It is difficult to imagine a company that does not print documents, does not sign them and does not make records. In other words, it does without stationery. They are taken into account as part of inventories. They reflect this type of materials at the purchase price (specified in the documents), including delivery costs. Office supplies are purchased either directly through the supplier or through the organization’s accountable persons.
Receipt of stationery: what applies to them
In accordance with Instruction No. 157 and paragraph 118, the office may include:
- paper;
- pens;
- rods;
- pencils;
- folders;
- paper clips;
- stapler;
- printer ink.
These are the basic items that can always be classified as stationery, but in reality there are many more. Sometimes they are defined as products that are used for correspondence or paperwork, but this is not a complete formulation.
In accordance with it, the office includes:
- drawing and school supplies (ready sets, rulers, pencil cases);
- office equipment (typewriters, scanners, calculators).
In addition to all this, the work of the enterprise is almost always associated with printing and preparing materials for storage. Therefore, this also includes:
- cross-linking agents;
- stamped goods;
- special threads in some cases;
- glue.
Business Solutions
- shops clothing, shoes, groceries, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
Separately, it is worth noting a few more items of inventory, which are also classified as CT:
- accounting books;
- plastic stationery;
- photocopying and duplicating equipment;
- paper cutting devices;
- means that provide a protective coating on sheets of paper;
- equipment for destroying documents;
- storage cabinets;
- hole punchers.
Instructions for use
The Ministry of Finance issued Order No. 94n in 2000. It approved instructions explaining how to apply the accounts from the plan in practice in accounting for financial transactions and economic activities of enterprises. The content, purpose and structure of articles according to economic significance are reflected. The procedure for maintaining synthetic records and a standard scheme for correspondence are indicated .
Balance sheet accounts are created to record trade turnover and reflect the availability and movement of property. Off-balance sheet accounts show the existence of valuables belonging to other companies transferred to the organization for temporary use.
The chart of accounts does not indicate when equipment or real estate is rented, so that this operation is reflected in the form of a balance sheet. Posting is carried out without using binary posting. When devices, parts, tools are accepted, they are written down as a debit; when the item is returned to the owner, the amount is indicated as a credit without correspondence.
The instructions establish categories of accounting accounts based on economic characteristics :
- Characteristics of assets with a debit balance, where the credit turnover shows the expense; incoming equipment and fuel, expressed in money and unit of account, are put in debit.
- The passive part of the balance sheet contains information about the sources of receipt of material assets.
- Financial results and business processes make it possible to control the supply and sale of manufactured goods.
In the structure created by the system, registers are allocated by purpose, classification is carried out in the form of articles:
- regulatory – to clarify the cost characteristics of the object;
- operating – to reflect the costs of procurement, production, sale of goods or services provided;
- financial-effective , where income and expenses are compared;
- inventory - indicate the presence of material assets;
- stock – show the formation of equity capital;
- settlement – reflect financial relations with partners and credit institutions.
In accounting entries, a binary notation is used, where the first value is the receipt for a specific account, the second value shows how much money was spent and transferred with the corresponding account in a specific transaction.
Accounting for stationery in accounting
It is worth noting that if a non-financial asset is classified as an office, this does not mean that it should automatically be classified as inventory. The main criterion for whether to count it as fixed assets or as inventories is the period of use. It is important to understand whether the item will be used constantly, repeatedly or only once.
How to lead correctly
They are usually accepted in the format of inventories (inventories), credited at the actual cost of the purchase, in other words, according to the amount of money spent on the purchase:
- in accordance with the invoice issued by the supplier;
- According to the traveler’s reporting, a receipt is attached to it if the employee bought “stationery” on a business trip.
Reception is issued according to the PKO (cash receipt order), which has form No. M-4. The movement will be reflected in accounting cards according to f. No. M-17. Everything is divided by type, product groups and other characteristics. The storekeeper fills out these documents according to the receipt and expenditure documentation, which is provided to him on the day the business operation is carried out. At the end of the month, balances are calculated and signed by an accountant after reconciling the analytical data with the actual data.
Chart of accounts for beginners by sections
The classifier includes all balance sheet accounts; they are listed in 8 sections under numbers such as:
- active;
- passive;
- active-passive.
Section I consists of the company's assets; it indicates operations with facilities for their commissioning, disposal, construction, and depreciation. This part reflects the turnover of fixed assets - buildings, structures, equipment. The status of intangible assets under patents and licenses is shown here.
In production inventories, section II of the balance sheet contains information about household supplies used during production processes.
Section III discusses production costs. An accountant needs to pay special attention to the interaction of registers that are involved in all types of activities of the enterprise. The actual productivity of the enterprise, the amount of profit and the calculation of product costs depend on the correct posting of expense items.
All data on the company’s funds are shown in section V - these are cash on hand or transfers to bank accounts, loans, credits, and securities.
Section VI reflects relationships with organizations, hired personnel, and internal financial transactions.
Section VII shows the state of investment:
- authorized capital;
- additional;
- reserve;
- shares;
- retained earnings.
Financial results, section VIII , ends with the chart of accounts. In this part, production results are summed up, profits with reserves are formed, and losses for the reporting period are indicated.
The plan consists of synthetic and analytical accounts. A sub-account is opened if necessary for detailed disclosure of the transaction.
Additional accounting theory is provided below.
How is this enshrined in law?
There are guidelines that indicate how to take these values into account. This is all included in paragraph 49 of the instructions:
- if they were purchased for cash or non-cash, then a receipt order is drawn up using a special form. No. M-4;
- everything will move around the warehouse according to types, varieties, colors, shapes and other differences, written in cards according to f. No. M-17, they are set up for each type of material separately.
All documentation will have to be maintained by the MOL (financially responsible person) on the basis of receipts and expenses with the date stamped when exactly the business transaction occurred, so that the CT can be taken into account at this cost.
Receipts are made through debit 10, which is called “Materials”. Then, according to the Instructions, the organization can independently determine subaccounts for each type of inventory. Therefore, in one accounting account it appears 10.01, which is responsible for CT, and in the other it is 10.09, necessary for other goods.
Table showing which subaccount is allowed to be used and how to properly capitalize various stationery items
| Dt | CT | What does it mean | Supporting documents |
| 60.01 | 51 | Paid to supplying company | Extract |
| 10.01 | 60.01 | Accepted | TN, filled in according to f. M-4 |
| 19.03 | 60.01 | Input VAT is taken into account | SF is added to the previous one |
| 68.02 | 19 | VAT accepted | Another invoice |
| 71 | 50 | Employees who go on business trips are given money | RKO |
| 10.01 | 71 | Acceptance of office from a traveler | A sales receipt is issued and supported by the case |
| 50 | 71 | Funds that accountable persons did not spend are returned | PKO |
Wiring example
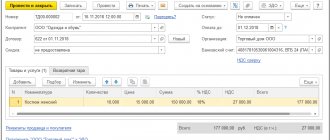
Talisman LLC is engaged in retail trade and for office needs purchased 5 waste baskets for 16,000 rubles with VAT 2000.
The purchase was paid for in the current month, so the transaction was displayed in the accounting documentation as follows:
- Dt10 Kt60: 14,000 rub. excluding VAT, goods received from the seller;
- Dt19 Kt60: 2,000 rub. VAT
- Dt68 subaccount “VAT calculations” Kt19 - 2,000 rubles. as a claimed VAT deduction from the cost;
- Dt60 Kt51: 16,000 rub. paid as payment for waste baskets.
To which account should stationery be attributed and how to take it into account?
The main one is 10, called “Materials”. Their appearance should be recorded as a debit on subaccount 10.09, but there are other options.
Regardless of the type of payment, the transactions should be entered in the following form:
| Procedures | Dt | CT | According to what |
| Office costs are paid | 60 | 51 | Documentation from the bank is attached |
| Everything is moved to storage areas | 10.09 | 60 | PKO f. M-4 or invoice from the supplier signed by MOL |
| VAT on the purchase of office supplies | 19 | 60 | SF from the supplying organization |
| Accounting for incoming VAT | 68 | 19 | |
| Processed by JSC | 60 | 71 | Advance documentation |
| Credited to CT | 10 | 60 | F. M-4 |
| Input VAT | 19 | 60 | Papers that confirm arrival |
| VAT included | 68 | 19 | A receipt showing VAT separately |
To which subaccount should I assign stationery and how to capitalize them later?
Organizations operate in two different ways:
- each item indicating price and quantity;
- a homogeneous group is isolated; as an example, different folders or writing instruments can be cited.
It is worth remembering that method 1 is more reliable; tax authorities have no questions about it. It is easy to use if you purchase a lot of office supplies, but it is sent to employees gradually, in small portions. Another advantage of the method is that you can calculate the need to ensure a normal workflow.
The main entries will be associated with accounts Dt 10 and Kt 60 and 71. There is no big difference in which sub-account everything is credited to, the main thing is to reflect your desire to conduct business in a certain way in the UP.
Examples of application of articles 310 KOSGU and 340 KOSGU in 2018-2019
Regarding the formation of 15-17 digits of account number 0 302 00 000 “Settlements for accepted obligations”, the provisions of Instructions NN 157n, 174n do not provide for any exceptions. Accordingly, when forming 1-17 digits of these accounts, the general procedure presented above is applied.
