Let us pay attention to one of the types of periodic inspections of the organization’s condition. Today, inventory before drawing up annual financial statements is carried out, in fact, without fail, and below we will look at why this happens, why, and what it gives. We will separately touch on the tasks and deadlines and go through all its stages. So much information - so that you understand how to act, and also realize the importance and relevance of the measures being taken.
Let us immediately note that literally all the nuances of this complex procedure are regulated by various documents. And this is even convenient in practice, since it protects against repeated mistakes: having corrected all the mistakes, you will not make them the second time. Below we will try to highlight all the nuances and pitfalls in as much detail as possible, so that there are initially fewer “filled bumps”.
Justification for the mandatory annual inventory
Yes, the audit is not carried out at will - it must be carried out by legal entities of any legal entity (organizational form), no matter what tax regime they apply. Two documents talk about this at once:
- Federal Law No. 402 of December 6, 2011, namely paragraph three of Article 11;
- PBU (accounting regulations) approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 34n dated July 29, 1998 - clause 27.
According to them, the procedure is necessary to ensure up-to-date accounting data. On the other hand, Article 14 of the same Federal Law No. 402 says that the results of the audit are not included in the reporting. This means that in the standard case, the tax office will not look at whether you performed an inventory at all. But if they suspect something and come with an inspection, it will turn out that you acted illegally, and this will entail sanctions.
However, it’s not just about compliance with regulations and legal business, but also about practical benefits. This procedure will allow you to assess the real state of affairs: directly verify the presence/absence of inventories (inventories) and debts, detect thefts and arrears, unaccounted income and expenses, violations by employees, and the like. So we suggest that you think positively and perceive it as an opportunity to analyze the state of the company, and not as an inappropriate necessity.
Reflection of inventory results in 1C
Also, the result of the inventory must be reflected in accounting using the program that the organization uses. For example, to reflect the inventory results in the 1C: Accounting 8 program, you need to go to the “Warehouse” section and select the document “Inventory of Goods”, and then fill out this document according to the inventory result.
Source:
Materials from the newspaper “Progressive Accountant”
Heading:
Accounting
inventory accounting
- Natalia Kovannaya, senior accountant of the accounting department
Sign up 7800
9750 ₽
–20%
What does an annual inventory give: reasons for conducting it
It is useful because:
- helps to identify actual assets (their volume and quantity), as well as establish the level of future expenses and the degree of fulfillment of undertaken obligations;
- makes it possible to notice shortages, surpluses, misgrading based on the results of comparison of statements of actual availability with the data of the last accounting;
- allows you to identify inconsistencies with the approved and used recognition criteria;
- detects property that has partially lost its consumer properties and initial qualities, is physically and morally obsolete, unused (applies to both material objects and not).
Agree, each of the listed factors is already a significant reason for verification, and brings practical benefits to the manager.
Postings during OS inventory: example
before the annual reporting, conducted an inventory of fixed assets. As a result of comparison of accounting and actual data, the following was revealed:
- shortage of a hydraulic machine with a purchase price of 42 thousand rubles. (28 thousand rubles residual value and 14 thousand rubles depreciation);
- shortage of a laptop (the culprit is Samokhin L. E.) worth 52 thousand rubles. (36 thousand rubles residual value and 16 thousand rubles depreciation);
- surplus hydraulic pump with a market value of 45 thousand rubles.
In accounting, the accountant recorded the following entries:
| Dt | CT | Amount (thousand rubles) | Wiring Description | Documentation | ||
| ||||||
| 01 disposal | 01 | 42 | The original cost of the hydraulic machine was written off | Act on write-off of fixed assets in form OS-4 | ||
| 02 | 01 disposal | 14 | depreciation of the hydraulic machine was written off | Accounting information | ||
| 94 | 01 disposal | 28 | The residual value of the hydraulic machine has been written off | |||
| 91 | 94 | 28 | Loss from machine write-off | |||
| ||||||
| 01 disposal | 01 | 52 | The original cost of the laptop has been written off | Act on write-off of fixed assets in form OS-4 | ||
| 02 | 01 | 16 | Laptop depreciation written off | Accounting information | ||
| 94 | 01 disposal | 36 | The residual value of the laptop has been written off | |||
| 73 | 94 | 36 | The shortage was attributed to Samokhina L.E. | |||
| 73 | 98.4 | 16 | The difference between the residual value of a laptop and the market value | |||
| 70 | 73 | 52 | The cost of the laptop was withheld from L. E. Samokhina’s salary. | |||
ATTENTION! The amount of damage caused by the shortage can be withheld from the employee’s salary within the limit - no more than 20% of the monthly salary (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
According to paragraph 36 of the Methodological Recommendations for the accounting of fixed assets, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance dated October 13, 2013 No. 91n, unaccounted for fixed assets identified during the audit are taken into account in the fixed assets accounts at market value. Therefore, the hydraulic pump should be registered with the following wiring:
- Dt 08 Kt 91 - the hydraulic pump discovered during the inventory was capitalized;
- Dt 01 Kt 08 - hydraulic pump put into operation
What is subject to inventory before annual reporting
According to the first paragraph of Article 11 of the same Federal Law No. 402, these are objects of four categories. Let's look at each of them right now.
