In which off-balance sheet accounts are inventory items recorded?
Inventory assets (TMV) include inventories, finished products, goods (clause 3.15 of the Methodology for Inventory, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated June 13, 1995 No. 49).
Off-balance sheet accounts are intended to comply with the requirement of property isolation (clause 5 of PBU 1/08, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 6, 2008 No. 106n).
IMPORTANT! Maintaining off-balance sheet accounting is the responsibility of a legal entity (Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, clause 5 PBU 1/08) in order to comply with the requirement for the reliability of reporting. An entrepreneur is not obliged to keep accounting, but can do it on his own initiative - in this case, off-balance sheet transactions should also be reflected correctly.
Inventory and inventory items are recorded on off-balance sheet accounts in the following cases:
- Acceptance for storage - this is what the account is intended for. 002 “Inventory and materials accepted for safekeeping” of the Chart of Accounts (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
- Commission agents account for goods for resale on the account. 004 “Goods accepted for commission.”
Acceptance of materials from other companies for processing - records of these operations are kept on the account. 003 “Materials accepted for processing.”
Let's take a closer look at the procedure for writing off materials from these off-balance sheet accounts.
Act of write-off of material assets
An organization's assets that have a tangible form are often referred to as tangible assets. These include, in particular, fixed assets, materials, goods, and finished products.
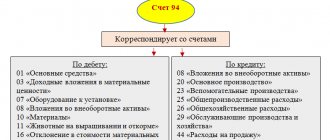
Those material assets that cannot be used for their intended purpose, are not capable of generating income for the organization in the future, or are disposed of, are subject to write-off. Write-off of material assets occurs in cases of their sale, transfer as a contribution to the authorized capital of another organization, identification of shortages or damage during inventory, etc. Operations to write off material assets involve crediting the accounts of the corresponding assets. In particular, accounts 01 “Fixed assets”, 10 “Materials”, 41 “Goods”, 43 “Finished products”, etc. (Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n). The basis for reflecting accounting records for the write-off of material assets is the primary accounting documents (Part 1, Article 9 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). We will tell you how to draw up an act for writing off material assets in our consultation.
How to write off materials from an off-balance sheet account?
Postings for capitalization and write-off from the account. 002 look like this:
Acceptance of inventory items for storage
Disposal of inventory items accepted for storage
Write-off of inventory items from the account. 002 is carried out on the basis of:
- form MX-3 or a similar document developed by the organization (taking into account the requirements of paragraph 2 of Article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ) to record the return of valuables accepted under a storage agreement;
- TORG-12, UPD or other documents - upon disposal of inventory items that were taken into account on the account. 002 within the framework of the supply agreement.
For operations with customer-supplied raw materials, the executing organization uses an off-balance sheet account. 003:
Received materials for processing
Recycled materials were transferred to the customer
If products are made from customer-supplied raw materials, then the entries in off-balance sheet accounting may be as follows:
Received materials for processing
Customer-supplied raw materials are transferred to production
Products made from customer-supplied materials have been capitalized
Manufactured products were transferred to the customer
With account 003 materials are written off based on:
- report on the consumption of customer-supplied raw materials (Article 713 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation);
- work acceptance certificate;
- invoice M-15 or other similar documentation agreed upon by the parties.
When selling goods under a commission agreement, the commission agent is accounted for according to the account. 004 there will be the following accounting entries:
Goods received under a commission agreement were capitalized
Products accepted for commission were sold
Write-off of inventory items from an off-balance sheet account. 004 is carried out on the basis of the primary document drawn up upon the sale of valuables - TORG-12, invoice, UPD or other documentation agreed upon by the parties to the commission agreement.
Write-off of materials to an off-balance sheet account
An organization can take into account not only other people's material assets on its balance sheet, but also its own. An example would be low-value property, household supplies and inventory that are used for more than 1 year, costing less than the limit for accepting an object for accounting as fixed assets (the organization sets this limit independently in its accounting policy, but it cannot be more than 40,000 rubles in accordance with p. 5 PBU 6/01).
