Any organization (individual entrepreneur) in its economic activities may be faced with the need to calculate and pay VAT to the budget, acting as not only a taxpayer, but also a tax agent. The peculiarities of accounting for VAT when performing the duties of a tax agent were considered by the Federal Tax Service of Russia in letter dated August 12, 2009 No. ШС-22-3/ [email protected] In this publication, methodologists tell how the provisions of this document are implemented in “1C: Accounting 8”. The procedure described in the article is planned to be implemented in all solutions based on 1C:Enterprise 8.
In accordance with Article 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, tax agents are persons who, in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, are entrusted with the responsibility for calculating, withholding from the taxpayer and transferring taxes to the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The obligations of a tax agent for VAT may arise for a business entity in the following situations:
- when purchasing goods (work, services) from foreign organizations that are not tax registered in Russia (clause 1 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- when leasing state or municipal property directly from state authorities and local self-government (paragraph 1, paragraph 3, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- when acquiring state or municipal property on the territory of Russia that is not assigned to state (municipal) organizations (paragraph 2, paragraph 3, article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- when selling property on the territory of Russia by a court decision (clause 4 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- when selling confiscated or ownerless property on the territory of Russia, as well as treasures, purchased valuables and valuables transferred to the state by right of inheritance (clause 4 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- when acting as an intermediary on the basis of commission agreements, commission agreements or agency agreements (with participation in settlements) in the case of the sale of goods (work, services, property rights) by foreign organizations that are not tax registered in Russia (clause 5 of Article 161 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, the performance of the duties of a tax agent does not depend on whether or not the business entity is a taxpayer for VAT. The tax agent, subject to the above-mentioned operations, will be any organization (individual entrepreneur), regardless of the applied tax regime or the availability of VAT exemption under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
However, the duty of a tax agent depends not only on the category of the business entity, but also on the category of the person for whom the obligation to pay tax is fulfilled. For example, “when selling property in pursuance of court decisions made in relation to persons who are not VAT payers, the authorized persons carrying out the sale of such property are not tax agents and, accordingly, they are not obliged to withhold and transfer value added tax to the budget "(letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 11, 2009 No. 03-07-11/300).
Considering that the procedure for accounting for VAT by tax agents is somewhat different from the generally accepted procedure provided for taxpayers, we will dwell on the main provisions of the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 12, 2009 No. ШС-22-3/ [email protected]
In this article, we will consider the features of issuing invoices and making changes to them, as well as the application of VAT deductions characteristic of two categories of tax agents - tenants/buyers of state (municipal) property and buyers of goods (works, services) from foreign entities.
It should be noted that in the standard configuration of 1C: Accounting 8, relatively rare (specific) operations are not automated, for example: fulfilling the duties of a tax agent for VAT when selling ownerless and confiscated assets. The sale of goods owned by foreign companies that are not registered with the tax authorities in the Russian Federation on terms of intermediation is implemented in the program. This issue has its own specifics, and we will not touch upon it in this article.
Who is a VAT tax agent?
At the same time, the company that actually pays the money is called the tax agent. To put it another way, it is she who acts as an intermediary between the company that received the actual profit and the tax service itself, which collects funds and transfers them to the budget. This way of handling money arose due to the fact that some organizations, for legal reasons, are not able to pay taxes on their own.
Who is the VAT tax agent?
There are a number of situations in which the state imposes agent duties on a company. They are listed in Article 161 of the RF NU.
In simple terms, an insurance agent is considered to be:
- If you buy foreign-made goods, services or work that are registered in the Russian Federation. Moreover, the place of sale is located in Russia.
- If you rent premises from government agencies, or purchased it.
- If you are selling property that is tied to treasure hunting: coins or other treasure contents, or other wealth.
- If you acquire the property of an organization that has been declared bankrupt.
- If you are an intermediary who sells services or goods whose owners are not located in the Russian Federation.
- If, after the transfer of ownership rights to you, you managed to build a vessel, but did not have time to register it in the International Register of Ships.
What VAT entries are reflected in the tax agent’s accounting?
As for VAT, the accountant uses only two entries:
- Debit 90, Credit equal to 68 - indicates that VAT is charged on the sale of goods and services provided in the main activity of the enterprise.