Money
An extensive group that includes:
- office and industrial buildings, utility rooms, land plots and other real estate;
- production equipment, special equipment used, automobiles and other vehicles;
- already produced products and raw materials for their production, as well as goods available for sale;
- any other stock that does not fall within any of the above cases.
Attention, both your own property and those in custody or taken for temporary use are subject to accounting, that is, the same passenger cars rented by the company are also included in this subcategory.
Company finances
An annual inventory is a mandatory check of money, both cash in the cash register and funds lying in the organization’s accounts. And not only them, but in general all assets of a similar nature: shares, investments, deposits.
Accounts receivable deserve special attention. It is necessary to make sure that they are supported by relevant business papers, for example, concluded and valid contracts or receipts drawn up according to all the rules.
The company's own debts
You need to look especially carefully at your current creditor obligations: loans, financial assets in reserve, payments not yet made to counterparties, partners, suppliers. You should also check your latest bank payments to ensure your balance is up to date and interest charges are up to date.
Intangible assets
Indeed, a competent annual inventory of property should take into account everything that the company spent money on (and continues to own at the moment). Including:
- registered trademarks, brands, trade names;
- licensed copies of software products, for example, all installed versions of 1C: Accounting.
Please note that the property and liabilities of all four of the above groups are subject to verification, regardless of their actual location. Even if some objects (for example, vehicles or industrial machines) are transported to a branch located in another city, they will still need to be reflected in the results, since they are on the organization’s balance sheet.
Results
An inventory of property and liabilities before drawing up annual reporting is a mandatory procedure, since it allows you to check the correctness of accounting data and make the necessary adjustments to accounting if inconsistencies are identified.
It is carried out within a certain time frame and in compliance with certain rules, including taking into account the features inherent in the inventory processes of each of the components of the inventory mass. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Objectives and goals of conducting an annual inventory of property
The essence of the procedure is to update the data presented in the reporting for the current period. It identifies all the changes that could have occurred over 12 months.
Ensuring all measures for implementation falls on the shoulders of either the owner of the company or an official authorized by him - the manager (according to the constituent documents). He also needs to create and maintain all the conditions for performing the inspection, outline its scope and duration (although in mandatory cases the latter is known in advance, as well as the frequency). He should also ensure that those carrying out the inspection have unhindered access to assets and archives.
conclusions
Carrying out control of the movement of material assets and funds in the form of a periodic inventory, despite some complexity of the process, is an effective tool for an objective assessment of the company’s assets and making competent decisions by the company’s management.
In addition, despite the fact that Russian legislation does not provide for direct liability for insufficient correct maintenance of inventory records, nevertheless, in a number of cases that lead to the discovery of facts of gross violation of financial reporting (for example, during a tax audit), measures may be taken against violators punishments.
This punishment can be applied within the framework of the Administrative Code of the Russian Federation (Article 15.11) with appropriate sanctions in the form of fines for guilty officials.
When is the annual inventory carried out at the enterprise?
Strictly before the balance sheet date and in accordance with paragraph 4 of PBU 1/2008, in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 106n dated October 6, 2008.
The start of work depends on the type of property:
1. If these are income, expenses, debts, liabilities (not counting unrealized provisions, mandatory insurance contributions, budgetary calculations), current biological objects, inventories, non-current assets (in the last two cases, the exception is items temporarily located outside the company’s possession) – You need to start 3 months before the day of summing up the results.
