Account 60 is used in the accounting of an organization to reflect information about settlements made with suppliers and contractors for goods and materials received, as well as work performed and services rendered, their surpluses, transportation services received, and others.
The account is credited for the cost of goods accepted for accounting (work performed, services provided) and corresponds with the accounts for their accounting. In synthetic accounting, the account is credited on the basis of the supplier's settlement documents, regardless of the assessment of values in analytical accounting.
The account is debited for the amounts of fulfillment of obligations, including advances and prepayments (they are accounted for separately) and corresponds with the accounts in which funds are recorded.
What is account 60 in accounting?
According to the chart of accounts (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), account 60 is called “Settlements with suppliers and contractors.” It reflects all transactions related to the acquisition and payment of inventory, work, and services. Here are a few special cases:
- consumption of electricity, gas, water, etc.;
- identification of surplus inventory items upon their acceptance;
- purchasing delivery and communication services;
- uninvoiced deliveries (for which documents were not received from the sellers).
Count 60 is active-passive. The balance on it can be either debit or credit. Increases and decreases in funds can be shown either by debit or credit (for more details, see: “Chart of Accounts in 2021”).
Analytical accounting is usually organized by suppliers, contractors and invoices issued by counterparties. Sometimes, depending on the specifics of the company, analytics are carried out in the context of contracts, products, etc. The main thing is to have access to information about overdue debts to sellers, as well as about debts that have not yet matured.
Maintain accounting and tax records for free in the web service
Acceptance of an invoice is...
The term invoice acceptance is regulated in stat. 438 Civil Code of the Russian Federation. According to this norm, acceptance is the unconditional and complete acceptance by the recipient of the addressed terms of the offer. In turn, an offer is a proposal for cooperation addressed to one person (or several), containing specific contractual terms. By its legal essence, acceptance implies the unconditional fulfillment of the obligation of the buyer of the product to pay the full cost of the product (or service). You cannot transfer funds partially or set your own conditions for fulfilling obligations.
An accepted invoice is the acceptance of consent to pay for a received document by non-cash debit. In this case, the exact terms of debt repayment are approved in the agreement with the supplier. This is the most common option for mutual settlements between consumers and utility service providers. In this situation, a contract for the supply of, for example, electricity is previously concluded, which specifies the terms of payment. The buyer is then issued an invoice, which goes directly to the bank based on an additional agreement between the bank and the client. And finally, the financial institution repays the acceptance within the established time frame, that is, debits the funds from the payer’s account in favor of the electricity supplier.
What does the debit of account 60 reflect?
Debit turnover is the amount that the organization paid to its partners - suppliers. These amounts include payment for completed deliveries (they are carried out under subaccount 60.01) and advances to sellers (they are carried out under subaccount 60.02).
REFERENCE . A debit balance on account 60 most often indicates that the company has transferred an advance payment, but the counterparty has not yet made the shipment (did not perform the work, did not provide the service). As a result, the seller has a debt to the organization.
Acceptance of an invoice from a supplier of goods or services
Let's look at examples of what is an accepted supplier's invoice for materials or services?
Let’s assume that Rostekhstroy LLC entered into an agreement for the purchase of building materials for RUB 236,000.00. (VAT – 18% in the amount of RUB 36,000.00). Under the terms of the transaction, the supplier ships the goods on November 14, 2017, and as part of the agreement with the buyer, an invoice for payment was issued on November 17, 2017. The obligations are fulfilled by Rostekhstroy LLC on the same day, in full, by debiting the required amount from the current account.
What does account credit 60 reflect?
Loan turnover is the cost of supplies received from the counterparty. If the shipment goes against a previously made advance, it is carried out according to subaccount 60.02. If payment has not yet been made, delivery is carried out using subaccount 60.01.
When the seller is on the general taxation system and pays VAT, the input value added tax is also reflected on the credit of account 60.
REFERENCE. Credit balance on account 60 means that the counterparty has shipped the product (provided a service, performed the work), but the company has not yet paid it off. As a result, the organization owes a debt to the supplier.
