Is it profitable to work on VAT or is it better to do without it? This is a question for novice businessmen who, at first glance, find working with value added tax burdensome. After switching to the simplified system, you do not need to pay tax, keep records and submit reports. However, each of the two options has both its advantages and disadvantages.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides entrepreneurs and organizations with the opportunity to independently decide whether VAT or without VAT: what to choose. By choosing a simplified taxation system, a businessman essentially refuses VAT, sometimes without thinking about the benefits of working with VAT and what benefits can be derived from being a payer of this tax. And often the absence of a dedicated VAT in the invoices of some organizations and individual entrepreneurs closes their path to profitable deals, since the VAT payers themselves want to work only with the same payers. And when it comes to the problems of small businesses, most of them are related to the main stumbling block - VAT. We will try to impartially consider the difference between working with VAT and without VAT for an LLC, using the example of an average LLC without VAT, and we will analyze all the pros and cons of each option.
Organizations on OSNO
First of all, organizations and individual entrepreneurs are required to pay VAT under the general taxation system. Every quarter, such companies submit VAT reports, and since 2014 this must be done electronically via the Internet. The Kontur.Extern system helps to cope with this task. Everything is simple in Externa - just come in and start working. The extern will review your report before submitting and point out formatting errors if any. Even if you are not at the computer, the system will notify you about the status of the report via SMS.
Take advantage of all the features of Kontur.Externa
Send a request
Can an LLC operate without VAT?
Companies working with individuals (including individual entrepreneurs who do not apply VAT) can avoid desk audits using the ASK VAT-2 system. To do this, they need to work without VAT, for example, using:
- simplified taxation system;
- tax benefits (including on the territory of Skolkovo).
If tax benefits depend on the type of activity, location and other objective circumstances, then the main limitation under the simplified tax system is the amount of revenue (you can read more).
Our company helps clients who have ordered accounting outsourcing services from us to find answers to any tax questions, including those related to choosing a taxation system. A proactive position is to tell the client in as much detail as possible about which tax system suits him best and makes his tax payments optimal.
Unfortunately, switching to the simplified tax system is not always possible for other reasons. For example, if the founders include a legal entity that owns more than 25% of the capital, or the company has opened a branch, then we offer an alternative - VAT exemption. This option is suitable for small clients, including individual entrepreneurs. A company can only obtain VAT exemption if it is very small.
Organizations combining UTII and OSN
If a company combines UTII and the general taxation regime, the income it receives from activities on the “imputed” basis is not subject to VAT. In order not to pay tax, it is necessary to keep separate VAT records for OSN and UTII, observing the following conditions:
- if, for activities under UTII, an organization or individual entrepreneur buys goods (services) with VAT, then the amount of VAT must be taken into account in the cost of these goods (including fixed assets and intangible assets);
- If, for activities on the OSN, an organization or individual entrepreneur purchases goods (services) with VAT, then the amount of VAT is deducted in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
But there are some costs for which it is impossible to separately account for VAT for UTII and VAT for OSN. Such costs include, for example, office rent or utility bills. In this case, the amount of “input” VAT should be distributed in proportion to how these goods (services) are used in each type of activity.
Also, do not forget to submit a VAT return and pay tax every month, no later than the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter.
Advantages of working with VAT
Many large enterprises prefer to work only with VAT counterparties. Organizations operating without VAT have a greater risk of being rejected by a potential client or supplier. This is the main benefit of switching to VAT. A company that is not a VAT payer has to think about how to increase its competitive attractiveness. This means that VAT evaders need to look for and advertise their advantages, which will make cooperation with them profitable. The main advantage of working with VAT is the ability to deduct tax on all purchased goods or services. Despite the fact that VAT is refunded only in the amount that was paid in the price of the goods to your supplier, this opportunity really allows you to save. But if the buyer is provided with goods without VAT on the OSN (for example, a sample invoice without VAT is issued), then he will not be able to reimburse it. Thus, this advantage of working on VAT is important only if the price of a product from a supplier who works with VAT is lower or equal to the price of a similar product from a supplier who works without VAT.
VAT for organizations using the simplified tax system
Entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are exempt from paying a number of taxes: in particular, organizations do not pay profit tax and VAT, and individual entrepreneurs do not pay personal income tax and property tax. But there are still a number of exceptions in which LLCs and individual entrepreneurs using the simplified tax system are required to pay VAT:
- when importing goods into the territory of the Russian Federation;
- if the taxpayer issues an invoice that includes VAT;
- when carrying out operations under a joint activity agreement or a property trust management agreement on the territory of Russia.
