An order for placing fixed assets on the balance sheet is one of the company’s basic documents, which ensures the commissioning of its property. When carrying out business activities, an enterprise needs transport, personal computers, equipment, etc. It is not enough to purchase all these things; they must be correctly reflected in the company’s accounting records.
- Form and sample
- Free download
- Online viewing
- Expert tested
FILES
What applies to fixed assets
Fixed assets include property objects that are used for the production of goods, services, work, and management. Also included in this subgroup are used assets, assets in reserve, leased or under conservation. Also included in this subgroup in accounting are items of property whose operating period is more than 12 months.
In addition, funds that fall into the OS group must comply with the following standards:
The facilities are operated for the production and management needs of the enterprise, or are leased out.- The property was not acquired for the purpose of subsequent resale.
- The facility is capable of generating profit for the organization.
Thus, the OS subgroup includes buildings, structures, production equipment, machinery, computer equipment, household equipment, breeding livestock, perennial forest plantings, etc.
There is also another important criterion - cost.
PBU states that property can be regarded as fixed assets when its acquisition price is more than 40 thousand rubles. At the same time, in NU the cost of an object classified as fixed assets should be from 100 thousand rubles.
What to do when fixed assets are purchased in installments?
The cost of property purchased in installments can be written off as an expense as it is paid. But it is impossible to take into account the amount paid immediately in the current quarter - it must be divided among the remaining reporting periods until the end of the year. That is, proceed by analogy with what you would do if you took into account the completely obtained OS. If the debt cannot be repaid by the end of the year, then the unpaid portions are transferred to the next year and are taken into account in the same manner.
Let's look at this algorithm using examples.
Example 8.
On September 2, 2021, the organization purchased in installments, accepted for accounting and began to use in its activities a boat worth 3,600,000 rubles, paying the seller 600,000 rubles. According to the terms of the agreement, the organization must repay the debt in the amount of 600,000 rubles quarterly. Let's consider how much the cost of purchasing a boat will be taken into account in expenses.
On September 30, 2021, expenses include half of the paid amount of 600,000 rubles / 2 = 300,000 rubles. The remaining half is taken into account in expenses on December 31, 2021. In addition, in the 4th quarter of 2020, the organization will transfer another 600,000 rubles, which should also be taken into account in expenses. As a result, on December 31, 2021, the organization will reflect 300,000 rubles in expenses. + 600,000 rub. = 900,000 rub.
In 2021, the organization will transfer 600,000 rubles to the boat seller quarterly.
600,000 rubles paid in the 1st quarter will be attributed to expenses in equal shares - 150,000 rubles each = 600,000 rubles. /4, the last numbers of four reporting dates: March 31, June 30, September 30 and December 31.
600,000 rubles paid in the 2nd quarter will be expensed in equal shares of 600,000 rubles. / 3 = 200,000 rub. the last numbers of three reporting dates: June 30, September 30 and December 31.
600,000 rubles paid in the 3rd quarter will be expensed in equal shares of 600,000 rubles / 2 = 300,000 rubles. the last numbers of two reporting dates: September 30 and December 31.
600,000 rubles paid in the 4th quarter will be expensed as a lump sum on December 31.
As a result, in 2021 expenses take into account:
March 31: 150,000 rubles
June 30: 150,000 + 200,000 = 350,000 rubles
September 30: 150,000 + 200,000 + 300,000 = 650,000 rubles
December 31: 150,000 +200,000 + 300,000 + 600,000 = 1,250,000 rubles
What is an inventory object
The acquired property must be defined as fixed assets; this process implies:
- registration
- assignment to the depreciation group in accordance with the regulations
If an object is a complex of several objects or devices, then difficulties may arise. For example, a building or structure is classified as an inventory object. The definition states that an inventory object is a completed device, object or complex of objects, which includes all the devices and devices that belong to it for the purpose of performing its intended functions.
It is possible to determine what exactly belongs to the object as an integral part using documentation, technical certificates, etc.
Inventory objects can be simple or complex, that is, consisting of more than one item. In addition, they are registered with the enterprise and assigned an inventory number.
Organizational and administrative documents
One of the key documents ensuring the commissioning of property is an order for registration of a fixed asset. Normative acts do not provide for a unified form of such an order. However, there is a list of information that must be present in this document. Among them:
- Name of the enterprise.
- Title of the document.
- Date of preparation.
- Reason for publication.
- Description of the object to be capitalized.
- An indication that the property is taken into account as part of the operating system.
- Determination of useful life and initial cost.