- Debit 91, Credit equal to 68 - if tax was calculated on the sale of a certain product or service, for additional activities. For example, if a company produces dairy products and simultaneously rents out refrigeration equipment to stores.
Postings for processing input VAT:
- Debit 19, Credit equal to 60 is used to take into account taxes on purchased goods and services.
- Debit 68, Credit 19 is used if VAT on purchased goods and services is accepted for deduction.
To account for input VAT and write it off as expenses, the following entries are used:
- Debit 19, Credit equal to 60 - this scheme is used if VAT on purchased goods is taken into account.
- Debit 19, Credit equal to 60 - an entry that is used if the tax on goods is included in their cost.
In some cases, it is impossible to calculate VAT on a certain group of goods or services. For example, you purchase slot machines that will be used in the gambling business. It is not subject to taxes, so there is nothing to charge VAT on. In such cases, the tax can be calculated into the cost of the machine by hiding it there.
For transactions that are used to recover VAT:
- Debit 60, Credit 68 This entry is used to recover the tax from the advance payment transferred to it. In this case, the reason why VAT is restored does not matter.
- Debit 91, Credit 68 - used to restore VAT on the balance of goods when switching to a special regime, or if a company or enterprise has received tax exemption.
If a tax that was previously accepted for deduction needs to be returned, then a lot depends on the reason for this action
In order for VAT to be transferred to the country’s budget, there is only one entry: Debit 68, Credit 51.
How to reflect VAT withholding?
Tax payment is required to be reflected in the financial statements. In order to fill out a VAT declaration to an agent, the issue must be approached with the utmost care and responsibility.
The declaration is submitted in electronic form. This must happen no later than the 25th day of the billing month, or at the end of the quarter.
Attention! From January 2021, the declaration is submitted on an updated form, which is approved by the Federal Tax Service. Be sure to fill out the title page, where you carefully enter all the basic data. Before submitting the form, double-check the cover page.
Next, the agent must fill out paragraphs 1 and 2. If you are not a tax payer, then paragraph 12 will be added to the previous paragraphs. As for paragraph 2, dedicated to agent taxes, they must be filled out separately for each company in relation to which the tax payer considered an agent. This means that if you pay tax not for one organization, but for several, then you will need to fill out all the fields about each of them on a separate sheet.
In paragraph 3, line 180, the tax agent can indicate tax deductions after paying VAT to the country's budget. You can immediately fill out sections 2 and 3 if the purchase of goods or services and the payment of tax on this transaction occurred in the same billing period.
When drawing up a document, the tax agent must rely on the norms for calculating the tax base. The declaration is filled out on the basis of information from the book of sales and purchases, and information obtained from accounting registers.
Filling out a payment order
In the payment order for the transfer of VAT to the budget, indicate:
- in field 101 “Status of the person who issued the document” – code 02 (tax agent);
- in field 104 “KBK” – VAT budget classification code;
- in field 106 “Basis of payment” – TP code (payment of the current year).
This procedure is provided for by the Rules approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 12, 2013 No. 107n.
If the accountant incorrectly fills out field 101 “Status of the person who issued the document” (instead of code 02 he indicates code 01), the amount of VAT that the organization should have transferred as a tax agent will be recorded in the tax inspectorate’s records as coming from the taxpayer organization. To learn how to correct this error, see What rights and responsibilities does a tax agent have?
Conditions for tax agent VAT deduction in 2016-2017
VAT paid by the agent can be credited to him. But in order to carry out this procedure, you need to decide on some questions that arise from the situation:
- Is the fact that the agent paid the tax even important?
- Is it necessary to capitalize the object, or is this procedure not necessary?
- Is it worth considering the place where the service was provided?
So, when filing a return as a tax agent, he should be extremely careful. You need to remember that the document must be submitted, like other taxpayers, before the 25th of the current month, or before the end of the billing period.
The declaration is submitted electronically and filled out in any place convenient for you where there is a computer and access to the Internet. Thanks to this service, you no longer need to stand in endless queues wasting time.
The tax agent fills out only the title page and paragraph 2.3 in the declaration. Most often, a tax agent acts as such not for one company, but for several. In this case, when filling out paragraph 2, you will need to work on several sheets, separate for each individual organization.
Still have questions? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now:
+7 (Moscow)
+7 (St. Petersburg)
8 For all regions!
It's fast and free!