Institutions regularly have questions about what type of asset - materials or fixed assets - should one or another stationery be classified as.
An inventory card is maintained in the accounting department for each object or group of objects. In the case of group accounting, the card is filled out by positional records of individual fixed assets.
A trade organization purchased 10 calculators, the cost of each is 300 rubles, including VAT 50 rubles, and put them into operation.
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
We count the entire receipt as one piece
If this option was chosen, then everything is credited as 1 unit and will be written off the same way. To use this method, you need to issue an order, on its basis the office will be accepted and immediately left for needs.
In this case, the PKO is attached to a copy of the delivery note from the supplier, this will allow the receipt to be tracked if necessary.
To deregister, employees’ applications are attached to an invoice or other similar document.
Among the advantages is ease of use. But this method can provoke a lot of questions from the tax inspectorate.
Acceptance by quantity
This is another option that is not used as often. Here only the purchased volume will be counted, without names or forms. It will look like “Stationery, 15 pcs.” This is convenient, but can create issues due to the large difference in cost. For example, disposing of one chair will cost many times more than a ballpoint pen.
How to keep records without counting 10
In practice, sometimes accounting is carried out without “Materials”. Typically, this method is chosen when it is planned to immediately use CT for the needs of the company. And these expenses can be recorded as services as expenses. All this is recorded in accounting entries, where Dt is 25-26 and 44, and Kt is considered as 60 and 71.
If only small amounts are used in this algorithm, then the tax authorities will not have any questions. But if a lot of money is regularly spent on this and the article is often repeated, then such an error will provoke the interest of inspectors.
Difficulties may also arise if it is necessary to deduct the amount of input VAT, because the purchase was not accepted for accounting according to the rules.
Another difficulty is trying to track what exactly was spent and in which workshop or department. When checking, it will be very difficult to understand which employees are ordering too much, and which departments are purchasing too much and is costly and unjustified.
BASIS: VAT
Input VAT presented when purchasing stationery can be deducted if you have an invoice (clause 2 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The exception to this rule is when:
- the organization enjoys VAT exemption;
- The organization carries out only VAT-free transactions.
In these cases, include input VAT in the cost of stationery. This follows from paragraph 2 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
If an organization carries out both taxable and non-VAT-taxable operations, distribute the input tax on the cost of stationery (clauses 4 and 4.1 of Article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
How to document the purchase and use of office supplies
There are two options to purchase and arrive:
- piece by piece;
- homogeneous groups.
A predetermined method should be noted in the company's accounting policy and always adhered to.
When CT scans are transferred to the person responsible for the materials, a certain action has to be taken:
- draw up a special receipt order using the unified form No. M-4;
- On the invoice that arrived from the supplier, put a stamp where the name of the company, the date of receipt of the MC and the cash register number will be entered.
In the second case, the responsible employee must sign this document. The cost of goods used will be expenses according to PBU 10/99, that is, it is considered that these are ordinary activities of the organization.
When they are issued to employees, they are written off in accordance with the drawn up invoice requirement according to f. M-11.
To simplify work and increase efficiency, it is worth having appropriate programs that will facilitate the preparation of documentation. To make it easier to choose among the variety of software, we recommend contacting Cleverence. Our specialists will help you find the right software for your business that automates work processes by combining the work of accounting systems and equipment, for example, data collection terminals. So, for those who use 1C: Accounting there is a software product called “OS Inventory”.
Accounting
In accounting, consider stationery as part of the materials on account 10-9 “Inventory and household supplies.” Document the purchase of stationery and reflect it in accounting in the usual manner prescribed for materials. For more information about this, see How to reflect the receipt of materials in accounting.
Situation: is it necessary to include stationery products with a useful life exceeding 12 months in accounting as part of fixed assets? For example, scissors, calculators, etc.
Stationery, the cost of which does not exceed the limit established in the accounting policy, can be recorded on account 10 “Materials” and written off at a time when put into operation.
Assets that meet all the characteristics of fixed assets and the cost of which does not exceed 40,000 rubles can be taken into account as part of the inventory (clause 5 of PBU 6/01). If an organization decides to exercise such a right, it must record this in its accounting policies for accounting purposes. In this case, you need to select a specific limit on the cost of objects with a useful life of more than a year, which will be taken into account as inventory. When setting such a limit, please note that its amount cannot exceed 40,000 rubles. (clause 5 of PBU 6/01).
When releasing office supplies from the warehouse, simultaneously with drawing up a demand invoice in Form No. M-11 or an act (report), make the following entries:
Debit 23 (25, 26, 29, 44...) Credit 10-9
– the cost of consumed stationery is included in expenses.
