Penalties are a penalty that must be paid in monetary terms for each day of overdue payments. This penalty applies when a person or company moves from being a taxpayer to being a debtor. Today we will look at how and to what extent penalties are charged for non-payment of taxes.
Penalties for non-payment of taxes
General rules for filling out a payment form for tax penalties
Penalties intended for payment to the Federal Tax Service are the amount resulting from the later payment of taxes to the budget compared to the deadlines established for this (clause 1 of Article 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). They are transferred to the same inspectorate where the corresponding taxes are paid.
The document for payment of penalties is drawn up according to the same principles as for the tax payment itself, but with a number of nuances. Just like for tax payments, the following is entered into it:
- name, TIN, KPP and bank details of the payer;
- name, TIN, KPP and bank details of the tax authority;
- order of payment, KBK, OKTMO, basis for payment;
- purpose of payment.
With its own characteristics, the payment of penalties reflects:
- Sequence of payment. Her choice will depend on the basis for which the payment is made.
- KBK. The basic set of numbers for penalties is always similar to that used for the tax for which penalties are paid, but signs 14–17 are necessarily 2100, indicated only for penalties.
- Basis of payment. Here there is not always enough reason for payment (there are several of them for penalties). Data may be required about the period for which the payment is made and the document against which the payment is made.
- Purpose of payment. It is indicated that penalties are paid and for what tax; there may also be a need for other information.
The rules for issuing payment orders for the payment of penalties on taxes from 2021 also apply to insurance premiums subject to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But when paying penalties on contributions for injuries that remain under the jurisdiction of the Social Insurance Fund, you will also have to take into account a number of features.
The basis for the payment indicated in the payment document for penalties depends on whether it is made voluntarily or according to a document issued by the Federal Tax Service:
- The voluntary nature of the payment will be indicated by the letters ZD entered in field 106. Their presence allows you not to make other notes related to the basis of the payment (about the payment period, number and date of the document), and limit yourself to putting numbers in the fields intended for them (107–109) 0. If the amount paid can be linked to a specific tax period, then in field 107 you can make a link to it in the format MS.05.2019 or KV.02.2019.
- Documents drawn up by the Federal Tax Service regarding penalties are divided into: Request for payment. According to it, in field 106 you should enter the letters TR, and in the fields following it - the payment period specified in the request (field 107), the request number (field 108) and its date (field 109).
- Checking act. For it, the letters AP will appear in field 106 and, just like for the demand, you will need to enter the payment deadline specified in the act, the act number and its date in lines 107–109.
Based on the basis of the payment, the order of payment will be determined (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 20, 2014 No. 02-03-11/1603):
- for voluntary payment, the number 5 should be entered;
- payment according to a document issued by the Federal Tax Service - number 3.
The tax period for which payment is made may be additionally indicated in the purpose of the payment.
Penalties on taxes: general information
Article No. 75 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation regulates all issues related to penalties for tax collections: in what cases this penalty is calculated, in what amount and in what order - forced or voluntary. The law states that penalties are paid if the taxpayer does not make the tax payments required to him on time, that is, he is late in payment. It does not matter whether part of the amount or the entire tax collection was paid late.
The code of laws also explains that the accrual of penalties does not contradict and does not exclude other liability for violation of tax laws. In other words, even if a person is given an additional fine, the obligation to pay penalties accrued for each day of delay will still be assigned to the debtor.
When paying tax, a person must ensure that the money reaches the state treasury no later than the date indicated by the deadline for payment. From the very next day, penalties will begin to accrue.
Article 75. Penalty
Important point! When all due tax amounts are paid, the accrual of penalties stops. That is, the figure for the accrued penalty is fixed at the time the debt is repaid, and if the penalty has not been paid, then additional penalties are not charged.
Penalties are calculated not only for tax payments, but also for advance payments for taxes and fees. Thus, not only taxpayers, but also tax agents are required to pay penalties.
The tax office sends a request for payment of the debt and penalties to the debtor’s address. The letter indicates the total amount of the debt, the deadline by which the tax levy should have been paid, as well as the amount of the penalty on the day the demand was sent to the payer. The document also specifies other measures to collect tax debt if a person does not intend to pay it. It is necessary to respond to the received demand, that is, to deposit the amount of debt into the state treasury, within eight working days from the date of receipt of the letter.
