An important point: if an employee voluntarily works longer than expected, such overtime work is not recognized and is not paid additionally. The employer must involve the employee in working beyond the norm, having received written consent. And in this case, management is obliged to calculate overtime work. In addition, if an employee’s employment contract establishes an irregular working day, working beyond the allotted time is also not considered overtime. Workers with irregular schedules are entitled to another benefit - additional leave.
Involvement in work beyond established standards
First, let's look at the definition of overtime work itself. So, this term should be understood as work that an employee performs on the initiative of the employer in excess of the required working hours established by the length of the working day. This is exactly the wording given by Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Now let’s try to understand the basic principles of attracting employees to additional employment.
Who is entitled to compensation?
In general, any person involved in such activities can count on compensation for hours worked in excess of the required standard hours. At the same time, the legislator clearly establishes the nominal number of man-hours for such processing. In particular, overtime work is allowed no more than 4 hours for two days in a row.
With a total calculation of such time - no more than 120 hours annually. However, the length of the working day varies among employees, and this fact must be taken into account when calculating time worked. It looks like this:
- Standard working hours are 40 hours per week;
- For persons under the age of majority - 24-35 hours per week, depending on age;
- For disabled people of groups 1-2 - no more than 35 hours;
- Health workers, teachers working in the Far North - 36 hours.
It follows that any work performed in excess of the established standards is considered overtime and is paid according to the established tariffs.
Who cannot count on compensation
If you follow the letter of the law, one of the mandatory conditions for overtime work is the initiative of the employer. In particular, the employer may ask the employee to work extra, or involve him in work in case of emergency situations, for example, to eliminate an accident. At the same time, the law does not prohibit an employee from remaining at his workplace beyond the prescribed hours on his personal initiative.
However, in this case, the employer is not obliged to pay overtime hours, although he may somehow encourage a conscientious employee.
Who should not be left overtime?
Firstly, it is unacceptable for any employee to work overtime if the overtime limit has been reached. For example, if for 2 days in a row a person worked 4 hours overtime, it will no longer be possible to involve him in such work on the third day. However, many employers ignore this requirement. In such situations, the employee’s rights are violated, which gives him the right to appeal to the labor inspectorate with a complaint.
Read also: Medical examination in Moscow parks
Secondly, the law clearly defines the categories of citizens who cannot be used overtime under any circumstances. These include:
- Minors;
- Pregnant;
- Single parents with dependent children under 5 years of age;
- Parents raising a disabled child.
Citizens caring for disabled relatives can stay overtime, but only on condition that they voluntarily express their consent.
Calculation example for a shift schedule
Let's consider this example of calculating overtime for a shift schedule: Ivanov I.I. works in shift production. His salary is 30,000.00 rubles. The standard working time for him is a 40-hour week.
In April 2021, Ivanov I.I. worked 17 shifts of 11 hours (187 hours). According to the production calendar, in April 2021 there are 175 working hours for a 40-hour week. Ivanova I.I.’s unscheduled work hours — 12 hours
Salary for April 2021 for actual time worked = (30,000.00 / 175) × 187 = 32,057.41 rubles.
Cost of one hour worked = 30,000.00 / 175 = 171.43.
Excessive employment - 12 hours. The first 2 hours are paid at a factor of one and a half: 171.43 × 1.5 × 2 = 514.29 rubles.
The remaining 10 hours are indexed by a factor of 2: 171.43 × 2 × 10 = 3428.60 rubles.
Total for processed 12 hours Ivanov I.I. will receive 3942.89 rubles.
In total for April 2021, Ivanov I.I. need to pay: RUB 32,057.41. + 3942.89 rub. = 36,000.30 rub.
Do employees need consent to work overtime?
Work exceeding approved standards at the initiative of the employer and with the consent of the employee is possible in the following situations:
- It is necessary to complete a set of activities that could not be completed during the work shift. This usually applies to cases where unfinished work may result in damage to company property, damage commercial interests, or cause harm to the health and lives of people.
- Carrying out repair work. For example, if a faulty conveyor or assembly line causes a disruption in the entire enterprise.
- With continuous work. For example, if the line cannot be stopped and the shift worker does not show up for work. In this case, the boss cannot leave the employee for the second shift, but he has time to find a replacement.
Involvement in additional work without the employee’s consent is possible in cases where we are talking about emergency and unforeseen situations that can lead to serious consequences. For example:
- Prevention of industrial accidents;
- Elimination of failures of systems responsible for people’s life support: lighting, centralized water supply, traffic;
- Elimination of emergency consequences - flood, man-made disaster, fire, etc.