This is stated in paragraphs 90, 93, 97 and 98 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n.
Write-off of stationery
All that remains is to figure out which accounting account to assign the spent office supplies to. Here it is worth remembering that this group of material assets is directly involved in the main activity. Therefore, you can write it off to your account. 26, which is responsible for general business expenses, and 44, which reflects sales costs.
When they are given to employees, they are taken from the warehouse. To do this, you need a demand invoice, which is filled out according to f. M-11. Another option is to use a standard form that the company developed specifically for this task, but in this case the document must be included in the accounting policy and always be used. It is imperative to indicate the cost of the CT scan as of the date on which the issuance took place.
In which accounting account should stationery items subject to write-off be reflected?
The accounting entry will look like this:
- Dt 26 or 44 - the amount is indicated for everything that was transferred for use.
The simplified version has a slightly different algorithm. They can legally write off all costs to standard and core activities immediately after acquisition. For this reason, they do not issue transfers to employees. All amounts will be recognized upon payment.
What the postings for writing off the office will look like - sample acts
If “stationery” was accounted for as production inventories, then the company has the right to completely remove them from the balance sheet when they are issued to the employee. There is no further control. This is formalized as Dt 91-94 and Kt 209.
As we have already said, if an item is issued from a warehouse, then form M-11 is filled out, which will become the basis for drawing up a write-off act. It can be written in any form, the main thing is that it is signed by MOL. It is also important to indicate all the names and costs of accessories.
The order in which CT will be written off
After we have figured out what account to include office supplies in, it is worth finding out how they are deregistered. When writing materials are transferred from the warehouse to responsible employees, it is necessary to complete the following paperwork:
- limit-fence card according to f. M-8;
- invoice-request M-11;
- invoice, which is drawn up in the interindustry form M-15.
Sometimes accounting includes refilling cartridges here, but this is the wrong approach. This is what pp. says. 2 from clause 1 in Article 254 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. These costs should be translated into material costs.
It remains to understand which accounting account to include the office that has served its purpose. First, a corresponding act is drawn up. It must include:
- consumption standard, if available;
- name and amount of costs;
- where everything was spent;
- price per piece and all items;
- additional information if required.
In accounting it will look like this:
| Dt | CT | Description | Base |
| 26 | 10.01 | Pens written off | Request-invoice |
What the documents will look like and who will sign them is established by internal regulations - instructions, orders, regulations.
How to work with VAT
We already know which accounting account to put office supplies into, but it is important to remember about taxation. Each company has the right to deduct all VAT charged to them by sellers. All this is done on the basis of pp. 1 and 2 tbsp. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Everything must be written down on a separate line in all settlement documents in accordance with Art. 168 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. The deduction occurs in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 172.
Tax applied to corporate profits
The cost of CT should be included in other expenses, this occurs on the day when they are transferred to employees for use, this is indicated in Article 264. Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
What do they pay under the simplified tax system?
Each company that operates according to this principle reduces its income by all incurred expenses specified in Art. 346. The office also belongs here if it complies with Article 264 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. VAT amounts are also included in costs, but they must be entered on a special line. Their cost is recognized as part of the amount spent after payment.
Cost estimation methods
Determine the cost at which office supplies are written off from account 10-9 in one of the following ways:
- at the cost of each unit of inventory;
- FIFO;
- at average cost.
This is stated in paragraph 58 of the Regulations on Accounting and Reporting and in paragraph 16 of PBU 5/01.
The method for estimating the cost of write-off office supplies should be established in the accounting policy for accounting purposes. Such rules are established by paragraph 73 of the Methodological Instructions, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 28, 2001 No. 119n.
Can I return it to the supplier?
It depends on the conditions under which they were purchased. It is important to determine in advance who bought and what is not suitable for CT. If the purchase was made privately by an individual for use, then the law “On the Protection of Consumer Rights” applies, which confirms the possibility of returning low-quality items or items that do not meet expectations.
But when registering such an operation by an enterprise, problems arise, since the Civil Code does not provide for the possibility of returning or changing quality goods. And the law that protects individuals has no effect on companies. We have to hope that the seller will meet you halfway.
We looked at what account office supplies go to, where to include their receipt, how to spend and write them off. This is a simple operation, but it raises questions and disputes among many specialists. We advise you to adhere to accounting by quantity in order to attract the interest of the tax authorities. This method will help you get rid of the difficulties with counting balances, controlling them and spending them.
In the video you can see how inventory is carried out in a warehouse using TSD and Warehouse 15 software from Cleverence.
Number of impressions: 15220