Example of a balance sheet for account 60
Let's give an example of a balance sheet for account 60 from the popular 1C program with full detail on sub-accounts and analytics:
For example, from the SALT it is clear that over the past year we paid the counterparty “Supplier LLC” 13,681 rubles, and received goods or services in the amount of 154,727 rubles. And the total debt on the final balance of the loan is 141,046, that is, our debt.
Accounting entries for account 60
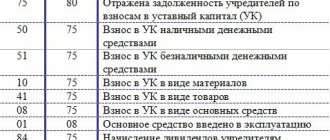
DEBIT 41 (07, 08, 10) CREDIT 60 - goods received and capitalized (equipment, non-current assets, materials)
DEBIT 20 (25, 26) CREDIT 60 - work and services written off to the cost of products (for general production, general business expenses)
DEBIT 19 CREDIT 60 - input VAT reflected
DEBIT 94 CREDIT 60 - the shortage identified during acceptance of inventory items is reflected
DEBIT 60 CREDIT 50 (51) - payment made to the supplier
DEBIT 60 CREDIT 91 - overdue accounts payable written off as other income
DEBIT 60 CREDIT 62 - mutual settlement with the counterparty has been made.
Fill out and print your balance sheet using the current form for free
Typical wiring
Let's look at the main transactions for account 60 in the table:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Wiring Description | A document base |
| 07/10/41 | 60 | Payment to the supplier for equipment/materials/goods | An invoice for payment |
| 60 | 50.01/51/52 | Payment of debt to the supplier | |
| 94/76 | 60 | Write-off of shortages within the normal natural loss/in excess of the norm, in case of an error or price discrepancy | Acceptance certificate |
| 19 | 60 | VAT on purchased assets | Invoice for payment, invoice |
| 50/51/52 | 60 | Payment of invoice to supplier/contractor | RKO, extract from current or foreign currency account |
| 10/15/41 | 60 Non-faculty supplies | Material assets were capitalized without invoices for payment | Material acceptance certificate |
| 60 Non-defective deliveries | 60 | Payment of invoices for previously recorded materials without payment documents | An invoice for payment |
| 60/91.02 | 91.01/60 | Writing off exchange rate differences on an account, positive/negative | Calculation |
| 91.02/63 | 60 Advances issued | Write-off of advance payment not returned by the supplier/contractor at the expense of profit/reserve for doubtful debts | Reference |
Characteristics of account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers”
The adopted chart of accounts establishes that account 62 “Settlements with buyers and customers” is active-passive. This means that he can have two balances at the same time - both debit and credit.
This means that this account can immediately show both the company’s receivables and payables:
- A balance in the debit of the account means that buyers have an unpaid debt to the company for work performed or goods shipped.
- The loan balance shows that the organization has received an advance payment for future deliveries of goods or performance of work, but has not yet fulfilled its obligations to buyers or customers.
What does the debit and credit of the account reflect:
- The debit of account 62 shows the amounts of work performed or goods shipped, for which documents for payment were issued to counterparties. In addition, debit can also take into account the amounts of payments that were returned to customers due to failure to fulfill obligations to them.
- Credit 62 of the account takes into account the amounts of money that were transferred by buyers of goods or customers of work for received goods and materials. The amounts that were received as an advance payment for future work or shipment of goods are also indicated here.
The process of determining the balance at the end of the period under review depends on what exactly the balance was at the beginning. If it was debit, then you need to add the debit turnover to it and subtract the credit turnover. If the result is positive, then this balance is entered as a debit at the end of the period. If it turns out to be negative, then it is transferred to credit, but without the minus sign.
You might be interested in:
08 accounting account - “Investments in non-current assets”
If at the beginning of the period under consideration the balance was in credit, then you must first add the credit turnover to it, and then subtract the debit turnover. When determining which part of the balance sheet to record the final balance in, a similar rule applies - if it turns out to be positive, then in credit, otherwise - in debit.
