulated that the Federal Tax Service, in general, must return the overpaid tax to the bank account specified by the taxpayer in the application for refund (new edition of clause 6 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The same applies to the refund of excessively collected tax (new edition of clause 5 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
8. It is indicated in which case the inspectorate will transfer interest for late tax refunds without the taxpayer’s application. This will happen if interest is accrued on the date of the decision to return the amount of overpaid tax. In all other situations, an application will be required (new edition of clause 10 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Submit an application for credit or refund of taxes (contributions) via the Internet Submit for free
Personal income tax
The Federal Tax Service has combined the calculation of 6-personal income tax with a certificate of income of an individual
For reporting for the first quarter of 2021, you will need to submit a 6-NDFL calculation using a new form. As part of it, you will need to submit certificates of income and tax amounts of an individual (now it is 2-NDFL). The specified certificates must be included in 6-NDFL once a year in the report for the tax period, i.e. in a year. In the annex to the order approved by the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, there is also a form of income certificate that is issued to employees.
Let's take a closer look at the most interesting innovations.
The calculation of personal income tax amounts calculated and withheld by the tax agent according to Form 6-NDFL has been revised. It now contains:
- title page;
- Section 1 “Data on tax agent obligations”;
- Section 2 “Calculation of calculated, withheld and transferred personal income tax amounts”;
- Appendix No. 1 “Certificate of income and tax amounts of an individual.”
Several technical corrections have been made for the title page For example, the field names have been changed:
- “Reporting period (code)” - instead of “Presentation period (code)”;
- “Calendar year” - instead of “Tax period (year)”.
- In the field that reflects the code of the reorganization or liquidation form, you will need to indicate the code for deprivation of authority or closure of a separate division. For this case, code 9 is assigned. Previously, the Federal Tax Service recommended a similar procedure for filling out 2-NDFL and 6-NDFL.
Sections 1 and 2 in the new form, in fact, change places: in section 1 it will be necessary to reflect information about the timing of personal income tax transfers and the amount of tax, and in section 2 - generalized information.
The innovations include the following:
- in both sections it is necessary to reflect the BCC;
- in general indicators it is necessary to indicate the amount of income accrued under employment contracts and under the GPA, as well as the amount of tax withheld in excess;
- Section 1 reflects only the deadline for transferring the tax and its amount, but the date of actual receipt of income, the date of tax withholding and the amount of income actually received is not necessary;
- separate fields in section 1 are provided to reflect personal income tax amounts returned in the last 3 months of the reporting period, broken down by return date.
Please note that by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 12, 2020 No. 236n, new BCCs :
| 182 1 0100 110 | in relation to the part of the tax amount exceeding 650 thousand rubles, related to the part of the base in excess of 5 million rubles. |
| 182 1 0100 110 | in relation to the tax on the amounts of CFC profits received by individuals who have switched to a special procedure for paying personal income tax based on filing a notification with the tax authority |
| 182 1 0100 110 | in relation to income in the form of interest (coupon, discount) received on circulating bonds of Russian organizations denominated in rubles and issued after January 1, 2021, as well as income in the form of interest on government treasury obligations, bonds and other government securities of the former USSR , member states of the Union State |
Thus:
- Section 2 should be formed in the context of Rate - BCC - Amounts of income and tax;
- Section 1 should be combined by rate and formed in the context of BCC - Deadline for tax transfer and Tax Amount.
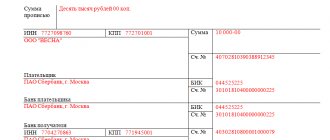
An example of the formation of 6-NDFL based on certificates:
Amendments to declarations and inspections (apply to declarations submitted after July 1, 2021)
1. If the declaration is submitted by a representative of the taxpayer, he must attach a document confirming his authority. From July 2021, this can be an electronic document signed with an enhanced qualified electronic signature (new edition of clause 5 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The format of such a document and the procedure for sending it will be approved by the Federal Tax Service.