- Inventory number of the object. It is indicated in a special card generated for each operating system or group of funds.
- The group or category into which the property is included.
- Full name of the employee responsible for the safety of the OS.
- The room/workshop where the asset will be located.
- Signature of the manager or other authorized employee.
- Signature of the financially responsible employee.
An order can be drawn up by a specialist in the accounting or legal department, as well as an assistant manager.
An attachment to the order is the acceptance certificate.
Receipt of fixed assets
OS is delivered to the enterprise using different methods. The norms for determining the initial cost of property and the accounting operations carried out in accounting depend on them.
OS are registered with the organization in the following ways:
for funds upon purchase- as a result of construction
- under a gratuitous donation agreement
- as a share in the contribution to the management company
- under barter agreements and others
Regardless of the methods of receipt of fixed assets on the balance sheet of the enterprise, an entry is made in accounting to the debit of account 08. Next, the object should be put into operation, this happens from account 08 to account 01. Synthetic accounting of fixed assets occurs on account 01.
Free OS receipt
When purchasing property under a gift agreement, the initial cost is taken to be the market price of the property existing on the date of registration of the fixed asset. In this case, make a record:
- Dt sch. 08 Kt sch. 98.
Please note that income from future periods will be included in other income as depreciation payments are calculated:
- Dt sch. 98 Kt. 91 (subaccount “Other income”).
For example, the company was given a machine free of charge, the use of which is expected in the main production. The market value of the equipment is RUB 218,300. The useful life of the machine is 37 months. Depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method. The table shows the entries made by the accountant.
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount in rubles |
| Receiving the machine | 08 | 98 | 218300 |
| Acceptance for accounting as part of OS | 01 | 08 | |
| Calculation of monthly depreciation | 20 | 02 | 218300 / 37 = 5900 |
| Recognition of a portion of future period revenues as income in the current period | 98 | 91 | 5900 |
Receipt of fixed assets as a contribution to the authorized capital
Fixed assets received on the company's balance sheet as a contribution to the capital are accounted for at their original cost. This is recognized as an official independent assessment of objects, confirmed by the participants in the protocol.
The size of the authorized capital can be determined by the balance on account 80; it must be identical to the information specified in the constituent documentation.
When the participants of the company decide to increase the size of the capital company with their own additional contributions, it is formalized by postings Dt 71/1 Kt 80.
When an asset is received in accounting, the following operation is carried out: Dt 08 Kt 75.
Receipt of additional expenses into the operating system
The initial cost of the purchased OS is formed not only from the price set by the seller, but also from other costs associated with installation work, transportation, and so on. Accordingly, it is necessary to consider a couple of documents:
- Receipt of additional expenses;
- Transfer of equipment for installation
They are accessed from the “OS and intangible assets” section. In the header you must enter information about the organization and the counterparty. In the tabular part of the document, through the “Main” tab, it is necessary to reflect the additional costs incurred, if any.
Through the “Goods” tab, the fixed asset itself accepted for accounting is indicated.
Formation of initial cost
The initial cost is formed based on the estimated cost of the operating system. It is according to this that the object is accepted for accounting. The norms for the formation of the initial cost depend on the order in which the object is entered onto the balance sheet of the enterprise.
Thus, the object is registered by the organization at a cost that is formed from the actual expenses for purchase, construction, and release minus VAT. When receiving fixed assets free of charge, its initial price is set at the current market price on the date of acceptance for accounting.
Reference
To register the acquisition of future fixed assets in the 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 configurations, two methods are available:
- quantitative nomenclature accounting
- individual accounting of objects
Quantitative nomenclature accounting
Quantitative accounting is supported using elements of the Nomenclature directory on account 08.04.1 “Components of fixed assets” (not to be confused with equipment for installation, which is accounted for on account 07 “Equipment for installation”). In this case, the use of all demand fulfillment procedures (for example, orders to suppliers) is available. All movements are performed according to the rules of quantitative movement of items.
This method is advisable to use in the case when receipt transactions are processed by supply service employees. Accounting account 08.04.1 “Components of fixed assets” is set for the financial accounting group of the item to which the incoming items belong, on the Own item tab in the Setting up reflection of documents in regulated accounting workplace.
Direct commissioning of fixed assets from account 08.04.1 “Components of fixed assets” is not provided.