Attention! The balances of account 62 must be shown when preparing the balance sheet, but in different sections. The debit balance is accounted for in accounts receivable and recorded as an asset. At the same time, it is shown minus the reserve for doubtful debts (if it was created). The credit balance constitutes accounts payable and is reflected in liabilities.
Reflection of accounts payable when identifying disagreements with a counterparty
When accepting GWS, shortages may be discovered, the full scope of ordered work may not be completed, while the full cost is indicated in the settlement documents. In addition, the error may be contained in the documents themselves, for example, an incorrect price or quantity. The buyer must inform the counterparty about the violation that has occurred and file a claim. Since the supplier may either agree or disagree with the presented requirements, in accounting the buyer will have to reflect the obligation for the full amount in accordance with the primary documents, showing the disputed amount in account 76, subaccount “Settlements for claims”:
- Dt 07, 08, 10, 15, 20, 23, 25, 26, 41, 44 Kt 60 - actually received GWS are accepted for accounting;
- Dt 19 Kt 60 - reflects the amount of incoming VAT on actually received GWS;
- Dt 76 subaccount “Calculations for claims” Kt 60 - the amount of the shortage (error) is attributed to settlements for claims.
The opposite situation is also possible, when accompanying documents were not received for the received goods, or surpluses were identified upon acceptance, or the volume of work performed was exceeded. If an organization, in compliance with the law, refuses to pay and decides to return such goods to the supplier, then their accounting is kept on the balance sheet, in account 002 “Inventory and materials accepted for safekeeping.” If an organization decides to accept such GWS, then it must capitalize them using the supplier’s prices and show the debt on the credit of account 60. Prices can be taken from the contract, accompanying documents for similar GWS, or based on an expert assessment.
Read about one of the most frequently used accounting registers for account 60 in the article “Features of the balance sheet for account 60.”
Postings for accepted transactions: the first event is making an advance payment (deposit) for the goods
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description | A document base |
| Prepayment (advance payment) | ||||
| 60-2 | 51 | 70 800 | An advance payment was made to the supplier of the goods in the form of an advance payment of 50% 141600 * 50% = 70800 rubles. | Payment order |
| 68 | 76 | 10 800 | The occurrence of a tax liability on the amount of payment. VAT deductible | Payment order |
| 10 | 60-1 | 120 000 | Goods received from supplier | Packing list |
| 19-3 | 60-1 | 21 600 | VAT was charged on goods received: 120,000 * 18% = 21,600 rubles. | Incoming invoice and delivery note |
| 60-1 | 60-2 | 70 800 | Advance offset | |
| 60-1 | 51 | 70 800 | Additional payment on the bill of the materials supplier (50%) | Payment order |
| 76 | 68 | 10 800 | The offset is shown for the advance payment | |
| 68 | 19-3 | 21 600 | The accrued VAT amount is accepted for reimbursement | Invoice |
| Providing a deposit | ||||
| 76-5 | 51 | 56 640 | An advance payment was made to the supplier of the goods in the form of a deposit of 40% 141600 * 40% = 56640 rubles. | Payment order |
| 009 | 56 640 | Formation of secured obligations | ||
| 10 | 60-1 | 120 000 | Receipt of goods from the supplier | Packing list |
| 19-3 | 60-1 | 21 600 | VAT was charged on goods received: 120,000 * 18% = 21,600 rubles. | Incoming invoice and delivery note |
| 60-1 | 76-5 | 56 640 | The issued deposit has been offset | |
| 009 | 56 640 | Write-off of deposits from secured obligations | ||
| 60-1 | 51 | 84 960 | Additional payment on the bill of the materials supplier (60%)141600 * 60% = 84960 rub. | Payment order |
| 68 | 19-3 | 21 600 | The accrued VAT amount is accepted for reimbursement | Invoice |
When should revenue be reported?
In accordance with current legislation, revenue is displayed subject to the following conditions:
- the amount of revenue cannot be determined;
- the organization has the right to receive its own revenue, which follows from the terms of the contract drawn up or is confirmed in some other way;
- there is a firm belief that after carrying out a certain transaction, an increase in economic benefits for the company may occur (this happens if the organization receives a certain asset as payment or there is absolutely no uncertainty regarding the receipt of the asset);
- after completing the work or providing a certain product to the customer, ownership rights are transferred to him from the company;
- the expenses that have been or will be incurred for this operation can be determined in advance.
