Account 84 Retained earnings (uncovered loss)
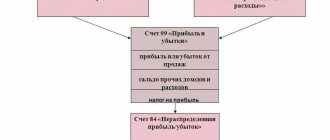
During the reporting year, the financial result of the organization’s activities (profit or loss) is reflected in account 99 “Profits and losses”.
On December 31 of each year, when reforming the balance sheet, the amount of net profit (loss) received is written off from account 99 to account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss).”
For the convenience of accounting for the use of profits, sub-accounts are opened for account 84:
- “Profit to be distributed”;
- "Retained earnings";
- "Uncovered loss."
Profit received at the end of the reporting year is reflected in the credit of account 84:
Debit 99 Credit 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” - reflects the net profit of the reporting year.
The loss identified at the end of the reporting year is reflected in the debit of account 84:
Debit 84 subaccount “Uncovered loss” Credit 99 - reflects the net uncovered loss of the reporting year.
Check procedure
An NU audit includes the following stages:
- Preparatory. It consists of reconciling analytical and synthetic accounting materials. In the accounting system, the indicators of analytical account 22 must coincide with the figures recorded in account 84 of synthetic accounting. In the general ledger, it is necessary to check the consistency of the total turnover indicators and the balance of account 84.
- At the main stage, auditors must make sure that the final balance of account 84 of the past period is equal to the similar indicators of the controlled year (at its beginning). The identity of the accounting values at the beginning and end of the period and the indicators of synthetic and analytical accounting of NU is checked. Inspectors also control the order of occurrence and accounting of losses.
Consequently, the final performance indicators of an economic entity are considered as NI. To reflect it, the same account is used as for IR.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Use of profits
The decision on the distribution of net profit is made by the owners (founders) of the organization at the general meeting of shareholders (in a JSC) or the general meeting of participants (in an LLC). This decision is usually made at the beginning of the year following the reporting period.
The distribution of net profit is within the exclusive competence of the general meeting of participants (shareholders) and cannot be carried out by the sole direction (order) of the head of the organization.
The meeting of shareholders (participants) of the organization may decide not to distribute the profit received at all (or leave some part of it undistributed).
Net profit can be used for:
- payment of dividends to shareholders (participants) of the organization;
- creation and replenishment of reserve capital;
- repayment of losses from previous years.
In the first two cases, the use of net profit is reflected in the debit of account 84:
Debit 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” Credit 75 (70) – dividends accrued to shareholders (participants) of the organization;
Debit 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” Credit 82 – net profit was directed to the creation and replenishment of the organization’s reserve capital.
If the owners of the organization decided to use the net profit to pay off losses of previous years, an entry is made in the accounting for the subaccounts of account 84:
Debit 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” Credit 84 subaccount “Uncovered loss” - net profit is aimed at paying off losses of previous years.
After you have recorded the use of profits (repayment of losses), the balance in the “Profit to be distributed” subaccount of account 84 shows the amount of retained earnings. This amount can be transferred to the appropriate subaccount:
Debit 84 subaccount “Profit subject to distribution” Credit 84 subaccount “Retained earnings” - reflects the amount of the organization’s retained earnings.
Accounting entries used
The use of entries depends on the methods used to reduce capital. Let's look at the transactions used as part of the mandatory reduction:
- DT 80 CT 81 . Applies in case of failure to pay the share.
- DT 80 CT 84. Applicable when the amount of the capital exceeds the size of net assets. By reducing capital, existing losses are closed.
When reducing the capital on the initiative of the enterprise, the following entries are used:
- DT 80 CT 75 . The posting is relevant when the founder leaves the company and withdraws his share.
- DT 81 CT 75, 50-52 , DT 80 CT 81 . It is used when repurchasing a share, canceling a withdrawn share, resulting in a decrease in capital.
- DT 80 CT 91. The reduction is carried out by reducing the nominal value. In this case, the difference remains with the company in the form of income.
- DT 80 CT 75. The par value is reduced, and the difference is paid to the participants in the form of income.
- DT 75 CT 91. The participant refused to receive the difference from the reduction in the nominal value. It is transferred to the organization's income.
