Any organization that produces products and/or sells them has costs. If an entrepreneur uses the accrual method in determining profits and costs, then the Tax Code in Art. 318 and 320 require expenses to be divided according to their relation to direct or indirect.
- What is the meaning of this division from a tax point of view?
- Which costs are considered direct and which are classified as indirect?
- Who makes the final decision in this matter – tax authorities and entrepreneurs?
- Is this separation always necessary?
Let us clarify in this material.
How are expenses divided into direct and indirect for income tax purposes ?
Implementation of services in 1C - step-by-step instructions
The organization entered into an agreement with the customer Lambriken LLC for the provision of services for the development of an office interior design project in the amount of 826,000 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
Direct costs for providing services amounted to RUB 165,100:
- Salary - 50,000 rubles.
- Insurance premiums - 15,100 rubles.
- Services of third parties - RUB 100,000.
On December 25, the parties signed an act for the provision of services for the development of an office interior design project under contract No. 137.
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Sales of services | |||||||
| December 25 | 62.01 | 90.01.1 | 826 000 | 826 000 | 700 000 | Revenue from sales of services | Sales (act, invoice) - Services (act) |
| 90.03 | 68.02 | 126 000 | VAT accrual on revenue | ||||
| Issuance of SF for shipment to the buyer | |||||||
| December 25 | — | — | 826 000 | Issuing SF for shipment | Invoice issued for sales | ||
| — | — | 126 000 | Reflection of VAT in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||
| Writing off as expenses the actual cost of services provided | |||||||
| 31th of December | 90.02.1 | 20.01 | 165 100 | 165 100 | 165 100 | Writing off as expenses the actual cost of services provided | Closing the month - Closing accounts 20, 23, 25, 26 |
It is also necessary
It is not enough to simply submit a claim for reimbursement of expenses incurred; it is also necessary to provide the court with documentary evidence of their actual incurrence.
Therefore, the application must be accompanied by:
- agreement with a representative;
- confirmation of settlements: bank statement on transfer or receipt of funds received;
- a copy of the power of attorney authorizing the representative to perform the necessary actions;
- act of acceptance of services provided;
Provision of services - regulatory regulation
The provision of services by one person to another person on a reimbursable basis is recognized as sales (Article 39 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). For the purpose of calculating income tax, organizations engaged in the provision of services take into account the income received and expenses incurred related to the provision of services.
Income:
- In the accounting system, revenue from the provision of services refers to income from ordinary activities (clause 5 of PBU 9/99) and is recognized at the time the service is provided (clause 12 of PBU 9/99). It is reflected in the credit of account 90.01.1 “Revenue from activities with the basic taxation system."
- In NU, income is revenue from sales excluding VAT (Clause 1, Article 248 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The date of receipt of income using the accrual method is the date of provision of services (Article 271 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Expenses:
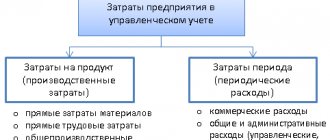
- In accounting, these are expenses the implementation of which is associated with the provision of services (clause 5, clause 9 of PBU 10/99). The composition of direct costs is determined by the technological process and type of activity. Accounting for services until they are provided is carried out mainly on the cost account 20.01 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 N 94n). At the time of provision of services, direct costs are written off to the debit of account 90.02.1 “Cost of sales for activities with the main taxation system.”
- In NU, the amount of expenses that reduce sales income includes direct expenses directly related to the provision of these services (clause 1 of Article 253 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), subject to economic justification and the availability of supporting accounting documents (Article 252 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Direct expenses may include (Article 320 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation): Expenses for raw materials and supplies used in the provision of services .
- Remuneration of workers providing services (including insurance premiums).
- Depreciation of fixed assets directly related to the provision of services.
- Other expenses taken into account in the accounting system on account 20.01 “Main production”.
The composition of direct expenses must be fixed in the Accounting Policy.
Who distributes the costs
It is not always necessary to distribute expenses into direct and indirect. The diagram will help you understand in which case this needs to be done:
As you can see, non-trading organizations in which income and expenses are determined on a cash basis do not need to divide expenses into direct and indirect. The same applies to those who use simplified or imputation instead of the general regime, as well as entrepreneurs. The latter, even if they are in the general regime, do not pay income tax.
All this follows from the provisions of Articles 272, 318 and 320 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Services in 1C 8.3
In the 1C Accounting 8 3 program, services are documented with the document Sales (act, invoice) transaction type Services (Act) in the section Sales – Sales – Sales (acts, invoices).
If for a service in 1C 8.3 it is necessary to automate the calculation of the cost of 1 unit of services, then you must use the document Provision of production services in the section Production - Production - Provision of production services.
Learn more Sales of production services. Calculation of the cost of 1 unit of services
Providing services in 1C
The header of the document states:
- Agreement - a document according to which settlements are made with the customer. Type of agreement - With the buyer .
In our example, calculations are carried out in rubles, which is noted in 1C in the PDF service agreement. Therefore, in the Sales document (act, invoice) the following sub-accounts are automatically established for settlements with the buyer:
- Account for settlements with the counterparty - 62.01 “Settlements with buyers and customers”.
- Account for accounting of settlements for advances - 62.02 “Settlements for advances received.”
If necessary, accounts for settlements with the buyer can be corrected in the document manually or configured for the automatic insertion of other accounts for settlements with the counterparty.
The tabular part indicates the services being sold from the Nomenclature directory with the Nomenclature Type Service . PDF
- Accounts are filled in the document automatically, depending on the settings in the Item Accounts .
