Accounting
Alexey Borisov
Leading expert on labor relations
Current as of September 15, 2019
When participating in relations with state extra-budgetary funds, the employer is obliged to keep records of each transaction carried out within the framework of these relations. Let's consider what entries are used to reflect calculations for insurance premiums, social insurance and social security.
Features and characteristics of the account
In addition to deductions for contributions made monthly, account 69 involves reflecting the following payments:
- fines;
- fines due to non-payment or late payments.
Using the debit of this reporting form, you can determine the amount of amounts for the specified positions of social insurance, Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund, funds to be reimbursed to employees for insured events, overpayments made, subsequently returned by government authorities.
The loan allows you to control the contributions to be transferred and the penalties required for payment.
The determination of activity and passivity of a characteristic is made on the basis of studying the balance at the beginning and end of the period for which the report is to be reported. Therefore, reporting item 69 is treated as a credit or debit.
The company's accountant has the right to write off the deductions expected to be paid as indirect or other expenses, based on the calculated position for personnel. This allows you to reduce the organization's taxable profit.
The calculation of social insurance contributions is carried out monthly, when calculating payments to personnel, with the corresponding frequency of contributions to government agencies no later than the 15th day of the month following the reporting month.
Assistant for payment of fixed insurance premiums
To calculate the amounts of insurance premiums and generate payment documents for the payment of insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs, the program provides a specialized assistant for Payment of fixed insurance premiums (hereinafter referred to as the Assistant).
The Assistant can be accessed in any of the following ways:
- Start page —{amp}gt; All tasks -{amp}gt; Contributions for yourself (for the relevant period);
- section Main -{amp}gt; Task list -{amp}gt; Contributions for yourself (for the relevant period);
- section Operations -{amp}gt; Payment of fixed insurance premiums (the current period is set by default).
Fixed insurance premiums can be paid either in one payment or divided into several parts, paid quarterly or monthly. Paying insurance premiums in several payments throughout the year allows you to reduce the tax burden of individual entrepreneurs.
When paying insurance premiums during the year, they are calculated in the program on an accrual basis, taking into account previously paid amounts. For a fixed contribution to the Pension Fund and for a contribution to the Pension Fund based on income, the calculation is performed separately, so the contribution to the Pension Fund based on income can be paid during the current year from the moment the amount of income exceeds 300,000 rubles.
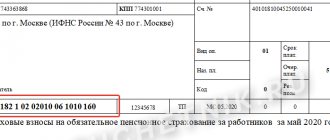
Individual entrepreneurs can pay taxes and contributions, including fixed insurance premiums, both from a current account and in cash through a bank cash desk. The payment method is selected in the Assistant form (Fig. 1).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
Rice. 1. Assistant “Payment of fixed insurance premiums”
Contents of the account
Calculations made for social insurance based on formation 69 can be represented by the following starting points:
- opening balance - with determination of the amount of receivables and payables (depending on the nature of the balance) at the beginning and end of the reporting period;
- debit or credit turnover;
- ending balance – shows the picture at the end of the period for which you need to report.
Related article: Loan insurance at Tinkoff Insurance, how to refuse it and return the money
If there is a debit balance, we are talking about the debt of government authorities to the enterprise. This situation is typical when taxes are overpaid in an amount exceeding the required amount.
In the case of a credit balance, amounts are formed that have to be paid as contributions to social insurance and other government bodies. Based on the subaccounts into which balances are posted, you can find out for which positions the debt remains.
Results
Changes in the accounting of social contributions are more related to innovations in the procedures for calculating and transferring these payments than to changes in the methodology for showing them in accounting.
At the same time, timely signing of the new version of the order on the accounting policy for separate accounting of old and new contributions will help you avoid possible troubles associated with incorrectly reflecting the amount of contributions in the reporting or paying incorrect amounts. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
What subaccounts exist
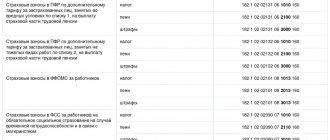
Account 69 is formed from the following sub-accounts, which allow obtaining data regarding deductions and contributions made on individual transactions, indicated by the following codes separated by a hyphen after the main number:
- 01 – displays payments made for social insurance and personnel support;
- 02 – for accounting for pension contributions; based on the nature of the enterprise’s work, it may provide for separate internal postings for additional sections (various categories of harmfulness, etc.);
- 03—for transactions and payments to compulsory medical insurance (at the federal and territorial level);
- 07 – deductions for the formation of funded pensions made at the request of the employee;
- 08 – contributions to non-governmental healthcare organizations serving employees;
- 11 – payments to the Social Insurance Fund, compensation for injured employees and occupational diseases.