In these situations, it is necessary to pay VAT and submit a VAT return.
If the counterparty (supplier) indicates VAT on the simplified tax system in the invoice, then the recipient of the goods on the simplified tax system can safely pay this invoice, since VAT in this case is the supplier’s tax. A buyer using the simplified tax system (regardless of the taxation option) is not required to pay tax and submit a VAT return. Goods purchased with VAT must be sold without taking into account the amount of VAT.
Disadvantages of working with VAT
The main disadvantage that discourages most businessmen from working with VAT is the need to pay this tax. VAT is rightfully considered one of the most important and complex taxes in Russia. In addition, it has federal significance. Moreover, it has been increased from 2021 to 20%. Therefore, being a VAT payer means maintaining full tax and accounting records. It means:
- carefully check your suppliers;
- reconcile all incoming primary documents containing VAT;
- maintain the necessary tax registers;
- fill out sales books and purchase books;
- prepare and submit tax returns;
- have an additional object registered for inspection and attention of the Federal Tax Service.
If an LLC without VAT applies the simplified tax system with the object “income minus expenses,” then for it the purchase of goods from suppliers who pay VAT makes it possible to take into account the received VAT as part of its expenses. Even if the tax is highlighted in the invoice. But an LLC on the simplified tax system with the object “income” does not have such an opportunity: the buyer will not be able to deduct VAT even if there is an invoice.
Organizations working on special tax purposes with VAT deal with more qualified and picky inspectors from the tax authorities. This is due to the fact that VAT is fraught with many pitfalls, and any detected mistake by the taxpayer will lead to many thousands of fines and penalties. Whereas taxpayers under preferential regimes are spared the possibility of making such errors by the very principles of the applied taxation regime.
Tax agents
VAT tax agents are required to pay value added tax to the budget and submit a declaration. The duties of a tax agent can also be performed by companies in special regimes.
The tax agent will have to report VAT if he:
- purchased goods (services) from foreign companies that are not registered for tax purposes in the Russian Federation;
- sells goods (services) of foreign companies that are not registered in Russia under intermediary agreements;
- rents or buys state property;
- buys property of a bankrupt, etc. (less common cases are described in Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Special procedure for exemption from VAT for Unified Agricultural Tax payers from January 1, 2021
- For those who are just switching to the Unified Agricultural Tax, an application for VAT exemption must be submitted in the same calendar year when the transition was made.
- If a company (IP) already applies the Unified Agricultural Tax, it is necessary that the amount of income from activities subject to agricultural tax does not exceed the limit. It is determined for the previous calendar year excluding VAT.
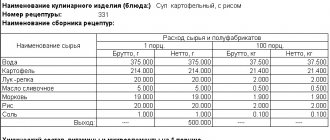
The maximum limit amounts are presented in the table.
Table 1. Income limit for VAT exemption for Unified Agricultural Tax payers
| Year of exercise of the right to VAT exemption | Year for which the limit needs to be calculated | Limit amount, million rubles. |
| 2023 and beyond | 2022 and beyond |
You must declare your right to VAT exemption. This must be done no later than the 20th day of the month from which the company (IP) expects to begin applying the exemption (clause 3 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Notification of the decision to exercise your right to VAT exemption must be submitted in the approved form.
Attention!
From April 1, 2021, the Notification has two forms (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 26, 2018 No. 286n).
For most taxpayers, especially those who have applied for an exemption previously, there will be no particular difficulties when filling out the form, since the changes are of a technical nature and minor. The main innovation is the second form of notification, which is intended for Unified Agricultural Tax payers, who from January 1, 2021 are also included in VAT payers.
In addition to the notification itself, the package of documents includes various extracts (clause 6 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, see Table 2). An exception is taxpayers using the Unified Agricultural Tax; they only need to provide a completed Notification.
Table 2. Appendices to the notice of exercise of the right to VAT exemption
| Name of the document from which an extract must be provided | The need to provide an extract (+), the absence of such a need (-) | |
| Companies | IP | |
| Sales book | + | + |
| Balance sheet | + | |
| Book of accounting of income and expenses and business transactions | + | |
There is no set format for statements; you can format them in the way that is most convenient for you.