If the tax agent, for some reason, does not pay tax, or is exempt from it due to the nature of his activity, but at the same time regularly issues invoices to taxpayers, allocating a certain amount of tax, then he will need to fill out additional paragraph 12, in addition to the mandatory first section and title page.
Procedure for issuing invoices
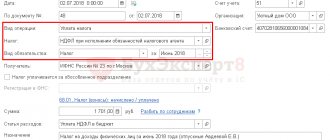
The organization (tax agent) draws up an invoice in the manner established by paragraphs 5, 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), no later than five days from the date of transfer of the advance (Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 12, 2009 N ShS-22-3 / [email protected] ).
Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 26, 2011 N 1137 “On the forms and rules for filling out (maintaining) documents used in calculations of value added tax” approved new forms of invoices, sales books and purchase books, as well as the form of the journal of received and issued invoices - invoices and the procedure for filling out these documents. Accordingly, tax agents should be guided by this document when preparing invoices. Taking into account the delay in the publication of this Resolution, the financial department considered it possible to apply two resolutions simultaneously in the first quarter of 2012 (Resolution dated December 2, 2000 N 914 and Resolution dated December 26, 2011 N 1137 (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 31, 2012 N 03-07-15 /11 and the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 02/01/2012 N ED-4-3/ [email protected] )).
Thus, from 04/01/2012, the tax agent should be guided by Government Decree No. 1137 and issue invoices using the new form. The new Rules for maintaining a journal of received and issued invoices require that this register be maintained not only by VAT taxpayers, but also by non-payers of this tax who are tax agents for VAT.
VAT defaulters must keep only part 1 of the accounting journal “Issued invoices” in those tax periods in which the corresponding invoices are registered (clause 2 of section II of Appendix No. 3 to Resolution No. 1137).
When filling out invoices using the new form, you can use the recommendations on the specifics of drawing up invoices by tax agents reflected in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 12.08.2009 N ШС-22-3/ [email protected] , since the Rules established by Resolution N 1137 do not take into account all the nuances of filling out such a document by tax agents, in particular, they do not contain clarifications on filling out the tabular part.
So, for example, when calculating VAT to be withheld and transferred to the budget by the tax agent, the estimated tax rate of 18/118 is applied (clause 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), therefore not 18% should be indicated in column 7 “Tax rate”, but 18/118.
The main feature of filling out an “agency” invoice for rent is the procedure for filling out line 5 “to payment document N _ dated...”. In this line, the tenant must indicate the number and date of the payment on the basis of which he transferred the rent or advance payment. This rule is contained in section. II Appendix No. 1, approved. Resolution No. 1137. Basically, the Rules for filling out “agency” invoices have not changed. As before, the invoice drawn up by the tax agent is registered in the sales book of the quarter in which the obligation to calculate VAT arose (clauses 2, 3 and 15 of Section II of Appendix No. 5, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
When accepting tax paid for deduction, the invoice is registered in the purchase book (clause 2 of section II of Appendix No. 4, approved by Resolution No. 1137).
Who is recognized as a tax agent for VAT?
According to the Tax Code (161 Tax Code of the Russian Federation), there is a certain list of situations in which even persons who are not obliged to pay VAT and report on it must pay tax for their partners. These include the following situations:
- in case of receiving supplies from foreign persons who have not received tax resident status in the Russian Federation;
- in case of receiving federal and municipal facilities for rent;
- when selling ownerless property, confiscated property, property that must be sold by court;
- in case of sale of a vessel that is not registered in the Russian International Register;
- in the case of the sale of raw scrap metal, hides and waste paper (except for entities on a special regime).
Important! A tax agent is understood as any business entity paying remuneration to a non-resident who is not registered with the Federal Tax Service. The exception is taxpayers who use special regimes such as UTII, simplified tax system, PSN and unified agricultural tax.