To form the initial cost of fixed assets, account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is used. The transfer of components to a future fixed asset item is carried out using the documents Internal consumption of goods with the transaction type Write-off to expenses/assets. Corresponding account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is specified by the totality of the expense item and the recipient department (in which the object will be accepted for accounting) on the Expenses tab in the Setting up reflection of documents in regulated accounting workplace. In operations, an expense item is used with the distribution option For non-current assets and the type of analytics Fixed assets, but if an asset item is used when writing off an item, then account 08.04.2 is indicated directly in the document.
Individual accounting of objects
It is possible to register a future fixed asset as a unique (without quantitative accounting) inventory item from the Fixed Assets directory. The initial cost is immediately formed on account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning”.
This option is convenient for use in cases where the receipt is registered by an accountant for fixed assets. It allows you to eliminate the entry of unnecessary data into the Nomenclature list. Receipts are documented in the documents Receipt of services and other assets. The targeted allocation of the cost of an incoming object to the initial cost of a fixed asset is determined by using an expense item with the distribution option For non-current assets and the type of analytics Fixed assets, which is indicated in the rows of the tabular part of the documents for the Purchase of services and other assets.
Corresponding account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is set for the totality of the expense item and the recipient department (in which the object will be accepted for accounting) on the Expenses tab in the Setting up reflection of documents in regulated accounting workplace. Account 08.04.2 “Preparation for commissioning” is also used in the case of creating a fixed asset object using the enterprise’s own resources.
General scheme of options for accepting a fixed asset for accounting after the formation of the initial cost:
As it was in 1C: KA 1.1 and 1C: UPP 1.3
In configurations 1C: KA 1.1 and 1C: UPP 1.3, in order to reflect the purchase of both low-value and expensive operating systems, it was necessary to credit everything to account 08.04 and take into account all fixed assets regardless of cost. And fixed assets that require configuration should first be accounted for in account 10, and then written off with the document Request-invoice to account 08.04 to form the initial cost and then taken into account
Let's look at the example of individual accounting of objects in the 1C:KA 2 configuration - the receipt of fixed assets, with subsequent acceptance for accounting and depreciation.
Master data setup and administration
Before completing the purchase of a fixed asset, you first need to set up our program so that it is possible to maintain non-current assets. To do this, go to the master data and administration section - Setting up master data and sections - Non-current assets
Default Accounting for non-current assets
disabled. Therefore, in order to correctly reflect the purchase of the OS, this option must be enabled.
In the example under consideration, the accounting parameters for non-current assets use version 2.2
Purchase of fixed assets
As was the case in 1C:KA 1.1 and 1C:UPP 1.3
In the configurations 1C:UPP 1.3, 1C:KA 1.1, to reflect the purchase of the OS, it was initially necessary to fill out the document Receipt of goods and services; in these configurations, this document does not need to be filled out.
There is an analogue here - Purchasing services and other assets
. The document is located in the section panel Regulated accounting - Fixed assets - Documents on fixed assets - Purchase of services and other assets.
The document looks like this
the Expenses and other assets tab
Important:
in order to include the cost of an incoming object as part of the initial cost of a fixed asset, it is necessary to indicate in the rows of the tabular part of the documents for the Purchase of Services and Other Assets the use of an expense item with the distribution option To non-current assets and the type of analytics Fixed Assets.
Also, in order for the program to understand that this is an OS object, it is necessary to indicate the Accounting account in the reg. on the Regulated Accounting and MFP tab. accounting, set the account 08.04.2
As it was in 1C:KA 1.1 and 1C:UPP 1.3
One of the obvious differences between 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 from previous configurations: when filling out the OS receipt document, you do not need to select the type of operation - Equipment.
Go to the Additional tab. This is a required field to fill in - Division, please indicate it.
Next, when we have filled out everything necessary, we submit the document. Now let's see what transactions the document made, click
We see that the program does not automatically make entries according to regulated accounting, to view preliminary entries
you must click More - Reflect in accounting when opening
Click Reflect in Reg. accounting
Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting
We move on to accepting the OS for accounting in the 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 programs. For this, as with the configurations of the previous generation, the document Acceptance for accounting of OS is used. It is located in the section Regulated accounting - OS documents - Acceptance for accounting of assets - Create.
Fill out the form
On the Main tab
- division in which the object is registered
- OS group
- depreciation group
On the Depreciation tab
- depreciation method
- useful life
On the Expense Reflection tab
— indicate the expense item for depreciation
In the expense item on the Regulated accounting and MFI tab, you must indicate the account for reflecting depreciation expenses
On the Fixed assets tab - select our fixed asset
The OS card in 1C:ERP and 1C:KA 2 is called Operation Objects.