Such materials are written off as expenses at a time. But due to the long period of use, it is necessary to organize control over their safety. For this purpose, you can create a record sheet for household supplies and equipment in use, or you can keep off-balance sheet accounting. In the Chart of Accounts, approved. By order No. 94n, there is no special account for these purposes, so the organization can develop an off-balance sheet account independently and approve the chosen procedure for writing off low-value materials in the accounting policy.
If you use the 1C:Enterprise computer program for accounting, then in the chart of accounts of this program, special off-balance sheet accounts are provided for accounting for low-value materials written off the balance sheet:
If the company decides to take into account the low value off the balance sheet, then the postings will be as follows:
Write-off of fixed assets: sample orders
The procedure for its implementation is regulated by the Methodological Instructions approved.
Inventory is also necessary to identify fixed assets that are unsuitable for use, or whose further use in the company’s activities is impractical. A sample order for an inventory of fixed assets can be downloaded at the end of the article. Inventory is required in the following cases (clause 1.5 of the Guidelines):
- change of financially responsible person;
- natural Disasters.
- identification of facts of damage and theft of property;
- preparation of annual reports (an inventory of fixed assets is allowed once every three years);
To carry out the inventory, the company's management appoints a commission.
Conducting an inspection can be mandatory and proactive.
Tell me how to spend and write off a purchased computer
here is a thread about decommissioning of equipment (so, to the heap)
if everything was purchased in parts, then it must be capitalized as materials, and then transferred to production as ordinary consumables) if not the budget, then 1C will tolerate it) and it’s certainly not worth making a fixed asset out of these spare parts
(2) krcsrgi, I don’t see the thread about writing off, maybe it’s not attached?! Everything was purchased on one invoice, that is, 1 receipt of goods and services. The total amount is 39990, including delivery of 390 rubles.
I credited the components to the accounting account at 10.6, and VAT as usual at 19.03, I’m wondering how to transfer these components to production (to which account should I put them)? And maybe there is an opportunity to somehow do without production by writing off these components?
Enterprise Accounting 8.2 edition 3.0
I support, sir. 26, services))
(7) You are equally happy - they haven’t told you anything about the case yet.
(12) -1 This is not a question of the requirements of specific individuals, but a question of legal requirements.
(14) +1 Ideally true, but. Rarely does anyone keep a count of 15 - only big ones. Small businesses, as a rule, do not use this scheme.
(0) Firstly, I recommend doing as the 1C company itself recommends: an OS costing up to 40,000 rubles. be taken into account when capitalizing on account 10.09 as materials, and not as fixed assets, and after write-off - on the off-balance sheet account MTs.04. In this case, account 08 is not used for capitalization purposes, i.e. reclassification of property - depreciable or not - occurs at the time of capitalization. Secondly, since the computer assembly needs to be done somewhere, but there is no account 08, it needs to be replaced with another account. I recommend using account 10.09 for assembly.
Then the wiring will be as follows:
Operation 1. Capitalization of components, document “Receipt of goods and for the amount of components 39,600 rubles, tab “Services” for the amount of delivery 390 rubles: Dt 10.01 - Kt 60.01
Operation 2. Assembling the computer: Dt 10.09 - Tt 10.01 I don’t immediately remember the document.
Operation 3. Write-off of the computer by amount, but the quantity continues to be accounted for on the off-balance sheet account, document “Transfer of materials for operation”, tab “Inventory and household supplies”: Dt 20/26/44 - Kt 10.09 Dt MTs.04
How to correctly write off account MTs.04 in 1C: 8.2 (OSNO)?
Good afternoon Please tell me which document in 1C:8.2 can be used to partially write off account MTs.04? Also, tell me, I first credit the MC to account 10, then with the document “transfer of materials for operation” I credit it to the MC.04 account, question: At what point are melon material assets written off as expenses to reduce profits?