Find out more about setting up item accounting accounts
- Income account - 90.01.1 “Revenue from activities with the main tax system.”
- Expense account - 90.02.1 “Cost of sales for activities with the main tax system.”
- VAT account - 90.03 “Value added tax”.
- Nomenclature groups - a nomenclature group related to the services sold is selected from the Nomenclature Groups directory.
The nomenclature group related to the sale of your own services must be indicated in the Nomenclature groups for the sale of products and services PDF in the Main section - Settings - Taxes and reports - Income Tax tab - link Nomenclature groups for the sale of products and services. The correct completion of the income tax return depends on this setting.
Read more Setting up accounting policies
Provision of services - postings in 1C 8.3
When posting the Sales document (act, invoice), only income from the sale of services is recognized (Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01.1). Recognition of expenses for services provided (Dt 90.02.1 Kt 20.01) is carried out at the Closing of the month.
Services in 1s 8.3 - postings:
- Dt 62.01 Kt 90.01.1 - revenue from the sale of services: in accounting accounting, including VAT;
- in NU excluding VAT.
Documenting
The organization must approve the forms of primary documents, including the document for the sale of services. The following basic forms are used in 1C:
- Certificate of provision of services PDF
- Universal Transfer Document PDF
Forms can be printed by clicking the Print button - Certificate of provision of services and Print - Universal Transfer Document (UDD).
Consider other printed forms of the Implementation document (act, invoice)
Income tax return
In the income tax return, the amount of revenue from the sale of services is reflected as income from sales:
Sheet 02 Appendix No. 1:
- page 010 “Proceeds from sales - total”, including: page 011 “... revenue from the sale of goods (works, services) of own production.” PDF
Issuance of SF for shipment to the buyer
The organization is obliged to issue an invoice within 5 calendar days from the date of shipment and register it in the sales book (clause 3 of article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
You can issue an invoice to the buyer by clicking the Issue an invoice document (act, invoice) . Invoice data is automatically filled in based on the Sales document (act, invoice) .
- Operation type code : “Sales of goods, works, services and operations equivalent to it.”
Documenting
You can print the form of the completed invoice by clicking the button Print the document Invoice issued or the document Sales (act, invoice) . PDF
Sales Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Sales Book section. PDF
VAT declaration
The amount of accrued VAT is reflected in the VAT return:
In Section 3 p. 010 “Implementation (transfer on the territory of the Russian Federation...): PDF
- the amount of sales proceeds, excluding VAT;
- the amount of accrued VAT.
In Section 9 “Information from the sales book”:
- invoice issued, transaction type code "".
Writing off as expenses the actual cost of services provided
If there were no sales of services in the reporting period, then direct costs for them can be taken into account (clause 2 of Article 318 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- at the time of sale: costs are distributed to the balances of work in progress;
- completely included in the expenses of the reporting period: without distribution to the balances of work in progress.
The chosen method must be fixed in the accounting policy
In 1C, to recognize direct expenses at the time of sale, you must set the following in the Accounting Policy settings: PDF
- Checkbox Perform work, provide services to customers .
- Costs are written off - Taking into account all revenue .
When providing services, direct costs are recorded in different documents depending on the type of costs, for example:
- Document Payroll PDF - to reflect labor costs (insurance contributions) of employees providing the service.
- Document Receipt (act, invoice) transaction type Services (act) PDF - to reflect expenses for services provided by third parties.
In order for costs to be taken into account when calculating the cost of services, they must be reflected in the same product group as sales.
Direct costs will be taken into account in the cost of services in the month of their implementation (December) when performing the operation Closing accounts 20, 23, 25,26 of the Month Closing procedure in the Operations – Period Closing – Month Closing section.
Postings according to the document
The document generates the posting:
- Dt 90.02.1 Kt 20.01 - writing off as expenses the actual cost of services provided.
Control
In November, for the Interior Design Project , costs were taken into account in the amount of:
- Salary - 25,000 rubles.
- Insurance premiums (including from NS and PZ) - 7,550 rubles.
- Services of third parties - RUB 100,000.
- Total for the month - 132,550 rubles.
Since the accounting policy establishes that direct costs are taken into account at the time of sale, at the end of November direct costs for services provided will remain in the balance in account 20.01 “Main production”. PDF.
In December, for the Interior Design Project , direct costs for services provided were also taken into account in the amount of:
- Salary - 25,000 rubles.
- Insurance premiums (including from NS and PZ) - 7,550 rubles.
- Total for the month - 32,550 rubles.
Let's generate a report Analysis of invoice 20.01 “Main production” for December for the product group Interior design project in the section Reports – Standard reports – Invoice analysis.
The report shows that according to the nomenclature group Interior Design Project :
- at the beginning of the month there was unfinished production of services - 132,550 rubles.
- at the end of the month all direct costs in the amount of 165,100 rubles. were written off as cost of services sold.
Income tax return
In the income tax return, the cost of services sold is reflected as direct expenses:
Sheet 02 Appendix No. 2:
- page 010 “Direct costs related to goods sold (work, services).” PDF
Test yourself! Take a test on this topic using the link >>
Indirect income tax expenses: list
In accounting, indirect expenses include general production and general business expenses, i.e., expenses associated with the production of different types of products that support the activities of the organization as a whole. In this regard, when calculating the cost, they need to be distributed. The basis for the distribution of indirect costs in accounting is established by the organization independently in its accounting policies.
How to reflect indirect costs in accounting policies, see the article “Reflection of indirect costs in accounting policies - sample.”