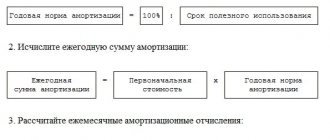
The useful life of a vehicle refers to the period during which the vehicle provides economic benefit. When determining this criterion, the depreciation of the car is taken into account - the degree of physical wear and tear. This data is necessary for tax and accounting reporting. In addition, calculating depreciation allows you to determine the service life of the vehicle, which is listed on the balance sheet of the enterprise, and draw up an estimate for maintenance and repairs.
Resistance classes
Of course, when labeling models, manufacturers indicate the resistance class and depreciation period. It is believed that the first number in the marking indicates this. However, everyone understands that this method of determining the service life of a car is questionable. Ideally, you need to look at the real experience of other drivers using the car, read reviews and get other practical data. It is generally accepted that new cars with the first, second or third class last from 3 to 5 years, cars of the fourth class will last 5-7 years, cars of the fifth are designed for 7-10 years of service.
The procedure for applying the new edition of the OS Classifier
Updated groups for establishing SPI came into force in connection with the adoption of new OKOFs. The specified standards must be applied to vehicles that began operation on January 1, 2021. It is not necessary to change the group and SPI for vehicles put into operation before 2021.
For example, in June 2021, the organization purchased a Kamaz-5320 flatbed truck, and the vehicle was put into operation in July. The accountant established the Kamaz depreciation group as the fourth (5-7 years), intended for general purpose on-board transport.
As can be seen from the table for the new Classification, the group has not changed for this type of freight transport.
Important! To facilitate the transition to new OKOF codes, Rosstandart created a comparative recommendation table - departmental order No. 458 dated April 24, 2016.
The operation of your own or leased transport requires tax and accounting to approve the parameters for calculating physical depreciation - period, monthly amount. Regardless of the depreciation method, the useful life of the vehicle is the determining criterion for the calculation.
Accounting legislation suggests that enterprises independently determine the time of productive operation. The Tax Code limits specialized classifiers, offering preferences. Example: the useful life of a leased car for tax purposes can be reduced by 2 times. To eliminate the occurrence of differences and to simplify accounting, paragraphs of tax legislation are used in practice.
Are cars included in the fixed assets register?
Motor transport can be considered a fixed asset (FPE) both in tax accounting and accounting if the criteria prescribed by law are met.
Criteria for inclusion in the register of fixed assets of a company in tax accounting in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 257 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation:
- exploited in the process of producing and selling products, providing services, carrying out work, and managing an enterprise;
- the cost of the object starts from one hundred thousand rubles .
Criteria for inclusion in the register of fixed assets of a company in accounting in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n “On approval of the Accounting Regulations “Accounting for Fixed Assets” PBU 6/01”:
- is exploited in the process of producing and selling products, providing services, carrying out work, managing an enterprise, leasing it temporarily for a fee;
- has been in use for more than a year >;
- the company does not intend to resell the property;
- it is planned to make a profit in the future .
What determines the actual service life of a car?
Standard service life calculations for a private owner are irrelevant. They are taken into account only for the financial statements of companies that have cars on their balance sheets. A private owner only needs to know that the car will behave normally in different situations on the roads and will be able to deliver it from one point to another.
It is possible to derive many criteria that affect the actual service life of a car, regardless of which class it is assigned to.
- Mileage per year. Of course, one of the most important factors is the one that determines how long the machine will last. If a car sits in a garage for ten years, it will only lose its appearance, but the condition of the internal parts and friction pairs will be ideal. Some drivers' cars cover 30-40 thousand kilometers per year. Naturally, the service life of such vehicles will be shorter in years.
- Transport storage. This is another important factor that plays a role and determines the condition of the car. If the car is always on the street, then corrosion will occur on the body. When stored in a garage, corrosion can be avoided for many years.
- Timely maintenance of the machine and replacement of all prescribed “consumables” on time. The manufacturer indicates in the instructions at what mileage or time it is necessary to change the oil, air, gasoline, oil filters, etc.
- Use of original consumables and spare parts during maintenance. Often there are analogues on the market that are cheaper than original spare parts. It is not recommended to use them.
- Quickly eliminate problems that arise during the operation of transport.
- Driving style, attitude towards the car.
- Condition of the roads. Cars in Europe last much longer than the same brands in Russia. One of the reasons is the quality of the road surface. If the vehicle drives on a perfectly smooth road with no potholes most of the time, it will last longer. In Russia and the CIS countries, the condition of roads is noticeably worse, which explains the frequent repairs of vehicle chassis.
The nuances of calculating depreciation on a car
What is a personal driver card and is it needed in 2018?
To calculate the wear and tear of a car more accurately, it is not enough to know the basic characteristics of the car. Typically, organizations use special directories for the most accurate calculation. Which indicate the make of the vehicle, as well as its book value by year of its manufacture.
If you take an indicator from a certain table and divide it by the number of months during which the car was in use, you get the cost of wear and tear on a given vehicle in use for one month.
This calculation does not include information on the cost of fuels and lubricants, weather conditions, as well as finances spent on minor cosmetic repairs.
Thus, the choice of methodology directly depends on the organization or individual
The main thing with different calculation methods is to remember the importance of all the indicators that are responsible for the performance of the vehicle
Home » Entrepreneur's Directory » Calculation » Calculation of depreciation using the linear method and its features
Determination of the depreciation group of passenger cars
According to the generally accepted classification in force in the Russian Federation, passenger cars are divided into 5 classes. The key criterion for such a division is engine size. It looks like this:
- class 1 - includes cars with engine volume less than 1.2 liters;
- class 2 - volume varies between 1.2-1.8 liters;
- class 3 - cars with an engine capacity of 1.8-3.5 liters;
- class 4 - vehicles with an engine capacity exceeding 3.5 liters;
- class 5 - executive cars, the engine size of which does not play a decisive role.
Important! Executive class cars of domestic production have a numerical classifier “5”, which is placed first in the model number. For foreign-made vehicles, such a classification is not provided: whether a car belongs to the highest class is determined by the manufacturer.
Classification of Russian cars
To determine the class of domestic cars, it is enough to pay attention to the model number: the first digit corresponds to the class. For example, VAZ 2109 indicates that the vehicle belongs to class 2, has an engine capacity of 1.2-1.8 liters, and has a useful life of 3-5 years.
An example of calculating the useful life period
We purchased a used Suzuki car that had been in use for a year and a half. The engine capacity of the car is 2.5 liters. Using these data as a basis, you can easily calculate the useful life. To do this you need to follow 3 simple steps:
- determination of depreciation group - engine size indicates that the car belongs to group 3;
- useful life period (total) - for this group the terms vary between 3-5 years;
- useful life period (remaining) - the operating period is subtracted from the total life.
As a result, the useful life period will be 1.5-3.5 years.
Executive class car
Considering that luxury cars are not determined by engine size criteria, other parameters apply to them. There are 3 main indicators:
- length - more than 5 meters;
- width - from 1.7 meters;
- model - by default, luxury vehicles include Mercedes, BMW, Lexus and other cars with the prefix “premium”.
The following parameters play a secondary determining role:
- market price;
- speed characteristics;
- body type;
- interior comfort;
- security: reservation.
It should be clarified that a combination of primary and secondary characteristics helps classify a car as a representative class. For example, a car may fit this category in terms of body size and model, but not according to secondary indicators. In this case, the car is included in depreciation group 3-4.
In addition, Russian and European classifications differ significantly. For example, in the Russian Federation, cars are divided according to engine size, while in Europe size is considered a key parameter. Therefore, the manufacturer’s statement that a foreign car belongs specifically to the executive class is not always true. Therefore, in order to classify a car as the highest category, an expert opinion is required.
Calculation by reducing balance
This is accelerated depreciation.
In the first years, the amount of write-off of the initial price is accrued at a faster rate than in subsequent years. The very first figure is annual deductions. It corresponds to the total cost of the car at the beginning of the accounting year. The monthly amount corresponds to 1/12 of its part. The acceleration factor is applied to the formula. Example. Auto Services LLC purchased a GAZ-Cruise bus for intercity transportation for 2,550,000 rubles, and paid 5,000 rubles for vehicle registration. The service life of the bus is limited to 8 years. The company decided to calculate the depreciation of the new bus using the reducing balance. Contribution rate: 2: 8 x 100% = 25% annually. Calculation:
| Year | Calculation | Annual depreciation |
| 1 | 2,555,000 x 25% | 638 750 |
| 2 | (2,555,000 – 638,750) x 25% | 479 062, 5 |
| 3 | (2,555,000 – 638,750 – 479,062.5) x 25% | 359 296 |
| 4 | (2,555,000 – ….– 359,296) x 25% | 269 472 |
| 5 | (2,555,000 –….– 269,472) x 25% | 201 933 |
| 6 | (2,555,000 –…. – 201,933) x 25% | 151 621 |
| 7 | (2,555,000 –….– 151,621) x 25% | 113 716 |
| 8 | (2 555 000 –….– 113 716) | 85 287 |
| Total | 2 299 137,5 |
By calculating this way, the initial cost will not be completely written off (2,555,000 – 2,299,137.5 = 255,862.5). The Ministry of Finance allows this amount to be included in the expenses of the last month of using the bus.
Method for calculating SPI in tax documentation using the Classifier
In the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated January 1, 2002 “On the Classification of fixed assets included in depreciation groups,” you can see the SPI Classifier according to the depreciation groups of transport.
All vehicles belong to separate depreciation groups; the group number is affected by the vehicle type, size, power, and area of operation.
For all cars, the SPI can vary from two to nine years .
The SPI TS classifier can be presented as the following table :
| No. | Depreciation group | SPI, years | Kind of transport |
| 1 | 2 | from two to three | Utility lifts with platforms |
| 2 | 3 | from three to five |
|
| 3 | 4 | from five to seven |
|
| 4 | 5 | from seven to nine |
|
Car depreciation. Subtle points
A car is no longer a luxury. Almost every organization has a need for this means of transportation. Some need a truck to deliver products to customers or stores from a warehouse. Another is a minibus for employees. Still others will be satisfied with a used car for a courier. Well, someone needs an expensive executive car for the director. There are many situations when you can’t do without an iron horse. Therefore, more and more organizations decide to buy a car. As you know, its cost will be written off as expenses gradually through depreciation. Our article will help you calculate it correctly.
A car on the balance sheet causes a lot of trouble for an accountant. Moreover, the problems are not only related to operating costs. Difficulties arise when calculating depreciation.