The penalty for failure to submit 3-NDFL depends on who had to submit this declaration and on what basis.
The last day for filing 3-NDFL in 2021 is July 30 (the deadline has been postponed from April 30 due to the coronavirus epidemic), the calculated amount of personal income tax should be paid at the same time. Administrative liability is provided for late declaration of income and non-payment of personal income tax (Articles 119 and 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let's consider what it is, the fine for failure to submit 3 personal income taxes in 2021.
Let us remind you, just in case, that we always submit an income statement for the previous year (that is, in 2021 we will submit a report for 2019).
Who serves
This reporting form is required to be submitted by individuals who have received income from the above sources and who are residents of the Russian Federation (persons permanently residing on its territory). Taxpayers are also non-residents who receive funds from sources located in the country. Such reporting is submitted by citizens in order to obtain a tax deduction. And we should not forget about individual entrepreneurs, lawyers, notaries, heads of farms, for whom the submission of this form is mandatory, regardless of whether they received income in the past year or not.
Results
The penalty for being late with 3-NDFL depends on the amount of tax payable reflected in the “late” declaration. It is 5% of the tax amount for each month of delay in filing 3-NDFL, but not more than 30% of the personal income tax amount.
Minimum fine of RUB 1,000. may be imposed for being late with 3-NDFL, if, according to the declaration, there is no tax payable to the budget.
Sources
- https://www.klerk.ru/buh/articles/443838/
- https://financc.ru/nalogi/shtraf-za-nepodachu-deklaratsii-3-ndfl.html
- https://verni-nalog.ru/deklaracija-3-ndfl/nepodacha-i-zaderzhka/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/ndfl/deklaraciya_ndfl/est_li_shtraf_za_nesvoevremennuyu_sdachu_deklaracii_3ndfl/
- https://www.klerk.ru/buh/articles/507342/
What is 3-NDFL
Most often, their employers account for the income of individuals. But there are cases when citizens must generate 3-NDFL on their own.
In accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, this reporting document is submitted in the following cases:
- upon receipt of income from the sale or disposal of property. It is necessary to report not only on the sale of real estate that was owned for less than the period established by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, but also on the sale of other things, for example, a fine for failure to submit a declaration on the sale of a car is possible if a vehicle that was owned for less than 3 years is sold and the obligation is not fulfilled on filling out reporting forms;
- realization of property rights (an assignment agreement has been concluded, a transaction for the assignment of rights of claim);
- a citizen has received a gift in the form of real estate, cars, shares from other citizens who are not close relatives;
- when receiving remuneration under agreements, including civil partnership agreements, from persons who are not tax agents under the law;
- when receiving winnings;
- when receiving income from sources located or located abroad of the Russian Federation.
If in these cases the report is not submitted, liability for failure to submit a 3-NDFL tax return inevitably arises.
Penalty
Please note that if the tax is overdue, you will have to pay additional penalties. The longer a taxpayer evades his obligations, the more he will ultimately be required to pay.
Currently, a penalty is charged in the amount of 1/300 of the Central Bank refinancing rate. This punishment increases daily. Therefore, it is difficult to say exactly what fine you need to pay for failure to file a return and not pay taxes. Sometimes you can get by with 20% of the tax fee, sometimes more.
When and where to provide
The reporting form is submitted to the inspectorate at the place of registration of the citizen. This must be done before April 30, otherwise a fine for late submission of the 3-NDFL declaration will be imposed even if there is a slight delay. Persons who prepare reports in order to receive the deduction provided for by the law of the Russian Federation submit them throughout the entire calendar year; this rule does not apply to them.
Learn more about what will happen if you do not file a declaration or violate the deadlines established by law.
Is it possible to reduce the size of sanctions and how to do it?
A reduction in the amount of the fine for failure to submit reports on personal income tax and other taxes is allowed under mitigating circumstances, as stated in paragraph 1 of Art. 112, paragraph 3 of Art. 114 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. You will need to prepare an appeal to the Federal Tax Service indicating the reasons for the violation.
Arguments used as mitigation:
- payment of tax on time;
- the violation was committed once;
- no debt in payment of other taxes.
Often tax authorities reduce the amount of punishment for failure to submit reports if the violation occurred for the first time and the company has paid the debt according to the audit report.
An enterprise has the right to file a lawsuit if the tax authorities refuse to reduce the amount of sanctions. To consider the case, you will need to attach documents confirming the plaintiff’s claim.
Responsibility for failure to provide 3-NDFL
In case of violation of deadlines or failure to submit, a fine will be imposed for late filing of the 3-NDFL declaration in accordance with Art. 199 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation in size. A fine under this article is imposed both in case of failure to fulfill the obligation to submit the form and in case of delay, that is, violation of the rule on the deadline for submitting the form. Thus, these offenses are equated by the legislator. The fine for late filing of the 3-NDFL declaration is collected in proportion to the late filing of tax reports. In case of non-payment of taxes - in the amount established by Art. 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
| Fine for late submission of 3-NDFL declaration | Fine for non-payment of taxes |
| 5% of the unpaid amount according to the reporting form | 20% of this amount |
In case of failure to provide the form, a fine will be collected for each full or partial month within 30%, but not less than 1000 rubles.
Methods for filing tax returns
A tax return is an official statement of the taxpayer, which contains information about the objects of taxation, income received and expenses incurred, sources of income, the tax base, tax benefits, the amount of tax payable, and other data that serves as the basis for calculating tax. .
Timely submission of tax returns is one of the most important responsibilities of taxpayers, and this procedure is regulated by Art. 80 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
There are two options for submitting tax returns: on paper; in electronic form.
The tax return can be submitted in the prescribed form on paper. In this case, the taxpayer can submit reports to the Federal Tax Service in person or through an authorized representative.
A tax return can be submitted either personally by the head of the organization (entrepreneur) or an accountant, or by an authorized representative of the organization (entrepreneur).
The date of filing tax returns by a legal or authorized representative of an organization is the date of their actual submission to the tax authority on paper.
To submit reports, it is not necessary to come to the Federal Tax Service in person; you can send it by mail.
When sending reports by post, you must make sure that a description of the attachment is attached.
When sending a tax return by mail, the day of its submission is considered the date of mailing.
Submission of declarations in electronic form is carried out via telecommunication channels (TCC) using an enhanced qualified electronic signature through electronic document management operators.
What papers does it include?
There are few of them, but they are all mandatory. The absence of at least one component entails non-acceptance of the entire package by the tax office .
- declaration 3-NDFL;
- TIN;
- income certificate;
- contract of sale;
- document on share participation;
- receipt for payment of the cost of the object;
- acceptance certificate (if we are talking about a new building).
More details about what documents need to be attached to the declaration can be found here.
What is considered as failure to submit a report?
Failure to submit a report will be considered if:
- failure by the employer to submit such an obligation, including failure to submit separate reports for separate divisions;
- delivery after the due date.
In relation to 6-NDFL, violations (not regarded as failure to submit) will also be considered:
- Inclusion of false information in the report. Responsibility for it will arise if the reporting person does not correct the report before the tax authority identifies this error (clause 2 of Article 126.1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
- Violation of the method of reporting. Only those employers with up to 10 employees can submit it on paper (Clause 2 of Article 230 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The rest must report electronically.
Here the question arises: does the wording “up to 10 people” mean “10 inclusive” or “less than 10” (that is, 9)? You will find the answer to this in ConsultantPlus. You can get trial access to the system for free.
Account blocking
But a much more sensitive punishment for a personal income tax agent is the freezing of financial assets in his accounts. Inspectors resort to this method when the calculation in question has not been submitted 10 days after the deadline for its submission.
Therefore, every accountant knows: it is better to submit Form 6-NDFL on time, even with inaccurate data, than to delay its submission. In most cases, the 6-personal income tax is then adjusted based on the appropriate explanations. In such cases, the fine may not be assessed at all.
Read also
17.06.2017
Bet sizes
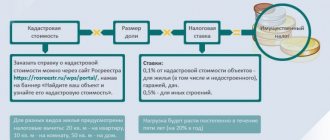
As mentioned above, tax rates on income received by citizens vary depending on the status of each individual person.
Table 1. Bet sizes depending on status
| Bid | Category of citizens |
| 13% | Deductions of 13% of the funds received are sent from the salaries and earnings of residents of the country. Let's take another example of wages. Imagine that you live in Russia for at least 183 days a year. Due to this circumstance, the personal income tax for you is 13% of the amount received by you. Let’s assume that the initial amount of your monthly salary is 55 thousand Russian rubles. We subtract 13% (7 thousand 150 rubles) and get 47 thousand 850 rubles. The difference is large, but if you were a non-resident, it would increase even more. |
| 30% | The second category of people, non-residents, are forced to give away as much as 30% of their hard-earned money. So, if you are a non-resident, then, when receiving wages at your workplace, instead of the 55 thousand rubles due to you, you will receive only 38 thousand 500 rubles (since 30% of 55 000 is equal to 16 thousand 500 rubles). |
Personal income tax rates
Criminal offense
As already stated, tax evasion is a criminal offense. The greater the debt, the more serious the punishment.
What threatens a person who has a debt of more than 600,000 rubles? In this situation, the exact amount of debt will play a role. If the debt has the status of a large one, you may be faced with the following measures to suppress repeated violations:
- fine from 100 to 300 thousand rubles;
- a fine in the amount of a citizen’s salary for 1-2 years;
- forced labor for 12 months;
- arrest for up to six months;
- imprisonment for a maximum of 12 months.
Tax debts in especially large amounts provide for more severe punishment. In this case, the taxpayer faces:
- fine 200-500 thousand;
- collection of wages for 1.5-3 years;
- forced labor for 36 months;
- imprisonment for a maximum of 3 years.
A large debt is considered to be a debt for the last 3 years in the amount of 900,000 thousand rubles (if the tax share is more than 10% of fees) or 2,000,000 rubles per year. A particularly large amount of debt is 4,500,000 rubles for 3 years (if the tax debt exceeds 20% of the fees payable), or 13,500,000 rubles.
The return has been submitted, but the tax has not been paid. What happens if you miss a payment?
Ignorance of Tax Code may result in criminal liability
If the 3-NDFL certificate is submitted on time, but if the fee is not paid by July 15, the taxpayer will pay penalties, which will be accrued daily.
Important! The taxpayer in the case considered does not fall under Articles 119 or 122 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
It is almost impossible to cover all aspects of the tax system of the Russian Federation, also because, in addition to coordinating the main aspects of taxation, it deals with many more matters covered at the beginning of the article. However, it is worth noting a fairly successful structure, comprehensively formed from the elements of the system, including all fees, payers and tax authorities. Only clear actions of the entire structure make it possible to successfully and fairly carry out the complex taxation process.
The result of all of the above is the undoubted need to know the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Taxes must be paid on time, and declarations must be filled out strictly according to the rules; this will protect citizens from fines and criminal liability before the law.
On January 1, the Declaration Campaign started in Russia. You must report income received in 2021 by April 30.
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 210 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when determining the tax base for personal income tax, all income of the taxpayer received by him both in cash and in kind, or the right to dispose of which he has acquired, as well as income in the form of material benefits, determined in accordance with Art. 212 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
It is necessary to submit a declaration if in 2021 the taxpayer, for example, sold an apartment or car that was owned for less than the minimum period of ownership, received expensive gifts not from close relatives, rented out property or received income from other sources.
Individual entrepreneurs, notaries, lawyers who have established law offices and other self-employed persons must also report their income.
If the tax agent cannot withhold personal income tax from income, then he is obliged to inform the tax authority and the taxpayer about this before March 1 of the year following the expired period. In this case, the tax authority will send a notification on the basis of which personal income tax must be paid this year no later than December 2.
The personal income tax calculated in the declaration must be paid before July 15, 2019. If the taxpayer does not submit a return by April 30 or does not pay the tax on time, then there is a penalty for this.
Providing reporting
Personal income tax reporting is provided in the form of forms filled out in accordance with government regulations. Their forms are also approved “from above” and are publicly available on the Internet.
Deductions of tax on personal income are a worldwide practice; all developed foreign countries use it. The state budget is filled with funds received from income taxes, funds from which are then used for the improvement of the country.
Companies with legal entity status, in addition, individuals who are individual entrepreneurs, hire workers and become tax agents. This circumstance obliges them to submit the previously mentioned completed forms for verification to the branch of the Federal Tax Service.
Filling out documents is done using information received for each individual employee of the organization. The basis for their transfer is that they are all represented by information about the funds received by employees and tax deductions sent to the treasury from the payments they receive.
Documents must be submitted to the inspection within the established time frame. For 2-NDFL reference, the deadline is the first day of April of the year following the current one.
The deadline for submitting the document to the inspection is the first day of April of the month following the reporting period of the year.
According to regulations and other regulations issued by the state, the declaration is required to be submitted by:
- individual entrepreneurs;
- owners of private legal organizations;
- citizens who received payment from which personal income tax was not withdrawn;
- entities that received monetary remuneration from an individual or legal entity that does not have the status of a tax agent;
- a citizen who received a cash prize;
- when selling real estate by its owner, if the desired name was in the possession of this person for less than a period of three years;
- members of the resident category of citizens whose source of funds was a foreign organization or other person;
- people who receive remuneration due to the status of the heir of the author of literary or scientific works;
- the subject who received the money as a gift, except in cases where the person giving the money is a relative.
In all other situations, a citizen provides reporting declaration forms in Form 3-NDFL only in order to receive the tax deduction due to him or to receive the missing amount that was not previously transferred by the employer.
Is it required to submit the “zero” 6-NDFL?
If the taxpayer did not make payments to its employees in the first three months of the year, there is no need to submit the form. This feature is specified in the corresponding letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation, issued on March 23, 2016 (BS-4-11/ [email protected] ). The paper states that if there are payments only in the 2nd quarter of the reporting year, the calculation of 6-NDFL in 2021 is transferred for 6.9 and 12 months, respectively. In this case, the first submission of reports (3 months in advance) can be avoided.
If there are no payments in the 3rd and 4th months, the taxpayer must complete only the first section for 9 and 12 months. As for the second section, it is not necessary to complete it. A similar practice is applied to separate divisions.
What are the features of form 6-NDFL?
The calculation is formed from several sheets. The first is the title one (the title of the document is given here). This is followed by section number “1”, which reflects generalized indicators, and the next one is the second section (it specifies the dates and amounts of profit received with personal income tax withheld). When reporting in 2021, each subsequent result will increase taking into account the results for the first 3,6,9 and 12 months.
General information
The tax system is a tax system established by law in the Russian Federation and levied throughout the country. The Russian tax code has two parts. The first, published in 1999, covers existing tax types, the procedure for their payment, the rights and obligations of members of the taxation system. The second part, published two years after the first - in 2001, indicates the rates and procedure for tax payment. The coordinated work of the entire taxation system characterizes the successful functioning of the entire state, determining its economic development.
Taxation in Russia is not only a payment complex. The Russian tax system also includes:
Official form:
- methods for establishing, implementing and paying local and regional fees;
- the basics and rules for the creation, transformation and completion of the duties of responsible persons for tax payment and collection, and the plan for fulfilling these duties;
- responsibility for neglecting the law;
- creation of a unified information network of the system;
- measures to monitor compliance with the rules of tax legislation.
Availability of tax classification in the Russian Federation
Tax Code of the Russian Federation in two parts
At this time, taxes and fees as central elements of the system can be classified according to different characteristics. Hierarchically it is classified into three types of taxes:
- Federal (the same and mandatory for taxpayers living in the Russian Federation).
- Regional (they are paid by taxpayers living in various territories of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation).
- Local.
It should be noted the classification of fees collected from the population of the country:
- Direct (withdrawn from property and income).
- Indirect (defined as markups on original prices and tariffs).
Important! It should be remembered that insurance premiums paid to individual entrepreneurs are separate; failure to pay them may mean the closure of the business.