How is overtime calculated?
According to the established rules, the first two hours worked overtime are compensated at one and a half times the rate, the rest - at double rate.
Here it is necessary to clarify that these are minimum standards. An employer may, on his own initiative, increase overtime pay, but paying compensation below the established rates will be considered illegal. To calculate overtime pay, it is necessary to determine the employee's wage rate per hour. To do this, the monthly salary is divided by the number of hours worked.
Calculation of overtime and night
Let's start with the night ones. Night time is considered to be from 22 pm to 6 am. The calculation is performed using the formula:
D = CHO × RDN × CCH,
Where:
- D - amount of surcharge;
- CHO - hourly part of the salary;
- RDN - the amount of additional payment for night work (minimum 20% of the salary or hourly tariff rate, etc.);
- KH - the number of hours worked at night.
RDN cannot be less than 20%, since this is the minimum value established by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 22, 2008 No. 554. More may be, less - no. The specific size is established by the employer by its local regulations.
Now let's return to Petrov, who worked 11 shifts in February, and consider how overtime hours are calculated along with night hours.
Let's determine that half of Petrov's shift was at night (8 per day and 8 per night). We count the night.
The hourly part of the salary is 94.94 (see example about shift work (15,000 / 159)). Next, we multiply this figure by 20% (0.20) and by the amount of time worked at night - 88. We get 1,670 rubles 94 kopecks.
We calculate overtime similarly to the shift schedule (see example above), the amount of additional payment was 3133 rubles 02 kopecks.
Fold it up.
The salary for the time actually worked will be 16,603.77 rubles (176 × (15,000 / 159).
The extra charge for the night was 1,670 rubles 94 kopecks.
The overtime bonus amounted to 3133 rubles 02 kopecks.
Total 21,407 rubles 73 kopecks excluding income tax.
Example
Ivanov works as a mechanic and receives a salary according to the staffing table of 50,000 rubles. He worked 168 hours per month. To calculate the hourly wage, you need 50,000:168. As a result, Ivanov’s hourly salary for the billing period is 297 rubles.
Considering that the first 2 hours worked overtime are paid at one and a half times the rate, the following formula is applied: 297 * 1.5 * 2 = 891 rubles.
Ivanov will receive this amount for the first two hours of overtime.
All subsequent hours worked in excess of the norm will be paid at double the rate - 594 rubles / hour.
How to use the calculator
There are a total of five windows in the calculator in which you will need to enter the following data:
- the cost of one working hour - in the first field;
- hours and minutes worked within the first two hours at a factor of 1.5;
- hours and minutes worked within subsequent hours at a factor of 2.
Immediately after filling out each field, an intermediate answer will appear, to which, as new values are added, adjustments will be made until the calculation is completed.
Principles for calculating surcharges
As mentioned above, the minimum overtime rate is:
- The first 2 hours are paid time and a half;
- Subsequent time - double compensation.
It is from these coefficients that you need to start when calculating wages. In this case, the employer can set his own rate, securing it in a separate regulatory act for the enterprise, and certifying the document with a personal signature.
Situations where overtime work occurs on holidays or weekends deserve special attention. In this case, the employee’s work is regarded as work on a day off, and is paid in accordance with the established tariff, regardless of the length of time.
Important! According to current legislation, when calculating overtime, days falling on official weekends and national holidays are excluded.
Rules for registering overtime hours
Some employers make the mistake of including a clause regarding the employee's ability to work overtime in the collective agreement.
This approach directly contradicts the provisions of labor legislation. Read also: Gift tax in Russia
According to established standards, each case of such employment is processed individually; there can be no generalization here. At the same time, the law does not oblige the employer to issue a separate order for the enterprise for each fact of employee overtime. Although there must be a legal basis for engaging in labor beyond established standards. For example, the head of a structural unit must prepare a memo to the director, which sets out the reasons for attracting a certain employee to work overtime. This may be the need to complete work or the absence of a shift worker during continuous production. This right can be assigned to department heads by a clause in the job description.
The second mandatory point is the employee’s written consent to stay overtime. The only exception to this rule is emergency situations provided for in paragraph 3 of Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Moreover, if citizens of preferential categories are involved in overtime work, they must be warned about the possibility of refusing to perform such work. You can notify the employee orally or in writing.
In the time sheet, excess employment of personnel is indicated by the digital code 04 or the letter “C”. In this case, the document usually provides two columns for standard and overtime time.