Let us note that as of 2021, a decision has come into force that the tax office has the right to send a letter informing about a citizen’s tax debt to his employer or other person paying income (pension, scholarship).
The letter from the tax office arrives in a branded envelope indicating all the contact details of the department.
Basis of payment
TP - current year payments
ZD - voluntary repayment of debt for expired tax periods when
no requirement to pay taxes (fees) from the tax authority
BF - current payments of individuals, bank clients, paid from their bank account
TR - repayment of debt at the request of the tax authority to pay taxes (fees)
RS - repayment of overdue debt
OT - repayment of deferred debt
RT - repayment of restructured debt
VU - repayment of deferred debt due to the introduction of external management
PR - repayment of debt suspended for collection
AP - repayment of debt according to the inspection report
AR - repayment of debt under a writ of execution
DE - customs declaration;
PO - customs receipt order;
CV - decree-receipt (when paying a fine);
CT - a form of adjustment of customs value and customs payments;
ID - executive document;
IP - collection order;
TU - requirement to pay customs duties;
DB - documents of accounting services of customs authorities;
IN - collection document;
KP - an agreement on interaction when large taxpayers make payments in a centralized manner;
When indicating the number of the corresponding document, the “N” sign is not affixed.
Deadlines for paying taxes by law
In the Russian Federation, a law has been in force since 2015, according to which firms and individuals are required to pay taxes no later than December 1 of the year following the reporting period. Accordingly, taxes for 2021 must be paid by December 1, 2018. This date is relevant for all types of tax collections, including personal income tax.
No later than thirty working days before the specified date, the taxpayer receives a “chain letter” - a document informing him of the need to fulfill his tax obligation to the state.
If the taxpayer does not pay the full amount of the fee, he faces a sanction in the form of a fine. In the usual case, you must pay a fine of twenty percent of the debt amount. If tax inspectors have reason to believe that the payer is deliberately hiding from payment, the fine will increase to forty percent of the debt amount.
What happens if you don't pay on time?
The tax authority has the right to sue the debtor in order to collect the amount of debt without his consent. A court order may order the debt to be written off from the tax evader's property, including the removal of the missing amount from bank accounts.
Tax evaders will be required to repay the debt by court decision
An appeal to the court is legal within three years from the date of the very first demand from the tax authorities to repay the debt. There are two possible scenarios:
- If the amount of the debt does not exceed three thousand rubles, a representative of the tax inspectorate can sue within six months after the expiration of the above-mentioned three-year period.
- If the amount of debt exceeds three thousand rubles, the tax authority can sue six months after the moment when the amount of debt exceeded three thousand rubles.
Important point! A court order can be issued without summoning the parties and proceedings if the information provided by the tax authority is obvious and indisputable. In this case, the debtor has twenty days from the date of sending him a copy of the court order to submit objections. Regardless of the nature of the objections, the order will be canceled and the case will be considered with the participation of the parties.
Who is to blame if the tax payment notice is not received?
If a citizen or company representative has not received a tax notice within the specified period, they must investigate it themselves. Knowing that you own property subject to taxation or have other obligations of this kind to the state, you yourself must ensure the flow of money into the treasury.
Failure to receive a letter from the tax office is not an excuse for non-payment of taxes or late payment. If the paper has not arrived, the payer must contact the Federal Tax Service at the place of registration to clarify the amount to be paid.
Article No. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation states that no later than December 31 of the year following the expired tax period, each payer must contact the tax service and provide specialists with information about each taxation object for which the corresponding notification has not been received. If the “chain letter” arrived earlier or the person is exempt from paying tax in accordance with any benefits, the information does not need to be reported.
Article 23. Obligations of taxpayers
What happens if you don't pay taxes on time?
The deadlines for paying taxes are determined by the Federal Tax Service.
Taxes have many functions: regulatory, fiscal, social. Even if a small percentage of citizens refuse to pay them, this can lead to serious consequences, which is why the state has various penalties for violators.
- To begin with, a person is assigned a penalty. If the taxpayer continues to delay, he is issued a fine, the amount of which depends on the period of delay and the type of tax.