So, from the month indicated in the Notification, the company operates without VAT. It must be taken into account that, having declared their right to exemption, enterprises operating without VAT fall under paragraph 4 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which means:
- the complete impossibility of refusing exemption for taxpayers using the Unified Agricultural Tax;
- mandatory application of the exemption: a whole year (12 consecutive calendar months) for all taxpayers, except for those using the Unified Agricultural Tax.
The only possibility of returning to VAT will be the loss of the right to exemption (clause 5 of Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) as a result of:
- exceeding the revenue limit (maximum - 2 million rubles for any three months, the main thing is that they follow each other);
- sale of excisable goods.
The loss of the right occurs from the 1st day of one of the following months:
- the last of three consecutive months;
- any month if an excess occurred in it (including the sum of two consecutive months).
Before switching to work without VAT, you need to weigh all the consequences of such a decision.
Attention!
Payers of the Unified Agricultural Tax, having once renounced the right to apply the VAT exemption, will not be able to claim it again.
Intermediaries are required to keep a log of invoices
Those agents and commission agents who apply special tax regimes and sell goods (services) of a principal registered under the OSN are required to keep a log of invoices received and issued. These journals must be submitted to the tax office electronically. Reporting in this way must be done no later than the 20th day of the month following the reporting quarter.
If a company works under intermediary agreements with a foreign company that is not registered in the Russian Federation, then it is obliged to send a log of received and issued invoices along with a VAT return in electronic form.
To make sure that you have submitted all reports and paid all necessary taxes, use the Kontur.Extern online service to request an official reconciliation report with the tax office, which will reflect all the information about your mutual settlements, submitted declarations and payments credited to the budget.
What does “VAT exempt” mean?
Submit your VAT return using the Kontur.Accounting web service. The system itself will generate a declaration based on primary documents and check it before sending. Get free access for 14 days
An extensive list of goods, works, services and transactions exempt from VAT is given in Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Here are the operations exempt from tax (a number of operations from the list require a license; if an organization does not have one, it cannot apply tax exemption):
- sale or transfer for one’s own needs of religious literature and paraphernalia;
- banking operations performed by banks (except for collection);
- sale of folk arts and crafts;
- services of insurers and non-state pension funds;
- lotteries held by decision of government authorities;
- sale of industrial products containing precious metals, scrap and waste;
- sales of rough diamonds to processing enterprises;
- transfer of goods, property rights, provision of services within the framework of charity;
- sale of tickets and subscriptions by physical education and sports organizations;
- loan and repo transactions;
- other operations listed in clause 3 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Here are the goods, works and services exempt from tax:
- medical, sanitary, cosmetic, veterinary services and goods;
- care services for the disabled, elderly and sick;
- child care and leisure services;
- funeral goods and services;
- food products produced by educational and medical institutions;
- transportation of the population;
- sale of postage stamps, envelopes, postcards and other postal products;
- warranty service of equipment;
- restoration and restoration of historical buildings, monuments and cultural objects;
- others listed in paragraph 2 of Art. 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Only companies that work in their own interests and not in the interests of others under agency agreements, commission or commission agreements have a chance to be exempt from VAT. Another important condition is to separate and separately account for taxable and non-taxable transactions.
Why and when is VAT compensation calculated?
VAT compensation is a tax instrument that gives simplified taxation tax payers the opportunity to work with customers on OSNO. Compensation allows you to take into account and deduct VAT paid by simplifiers when purchasing raw materials, materials, fuels and lubricants used in construction work. The amounts of such VAT form the contractor’s costs, which must be covered by the contract price (Article 709 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Check with your counterparties for free to receive a full VAT refund
When a contractor using the simplified tax system performs work for the customer using OSNO, both are at risk in the event of errors in accounting. The customer - in that the tax paid to the contractor will not be included in the VAT deduction. The contractor runs the risk that the tax authorities will recognize the tax amount as unjust enrichment and reduce the contract price by the tax amount. To prevent this from happening, it is important to correctly prepare all primary and accounting documents from the very beginning.
The general scheme of interaction between the parties to a construction contract looks like this:
- Determining the scope of work and preliminary drawing up an estimate.
- Coordination of all conditions and conclusion of the contract.
- Execution of work.
- Acceptance of work and final payment.
The estimate is the primary document that is drawn up at the first stage of interaction when carrying out construction or other contract work. It describes the stages and order of work and fully takes into account all the contractor’s costs. All subsequent documents (invoices, acts, KS-2, KS-3 and others) are drawn up only on the basis of the approved estimate.