The main responsibility of the tax agent is the timely withholding of the tax liability from the remuneration due to a non-resident or a VAT defaulter. It is necessary to withhold the tax in full, and then submit written information to the Federal Tax Service in accordance with 24 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Tax agent obligations for VAT from January 1, 2021
The main change of the new year was the increase in the VAT rate to 20%. In addition, the settlement rate has also increased, which is now 20/120. Innovations also include the fact that since 2019, foreign organizations that provide services in electronic form in the Russian Federation are required to independently organize the payment of VAT and submit the appropriate reports (rate 16.67%) in accordance with Law 303-FZ. This can be done in one of the following ways:
- when sales are carried out by an agent under a contract, the VAT report and payment are made by the representative;
- when a foreign company is directly involved in sales, it is necessary to register with the Federal Tax Service, obtain a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) in the Russian Federation, and then pay VAT independently.
In the second case, refusal to register as a Russian taxpayer does not oblige the buyer to become his tax agent and pay fines. That is, an organization or entrepreneur will not receive a VAT deduction, even if one of them decides to pay VAT on their own.
In this case, electronic services mean the following types of services provided in the customs territory of the Russian Federation:
- providing access to programs and computer facilities via the Internet;
- hosting and data storage abroad;
- advertising and promotion of goods on the Internet;
- design, support, and website administration remotely;
- access to repositories of electronic books and publications;
- search, delivery of information.
Important! It should be remembered that electronic services do not include services for ordering goods online, consultations by e-mail, software implementation, or organizing access to the Internet.
Let's look at the tax agent's VAT transactions using a specific example. Let’s assume that a non-resident supplier provided services worth RUB 200,000 to a Russian entrepreneur in 2010. At the same time, the agreement concluded between them does not say anything about the inclusion of VAT in the cost of products. According to current legislation, an entrepreneur must withhold and pay to the budget an amount of 40 thousand rubles.
| Business transaction | D | TO |
| The tax agent charged VAT (on the advance amount paid) | 76 (NA) | 68.32 |
| The tax agent transferred the obligation to the budget | 68.32 | 51 |
| A previously paid service was provided | 26 | 60 |
| The buyer has allocated input VAT | 19.04 | 76 (NA) |
| VAT offset for deduction | 68.02 | 19.04 |
The main problems that have arisen as a result of the transition period and the increase in the VAT rate in 2021 relate to transactions carried out between VAT payer organizations. Tax agents are required to pay the obligation in full on the day the remuneration for goods and services is paid. That is, there are two options for calculating and paying VAT:
- An advance transferred before the beginning of 2021 is subject to VAT at a rate of 18%, VAT on goods in 2021 is charged at a rate of 20%.
- If products delivered before 2021 are paid for only in the new year, then the tax rate will be 20%.
This scheme does not apply to the following entities:
- carrying out transactions with confiscated property sold in court or ownerless valuables;
- works through a representative (agent) in the Russian Federation with a foreign entity;
- carries out railway transportation within the Russian Federation in the interests of a non-resident;
- buys and then sells animal skins, nonferrous and ferrous metal scrap, and waste paper.
These entities will pay VAT (20%) on sales from the beginning of 2021. Compensation of the 2% rate is carried out at the expense of the buyer.
Responsibility for failure to fulfill obligations
If a tax agent untimely or intentionally fails to withhold VAT from remuneration to a supplier who is not registered with the Federal Tax Service and does not have resident status, then he is subject to the following penalties:
- 20% of the amount of unwithheld and unpaid tax (123 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- penalties for each day of delay (75 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- 200 rubles for failure to submit a VAT return on time upon fulfillment of the duties of a tax agent (126 Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- 5% of the amount of the unpaid obligation for each month of delay in case of failure to submit or late submission of the declaration, but not less than 1000 rubles and not more than 30% (119 Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
From the point of view of tax legislation, it is considered incorrect if the unrecovered VAT is paid at the expense of the buyer. In this case, a fine of 20% will be charged, as well as penalties for the entire time of non-payment of the obligation. In this case, the agent must withhold VAT from the remuneration amount for the subsequent delivery and transfer the non-payment to the budget. If the transaction was a one-time transaction, then the law does not explain further actions in such a situation. That is, repaying the debt with the buyer’s funds will still be preferable. Bring the tax agent to criminal liability under Art. 198 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation should not, since this measure provides for fairly large amounts of fines, forced labor, as well as imprisonment for repeated intentional violations on a large and especially large scale.
Rate the quality of the article. We want to become better for you: Tags: VAT tax agent:, vat, VAT tax agent
Example.