2. If this is money, deductions for targeted financing, investments, unfinished capital investments, semi-finished or unfinished products - then 60 calendar days before the balance is completed.
3. If these are assets sent somewhere for long periods of time (for example, ships and cars leaving on voyages) or material assets that will definitely be outside the company - then up to temporary disposal.
Yes, the reason for inventory is annual reporting, but there are still three exceptions:
- it is permissible not to inspect property that has already been inspected during the period from October to December of the year that has not yet expired;
- the frequency of all work on updating available data is once every 36 months for fixed assets and once every 5 years for library collections;
- those companies and organizations that operate in the Far North have the right to inspect materials, goods and raw materials stored on their balance sheet during periods when their availability is running out (with the smallest balance).
Please note that if the owner wishes, this issue can be dealt with more often, but not less often than required.
Stages of the annual inventory
In general, the procedure can be divided into 4 steps - they are simple, logical and understandable, so we will consider them briefly.
Preparatory
At this stage, commission members are appointed who take preliminary measures - sealing warehouses and so on. We will present a more complete list of actions separately below.
Check
Direct work takes place here: counting the amount of inventory, establishing the condition of assets, measuring the dimensions of goods or equipment (if necessary) and drawing up statements. The latter are especially important; they are filled out separately and in two copies - by the authorized auditor and the financially responsible person.
Comparative-analytical
At this stage, previously compiled inventories are compared with each other and/or with existing documents. This is done to identify inconsistencies, errors or even cases of fraud. Exactly what caused the data discrepancy is clarified during the consideration of each problematic case.
Final
A protocol is filled out, which indicates all controversial issues and measures to resolve them - the need for a repeat inspection, testimony of financially responsible persons, statements to law enforcement agencies regarding theft or theft. If there are no difficulties, this document is also prepared. And in both cases, it goes to the head of the enterprise for consideration. As soon as the head of the company puts his signature, the business paper acquires administrative force, and statistical information from it is transferred to the financial statements.
Preparatory activities
Before conducting a direct inventory at the end of the year, you need to:
- issue an order for inspection - this is done by the head of the company;
- establish deadlines for the completion of all work depending on the volume and types of property being inspected;
- form a commission, distributing roles and responsibilities among its members, and instruct them;
- stock up on forms for filling out inventories and protocols;
- display the balances of assets for the previous reporting period.
The auditors themselves need to do something, for example, limit general access to storage facilities - seal them - and collect receipts from responsible persons. Such preparation will take literally a couple of days (and with proper planning, even less), but it will significantly simplify the further stages of the procedure.
Inventory of goods using special programs and services
We have already said that accounting automation simplifies inventory. You always know how much product should be in the store or warehouse. When entering actual data, you can quickly see shortages and surpluses: both in pieces and in money.
But closing a point or department for inventory still means stopping sales for a while, so it’s important to carry it out as quickly as possible. This problem can be solved if re-registration is made automatic. To do this, you need to link the program in which you keep records - for example, MyWarehouse - with the data collection terminal. During inventory, simply scan the barcodes of items in the warehouse. The system will check discrepancies automatically, without your participation. At the end, MyWarehouse will issue a completed inventory list. Setting up this automatic process is very simple - read the instructions. You don’t even need to carry a laptop and a huge amount of paper with you: just a smartphone is enough - MySklad has convenient and free mobile applications in which you can carry out an inventory of goods.
When accepting goods, the storekeeper may register it incorrectly, the cashier may make a mistake when releasing the goods to the buyer, or upon delivery no one will check the order contents. Because of this, misgrading occurs, unnecessary paperwork occurs, and the goods have to be returned to suppliers. The solution is to make sure that the equipment is checked automatically. This is possible in MyWarehouse: the service itself will find discrepancies in the orders of buyers and suppliers or, for example, when moving goods from the warehouse to the sales floor. You can check not only the quantity, but also the marking codes with the documents. How to do this - read here.
And in MySklad you can download or fill out online all documents for inventory: forms INV-3, INV-5, TORG-16, samples of orders, commodity inventory, matching sheet INV-26 and others. It's all free - try it now!
Try MySklad
Procedure for conducting annual inventory
In general, it takes only 5 steps. Each of them separately does not represent anything complicated and will be discussed below.
Create a commission
It is formed from representatives of different departments of the company: it should include a member of the administration, an accountant, leading specialists (chief economist, engineer, technician, and so on). It is also possible to attract independent experts and outsourcers to obtain an objective opinion from the outside. It is approved by the manager.