It is worth noting that there is a certain peculiarity in how accounting account 62 is compiled. What it is? To reflect the proceeds from the sale, all the above conditions must be met at once, and if at least one of them is not met, then any assets or funds that the organization received as payment for its services or goods will be recognized in the company’s accounts as accounts payable, and not in the form of repayment of existing accounts receivable.
The consumer's receivables in the company's accounting must be formed along with the reflection of complete information regarding the proceeds from the sale of certain goods or services if all specified conditions are met by making an entry in the accounts.
HIGHLIGHTS OF THE WEEK
01/21/202109:00 Legal disputes
How did a “penny” test purchase ruin an individual entrepreneur, a pensioner?
25.01.202114:58
Business organization
Debtors will retain a minimum income
yesterday at 09:0009:00
Taxes
Tax deductions can be obtained without 3-NDFL
25.01.202109:00
Personnel
The Ministry of Labor is considering indexing pensions for working pensioners
25.01.202109:22
Personnel
New requirements for non-cash payments are coming soon
PODCAST 4.12.2020
What has changed in taxes and reporting since 2021?
All episodes
Comments on documents for an accountant
Do I have to pay personal income tax if a company pays for the issuance of bank cards for employees?
01/26/2021 Payment by the employer of the bank commission for issuing and servicing employee salary cards is not…
Payment of income to a foreign company that does not have the actual right to it: tax consequences
01/26/2021 A foreign organization that directly receives income and is not a private income fund cannot claim...
Is the New Year bonus for employees not subject to insurance contributions?
01/25/2021 The court supported the Pension Fund of Russia, which fined an organization that paid bonuses to all employees and did not accrue...
‹Previous›Next All comments
Types of AK in used
The concept of AK relates more to banking and finance, and to a lesser extent to accounting. In our case, AK occurs only when making payments through a company’s bank account. The main types of such settlements are payment order (hereinafter referred to as PP) and payment request (hereinafter referred to as PT). The difference between them is that with the help of a PT, the deliverer demands payment from the payer for a product, service or work (issues an invoice), and with the help of a PT, the payer instructs the bank to pay from his account for a product, service or work from the delivery person.
AK occurs when paying through PT, which comes in two types: with AK and without AK. PT with AK means that the payer must agree to this (accept the invoice) within three days before paying the invoice. After this period, if the payer has not accepted or refused to pay, the PO is considered accepted. PT without AK does not include the payer’s consent, and money is transferred from the payer’s account to the deliveryr’s account immediately. This type of payment (without AK) is possible only if it is specified in the agreement between the deliverer and the buyer (payer).
Transactions with transactions accepting the supplier's invoice for received materials are carried out on the basis of the acceptance type of PT. Refusal from AK (payment of invoice) can be complete or partial. In case of complete or partial refusal, the buyer must make a statement of refusal to his bank with a covering letter stating the reasons for the refusal and an indication of those clauses of the contract that were not fulfilled. The bank does not accept unfounded refusals by the payer, and the bank does not consider all possible disputes between the buyer and the delivery person.
There are also such concepts as preliminary and subsequent AK. In BU they are almost never used, but they can occur. These concepts relate more to the field of finance. Pre-AK is the type of AK described above. That is, the payer in this case must give prior consent before payment. Subsequent AK means the same procedure as an invoice without AK, when money is withdrawn from the payer’s account immediately, but at the same time the buyer retains the right to subsequently refuse AK after the withdrawal of funds. The subsequent AK has not been used in the Russian Federation since 1992.
Results
Account 60 is present in almost every transaction of a business entity, forming transactions for purchased goods, works or services.
Posting Dt 60 Kt 60 allows you to reflect a business transaction that is quite common in practice - repayment of debt for goods using an advance payment transferred to the supplier. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.