Good afternoon Let's go in order:
10.09/60 (71) bought goods and materials
the document “transfer into operation” wrote off the cost of inventory items as expenses 26 (44) / 10.09 on d-account MTs.04
Next, something from the inventory and materials has become unusable and you need to remove it from accounting, you can do this with the document “writing off materials from service: kit MTs.04
Quote (Greek Vera): Good afternoon! Let's go in order:
10.09/60 (71) bought goods and materials
the document “transfer into operation” wrote off the cost of inventory items as expenses 26 (44) / 10.09 on d-account MTs.04
Next, something from the inventory and materials has become unusable and you need to remove it from accounting, you can do this with the document “writing off materials from service: kit MTs.04
Quote (Greek Vera): Good afternoon! Let's go in order:
10.09/60 (71) bought goods and materials
the document “transfer into operation” wrote off the cost of inventory items as expenses 26 (44) / 10.09 on d-account MTs.04
Next, something from the inventory and materials has become unusable and you need to remove it from accounting, you can do this with the document “writing off materials from service: kit MTs.04
The formulation is not entirely correct: the cost of inventory items is not written off as expenses immediately, but at the time of actual transfer for use, i.e. While the materials are listed in the warehouse, they remain on account 10.
Quote (Greek Vera): Good afternoon! Let's go in order:
10.09/60 (71) bought goods and materials
the document “transfer into operation” wrote off the cost of inventory items as expenses 26 (44) / 10.09 on d-account MTs.04
Next, something from the inventory and materials has become unusable and you need to remove it from accounting, you can do this with the document “writing off materials from service: kit MTs.04
The formulation is not entirely correct: the cost of inventory items is not written off as expenses immediately, but at the time of actual transfer for use, i.e. While the materials are listed in the warehouse, they remain on account 10.
In my answer, I believe that I correctly explained the situation: first, the cost of inventory items is written off, and then they are listed on an off-balance sheet account
Sales in 1C of inventory and office equipment transferred for operation
Transfer of inventory and office equipment into operation
The transfer of inventory into operation is documented in the document Transfer of materials into operation from the section Warehouse – Workwear and equipment – Transfer of materials into operation.
In the document, you should fill in the field Method of reflecting expenses , where you indicate the Cost account , where the cost of the scanner will be allocated.
At the same time, the cost of inventory is taken into account in the off-balance sheet account MTs.04.
Postings according to the document
Sales of inventory and office equipment
The sale of inventory is carried out using the document Sales (act, invoice) section Sales – Sales – Sales (act, invoice). In the Accounts , indicate:
- Accounting account – МЦ.04;
- Income account — 91.01;
- Other income and expenses – Other non-operating income (expenses);
- Expense account – 91.02;
- VAT invoice – 91.02.
Off-balance sheet accounts
Off-balance sheet accounts
– these are accounts intended to summarize information about the presence and movement of values that do not belong to an organization-economic entity, but are temporarily in its use or disposal.
Off-balance sheet accounts are subsidiary accounts of accounting.
They are used when the accountant needs information that is not on the balance sheet accounts.
Balances on off-balance sheet accounts are not included in the balance sheet, but are shown after its total, i.e. behind the balance.
The data from these accounts does not affect the financial result and does not need to be reflected in the company’s reporting.
What assets should be taken off the balance sheet?
Off-balance sheet accounting rules apply to assets that an enterprise does not own, but can legally temporarily dispose of.
This group includes strict reporting forms and leased property. Such resources cannot be reflected in the balance sheet, since they will distort the real financial position of the business entity. But registering them is necessary to control their safety, so off-balance sheet accounting of material assets is being introduced.
The following assets are taken off the balance sheet:
- fixed assets that the company actually operates, but they do not belong to it; the basis for the disposal of property is a lease agreement;
- funds received by the company for use free of charge;
- raw materials that suppliers provided to the company for processing;
- equipment that needs to be installed and adjusted under a contract for the provision of paid services;
- commercial products accepted by a business entity on commission;
- valuables that were shipped by mistake by the supplier;
- rejected products received under a supply transaction;
- property located on the territory of the company, but according to documents, it is registered as issued to the buyer;
- strict reporting forms.
Thus, the leased resources from the user are displayed on the balance sheet, and the owner has these assets on the balance sheet: the owner calculates depreciation and taxes using them.