2. During a desk audit, the inspectorate may demand from companies and individual entrepreneurs an explanation of the operations (property) in respect of which the benefit was applied. As well as documents confirming the right to benefits. Thanks to the amendments, it is possible to present the register of documents in electronic form as clarifications. The appropriate form, format and procedure for filling out will be approved by the Federal Tax Service (new edition of clause 6 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Receive requests from the Federal Tax Service for free and send the requested documents via the Internet
3. A list of reasons is provided for which inspectors will consider reporting unsubmitted. This is the signing of a declaration by an unidentified person; disqualification of the person who endorsed the statements; discrepancy between VAT return indicators and control ratios; and so on. (new clause 4.1 of Art.; see “A list of cases has been defined when reporting will be considered unsubmitted”). The desk audit of such a declaration is terminated. If this declaration has been clarified, then the verification of the source or the previous “clarification” will be resumed at the same time. At the same time, the period of “detention” on the declaration, which is recognized as not submitted, is not included in the period of the resumed inspection (new edition of clause 9.1 of Article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
VAT registers (0%)
New formats have been approved for registers of declarations confirming VAT (0%),
In addition, a new form was approved - “Register of documents confirming the validity of the application of tax benefits”, its KND 1155127.
As the Federal Tax Service explains, when a taxpayer receives a request to provide explanations (documents), he can respond to it, instead of a package of documents confirming a tax benefit, by submitting a register of documents confirming the validity of the application of tax benefits in the context of transaction codes.
Based on the information contained in the submitted register, the tax authority must request documents confirming the validity of the application of tax benefits for individual transactions. The volume of such documents is determined for each transaction code. At the same time, at least 50% of the volume of documents must confirm the largest amounts of transactions for which tax benefits are applied.
If the register is not provided, the documents will be requested in full.
Innovations in personal income tax (come into force on January 1, 2021)
1. Clarifications have been added regarding compensation for expenses for a vacation abroad if a person works and lives in the Far North. The cost of travel or flight of an employee (and non-working members of his family) from the place of departure to the checkpoint across the border of the Russian Federation is exempt from personal income tax. Including to the international airport, where the employee and his family undergo border control. Also, the carriage of luggage weighing up to 30 kg to the specified point is not subject to personal income tax (new edition of subparagraph 1 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
2. Travel expenses not subject to personal income tax include a resort tax (new edition of subclause 1 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
3. An addition has appeared: personal income tax does not include a lump sum payment, including financial assistance, received by an employee who has established custody of a child. We are talking about the amount issued in the first year after the establishment of guardianship within 50 thousand rubles. per child (new edition of subsection 8 of article 217 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Positive changes in tax legislation
1. Transitional “simplified”
The transitional “simplification” was planned in the Main Directions for Tax Development in 2021.
From January 1, 2021, new changes regarding the simplified tax system will come into force. The Federal Law “On Amendments to Chapter 26.2 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Article 2 of the Federal Law “On Amendments to Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation” No. 266-FZ dated July 31, 2021 introduced transitional provisions for those who during the year still exceeded the limits on income and (or) number of employees.
If, at the end of the reporting period, the taxpayer’s income exceeded 200 million rubles and (or) the average number of its employees exceeded the limit by more than 30 (to be more precise, more than 130) people, then such a taxpayer is considered to have lost the right to apply the simplified tax regime from the beginning quarter in which the specified excesses were allowed. This innovation will allow taxpayers to stay on the simplified tax system and not be kicked out immediately.
The advantage is the ability to apply lower tax rates. The tax rate for taxpayers paying income tax increases from 6 to 8 percent, and for taxpayers whose object of taxation is “income minus expenses” - from 15 to 20 percent.
2. Establishment of tax benefits for IT companies
Currently, new technologies are being actively developed abroad, and in order to develop them at the level of foreign countries, it is necessary to provide some preferences to our companies.
The preference package includes 2 offers.
Firstly, to permanently reduce the insurance premium rate from 14% to 7.6%.
Secondly, indefinitely reduce the income tax rate from 20% to 3%. The law with these and other amendments has already been adopted and will come into force on January 1, 2021.
A lot of companies will appear on the market, between which there will be a struggle for tenders and orders. The main competitive advantage with equal quality of services will be their low cost. The winner will be the one who can be the most flexible in terms of price formation.
At the same time, it is important to remember that such preferences will not be provided to all companies; it is necessary to meet a number of criteria:
1) Receive at least 90% of income from the following activities:
- development and sale of software and databases (hereinafter referred to as software);
- installation, testing, adaptation, modification, software maintenance (hereinafter referred to as software maintenance).
2) Have at least 7 employees.
3) Obtain accreditation from the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications.
3. Maintaining reduced insurance premium rates in 2021
In 2021, due to the coronavirus, reduced insurance premium rates were established. Such tariffs were adopted as a measure to support small and medium-sized businesses.