You sell TVs. You bought a TV from the manufacturer for 1000 (one thousand) rubles and sell it for 1100 (one thousand one hundred) rubles. Your added value is one hundred rubles. You pay VAT on them. Added value is what you add to the cost of a product or service to make your profit. You bought a TV for 1000 rubles, including VAT (18%) - 152 rubles 54 kopecks. Sold for 1100 rubles, including VAT (18%) - 167 rubles 80 kopecks. Next, from your VAT (167 rubles 80 kopecks) you subtract the VAT of the seller-manufacturer (152 rubles 54 kopecks)
and get 15 rubles. 26 kopecks This is the VAT that you must pay to the state. How to find out how much VAT is included in the price of a product? If the price is indicated with VAT, then take this price as 118%, find the cost of 1% and multiply to determine how much 18% will be. (1100 rubles: 118 x 18 = 167 rubles 80 kopecks) Every quarter you calculate how much VAT is in all your sold goods and services. You deduct all VAT that you purchased (raw materials, rent of premises, purchase of goods, etc.). And you give the difference to the state - this is your VAT.
Bottom line.
VAT remitted to the state is calculated as the difference between purchase VAT and sales VAT. Therefore, if you work according to a simplified tax system (without VAT), and your customers are in the classical taxation system (with VAT), then they cannot reduce their VAT by the amount of your VAT (you do not have it). And they are forced to pay more taxes to the state. If your competitor works with VAT, and you work with a simplified system (without VAT), then your client-buyers (other things being equal) will choose not you, but your competitor, because the customer-buyer will be able to reduce his VAT by the competitor’s VAT.
Regular (general) VAT refund procedure
The taxpayer can return VAT from the budget if, at the end of the tax period, the amount of deductions exceeds the amount of VAT calculated in the general manner (clause 2 of Article 173 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax refunds in most cases are carried out in the usual manner, which involves the following actions (Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- The taxpayer submits a VAT return and an application for tax refund to the Federal Tax Service.
- The Tax Service conducts a desk audit, during which it detects the presence of violations of the requirements of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and, if necessary, requests documents confirming the taxpayer’s calculations.
- If no violations are found, within seven days after completion of the audit, the tax service makes a decision to refund the VAT.
- If violations are found during the inspection, the tax inspector draws up a report within 10 days after the inspection. The act and documents confirming the tax violation are handed over to the taxpayer within five days, who has 15 days to file objections in writing.
- After the deadline for filing objections, the head of the Federal Tax Service or his deputy must review the inspection materials and decide whether or not to reimburse VAT (part of it). The decision made in writing is sent to the taxpayer within five days.
- If the tax inspectorate makes a positive decision, the money is returned to the taxpayer’s current account, provided that he has no debt on federal taxes and other fees. Otherwise, the amounts will automatically be offset against arrears.
Please note that the VAT refund is carried out by the Treasury no later than five days from the moment the Federal Tax Service Inspectorate made the corresponding decision. If the specified deadline is violated, the taxpayer will receive late interest at the current refinancing rate.
Accounting for VAT amounts
Value added tax is an indirect tax, which is a form in which a certain amount is collected and transferred to the budget, calculated at the tax rates established by law.
This amount is added to the cost of goods (work or services).
Value added tax is a federal tax and its application is mandatory throughout the Russian Federation. The object of taxation with this tax is four types of transactions:
- sales of goods (works or services) carried out on the territory of the Russian Federation, including the sale of collateral and transfer of property rights;
- transfer on the territory of the Russian Federation of goods (work or services) performed for one’s own needs, if expenses on them are taken for deduction when calculating income tax;
- construction and installation work carried out for own consumption;
- operations for the import of goods into the territory of the Russian Federation.
The determination of the tax base for the purpose of calculating value added tax is based on the cost of goods (work or services) sold, taking into account the excise tax (if the goods are excisable).
The price of goods, which is set by the parties to the transaction, must correspond to market prices.
Control over the correct application of prices is carried out by tax authorities.
A peculiarity of the calculation of value added tax is that he has the right to deduct VAT on goods purchased by the taxpayer in the tax period in which he calculates VAT, including the receipt of advance payments.
The moment of determining the tax base, which is the earlier of the following dates, plays an important role in VAT accounting:
- date of shipment of goods;
- date of payment for the upcoming delivery of goods.
The tax period for calculating and paying value added tax is assumed to be one quarter.
Tax rates depend on the type of goods and are set at 0%, 10%, 18%.
When goods, works or services are sold, the seller adds VAT to the price of his goods.
The basis for deducting VAT, which is presented by the seller to the buyer, is an invoice.
Taxpayers are required to keep a log of invoices they have received and issued, as well as a ledger of purchases and sales.
Acceptance of leased property for accounting
Accounting for leased property is organized on off-balance sheet account 001 “Leased fixed assets” at the cost specified in the agreement (Instructions for using the Chart of Accounts, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n). Analytical accounting is maintained for each leased property.
Reflection of leased non-residential premises in accounting is documented in the document Transaction entered manually, type of transaction Transaction in the section Transactions – Accounting – Transactions entered manually.
Let's look at the features of filling out the document Operation entered manually according to this example:
- Dt – account 001;
- Subconto 1 – lessor, selected from the Counterparties directory;
- Subconto 2 – leased fixed asset, selected from the Fixed Assets directory;
- Amount – the cost of the leased property, usually specified in the lease agreement.
If the contract or the transfer and acceptance certificate does not indicate the value of the leased property, and it is not agreed upon in an additional agreement, then it is recommended to establish in the accounting policy a method for determining the value of the leased property (clause 7 of PBU 1/2008), for example, based on the market value property.
It is recommended to open an inventory card for the rented premises (clause 14 of the Guidelines for OS accounting).
Calculation of value added tax
When performing a taxable transaction, taxpayers have the obligation to calculate VAT. The procedure for calculating value added tax is established by the provisions of Article 166 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
VAT amounts are calculated at the appropriate tax rate, which is a percentage of the tax base.
If transactions are taxed at different rates, separate accounting is maintained, and the amount of VAT is determined by adding up the tax amounts calculated separately for each transaction.
The taxpayer is also required to maintain separate accounting if part of the transactions he carries out are exempt from taxation.
VAT is calculated based on the results of each tax period, and payment is made no later than the 20th day of the month following the expired tax period.
The calculated VAT is reduced by the amount of the tax deduction. The amount of tax that the buyer paid when purchasing goods on the territory of the Russian Federation or when importing goods into the customs territory of the Russian Federation is accepted for deduction.
Only VAT payers have the right to use tax deductions.
If the taxpayer does not calculate the tax base for VAT, then he has no reason to deduct the amount of VAT paid in the cost of the purchased goods.
A taxpayer can deduct input VAT only if he has accepted for accounting the goods, works, and services purchased by him, which is confirmed by the relevant primary documents and invoices issued by the supplier.
In order to be able to apply a tax deduction, the Tax Code establishes certain requirements, failing which the taxpayer cannot apply the tax deduction. A tax deduction cannot be applied if:
- the taxpayer's expenses are economically unjustified;
- its business operations are unprofitable and unprofitable;
- invoices are not reflected (untimely reflected) in the accounting journal;
- there is no state registration of the acquired object, if it is mandatory;
- the counterparty was chosen without due diligence and caution, the counterparty from whom the taxpayer purchased the property did not comply with the requirements of tax legislation;
- the taxpayer’s actions are seen as a desire to extract unjustified tax benefits.
Rules for applying the deduction of VAT paid for work and services
For work and services purchased on the territory of Russia from foreign legal entities not registered with the Russian tax authorities, VAT is transferred to the budget simultaneously with payment for work (services) to the foreign supplier (paragraph 2, clause 4, article 174 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, you can claim deductions in the same period. This is confirmed by the Ministry of Finance of Russia in letters dated October 23, 2013 No. 03-07-11/44418, dated January 13, 2011 No. 03-07-08/06, November 29, 2010 No. 03-07-08/334, dated March 5, 2010 No. 03 -07-08/61.
The courts also agree with this (resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Northwestern District dated January 28, 2013 in case No. A56-71652/2011, FAS Moscow District dated March 29, 2011 No. KA-A40/1994-11, dated October 21, 2010 No. KA-A40/ 12967-10, FAS of the North Caucasus District dated 08/09/2010 No. A32-21695/2008-46/378-34/283-2010-11/1).
The VAT return for the corresponding tax period should reflect simultaneously:
- the amount of tax that was paid along with payment for work (services);
- the amount to be deducted for this transaction.