We carry out the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets. Let's look at the wiring
Determination of service life
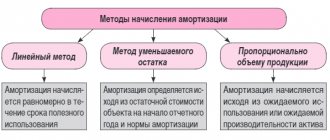
The service life or useful life (SPI) is the most important factor necessary for calculating income and property taxes. SPI is the period during which the operating system serves the company. The amount of write-offs for depreciation depends on it.
The SPI is determined taking into account the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and the Classifier approved by the Government.
If it happens that a specific OS is not in the classifier, then it is necessary to determine the SPI for it, focusing on the technical data in the documents from the manufacturer. The enterprise has the right to increase the SPI if modernization or reconstruction was carried out for this purpose. In this case, it is not allowed to change the depreciation group.
By purchasing a used OS, a company can determine for itself its SPI according to the classifier, lowering it for the period of use by the former owner. Or you can take the SPI, which was determined by the previous owner, reducing it for the period of operation.
If the result of the SPI is zero or completely negative, then the organization can determine it independently, taking into account safety standards and other nuances.
OS costs
In accordance with sub. 1-2 p. 1 tbsp. 346.16 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, entrepreneurs and organizations using the simplified tax system can reduce their income for expenses on subsequent grounds.
- For the acquisition (construction, production) of OS;
- For retrofitting, reconstruction, modernization and technical re-equipment of OS;
We emphasize that we mean fixed assets included in depreciable property. It was clarified above that non-depreciable fixed assets do not reduce the taxable base of taxpayers under the simplified tax system. But this does not mean at all that costs for any non-depreciable property are not recognized as expenses under the simplified tax system.
Example 1: a laptop was purchased for 80,000 rubles . Since the cost of a laptop exceeds 40,000 rubles, and its useful life is, for example, 5 years, it should be accounted for in accounting as an operating system. In tax accounting according to the simplified tax system, a laptop is classified as non-depreciable property, since its initial cost is less than 100,000 rubles. On the other hand, this object fits the definition of material expense. Therefore, the cost of its acquisition can be taken into account as a material expense. To do this, in the document “ Acceptance for accounting > Equipment > Tax accounting (STS) tab > field Procedure for including costs as expenses, ” you must set the value “ Include as expenses .”
Under these conditions, expenses for a laptop will be taken into account according to the settings specified in the form “ Main > Settings > Taxes and reports > Simplified tax system > Procedure for recognizing expenses > Material expenses .”
Example 2: a plot of land was purchased . We assume that its cost exceeds 100,000 rubles. The fact that land is non-depreciable property is clearly indicated in paragraph 2 of Art. 256 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. However, this does not mean that land cannot be fixed assets and a commodity. To understand whether land costs can be recognized as expenses under the simplified tax system, you need to know the purpose of its acquisition.
If a plot of land is acquired for the purpose of resale, then the land must be accounted for as a commodity. Under these conditions, land costs can be included in the costs of goods. At the same time, they will be recognized as expenses in accordance with the settings specified in the form “ Main > Settings > Taxes and reports > Simplified tax system > Procedure for recognizing expenses > Expenses for the purchase of goods .”
Another question is if a plot of land was purchased for use in economic and production activities. For example, an organization plans to build a parking lot on it. With this option of using a land plot, it acquires the status of an asset, but in tax accounting it is not included in the OS, since it is not subject to depreciation. And if so, then the costs of the land plot cannot be recognized as expenses in connection with the application of the simplified tax system.
Such clarifications are provided in letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-11-06/2/101 dated June 30, 2011, No. 03-11-06/2/145 dated September 16, 2010, No. 03-11-06/2/5946 dated February 28. 2013, No. 03-11-06/2/46 dated 04/08/2011.
Assigning an inventory number
An inventory identification number is assigned to a property at the time it is registered. It is registered in the inventory card f. OS-6. This is necessary to be able to control and record the assets of the enterprise.
The inventory number must meet the following requirements:
- it must be unique in accounting
- assignment is in order
Setting the structure, duration and other characteristics for numbers is determined by the internal regulations of the organization.
Practical task
Register the receipt of equipment:
- Supplier: KVADROKOM LLC
- Agreement: 1601 dated 01/16/2015
- Invoice 1601 dated 01/16/2015, Invoice: 1601 dated 01/16/2015
- Equipment: Automatic striping machine. Ergonomic pallet strapping system ErgoPack 725E – 1 piece for 720,000 rubles.