Calculation of overtime with summarized recording of working time
According to Art. 104 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in cases where it is impossible to comply with the daily (8 hours in the general case) or weekly (40 hours) standard working time, it is permissible to introduce a summarized recording of working time in the organization. Working hours are counted not for a week, but for the period established by the organization. This could be a month, a quarter or a year. Such accounting is introduced so that the duration of working hours does not exceed the normal number of working hours in the entire allotted period. In this case, one week an employee may work more than normal, and the next week, on the contrary, less. The employer will evaluate the time worked after the end of the accounting period - month, year or quarter.
Summarized accounting is convenient for companies with a shift schedule, in which employees work every other day, two to two, or several shifts a day. With such accounting, overtime may also arise, for which it is necessary to calculate payment.
Additional payment for extracurricular work in the case of cumulative recording of working hours is made after the end of the accounting period. Let's look at how overtime is calculated using an example.
Options for receiving compensation
If an employee stays overtime, company management can compensate for this time in two ways. The first is a cash payment in one and a half or double amounts.
The second is the provision of additional days of rest. Here it is necessary to clarify that in this case, overtime work is still paid, but based on the amount of a single hourly earnings. The duration of the days off provided cannot be less than the time spent on overtime work. The procedure for compensation is achieved by mutual agreement. For example, an employer cannot refuse to accrue cash payments for overtime work, at its discretion replacing financial compensation with additional days off. Moreover, such rest days are necessarily reflected in the working time sheet and are not taken into account when calculating wages.
Stages
Let's consider the procedure for engaging in overtime work: what kind of work is classified as overtime and when it is allowed.
There are two main stages in attracting an employee to work overtime.
First stage:
It is important for the employer to remember that he is obliged to notify certain categories of employees by signature of the right to refuse such work. All verbal agreements with employees can lead to disputes. To avoid this, it is necessary to adhere to the position that all employee-employer agreements are documented. Therefore, the employer must:
- obtain the employee’s written consent;
- make sure there are no medical contraindications;
- notify employees under personal signature of the right to refuse to perform overtime work.
The employee notification does not have a special form, but contains information:
- Name;
- notification number and date of preparation;
- Full name and position of the specialist involved;
- the reasons why there was a need to be present at work overtime;
- the date when you need to work “extra” hours (you can specify a time interval);
- conditions - increased wages or compensation in the form of additional rest due to the employee.
The notice is signed by the head of the employing company. An employee can express his will by signing in the “Agree” or “Disagree” field.
A sample written consent to engage in overtime work can be viewed here.
Second phase:
The employer issues an order requiring overtime work and must familiarize the employee with it. The unified form of such an order has not been approved, so the employer draws it up in free form. The order must indicate:
- the reason for involving the employee in overtime work;
- work start date;
- surname, name, patronymic of the employee;
- his position and details of the document in which the employee agreed to be involved in such work.
This is also important to know:
Pre-holiday day for part-time work: duration of working hours and payment procedure
A sample order for overtime work can be found here.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
If a collective agreement or local regulation establishes the amount of additional payment, then it is possible to indicate this amount in the order. The amount may also be determined by agreement of the parties. The employee must be familiarized with the order and signed.
When inviting employees to work overtime, it is worth remembering that the duration of such work should not exceed four hours for each employee for two consecutive days and 120 hours per year. To do this, the employer is obliged to ensure accurate recording of the duration of overtime work for each employee.
In the working time sheet, overtime work is indicated either by the numbers “04”, and next to it the number of hours worked in excess of the norm is indicated. If standard daily records of hours worked are maintained for employees, on days of overtime work it is recommended to reflect separately standard and excess working hours in two lines. And if summarized accounting of working hours is used, overtime is reflected at the end of the accounting period.
Payment order
De jure, financial compensation for overtime work is not compensation in its pure form.
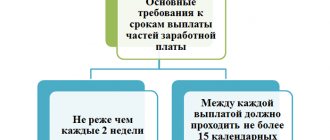
This is a component of wages, so employees receive money for overtime on payday, along with salary, bonus payments and other monetary incentives. Currently, wages at enterprises are paid at least 2 times a month; the employer decides which of these parts includes payment for overtime hours. It should be noted that management may refuse to pay overtime. The reasons for this may be the following:
- The employee stayed late at work on his own initiative;
- The employee agreed to be provided with additional rest time;
- The work was carried out on a day off;
- The employee agreed to work overtime, but without completing the assigned tasks, he left the enterprise without permission.
Read also: Where you can grill kebabs