In addition to the listed items, the accounting department of an enterprise can make entries for other subaccounts, taking into account which structures the company interacts with.
Insurance for individual entrepreneurs
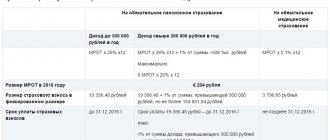
Insurance coverage for individual entrepreneurs (in relation to themselves) differs significantly from the norms provided for employers. Thus, for the reporting year, a businessman is obliged to transfer fixed payments to the budget:
- 29,354 rubles in 2021 - for OPS;
- 6884 rubles - for compulsory medical insurance.
However, if his income exceeds 300,000 rubles per year, then from the excess amount he will have to additionally transfer 1% to the Federal Tax Service for compulsory pension insurance. For more information about mandatory payments of individual entrepreneurs for themselves, read the article “What contributions should individual entrepreneurs pay for themselves in 2021.”
How to make postings? If the individual entrepreneur does not resort to hiring employees, then there is no need to reflect the calculation of insurance premiums of the individual entrepreneur for himself with postings. Why? Small businessmen are exempt from the obligation to maintain accounting records according to general rules. They have the right to keep simplified accounting, complete accounting, or completely abandon accounting. Therefore, it is not necessary to reflect the SV with postings.
However, if the individual entrepreneur decided to conduct accounting according to generally accepted standards and enshrined such a decision in his accounting policy, then the accrual of fixed payments to the individual entrepreneur (postings) is drawn up in a similar way, using accounting account 69 and the corresponding subaccount to it.
About accounting entries for account 69
It is necessary to take into account the interaction of account 69 with other transactions reflecting accruals made on the earnings of employees.
69 in debit correlates with the following postings by section:
- the fifth – 50, 51, 52, 55, reflecting transactions in cash and non-cash payments (including foreign exchange);
- sixth (70) – where employee earnings are calculated.
The interaction of credit 69 with transactions from the following sections is noted:
- first (for non-current assets) – 08;
- third (for production expenses), including insurance transfers for personnel of various productions;
- fourth (for finished products and products) – 44 (for enterprises in the trading industry);
- fifth – 51, 52;
- sixth – for transactions made with employees (70, 73);
- eighth (based on financial performance) – 91, 96, 97, 99.
Article on the topic: Peculiarities of aggregate and non-aggregate insurance amounts for CASCO
A relationship is possible with transactions indicating the company’s expenses and receipts.
About the main transactions for extra-budgetary funds
Debit entries are made for the following main items:
- Kt50 – contributions paid in cash;
- Kt51 – payments made to social insurance and other government agencies (including payments for debt payments) by non-cash method;
- Kt52 – deductions on repaid debt for the unified social tax, made in foreign currency;
- Kt55 – deductions for debt for unified social tax using special company accounts;
- Kt70 – compensation payments accrued to personnel within the framework of social insurance.
Credit transactions include the following lines (the index Kt69 is additionally used at the end of the designation):
- 08-1 – for deductions of contributions made for workers engaged in landscaping;
- 08-3 – for deductions for unified social tax and insurance payments caused by construction carried out on one’s own;
- 20 – transfers for key production personnel;
- 23 – funds that the enterprise pays for support personnel;
- 25 – deductions for employees of working structural units;
- 26 – fees for managers;
- 28 – personnel correcting defective products;
- 29 – service sector;
- 44 – for employees of the trade sector;
- 51 – for the return of overpaid social insurance contributions;
- 52 – for the return of currency overpayments;
- 55 – returns on special company accounts;
- 79 – deductions from earnings for sanatorium treatment paid for by the Social Insurance Fund;
- 91-2 – social contributions for personnel receiving other payments;
- 99 – penalties and penalties for social payments.
Analysis of transactions on the listed sub-accounts allows you to get a complete picture of the deductions that were made through postings for social insurance.