From April 1, 2021, reduced insurance premium rates have been established for insurance premium payers - SMEs, in relation to the part of payments in favor of an individual, determined based on the results of each calendar month, as an excess over the minimum wage established by federal law at the beginning of the billing period:
- for compulsory pension insurance:
- within the established limit value of the base for calculating insurance premiums for this type of insurance - 10.0 percent;
- over the established limit value of the base for calculating insurance premiums for this type of insurance - 10.0 percent;
- for compulsory social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with maternity - 0.0 percent;
- for compulsory health insurance - 5.0 percent.
In relation to the part of payments in favor of an individual, determined based on the results of each calendar month, in an amount less than or equal to the minimum wage, insurance premiums are calculated at general rates.
In 2021, the salary was 12,130 rubles.
The minimum wage, using the new calculation method of the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, which takes into account average per capita income, will increase in 2021 to 12,792 rubles, the cost of living for the working population - to 12,702 rubles.
4. Application of the direct payment mechanism
The Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation wants to extend the mechanism of “direct payments” for sick leave and maternity benefits in all regions of the country from January 1, 2021.
The legislation provides for a phased transition until December 31, 2020 for most entities. Now for these payments in a number of regions the “offset” principle is used, when the employer pays these benefits to employees at his own expense, and in the future the amount of insurance contributions to the Federal Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation is reduced in proportion to the payments made to employees. From January 1, 2021, all constituent entities of the Russian Federation will switch to a new mechanism for paying insurance coverage.
5. Tax holidays for individual entrepreneurs have been extended until the end of 2023
Individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system and a patent will be able to take advantage of the zero rate if they registered for the first time, conducted business in the industrial, social, scientific spheres, or provided household services to the population.
Subjects of the Russian Federation have the right to establish tax rates of 0% under the simplified tax system and PSN for newly registered entrepreneurs operating in the production, social and scientific spheres, as well as in the field of consumer services to the population and services for providing places for temporary residence (Federal Law of July 31, 2020 No. 266-FZ “On Amendments to Chapter 26.2 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Article 2 of the Federal Law “On Amendments to Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation”).
New types of risks
There are also new types of risks.
1. Resumption of tax audits
According to the Ministry of Finance, the federal budget deficit of the Russian Federation in 2021 will amount to 4.72 trillion rubles. or 4.4% of GDP. Russian Finance Minister Anton Siluanov told reporters about this.
According to him, Russian budget revenues in 2021 will amount to 17.84 trillion rubles, and expenses - 22.56 trillion. rub. At the same time, the non-oil and gas budget deficit is estimated at 9.84 trillion rubles, or 9.2% of GDP.
Such negative consequences cause additional audits, and it is clear that the purpose of the tax audit is to assess additional taxes.
Let us remind you that the tax authority has resumed tax audits.
The Federal Tax Service has resumed on-site tax audits of organizations and individual entrepreneurs, while changing the procedure for conducting them taking into account the sanitary and epidemiological situation.
In accordance with the order of the Federal Tax Service dated 07/09/2020 No. BS-7-2 / [email protected], tax authorities are allowed to resume the following tax control activities:
- inspection of territories (premises) of taxpayers;
- carrying out interrogations;
- carrying out inspections;
- calls to the tax authority;
- organizing excavations, conducting inventories, etc.
2. The emergence of new types of checks
New types of tax controls also have negative consequences, as they will put pressure on businesses already affected by the coronavirus. They want to include a section on operational control in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Tax officials will monitor the correctness of calculations, including the completeness of revenue accounting.
Operational control is going to be carried out in two forms:
- operational checks;
- monitoring.
It is proposed to carry out operational inspections at the place where organizations and individual entrepreneurs actually carry out their activities. Tax authorities will be able to involve the FSB in such audits.
As a general rule, it will be possible to control a period not exceeding three calendar years preceding the year in which the decision to conduct the inspection was made.
Earnings above 5 million rubles. per year will be subject to 15% personal income tax.
Federal Law No. 372 changes the approach to taxation of high incomes of individuals. It applies to those whose annual earnings exceed 5 million rubles.
The law introduces a differentiated approach to setting the personal income tax rate; its value will depend on the amount of income and the type of income. The concepts of “main tax base”, “set of tax bases” are introduced, lists of individual types of income are established, the set of tax bases for which are subject to different personal income tax rates.
What personal income tax rates are introduced:
- 15% - for income exceeding 5 million rubles.
- 13% - for income up to 5 million rubles inclusive.
The increased personal income tax rate also applies to income from the sale of securities, but does not apply to income from the sale of property, insurance and pension payments.