TOTAL: 720,000.00 incl. VAT 109,830.51
Register the OS for registration:
- Date: 01/31/2015
- MOL: director
- Location: Production workshop
- Equipment: Automatic striping machine. Ergonomic pallet strapping system ErgoPack 725E
- Main equipment: Automatic striping machine. Ergonomic pallet strapping system ErgoPack 725E OS accounting group: Machinery and equipment (except office)
- Depreciation group: Fourth group (over 5 years up to 7 years inclusive)
- Method of receipt: Purchase for a fee
- The procedure for including cost in expenses: Calculation of depreciation
Register the receipt of equipment:
- Supplier: LLC "COMMERCIAL VEHICLES - GAZ GROUP" INN/KPP: 5256051148/ 525601001
- OGRN: 1045207058687
- Address: 603004, Nizhny Novgorod region, Nizhny Novgorod, Ilyich Ave., building No. 5
TOTAL: 680,000.00 incl. VAT 103,728.81
Register the OS for registration:
- Date: 01/31/2015
- MOL: director
- Location: Administration
- Equipment: GAZelle NEXT
- Fixed asset: GAZelle NEXT Fixed asset accounting group: Vehicles
- Depreciation group: Third group (over 3 years up to 5 years inclusive)
- Motor transport: Yes
- Vehicle registration: Vehicle type code: 51004
- Identification number (VIN): 4564134
- Make: GAZelle NEXT
- Registration plate: а777кв77
- Engine power: 120.00 hp
- Tax rate: 45.00
- Method of receipt: Purchase for a fee
- The procedure for including cost in expenses: Calculation of depreciation
Calculate depreciation for the month of January.
Next Previous
These features are available to both users of local versions and cloud solutions, for example 1C:Fresh, 1C:Ready Workplace (WWW) . To purchase boxed versions or rent the 1C:Accounting 8 program in the cloud, please call +7(499)390-31-58, or e-mail: [email protected]
We recommend that you read the sections
Cash accounting in 1C Accounting
| Preparing to work with 1C Accounting |
| Directories. Documentation. Operations. |
| Personnel accounting. Calculation of wages, taxes and contributions from salary |
| About the course... What the 1C:accounting tutorial is about and how to work with it. |
Documentation of the OS
The legislative regulations of the Russian Federation do not establish strict requirements regarding documentation for the OS. However, the methodological recommendations state that the organization is obliged to record the fact of the arrival of the OS at the time of signing the acceptance certificate by management. It is compiled for each individual property object. With the exception of a group of objects of the same type, at the same cost, then it is possible to create a common document.
This is a primary document, therefore the company can develop its form independently, focusing on the existing unified forms.
The Government Decree also specifies the forms that an enterprise can use to document OS:
- OS-1 for arrived property objects
- OS-1b, taking into account a group of property objects of the same category
- OS-14 for the purpose of capitalization of equipment for installation
After receiving the OS, the accountant opens an OS-6 or OS-6a card (for a group of objects). It is possible to create an inventory book f. OS-6.
OS wear and tear
To reflect it, use off-balance sheet account 010. Information on it is reflected if the property is:
- property of an NPO;
- an object of housing stock, external improvement, navigation conditions, road/forestry, if they were registered before 01/01/2006.
The latter provision also applies to productive livestock and domesticated animals.
Depreciation is calculated using the linear method according to dt. 010 monthly. The amounts are not included in the company's costs.
Recognition of costs for the acquisition of fixed assets
The definition of expenses when purchasing a property includes:
amount transferred to the seller- transportation costs and preparation costs for work
- customs duties
- services when purchasing an OS
- tax contributions, duties paid upon purchase of an object
- payments to intermediary companies
Organizational expenses that are related to the purchase of operating systems are allowed to be taken into account only if documentation is available. Without this, postings are not made, and tax expenses are not allowed to be taken to reduce the base.
Moving the OS to 1C
The movement procedure is not fundamentally different from working with goods, except that fixed assets are moved not between warehouses, but between the structural divisions responsible for them.
In cases where, after moving an object, it is planned to apply depreciation to it, you will need to additionally fill in the details “Accrual of depreciation” and “Method of reflecting depreciation expenses”. In this case, depreciation is calculated based on the results of the month, so the columns in the document remain blank.