Strict reporting forms (SSR) purchased by an enterprise are designed to ensure the display of important acts of economic activity, including certification of the rights of third parties to perform certain actions. The Company is responsible for the cost of each such form, so accounting must cover:
- all completed and issued documents;
- damaged forms.
Vivid examples of BSO are a work book and inserts in it, a diploma, a checkbook.
Also see “Accounting for non-financial asset assets on off-balance sheet accounts”.
For what purposes are off-balance sheet accounts used?
Typically, on off-balance sheet accounts:
1) records are kept of the presence and movement of property (to ensure its safety):
or not owned by the organization;
or the organization’s own property, the cost of which is written off as expenses.
2) information is collected that needs to be disclosed in the notes to the balance sheet and the income statement.
The main objectives of off-balance sheet accounts are:
ensuring control over the use of material assets that do not belong to the enterprise;
control over the safety of material assets listed on these accounts, over the timely execution of documents for the receipt and disposal of these funds;
ensuring the correct organization of accounting on these accounts;
providing comprehensive and complete information on these accounts to assess the creditworthiness and financial stability of the enterprise.
Types of off-balance sheet accounts
There are the following off-balance sheet accounts provided for in the Chart of Accounts.
To account for property that does not belong to the organization, off-balance sheet accounts are used:
001 “Leased fixed assets.” This account reflects the leased fixed assets at the valuation specified in the agreement;
002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping.” If inventory items are received by the company, but under the terms of the contract, ownership of them is transferred to the organization after certain conditions are met (for example, after transfer of 100% of payment), then the company reflects such inventory items on off-balance sheet account 002;
003 “Materials accepted for processing.” This account reflects the customer's raw materials and materials accepted for processing (supplied raw materials), which are not paid for by the manufacturer;
004 “Materials accepted for commission” This account reflects goods accepted by the commission agent for sale;
005 “Equipment accepted for installation.” This account reflects the equipment received by the contractor from the customer for installation.
To account for the organization's property written off as expenses, off-balance sheet accounts are used:
006 “Strict reporting forms.” This account reflects strict reporting forms - receipt books, forms of certificates, diplomas, various subscriptions, coupons, tickets, forms of shipping documents;
007 “Debt of insolvent debtors written off at a loss.” This account reflects the debt of insolvent debtors, taken into account on the balance sheet for five years after write-off in case of a change in the property status of the debtors.
To collect information for disclosure in notes to financial statements, off-balance sheet accounts are used:
011 “Fixed assets leased out.” If, under the terms of the lease agreement, the property is taken into account on the balance sheet of the tenant (tenant), then for the owner it is reflected in account 011 “Fixed assets leased”;
008 “Securities for obligations and payments received.” Account 008 “Securities for obligations and payments received” is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of guarantees received to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments, as well as security received for goods transferred to other organizations (individuals);
009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued.” Account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued” is intended to summarize information on the availability and movement of guarantees issued to secure the fulfillment of obligations and payments. If the guarantee does not specify the amount, then for accounting purposes it is determined based on the terms of the contract.
At the same time, the Organization can also open off-balance sheet accounts not provided for in the Chart of Accounts.
It should be noted that you should not neglect accounting for business transactions on off-balance sheet accounts, since during a tax audit, goods, fixed assets, etc., not accounted for anywhere, can be regarded as surpluses, which in accounting are classified as non-operating income and on which income tax must be paid .
The procedure for accounting for material assets in any existing construction organization
All tracking is carried out in accordance with primary documentation, which is compiled exclusively in a pre-approved form.
How to reflect receipt: necessary documents, statements
The following can be accepted for balance:
- raw materials that will be used for creation in the workshop;
- products that await further sale;
- assets if management needs them.
How this will be reflected depends on several parameters:
- where is the acceptance taking place?
- how many goods arrived, in what quality they were;
- to what extent the contract corresponds to the accompanying papers.
What transactions are created upon receipt
If the product came from a supplier, then the following is recorded:
- Dt 10, Kt 60.1 – valuables arrived.
- Dt 19.3 Kt 60.1 – incoming VAT is noted.