Postings allow you to reflect all transactions carried out by the organization.
Uncovered loss
The decision on how to pay off the resulting loss is also made by the owners (founders) of the organization (general meeting of shareholders or meeting of participants in an LLC).
The loss can be repaid through:
- targeted contributions from shareholders (participants) of the organization;
- reserve capital funds;
- funds of retained earnings from previous years.
In the first two cases, entries are made to the credit of account 84:
Debit 75 (70) Credit 84 sub-account “Uncovered loss” - targeted contributions from the organization’s shareholders (participants) were sent to repay the loss.
Debit 82 Credit 84 subaccount “Uncovered loss” - reserve capital funds were used to repay the loss.
If the owners of the organization decided to pay off the loss using retained earnings from previous years, an entry is made in the accounting to the subaccounts of account 84:
Debit 84 subaccount “Retained earnings” Credit 84 subaccount “Uncovered loss” - retained earnings from previous years are used to repay the loss.
The loss can also be written off from the balance sheet if the general meeting decides to reduce the authorized capital to the amount of the organization’s net assets.
After the corresponding changes in the constituent documents have been registered, make the following entry:
Debit 80 Credit 84 subaccount “Uncovered loss” - the authorized capital is reduced to the amount of the organization’s net assets.
Size and composition of authorized capital
Authorized capital is a prerequisite for the following types of companies:
- A limited liability company, where the minimum size of this fund is 10 thousand rubles.
- A national enterprise (over 75% of shares are owned by company employees), the minimum amount of authorized capital is equal to one minimum wage established on the day the company opened and multiplied by a thousand.
- Public joint stock company, minimum capital is 100 thousand rubles.
- Non-public joint-stock company, the minimum amount of the authorized capital is 10 thousand rubles.
There are a number of entrepreneurial categories for which a different lower threshold of starting capital is defined:
- private security – 100,000 rubles;
- betting and gambling – RUB 100,000,000;
- founders of banks - 300,000,000 rubles;
- non-banking financial companies (depending on the license) – 90,000,000 – 180,000,000 rubles;
- companies providing health insurance services – 60,000,000 rubles;
- other types of insurers - 120,000,000 rubles, multiplied by the coefficient of the specific insurance sector;
- producers of strong alcohol – 80,000,000 rubles;
Also, different regions have their own characteristics of the size of the management company; they are established by local legislative acts.
The law does not set a maximum limit for start-up capital, so the founders themselves can choose the size of a large authorized capital. But do not forget that this indicator must be indicated in the constituent documents.
If a company is declared bankrupt, debts are closed in an amount corresponding to the company's charter capital. This is important to understand when talking about the positive and negative aspects of a large authorized capital.
What values can be included in the authorized capital? The minimum amount fixed by law is paid exclusively in cash (Clause 2 of Article 66.2 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Anything above this size may be entered differently. So, in addition to money, part of the contribution can be:
- material values;
- securities;
- property rights that can be valued in money.
Attention! A patent or other object of intellectual property cannot become part of the authorized capital (according to the resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 1, 1996 No. 6/8). The right to use an object of copyright, registered in accordance with all the requirements of the law, is considered a property right, which means it is allowed to be included in the Criminal Code.
Instructions 84 count
Instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations in accordance with Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000:
Account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” is intended to summarize information about the presence and movement of amounts of retained earnings or uncovered losses of the organization.
The amount of net profit of the reporting year is written off with the final turnover of December to the credit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” in correspondence with account 99 “Profits and losses”.
The amount of the net loss of the reporting year is written off with the final turnover of December to the debit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” in correspondence with account 99 “Profits and losses”.
The direction of part of the profit of the reporting year to pay income to the founders (participants) of the organization based on the results of approval of the annual financial statements is reflected in the debit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” and the credit of accounts 75 “Settlements with founders” and 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” " A similar entry is made when paying interim income.