Postings in accounting upon receipt
As a rule, fixed assets enter the balance sheet of an enterprise as a result of a transaction for the acquisition of fixed assets. In this case, the organization makes the transactions described in Table 1.
| Household operation | Dt | CT |
| OS object purchased from suppliers | 08 | 60 |
| VAT on purchase included | 19 | 60 |
| VAT deductible | 68 | 19 |
| Delivery costs are taken into account | 08 | 60 |
| OS put into operation | 01 | 08 |
Video instructions for working in 1C:
When receiving an object free of charge, you must make the following transactions:
- Dt 08 Kt 98
- Dt 98 Kt 91
If the object is created on its own, then costs for raw materials, labor, depreciation of equipment, etc. are generated. In accounting, such entries occur according to Dt 08 and Kt 02, 05, 10, 70 and others.
Conditions for recognizing fixed assets expenses
In management accounting, fixed assets expenses can be recognized at the time they are paid. This rule does not work in tax accounting under the simplified tax system. Expenses on fixed assets are recognized in the reporting period in which the following conditions are simultaneously met.
- OS paid, clause 2 of Art. 346.17 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- OS is depreciable property, clause 4 of Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- OS put into operation, sub. 1-2 p. 3 tbsp. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- For OS subject to state registration, it is necessary to go through the state registration procedure, paragraph. 9 clause 3 art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
- The OS is used in business activities, subclause 4 p. 2 tbsp. 346.17 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The fourth and fifth conditions are not automatically taken into account in the program. Therefore, the user must exercise control over their implementation independently.
Revaluation of fixed assets
Changing the original price of fixed assets at which it was accepted for accounting is allowed only in the following situations:
additional equipment has been carried out- reconstruction work
- modernization
- completion
- revaluation
The purpose of the revaluation is to bring information about the cost of fixed assets in accordance with the market situation and reproduction standards at the date of the revaluation.
Revaluation is a right, not an obligation of an enterprise. However, if a company has carried it out once, then in the future it will be obliged to reflect this regularly.
All fixed assets that are included in the subgroup of homogeneous assets are subject to revaluation. During the procedure, the initial, current cost, and depreciation charges are recalculated. The results are reflected in accounting.
Receiving OS under an exchange agreement
Execution of the barter agreement is carried out by non-monetary means. In this case, when accepting the OS, the price of the values transferred or to be transferred in exchange is recognized as the initial item. It usually equals the cost at which the company sells the relevant objects. If it is not possible to determine the price of these items, the market value of similar assets is taken into account.
The accountant's entry when receiving fixed assets under an exchange agreement is generally no different from the entry when purchasing for a fee:
- Dt sch. 08 Kt sch. 60.
At the same time, other entries will be generated for this entry, reflecting the sale of the property transferred in exchange, as well as the offset of mutual claims.
Let's say an enterprise using OSNO in exchange for its goods worth 312 thousand rubles. (plus VAT 56,160 rubles) receives equipment from a company using the simplified tax system. The transaction is recognized as valid - the exchange is equivalent. The cost of finished products is 298 thousand rubles.
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Sum |
| Reflection of revenue from product sales | 62 | 90 | 312,000 + 56,160 = 368,160 rubles. |
| Write-off of the cost of finished products | 90 | 43 | 298 thousand rubles. |
| VAT accrual on sales | 90 (subaccount “VAT”) | 68 (subaccount “VAT”) | 56160 rub. |
| Receiving equipment in exchange for products | 08 | 60 | RUR 368,160 |
| Reflection of debt offset under the agreement | 60 | 62 | RUR 368,160 |
| Acceptance of equipment for accounting as part of the operating system | 01 | 08 | RUR 368,160 |
Acceptance of VAT for deduction on fixed assets
It is possible to deduct VAT on the acquisition of fixed assets provided that the transaction meets the following requirements:
- the object was purchased and registered
- less than three years have passed since registration
- in stock SCHFK from the seller
When creating a property object on your own, it is necessary to use the SFC from organizations supplying materials, providing services, and carrying out work.
Nuance
An accountant can detect an unaccounted asset object without conducting an inventory. How to post it in this case?
Registration of such objects is carried out only after an inventory has been carried out. Accounts for the OS on the date of inspection.
Depreciation on such assets is calculated in accordance with the general procedure.
Registration of fixed assets for off-balance sheet accounting
Information about some types of property may be reflected in special accounts on the balance sheet. This happens when:
- Transfer/receipt of OS for rent (leasing).
- Acceptance of equipment for installation.
- Accrual of depreciation of certain types of operating systems.
Let's look briefly at each situation.
Types of wear
The following types of wear exist:
physical, when the decrease in value is associated with the loss of physical, biological, chemical and other similar qualities- moral, when analogues with lower cost or analogues with greater productivity appeared
- social wear and tear, when the OS has lost value because more comfortable or secure analogues have appeared
- environmental, when sanitary standards are tightened
At the same time, social and environmental wear and tear are taken into account very rarely and exclusively in certain areas. Basically, physical and moral wear and tear are calculated.