If audits are carried out regularly, its composition and nature of activities can be constant. If a significant amount of work is expected and there is a need to perform operations in different warehouses, several groups can be involved in resolving the issue at once, which will inspect the assets in parallel.
Issue an order to conduct an inventory before annual reporting at the enterprise
This document must contain:
- clearly stated duration of activities;
- reason for inspection;
- composition of the commission.
This business paper should also be registered in the control book, in accordance with clause 2.3 of the MU.
Determine asset balances at the start of the audit
Inspectors need to obtain information on receipts/expenses, cash flow reports, inventory items (inventory items) and inventories. All this must be endorsed by the chairman, making sure to put the date.
In addition, financially responsible persons are required to submit receipts in which they confirm that they provided all the necessary documentation and capitalized valuables or accountable amounts/powers of attorney, and wrote off all disposed assets.
Direct inventory for annual reporting
At this stage, the actual presence of objects and the reality of the obligations taken are clarified. All information, measurements and identified inconsistencies are entered into the corresponding inventories and acts, each of which must be made in (at least) two copies - for subsequent comparison.
The inspection must be carried out in the presence of the person bearing financial responsibility (in accordance with clause 2.8 of the MU).
Registration of results
All received data is entered into statements, which are then correlated with financial statements. If surpluses are identified during the audit, they are entered into the general income item, while shortages are written off separately (with consideration of why they occurred).
Rules for filling out inventory documents
- All these materials are compiled in quantities of 2 copies; You can enter values into them either by hand or electronically.
- Objects in inventories must be clearly presented - divided by name (article), units of measurement, subaccounts, storage location, and responsible person.
- The serial number and total natural amount of assets must be written down in words on each page.
- It is imperative that the audit object be identified and comparable with the financial statements.
- All lines on each sheet should be filled in with the exception of the last one, on which the empty space should be crossed out.
- The document requires the signature of each member of the commission and all financially responsible persons.
- Erasures and blots are strictly prohibited - if a mistake is made, it must be crossed out by writing the correct version on top (and this is important to do with all copies).
What to do with surpluses and shortages
Identification of excess balances of goods is charged at market value. The corresponding amount is reflected in the financial result and increase in the organization’s income.
The shortage within the normal natural loss rate is attributed to production costs. If the identified defects of the goods are greater than the norms of natural loss, then the loss is compensated at the expense of the guilty parties.
If the perpetrators are not identified, all losses from the shortage are written off to the financial result of the organization and increase expenses. A document is created to write off the deficiency in excess of the norm. It must be accompanied by decisions of investigative or judicial authorities confirming the absence of guilty persons, or refusal to recover damages from financially responsible persons. The result of the inventory is reflected in accounting in the month in which it was carried out. If an annual inventory is carried out, it is reflected in the annual report.
We compare the results with the credentials
All endorsed materials are sent to the accounting department, whose employees make comparisons and fill out statements for fixed assets and intangible assets in a general manner or separately - in relation to assets temporarily owned by the company.
The reasons for the discrepancies are clarified and recorded in special protocols. These documents are submitted to the head of the organization, who approves them within 5 working days, along with the decisions and recommendations of experts. Thus, business papers acquire administrative power and become primary. It is on their basis that accounting entries are updated.
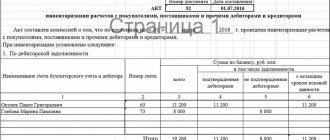
Inventory of receivables and payables
Forms of documents for registration of the inventory and results:
- Inventory report of settlements with buyers, suppliers and other debtors and creditors (INV-17).
- For settlements with counterparties (accounts 60, 62, 76), settlement reconciliation acts are drawn up. The act is drawn up with each counterparty in 2 copies: one for the organization, the other for the counterparty. The act is signed by the heads of the organizations and the debt is considered agreed upon.
- For loans and credits received (accounts 66, 67), the debt is shown taking into account the interest due at the end of the reporting period.
- For each accountable entity (account 71), it is necessary to verify the data on money received, spent and returned and on the primary documents reflected in the accounting.
- For settlements with the budget and extra-budgetary funds (account 68, 69), it is mandatory to obtain from the Federal Tax Service, Pension Fund and Social Insurance Fund documents confirming the amount of debt (clause 74 of the Accounting Regulations No. 34n). Leaving unresolved amounts for these settlements on the balance sheet is not permitted.