Nuances of transactions with extra-budgetary funds
It is necessary to take into account some of the nuances of ensuring transactions related to extra-budgetary funds, including social insurance expenses:
- if the income subject to taxation relates to bonuses and not wages, it is written off as other expenses;
- in the case of payment of a certificate of incapacity for work, requalified for payments for an industrial injury, the reversal of amounts involves the employer for three initial days, for all subsequent days - to be attributed to the Social Insurance Fund;
- sometimes the Social Insurance Fund refuses to accrue compensation payments due to erroneous calculations or excess accruals (in relation to documented ones); in this situation, the company requires the employee to return the overpaid amount - voluntarily or in court; funds can be returned by the employee or withheld from earnings;
- in case of unsuccessful deduction posting, the money is applied to other expenses (Dt 91.2 Kt 73).
Article on the topic: What is an insured person in insurance?
Briefly summarizing the above, it should be noted that the entries made for accounting transactions related to the field of social insurance and other extra-budgetary structures must be properly reflected in the reporting documentation. Otherwise, problems may arise during audits initiated by tax authorities.
Accounting for expenses of individual entrepreneurs with hired employees when combining modes
We will consider the features of reducing UTII by the amount of paid fixed insurance premiums using the following example.
We suggest you read: Do they provide insurance without a technical inspection?
Example 1
| IP Belkin A.A. provides motor transport services for the transportation of passengers and is a payer of UTII for this type of activity. IP Belkin A.A. does not use hired labor. |
In the information register Accounting Policies (section Main), it is necessary to indicate the one used by individual entrepreneur A.A. Belkin. taxation system - UTII. To store in the accounting system information about types of activities subject to a single tax on imputed income, starting from version 3.0.43.162, the Types of Activities directory is intended.
The following information is indicated in the form of the directory element Types of Activities (Fig. 2):
- name and code of the type of activity (selected from the Classifier of types of entrepreneurial activities);
- address of the place of activity;
- date of registration and deregistration;
- The collapsible group Tax Inspectorate stores information about the tax authority with which the organization is registered as a UTII taxpayer. If the user has a 1C:ITS contract and Internet support is connected, then after entering the address of the place of business, information about the inspection (including payment details) is filled in automatically;
- in the Tax calculation group, you can estimate the amount of tax for the quarter based on the current value of the physical indicator, and also view the history of changes in physical indicators, the adjustment coefficient and the tax rate.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcopyrightru
Rice. 2. Type of activity of individual entrepreneur
From the directory, you can generate an application for registration or deregistration of an organization as a UTII taxpayer.
Debit 69.06.5 Credit 50.01 - for the amount of the fixed contribution to the Pension Fund (4,839.12 rubles); Debit 69.06.3 Credit 50.01 - for the amount of the contribution to the FFOMS (949.21 rubles).
If the amount of imputed income for the second quarter of 2021 does not decrease, then the income will exceed 300,000 rubles, therefore, when calculating fixed insurance premiums for the first half of 2021, the Assistant will also calculate the contribution to the Pension Fund from income.
When applying UTII, the reflection of fixed insurance premiums in accounting is carried out only at the end of the year through the regulatory operation Calculation of insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs.
Debit 91.02 Credit 69.06.5 - for the amount of the fixed contribution to the Pension Fund; Debit 91.02 Credit 69.06.5 - for the amount of contribution to the Pension Fund from income; Debit 91.02 Credit 69.06.3 - for the amount of the contribution to the FFOMS.
The calculation of expenses that reduce UTII is performed quarterly by a regulatory operation of the same name, which is included in the Month Closing processing. When performing a routine operation, the costs of paying insurance premiums for employees, insurance premiums in a fixed amount, and sick leave at the expense of the employer are automatically calculated. When posting a document, entries are made in the accumulation register of Expenses that reduce tax under certain taxation regimes.
In Example 1, there are no employees, so the fixed premiums paid reduce the tax without the 50 percent limit. Figure 3 shows a reference calculation of expenses that reduce UTII for the first quarter for individual entrepreneur A.A. Belkin.
Rice. 3. Certificate of calculation of expenses that reduce UTII
Debit 99.01.2 Credit 68.11 - for the amount of calculated tax.
A certificate for calculating the single tax on imputed income, taking into account expenses that reduce the amount of tax, is presented in Figure 4.
Rice. 4. Help-calculation of UTII
Now let’s look at the features of tax reduction when combining the “STS-income” and UTII regimes.