Physical deterioration
Physical wear and tear is a decrease in the original value of property for the consumer. It is calculated in two ways, see table 2.
| Name | Description | Formula | Decoding |
| Based on scope of work | It is suitable for items with established performance | I = (Tf x Pf) / (Tn x Pn) | Tf – time that the object actually served Pf – average quantity of products produced per year Tn - SPI according to the norm Mon – normal productivity |
| By period of use | It is established by comparing the actual and normative SPI. Valid for determining the wear and tear of any OS. |
Calculation formulas on video:
Accounting for non-depreciable fixed assets with non-zero tax value
Let's assume that the organization does not exclude the possibility of selling non-depreciable assets in the future. In this case, the tax value of the object should not be written off, otherwise it cannot be taken into account as expenses upon sale or other disposal.
Example 2
The organization KRUG LLC applies OSNO, PBU 18/02 using the balance sheet method and pays VAT. The income tax rate is 20%.
In January 2021, the organization takes into account residential premises, which are used as a service apartment for the temporary accommodation of arriving specialists. The initial cost of the apartment in accounting and tax accounting is the same and amounts to 8,000,000 rubles.
The organization has established a useful life of 400 months for the apartment. The linear method of calculating depreciation in accounting and tax accounting is used. In accounting, depreciation expenses for the apartment are taken into account on account 26.
Despite the fact that a service apartment under the conditions of Example 2 is used for production purposes, in the opinion of the Russian Ministry of Finance, such an object does not meet the criteria for depreciable property, therefore, for profit tax purposes, it does not belong to fixed assets subject to depreciation (letters dated January 24, 2019 No. 03-03-06/1/3843, dated November 24, 2014 No. 03-03-06/2/59534). At the same time, there is a court decision according to which the calculation of depreciation on housing assets is legal (resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the East Siberian District dated July 16, 2009 in case No. A33-14312/2006).
Regulatory authorities allow depreciation to be charged on residential premises if they clearly generate income, for example, in the form of rent. Expenses in the form of depreciation of a service apartment must be confirmed by a lease agreement drawn up in accordance with the law (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 7, 2009 No. 03-03-06/2/231, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 12, 2012 No. 16- 15/ [email protected] ).
Let's assume that the organization does not want disputes with the tax authorities and does not include a service apartment as part of the depreciable property. However, the tax value of the property is not written off, since the apartment can be rented out or sold in the future.
In this case, when preparing the document Acceptance for accounting of fixed assets
on the
Tax Accounting
Accrue depreciation
checkbox should be cleared (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Acceptance of non-depreciable fixed assets with non-zero cost for accounting
When posting a document, an accounting register entry is entered:
Debit 01.01 Credit 08.04.1
- for the initial cost of the fixed asset (RUB 8,000,000).
At the same time, special fields of the accounting register are filled in:
Amount Dt NU: 01.01
and
Amount Kt NU: 08.04.1
- for the tax value of the apartment (RUB 8,000,000).
Thus, at the end of January there is no difference between the book value and tax value of the fixed asset.
When performing a regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18
for January, deferred tax for the type of asset
Fixed assets
is not recognized.
Starting from February 2021, the service apartment begins to be depreciated only in accounting. When performing a routine operation Depreciation and depreciation of fixed assets
An accounting entry is generated:
Debit 26 Credit 02.01
- for the amount of depreciation of the apartment (8,000,000 rubles / 400 months = 20,000 rubles).
In tax accounting, depreciation is not calculated in accordance with the established settings. At the end of February, the book value of the apartment decreases and amounts to RUB 7,980,000. (RUB 8,000,000 – RUB 20,000). The tax value of the property does not change and remains RUB 8,000,000. The resulting difference is a deductible temporary difference, since it will lead to the formation of deferred income tax, which, with a certain degree of probability, can reduce the amount of income tax payable to the budget in subsequent reporting periods (clause 11 of PBU 18).
When performing a regulatory operation Calculation of deferred tax according to PBU 18
, a deferred tax asset is recognized by type of asset
Fixed assets
Debit 09 Credit 99.02.О
- for the amount of ONA recognition (20,000 x 20% = 4,000 rubles).
A detailed calculation of IT is presented in the Help-calculation of deferred tax
for January 2021 (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6. Help-calculation ONA
As the apartment is depreciated in accounting, a temporary difference by type of asset Fixed assets
will increase monthly by 20,000 rubles.