- In the event that a person has not filed an income tax return in Form 3-NDFL, the fine will be 5% of the tax amount. If the delay lasts more than six months, the percentage will increase to 30%.
- If the deadline for paying the duty is violated, the fine will be 20% of its amount. If intentional evasion is proven, it will be twice as large and amount to 40%.
- If, 6 months after the debt began, a person still does not pay the overdue amount, then the tax authority has the right to file a claim in court for collection. The missing funds are forcibly collected from the account. If they are not enough to pay off the debt, then a lien may be placed on the person’s property.
- If a taxpayer deliberately does not pay an amount of more than 600 thousand rubles, then he will be held criminally liable. The violator is fined from 100 to 300 thousand rubles. If this does not have the desired effect, then the person is sentenced to imprisonment for up to six months.
When will personal income tax become overdue?
A delay in personal income tax occurs when a person obliged to remit personal income tax violates the deadline established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Let us remind you that tax agents must transfer calculated and withheld personal income tax no later than the day following the day the income was paid. Personal income tax on sick leave benefits and vacation pay is transferred no later than the last day of the month in which such payments were made (clause 6 of Article 226 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Individual entrepreneurs who do not apply special regimes, as well as notaries engaged in private practice, lawyers who have established law offices, and other persons engaged in private practice, pay personal income tax independently on the basis of a submitted tax return no later than July 15 of the year following the previous year (clause 6 Article 227 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). In addition, such persons must pay advance payments during the year within the time limits specified in clause 9 of Art. 227 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Individuals who, for example, owned property for less than the maximum period and sold it in the reporting year, or received non-monetary gifts from other citizens (who are not individual entrepreneurs, family members or close relatives of recipients), as well as in some other cases specified in Art. 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, also pay personal income tax no later than July 15 of the following year based on the submitted tax return.
For some income (for example, the employer was unable to withhold personal income tax from an individual and reported this to the tax office), personal income tax is paid by individuals no later than December 1 of the following year on the basis of a notification received from the tax office (clause 6 of article 228 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If an individual or tax agent complies with the deadlines for transferring personal income tax, there will be no grounds for charging a penalty.
Otherwise, a penalty will be payable for each day of delay.
Conclusion
Tax penalties are an annoying additional expense, which is most often assigned to inattentive fee payers who have missed one or more transfers of funds. We would like to warn you that the tax service will not wait for payment from you forever, sitting with folded hands. Some time after non-payment of the fee, as well as non-payment of penalties, and possibly also a fine, your case will be transferred to the bailiffs, who will visit you until they are convinced that you have fulfilled your financial obligation to the state. By the way, since you are the reason for the forced involvement of bailiffs in the process of receiving money due to the country, subsequently the monetary compensation for their work will also fall on the shoulders of your organization.
How to draw up a payment order
For each line of the request, it is necessary to generate a separate payment order. This can be done manually - transfer the data from the received request to fields 24 and 104-109 of the payment order.
When filling out a payment slip, you can use this table, which will tell you what value you need to indicate in each field. Be careful when entering data - an error in even one figure will lead to the fact that the organization’s money will not go to its intended destination, and the debt will not be repaid.
You can read complete instructions on how to generate a payment order on the Accounting Online website.
The second option to prepare a payment order is to generate it automatically. This function has recently been available to Kontur.Extern users.
Having received an electronic request for payment in Externa, notify the Federal Tax Service about this by clicking on the button “Send an acceptance receipt to the Federal Tax Service.” Then proceed to create a payment order: follow the “Create payment order” link and enter the name of your bank and current account. The system itself will insert all other data from the request into the appropriate fields of the payment order. You can also choose what type of debt to make a payment for and, if necessary, change the payment amount.
You can create a ready-made payment slip either in Word format and then print it, or download a special text file to then upload to the Internet bank.
When are penalties not charged?
There are also several moments in the event of which penalties will not be charged. These include:
- An overpayment of the required tax, covering a payment that has not yet been made.
- Overpayment of the required tax, covering the amount of the penalty.
If the overpayment partially covers the resulting debt, penalties will be charged only on the difference, and not on the entire debt.
An overpayment is the amount of tax fees, as well as previously paid fines or other contributions that the payer transferred in excessive quantities or the tax authority collected excessively. In this case, the overpayment will be automatically counted instead of arrears or penalties. If a person knows that there is “extra” money in his account, he does not need to do anything - the tax authorities will recalculate the numbers themselves.
Let's look at an example. Ivan Sergeevich Semyonov owns a 2006 Honda Fit car, for which he pays about 900 rubles annually as transport tax. If in 2021 Semyonov pays two thousand rubles at once, he will not have to pay tax in 2021, accordingly, the amount of the penalty will not be accrued - the payment will go through automatically. If Semenov paid a thousand rubles in 2021 instead of 900 rubles, and then was late for three months, he will also not have to pay penalties. Why?
According to the calculation formula, penalties will be accrued as follows: (900 rubles x 8.25% x 1/300 x 16 days) + (900 rubles x 7.75% x 1/300 x 56 days) + (900 rubles x 7.5% x 1/300 x 19 days) and will amount to 21 rubles 26 kopecks, which is completely covered by the overpayment of 100 rubles.
Calculation using the online service
There are many websites where an online calculator will calculate the penalty for any overdue tax. To find such a resource, just enter the corresponding query into the Yandex or Google search bar.
The ConsultantPlus web service has a selection of tools for legal entities and individuals that inspire maximum confidence. As a rule, these are websites of government organizations that provide various government services.
For legal entities, the glavkniga.ru platform is offered, where, in addition to specific accounting information, there is a calculator section.
Other resources:
- nalog-nalog.ru/kal_kulyator_penej/;
- kontur.ru/calculators/peni;
- b-kontur.ru/profi/kalkulyator-peney;
- audit-it.ru/inform/peni/nalog.php.
All calculators operate according to the same algorithm:
- select the tax for which you want to calculate the penalty;
- the date from which the accrual of penalties begins is indicated;
- the date when it is planned to be repaid;
- tax amount required to be paid.
In some options, instead of the type of contribution, it is proposed to choose a form of ownership - individual entrepreneur or individual.
How to avoid paying too much
When processing a claim, it is important to know about the peculiarity of indicating amounts in the “Arrears” field. If the amount is marked with an asterisk, then you do not need to pay it - this information is for reference only.
When you create a payment order in Externa, you will never include an amount with an asterisk in it by mistake. This amount will be in the general list, but you cannot select it to generate a payment order.
kontur.ru
Payment of penalties by payment order in 2021
Such a payment order has both similarities with a regular one (it states the same status of the payer, indicates the same details of the recipient, the same income administrator), and differences. We will dwell on the latter in more detail, and then we will provide a sample payment slip for penalties for personal income tax 2021.
The first difference is KBK (props 104). For tax penalties there is always a budget classification code, in the 14th–17th digits of which the income subtype code is indicated - 2100.
The second difference between a payment order for penalties is detail 106. The following options are possible:
The third difference is detail 107. Its value depends on what served as the basis for the payment:
If you pay penalties yourself, enter 0 in fields 108 and 109.
In all other cases, in field 108, provide the document number - the basis for the payment (for example, a claim), and do not put the “No” sign.
gosuchetnik.ru
See also:
- Amount of benefit for the birth of a third child Child benefits in 2018 in the Rostov region In Rostov-on-Don and the region, families raising minor children are paid various types of social support measures. They […]
- Living of a child before divorce How to determine the order of living and raising a child after a divorce? If spouses have common minor children, divorce occurs in court. The exception is [...]
- Rules for using the children's library Rules for using the library Users of the children's library can be: children and adolescents under 15 years of age, students in grades 1-9, preschoolers, teachers, educators, […]
- Dismissal from work in the Republic of Belarus Dismissal from work in the Republic of Belarus At the request of the employee, a fixed-term employment contract can be terminated. Termination of a fixed-term employment contract at the request of the employee is not allowed. Don't confuse […]
- How to number an order Numbering orders in personnel records Update: October 19, 2021 Personnel documentation is an extensive set of orders, forms, statements and other documents. For […]
- Novosibirsk unemployment benefit amount Unemployment benefit This benefit is a form of support for unemployed citizens. It is paid regularly, but not constantly, but within a certain period. And they have the right to it [...]
Innovations for 2021 regarding penalties for taxes
Since the beginning of 2021, the law regulating tax obligations has extended to insurance premiums (medical, pension, disability and maternity leave). Accordingly, penalties are also calculated for these types of contributions in case of late payment.
Penalties are calculated the same for both individuals and legal entities, but at different interest rates
Starting in the fall of 2021, according to the new rules, penalties began to be calculated for firms, companies and organizations - legal entities. For them, the interest rate of the penalty has changed.
Penalty interest rate
For individuals, including individual entrepreneurs, penalties are calculated at an interest rate equal to one three hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the country. For legal entities the interest rate is different.
Table 1. Interest rate for legal entities
| Overdue period | Penalty calculation formula |
| Firms that are late in payments by no more than thirty days inclusive will pay penalties at a rate of one three-hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (as well as individuals). | Formula for calculating penalties for legal entities as a general rule |
| Firms that are overdue for tax payments by more than thirty calendar days will pay for the period of those same thirty days at the standard rate (1/300 of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation), and starting from the thirty-first day of debt - at a rate equal to one hundred and fiftieth (1 /150), that is, half as much. | Formula for calculating penalties for legal entities for the first 30 days of delay Formula for calculating penalties for legal entities starting from 31 days of delay |
Let's look at an example . is obliged to pay UTII in the amount of ten thousand rubles for the third quarter of the year no later than October 25, 2021. In fact, the money entered the state treasury only on November 30 of the same year. The refinancing rate during this period was 8.5 percent. Accordingly, “Belye Rosy” will have to pay a penalty in the amount of 113.3 rubles. How did this amount come about?
According to the 2021 innovations that we mentioned, for the first thirty days of delay the formula will be as follows: 10,000 rubles debt x 8.5% x 1/300 x 30 days (from October 26 to November 24). The next period is calculated differently: 10,000 rubles of debt x 8.5% x 1/150 x 5 days (from November 25 to November 29).
Calculation of penalties: formula
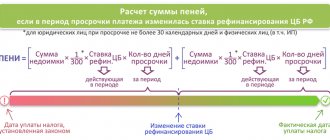
As we indicated above, penalties are calculated as a percentage of the amount of tax not paid on time. The classic formula for calculations is as follows:
Amount of tax debt x Refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation for the period of delay x 1/300 x Number of days for which payments are overdue
The current value of the Central Bank key rate needs to be clarified for the period of existing debt
Important point! From the beginning of 2021, the concept of “refinancing rate” has been abolished. The Central Bank approves the key rate, which corresponds to the abolished value. As of March 2021, the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation is 7.5 percent. Taking this fact into account, penalties must be calculated separately for each period if the rate was adjusted at that time.
Next, you need to figure out how to calculate the number of days in which the payment was overdue. According to Article No. 75 of the country's tax code, the delay begins to be considered from the day following the due date for payment of the tax fee (the date when it was necessary to pay, but this did not happen) until the day preceding the actual payment. That is, the delay in basic tax payments in any case is considered from December 2 (as we remember, the deadline for depositing money is December 1 of the year following the tax period). For example, a person needs to pay taxes for 2021. He did not do this on time, but transferred the money on March 16, 2021. The number of days of delay in his case is thirteen. Accordingly, if the payment was late by only a day, the payer would not face a penalty.
Do not forget that penalties are also charged on advance tax payments that are not transferred on time. In this situation, the number of days of delay is calculated individually, depending on the schedule for making advances. This information is relevant only for legal entities.
You may be interested in information on how to record tax penalties. In the presented material we will tell you what transactions exist for accruing and depositing funds for debt of the required type.
Video - How to calculate tax penalties according to the new rules?
Check the details in the payment order
In the payment order for penalties in 2021 (sample at the end of the article), put the same payer status and recipient details as in the tax payment. A payment order for the payment of penalties differs from a tax payment order:
Urgent news from the Central Bank of the Russian Federation: banks are prohibited from accepting payment orders with such words in the payment purpose>>>. Read more in the Russian Tax Courier magazine.
Since 2015, field 110 “Payment type” has not been filled in. This field is left blank. You can determine the purpose of the payment using the KBK.
Which BCC to indicate on the payment slip when paying a fine, see the article “Tax officials told how to correctly fill out a payment slip for a fine”