The write-off of the loss of the reporting year from the balance sheet is reflected in the credit of account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” in correspondence with accounts: 80 “Authorized capital” - when the amount of the authorized capital reaches the value of the organization’s net assets; 82 “Reserve capital” - when funds from reserve capital are used to pay off losses; 75 “Settlements with founders” - when repaying the loss of a simple partnership at the expense of targeted contributions of its participants, etc.
Analytical accounting for account 84 “Retained earnings (uncovered loss)” is organized in such a way as to ensure the generation of information on the areas of use of funds. At the same time, in analytical accounting, funds of retained earnings used as financial support for the production development of the organization and other similar activities for the acquisition (creation) of new property and not yet used can be divided.
Alternative measures
It is possible that after writing off the loss, the financial picture will improve. However, there are several legal ways to pay income to the founder if there is no profit.
"Surcharge"
If the founder is an employee of his own company, he can receive his income in the form of an increased (compared to the usual “rates”) salary (do not forget to draw up a staffing table).
The amount of the “surcharge” will reduce income tax. From the point of view of salary taxes, it needs to be subject to all of them in full. This will also reduce taxes.
The founder-employee will have to pay personal income tax at a rate of 13% (it is the same for salary and dividends). Of course, from paying income to the founder in the form of additional wages, the company will suffer significant losses in the form of “real” money.
"Present"
You can choose the option with a gift. Whom to reward and in what amount is a matter for the company. The main thing is that it is not often and in accordance with a written gift agreement. Remember: giving money is not prohibited. The amount of the gift cannot be included as expenses, but insurance premiums do not need to be charged. The main thing is to check whether the issuance of gifts is provided for in the employment or collective agreement. If provided, then they are part of the remuneration. This means that insurance premiums will have to be calculated, even if there is a written gift agreement.
As for personal income tax on a gift, it will have to be withheld from an amount exceeding 4,000 rubles - in accordance with the general procedure. In general, be careful - there are quite a lot of nuances associated with the “gift issue”.
Gifts can be presented on the occasion of a specific event (birthday, wedding, New Year, other public or professional holiday) or for no reason.
According to the gift agreement, the donor (clause 1 of Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation):
- transfers or undertakes to transfer ownership of an item (including money and gift certificates) to the donee free of charge;
- transfers free of charge or undertakes to transfer to the donee a property right (claim) to himself or to a third party
- releases or undertakes to release the donee from a property obligation to himself or to a third party.
To avoid the need to charge and pay insurance premiums on the value of the gift, the fact of its transfer must be properly documented. The agreement for the donation of movable property must be concluded in writing in the case where the donor is a legal entity and the value of the gift exceeds 3,000 rubles (clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Companies can give gifts only to individuals, for example, employees (including former employees), clients, and employees of counterparties.
If a gift agreement is concluded when transferring a gift, you will not have to pay contributions on its value (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 4, 2017 No. 03-15-06/80448, letter of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated September 22, 2015 No. 17-3/B-473). In this case, the object of taxation by insurance premiums does not arise regardless of the value of the gift.
Payments made under civil law contracts, the subject of which is the transfer of ownership or other proprietary rights to property, are not subject to insurance premiums. Such agreements include a gift agreement (Article 572 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, gifts formalized by a gift agreement are not included in the base subject to insurance contributions (Part 4 of Article 420 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
note
If the available sources to repay the uncovered loss of the reporting year are not enough, the uncovered loss is left on the balance sheet. However, an organization that has suffered a loss at the end of the year should pay special attention to the value of its net assets.
Officials also note that the donation agreement for movable property must be made in writing in the case where the donor is a legal entity and the value of the gift exceeds 3,000 rubles (Clause 2 of Article 574 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Does this mean that if the value of the gift is less than 3,000 rubles, such an agreement can be concluded orally and insurance premiums do not need to be charged on its value?
We will find the answer in letters from the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated March 5, 2010 No. 473-19 and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation dated September 29, 2010 No. 30-21/10260. It says that the object of taxation by insurance premiums does not arise if the gift agreement is concluded in writing, regardless of the value of the gift.
In addition, if the issuance of gifts is provided for in the employment or collective agreement, then they are part of the remuneration. This means that the cost of gifts must be included in the calculation base for calculating insurance premiums.