Accordingly, the amount of recognition of ONA will increase. By the end of 2021, BP by type Fixed assets
is 220,000 rubles, and IT is recognized in the amount of 44,000 rubles. (RUB 220,000 x 20%).
If the apartment is not sold during its useful life, then after 400 months the object will be fully depreciated and the book value will become zero. The tax value will not change and will be 8,000,000 rubles, therefore, IT will be recognized in the amount of 1,600,000 rubles.
Now let’s assume that from October 2021, the service apartment begins to generate income in the form of rental payments. From this moment on, the fixed asset can be depreciated in tax accounting. Then in September 2021 you will need to create a special document Changing the state of the OS
(section
OS and intangible assets
-
OS depreciation parameters
), which is intended to suspend or resume the calculation of depreciation on fixed assets.
Document header Changing the OS state
should be filled in as follows (Fig. 7):
- in field Event
– indicate the name of the event in the life of the fixed asset, which is reflected in the document.
Events that happen to fixed assets are stored in the OS Events
, which is filled in independently by the user; - don't set flag Reflect in accounting
, since nothing changes in accounting;
- set flag Reflect in tax accounting
, since a change in state affects tax accounting;
- set flag Affects the calculation of depreciation (wear and tear)
, since the document will affect the calculation of depreciation;
- set flag Calculate depreciation (wear and tear)
to resume accrual of fixed assets depreciation. This change will apply starting next month.
In the Fixed Assets
indicate the name of the service apartment for which depreciation is included in tax accounting.
Rice. 7. Changing the OS state
When posting a document Change of OS state
accounting entries are not generated, but entries are entered into the registers of the OS accounting subsystem:
- Calculation of depreciation of fixed assets (tax accounting)
;
- OS Events
.
By the end of September 2021, the taxable difference by type of fixed assets
is 160,000 rubles, and IT is recognized in the amount of 32,000 rubles. (RUB 160,000 x 20%).
From October 2021, the apartment begins to be depreciated also in tax accounting, therefore the resulting amounts of VR and ONA by type of assets and liabilities Fixed assets
don't change.
The further “fate” of BP and ONA will depend on many factors. For example, on whether the accrual of depreciation in accounting and (or) tax accounting will be continued or suspended.
Obsolescence
This type of wear shows the loss of effectiveness of using the OS before the end of its STI. It is divided into two categories: the first and second types.
Obsolescence of the first type manifests itself due to a decrease in the cost of the OS, due to cheaper analogues. Calculated as follows:
I = (Фп – Фв) / Фп, in this case
- Fp – initial price of OS
- Fv – replacement cost (or costs of purchasing an analogue)
Obsolescence of the second type is associated with the emergence of analogues with greater productivity. It can be complete, partial and hidden.
Complete – depreciation, as a result of which its further use will lead to losses in production.
Partial implies the loss of part of the price of the OS fund.
Hidden is a rare occurrence. Represents a decrease in the price of the OS, in connection with an order to produce new equipment with greater productivity and efficiency.
When calculating obsolescence of the second type, one should evaluate the feasibility of purchasing new equipment to replace outdated equipment. The calculation is made using the formula:
I = 1 – (Ts/Tsu), in which
- C – cost of the product on outdated equipment (y)
- (c) in modern
These indicators are calculated as follows:
C = Fp / (P x T) P, while
- P – performance of an obsolete item
- Fp – initial cost
- T – remaining SPI
Registration of fixed assets is a responsible and important stage of accounting. Its careful execution guarantees the accuracy, transparency and relevance of the company's accounting.
Top
Write your question in the form below
Depreciation calculation
Next month it is necessary to calculate depreciation on fixed assets. The document Depreciation of fixed assets can be created automatically when performing routine operations when closing the month. Menu item Financial result and controlling - Month closing
Or if you need to first look at the amounts for depreciation, then you can only post the document Depreciation of fixed assets. The document can be found in the same section Regulated accounting - Fixed assets - Depreciation of fixed assets
We create a document Depreciation, indicate the date of the document and post it.
In this way, accounting for fixed assets can be organized in 1C:KA and 1C:ERP 2, of course, there are many more nuances in accounting for non-current assets, when a fixed asset is assembled from several components, modernization and depreciation charges after modernization, changing the parameters and state of the operating system, accounting leasing operating systems and much more. Therefore, this area of accounting requires special attention and detailed study. If you encounter a problem in accounting for fixed assets, then leave a request on our website and we will definitely help you!