Example 2
| IP Skvortsov P.A. provides computer equipment repair services, applies the simplified tax system with the object of taxation “income”. In addition, IP Skvortsov P.A. sells computer components to individuals through a retail store and is a UTII payer. Imputed income for the quarter is RUB 242,730.00. IP Skvortsov P.A. does not use hired labor. |
In the register of information Accounting Policies (section Main) it is necessary to indicate the one applied by individual entrepreneur P.A. Skvortsov. the main taxation system is Simplified, and on the simplified taxation system tab indicate the object of taxation - Income. On the Patents and UTII tab you need to set the following flags:
- An entrepreneur is a payer of the single tax on imputed income (UTII);
- Retail trade has been transferred to the patent system or payment of UTII.
On the same tab, you should follow the Types of activity link and enter into the directory data on the type of activity subject to UTII.
We remind you that proceeds from the sale of goods (work, services, property rights) are recognized as income from sales for the purposes of calculating tax paid under the simplified tax system, and the date of receipt of income is the day of receipt of funds, as well as the day of payment to the taxpayer in another way - the cash method (p 1 Article 346.17 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In Example 2, revenue from the sale of services within the framework of the simplified tax system was reflected in the program by the documents Sales (act, invoice) with the transaction type Services (Purchases section), and the receipt of funds from customers - by the documents Cash receipt with the transaction type Payment from the buyer.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
After processing the documents registering the receipt of funds, entries are automatically entered into the accumulation register of the Book of Income and Expenses (Section I), which takes into account income for the purposes of the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system.
We invite you to read: Replacing the compulsory medical insurance policy when changing your last name
According to tax accounting data, the revenue of individual entrepreneur P. A. Skvortsov from the sale of services for the first quarter amounted to 30,000 rubles.
The Assistant is also used to calculate fixed insurance premiums.
The calculation of expenses that reduce taxes when combining regimes is carried out quarterly by the regulatory operation Calculation of expenses that reduce the tax of the simplified tax system and UTII.
When posting a document, entries are made in the accumulation registers:
- Book of accounting of income and expenses (section IV);
- Expenses that reduce tax under certain tax regimes.
Entries entered into these registers in March 2016 indicate that paid insurance premiums reduce the simplified tax system, but not the UTII tax. The same result is shown by the Certificate-calculation of expenses that reduce the simplified tax system tax and the Certificate-calculation of expenses that reduce UTII generated for the first quarter. Currently, this is how the program works in accordance with the adopted design decision: when combining the simplified tax system and UTII, only the tax under the simplified tax system is automatically reduced.
An individual entrepreneur who combines the simplified tax system and UTII and does not make payments and rewards to individuals can choose which of these special regimes he will use to reduce the tax (advance payment) for the entire amount of fixed insurance premiums without limitation (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 17, 2014 No. 03-11-09/57912).
If a taxpayer, combining the simplified tax system and UTII modes, has decided to reduce UTII, he must manually adjust the movements of the regulatory operation Calculation of expenses that reduce the simplified tax system and UTII tax.
Let's see how economically justified it is to reduce the simplified tax system under the conditions of Example 2.
We will carry out quarterly regulatory operations Calculation of the simplified tax system and Calculation of UTII and generate the corresponding certificates and calculations. A certificate calculating the advance payment of the tax paid in connection with the application of the simplified tax system for the first quarter (Fig. 5) shows that the amount of insurance premiums paid exceeds the calculated tax; accordingly, not all expenses can be accepted for reduction.
Rice. 5. Certificate of tax calculation for the simplified tax system
For the imputed income indicated in Example 2, the amount of calculated UTII is 36,410 rubles, so it makes sense to reduce this tax by the insurance premiums paid. To do this, open the routine operation Calculation of expenses that reduce the simplified tax system and UTII tax (Show transactions command) and set the Manual adjustment flag (allows editing document movements).
In the register entries in the Book of Income and Expenses (section IV), you need to delete the lines automatically generated by the program, and in the entries in the register Expenses that reduce tax for certain tax regimes, you need to make the following changes (Fig. 6):
- fill in the field Registration with the tax authority (UTII);
- transfer the amounts from the Amount of STS Expense column to the Amount of UTII Expense column.
Rice. 6. Manual register adjustment to reduce UTII
Now let’s re-perform the regulatory operations Calculation of the simplified tax system and Calculation of UTII.
Debit 99.01.1 Credit 68.12 - for the amount of calculated tax excluding expenses.
A Certificate-calculation of the single tax on imputed income shows that paid insurance premiums reduce the tax in full (Fig. 7).
Rice. 7. Help-calculation of UTII