- For debts to employees (account 70), unpaid amounts of wages are identified that are subject to transfer to the depositors' account, as well as the amounts and reasons for overpayments to employees.
One of the main tasks of inventory is to identify overdue debts that need to be written off.
What happens if inventory is not carried out before the annual report?
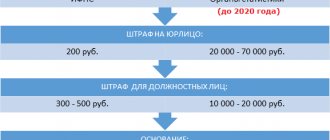
There are no separate penalties for this, but a completed check will help show that everything is in order at the enterprise if the tax office suddenly discovers something suspicious and comes with an inspection. If you do not have convincing evidence of the transparency of business, you will receive a fine of up to 20 thousand rubles, although the main trouble is the possible blocking of the company’s activities for a period of 1 to 3 years. Plus, if the violation is considered gross, from a tax point of view, you will be charged an additional 10 to 40 thousand rubles.
In addition, it is better to carry out audits regularly to optimize your work. Because it will give an idea of the real state of assets, the amount of stored products and raw materials, the obsolescence of equipment and many other important things.
Documentation of inventory of fixed assets (nuances)
Assets that are under repair during the inventory are reflected in the statement in the INV-10 form , indicating the cost and expenses of the enterprise for repairs.
For fixed assets transferred for lease or safekeeping, a separate inventory is drawn up indicating documents confirming the acceptance of the property by the counterparty.
Also, a separate inventory is drawn up for fixed assets that cannot be used in the company’s business activities and cannot be restored: members of the commission indicate the time of commissioning and the reasons why it is now impossible to use the property.
If during the reconstruction or restoration of the OS the purpose of the object has changed, then new information should be added to the inventory. If, as a result of the work carried out, the book value of the fixed assets has changed, but this data is not recorded in accounting, then this fact should be reflected in the inventory.
If the inventory commission reveals errors in the characteristics of objects, then the commission members include the correct information and technical indicators in INV-1.
Officials demand that unaccounted fixed assets identified during the inventory be equated to non-operating income (clause 20 of Article 250 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) and subsequently accrue depreciation on it in accordance with the market value and actual wear and tear recorded by the inventory commission. Information about the cost of fixed assets must be confirmed by documents or by examination (clause 10.3 of PBU 9/99).
ATTENTION! A depreciation bonus cannot be applied to unaccounted for fixed assets discovered during the inventory.
The inventory results are recorded in the statement using the INV-26 form .
EXPLANATIONS from ConsultantPlus: Inventory of real estate (land plots, buildings, structures, other objects firmly connected to the land, aircraft, sea and river vessels), recorded as part of fixed assets, is generally carried out in the same way as the inventory of other fixed assets, but taking into account some features. Find out which ones exactly at K+ by getting trial demo access. It's free.
Who sets the procedure?
In addition to the legal requirements set out in the Methodological Recommendations, all other nuances of the inventory remain the responsibility of the organization’s management. Naturally, they must be recorded in the local documentation of the enterprise. The Directorate needs to clarify the following issues:
- how many inventories need to be carried out during the working year;
- at what time should this be done;
- listing the types of assets subject to inspection;
- appointment of the head and members of the inventory commission;
- possibility of selective (sudden) inventory.
When is inventory required?
It is customary to distinguish between voluntary and mandatory inventories. If we are talking about a voluntary procedure, then the inventory is initiated by the manager or responsible person. Inventory is required for everyone, without exception, in the following situations:
- before the start of the formation of the annual financial report;
- in the event of the dismissal of a materially responsible person (MRP) or the hiring of another person in his place, the rules for conducting an inventory assume the removal of powers from one and their assignment to another employee (read the article for more details);
- it is planned to reorganize or close (liquidate) the company;
- if during the inspections it was established that part of the assets on the balance sheet was stolen or damaged (this can also include abuse of the powers of the MOL, the inventory procedure in this case is the same);
- the occurrence of emergency situations resulting in damage to property (fire, flood or natural disaster);
- leasing, purchasing or selling property;
- there was a transformation of an enterprise that had the status of a state or municipal institution.
The reasons for conducting an inventory are clear. But not all responsible persons know how inventory is carried out. This is a labor-intensive process that requires certain knowledge and the use of various forms of documents.