The courts do not have a uniform approach to the situation.
Loan day
Now consider the option of an interest-free or low-interest loan from the company. This method has its negative sides. Firstly, the recipient’s income will be savings on interest - the so-called material benefit. It is determined on the last day of each calendar month and is subject to personal income tax at a rate of 35%.
If an employee receives a loan from an organization, then a material benefit arises provided that he pays interest for the use of funds at a rate that is lower than 2/3 of the refinancing rate (key rate) of the Bank of Russia (for loans issued in rubles) or 9% per annum (for loans issued in foreign currency). The rate of personal income tax levied on amounts of material benefits at preferential interest, as already mentioned, is 35%.
The tax is imposed on the difference between the amount of interest calculated based on 2/3 of the refinancing rate (key rate) of the Bank of Russia (for ruble loans) on the date of actual receipt of income or 9% per annum (for foreign currency loans), and the amount of interest that a person must pay on loan according to the agreement. The date of actual receipt of income in the form of material benefits from savings on interest is determined as the last day of each month during the period for which borrowed (credit) funds were provided (subclause 7, clause 1, article 223 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Let us recall that previously, until January 1, 2021, income in the form of material benefits on loans was determined on the day of payment of interest on the borrowed funds received.
Please note: the company must withhold and pay tax on income from material benefits.
To determine the amount of material benefit, the accountant must:
- calculate the amount of interest on borrowed funds based on 2/3 of the refinancing rate (key rate) of the Bank of Russia (for loans issued in rubles) on the date of actual receipt of income or 9% per annum (for loans issued in foreign currency);
- deduct from the amount of interest determined based on 2/3 of the refinancing rate (key rate) of the Bank of Russia (for loans issued in rubles) on the date of actual receipt of income or 9% per annum (for loans issued in foreign currency), the amount of interest that should repay the employee's loan.
The amount of interest is calculated based on 2/3 of the refinancing rate (key rate) of the Bank of Russia (for loans issued in rubles) on the date of actual receipt of income according to the formula.
Formula for calculating the amount of interest on loans in rubles
The amount of interest is calculated based on 9% per annum (for loans issued in foreign currency) according to the formula.
Formula for calculating the amount of interest on loans in foreign currency
Income in the form of material benefits when using an interest-free loan arises as long as the borrower uses the loan provided to him.
When using a loan received for the construction or purchase of housing, tax is not withheld, even if the interest on it is below 2/3 of the current refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. The right to tax exemption must be confirmed by a notification from the tax office, since it is associated with a property deduction (clause 1 of Article 220 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
If the company forgives the borrower's debt, income in the form of material benefits no longer arises. The former borrower acquires the right to dispose of all the money received (or the outstanding part) at his own discretion, that is, he already receives economic benefits. Such income is also subject to personal income tax. The amount of the forgiven debt (gift) is the taxpayer’s income, subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13% (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 15, 2014 No. 03-04-06/34520).
Please note: the tax accrued on material benefits is not excessively withheld and does not need to be returned (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 10, 2018 No. 03-04-05/310).
Finally, the loan will have to be repaid sooner or later. If the return was not expected, and the company forgives the borrower’s debt, there will be no income in the form of material benefits. But income will appear in the form of economic benefit, and such income - this will be a non-repaid loan - is subject to personal income tax at a rate of 13%. The date of receipt of income upon debt forgiveness is the date the debt is written off from the organization’s balance sheet. This date can be delayed if the borrower confirms his debt from time to time and extends the statute of limitations.
When writing off a loan debt, there is no need to pay insurance premiums, since in this case there is no taxable object. There is another method, but it is safe to use if there are several founders and you just need to come up with an additional form of payment for them, and the founders themselves are not against providing financial assistance to the company . The main thing is that everyone’s share in the authorized capital is less than 25%.
The founder, whose share is less than 25%, provides the company with a loan at a very high interest rate. He will receive his income in the form of this percentage and pay personal income tax on it at a rate of 13%. There is no need to accrue contributions, because in this case, just like in the previous one, there is no object of taxation.