In some cases, things come from the founders or other persons. Then they open sub-accounts and keep the following records:
- DT10 KT75.1. Coming from the co-founder.
- DT10 CT 71. From a person on a business trip (accountable).
- DT10 KT20. Creation in the same company.
If the products arrived only for further resale, then 41 accounts will be used.
How to store it all
They do not always label only purchased materials. Sometimes they even reflect something that does not belong to the organization. This happens when something was put into safekeeping or was created as a result of dismantling at the customer’s place. In this case, everything is accumulated on off-balance sheet 002, indicating the circumstances of occurrence, price and period.
Movement of goods and materials within the company: documents, postings
The cycle of an item is not always acceptance and disposal. Sometimes he moves from one warehouse to another, goes to a branch or returns to the central premises. The transfer of raw materials to the production floor also refers to this part of the product's life. An invoice is prepared.
When is it relevant:
- what is produced will be used by the enterprise;
- return object;
- production waste or defective parts are handed over.
How to write off
The last, necessary part of the life cycle of assets. It is important to ensure that the actual quantity always matches the one recorded in the accounting department. An act is drawn up for disposal. Everything that is indicated in it cannot be subject to further application. All parameters are entered - weight, number, reason for write-off.
The accountant's task is to reflect the value of what will be removed from the balance sheet. You can calculate by:
- average cost;
- the price of an individual object;
- FIFO.
Postings
There are three options in which the score in Dt is set as 20, 23 or 25, and in Kt there will always be 10.
Disposal of inventory items: documents, postings
Withdrawal from balance is a normal workflow, since nothing can be used indefinitely. They are regularly sent for processing, sale or write-off. Each release from the pantry is processed separately, with different accounting documentation. If these are limited materials, then there is a limit card; if there are no consumption standards, then the requirement is an invoice. For sales - invoice according to f. No. 15, like a vacation on the side.
Off-balance sheet accounting
Off-balance sheet accounts, like regular accounting accounts, are a two-way table: debit and credit.
Accounting for off-balance sheet accounts is carried out using a simple system.
Double entry on off-balance sheet accounts is not used, that is, when making entries on off-balance sheet accounts, there is no need to reflect the same amount in the debit of one account and the credit of another account.
The debit of off-balance sheet accounts reflects the receipt of property, receipt and issuance of security, and the credit reflects the disposal of property and termination of security.
The balance at the beginning of the month reflects the availability of the type of funds accounted for in the account.
The debit reflects the receipt, and the credit reflects the write-off of these funds.
The balance at the end of the month by debit shows the balance of funds at the end of the month and is calculated using the formula:
Balance at the end of the month = Balance at the beginning of the month + Debit turnover - Credit turnover.
The ending balance of such an account is always a debit.
Still have questions about accounting and taxes? Ask them on the accounting forum.
A simple reminder for correct off-balance sheet accounting
The accountant made the entry: Credit 012 - 5,700.
7 clause 32 PBU 6/01, clause 27 PBU 4/99). If such records are not kept, the company may be fined (Article 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation, Article 120 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The receipt of leased funds is reflected in the debit of account 001, the return to the lessor is reflected in the credit of the account. Leased property is recorded at the cost specified in the lease agreement. If the contract does not indicate the cost of the object, then it can be taken into account without the price.
Commission agents reflect goods accepted for commission in the debit of account 004.
How to write off MC from an off-balance sheet account?
Good afternoon . I read a lot of materials, and a rather vague opinion formed in my head. We have an account MTs 04. The following are in use: - telephone handset - laptop - water dispenser - printer - mouse - payment terminal
I can’t fully understand how I can write this off (it is planned to close the legal entity in the future). As far as I understand from what I've read. 1) we need a commission (of whom it can consist, if we have one director to work for the good) and we simply draw up an act and sign it (an act for writing off low-value materials) 2) we need to hire (since there is no one on staff) for the disposal of org. technology company.. have reasons..
Let's say this product is not available. I came, the booze was working before me. another. There is neither a laptop nor a telephone handset... but they are listed on MC 04. What are my actions? (tell me what to support for the act?)