And the company will have accountable expenses. There is virtually no risk of negative consequences. The inspectorate cannot control prices when the transaction does not relate to controlled transactions between related parties (Article 105.14 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Interdependence is determined by the authority to appoint the company's management, official subordination, and family ties. And one of the cases of recognizing persons as interdependent is their participation in the authorized capital of another person, if the share of direct or indirect participation is more than 25%. In our case, the share is less than 25%.
There are no specific accounting features or restrictions on the amount of interest on debt obligations on transactions between related parties if such transactions are not recognized as controlled.
You can establish the “needed” percentage to be paid by comparing the financial result without it and the acceptable (or desired) financial result taking it into account.
Sergey Danilov,
PB correspondent
Partner news
Deadlines for submitting reports for 2021
On what days is it correct to pay wages: clarifications from the Ministry of Labor
Again about waybills: clarifications from the Ministry of Transport
Primary documents: we prepare them correctly
When can you refuse to use PSN?
Children's camps are required to register by June 1, 2021. Everyone will be counted
Property tax news: don't miss it!
The Pension Fund has clarified the mechanism for paying pensions to working pensioners
Typical postings for account 84
By debit of the account
| Business transactions | Debit | Credit |
| Expenses were paid from retained earnings (by decision of the founders of the organization) | 84 | 51 |
| Expenses were paid from retained earnings from a foreign currency account (by decision of the founders of the organization) | 84 | 52 |
| Expenses were paid from retained earnings from a special bank account (by decision of the founders of the organization) | 84 | 55 |
| Dividends (income) are accrued to the founders (participants) who are employees of the organization | 84 | 70 |
| Dividends (income) accrued to the founders (participants) of the organization | 84 | 75-2 |
| Income accrued to the participants of the simple partnership (on a separate balance sheet of the joint activity) | 84 | 75-2 |
| Net profit is aimed at covering the loss from the activities of the branch, allocated to a separate balance sheet (posting in the accounting of the head office of the organization) | 84 | 79-2 |
| Net profit is aimed at covering losses of the head office of the organization (posting in the branch accounting) | 84 | 79-2 |
| The authorized capital was increased due to net profit | 84 | 80 |
| Reserve capital has been formed (increased) at the expense of net profit | 84 | 82 |
| Aimed at forming (increasing) additional capital and net profit | 84 | 83 |
| Subaccounts reflect the use of net profit for production development | 84 | 84 |
| The loss of previous years was repaid at the expense of net profit (posting to subaccounts) | 84 | 84 |
| The loss of the reporting year during the balance sheet reformation is reflected | 84 | 99 |
By account credit
| Business transactions | Debit | Credit |
| The loss is covered by targeted contributions from employees | 73 | 84 |
| The loss is covered by targeted contributions from the founders (participants) of the organization | 75 | 84 |
| The share of net profit due to a separate division of the organization is reflected (posting in the accounting of the head office of the organization) | 79-2 | 84 |
| The authorized capital is reduced to the amount of net assets (after amendments to the constituent documents) | 80 | 84 |
| Reserve capital used to cover losses | 82 | 84 |
| Additional capital is written off upon disposal of fixed assets that were revalued | 83 | 84 |
| Additional capital used to pay off losses | 83 | 84 |
| The net profit of the reporting year is reflected during the balance sheet reformation | 99 | 84 |
What can influence the indicator
The NU indicator, like the NP amount, may change over the year. The magnitude of the indicators depends on the management decisions made.
Table 2. Actions that may cause an increase or decrease in losses.
| Downgrade of the company's indicator | Increase in company indicator |
| If the indicators of net assets and authorized capital are equalized by reducing the amount of the latter | If the NP, by agreement of the management, was transferred to the reserve fund |
| If, based on the results of the revaluation of retired non-current assets in the current year, which increased additional capital, a decision was made to redistribute it to losses | When profits are used to increase the amount of authorized capital |
| By the amount of net profit for the reporting period | When calculating and paying dividends |
| If there are dividends that were declared but not claimed before the end of the limitation period | If there is a net loss in the reporting period |
Reflection in accounting on video: