Author: Ivan Ivanov
Inventories represent one of the most important parts of financial statements. The decisive role is played by the correct assessment, in accordance with which they are recorded and subsequently reflected in the reporting.
In this regard, new approaches to determining the value of assets are emerging in international practice. One of them is the formation of appropriate reserves for reducing the cost of material assets. They are reflected in account 14 of accounting.
Purpose of the designated position in the balance sheet
Many companies store material and raw materials in warehouses, the value of which may periodically decrease. It is for this reason that organizations create a reserve fund, which is designed to cover losses in the event of a similar situation.
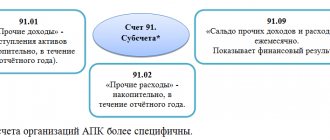
The designated account, called “Funds for the event of a decrease in the value of inventories,” is designed to collect and summarize information about the reserves that the organization has created in order to reflect the deviations that have arisen from the price of inventories established at the time of purchase from the current one. This position is also used to summarize information about reserve funds formed in case the price of other working capital decreases, including work in progress, finished products, goods, etc.
The formation of funds is accounted for by the credit part of the designated account and the debit part of 91 positions, which is called “Other expenses and income.” As for the formation of Form No. 1 of financial statements, the amount of the created fund is not reflected in it, since the inventories are shown in this reporting form according to the already specified estimate, minus the formed reserve.
Businessman working in the office
Creating a reserve with an example
The reserve, as already noted, represents the difference between the actual cost and the market price. If the second parameter in relation to a product created from materials is greater than or equal to the physical cost, a reserve is not formed, as stated in the relevant Guidelines for accounting for inventories.
Accounting for the fact of creating a reserve is carried out according to Kt 14. Let's consider the process of its formation step by step using practical examples and using existing transactions.
The organization Fomich LLC has homogeneous materials in its calculation - pigment. Starting price – 600,000 rubles, including 100,000 rubles. – VAT. At the end of the reporting period, an inventory process took place, and in the end it was found that the market price had decreased and was equal to 300,000 rubles. The company decided to create a reserve.
This operation will be recorded as follows (to simplify accounting):
600,000 – 100,000 = 500,000 rub.
Dt 19 Kt 60 = 100,000 rub. – input parameter of value added tax in the process of receipt of materials.
Dt 10 Kt 60 = 500,000 rub. – direct receipt of materials to the warehouse.
Dt 91 Kt 14 = 300,000 rub. – acceptance of input VAT for deduction.
Features of financial statements
The enterprise must create the specified fund in the case where there is an agreement on the purchase and sale of finished products at a price that is lower than their cost. In addition, these funds should be created for such inventories that were used in the production process of these products. All these inventories should be shown on the balance sheet at a price adjusted by the amount of the reserve.
If it so happens that the company has not created the specified fund, then in this case there is a violation of the principle of reliability of financial reporting. In these circumstances, for a gross violation of accounting rules, the head of the company, as well as the head of the financial service, may be held administratively liable by paying a fine in the amount of 2000 rubles. Up to 3000 rub. provided that the information in the balance sheet is reflected unreliably by more than 10%.
Write-off of reserve
The reserve is written off in the following cases:
-If the market value of materials has increased.
-Materials are transferred to production or sold.
A) If the market value of materials has increased, in the next reporting period the following entry is made:
Debit 14 Credit 91-1 - The reserve for those materials for which the market value has increased has been written off. (the reserve for account 14 decreases, income previously accepted as expenses increases, i.e. is cancelled)
B) If materials were transferred to production or sold, the reserve is also restored by posting:
Debit 14 Credit 91-1
Let's consider an example when materials are sold using those materials for which a reserve was created.
Before drawing up the balance sheet, the book value of the brick was 10 rubles, the market value of the brick was 8 rubles. Bricks in quantity of 100 pieces. The following year, these materials were sold in the amount of 50 pieces. The reserve at the beginning of account 14 was 1000 rubles.
- Debit 91 Credit 14-200 rubles ((10-2)*100) A reserve was created.
- Debit 91 Credit 10-500 rubles (10*50) - The cost of materials for materials sold (bricks) has been written off.
- Debit 14 Credit 91-100 rubles ((10-8)*50) - The reserve for the materials for which it was created is written off.
Examples of accounting entries
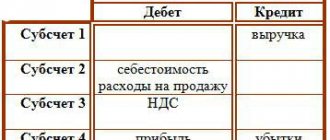
To begin with, it is necessary to emphasize that the 14th count is active-passive in nature. The created funds are reflected in the credit part of the account, and the restored amount of the reserve or the amount by which the market price exceeds the actual one should be indicated in the debit of the account.
As for analytical accounting, it is maintained for each created fund separately.
Typical accounting entries for the designated position of the Chart of Accounts are as follows:
Creation of a fund, which at the end of the reporting period is formed for each type of inventory by reducing financial results:
Dt 91/2
Kt 14.
Reduction in fund volume as a result of disposal of inventories or increase in their market value:
Dt 14
Kt 91/1.
Postings with examples
The creation of reserve points is traditionally carried out before drawing up the annual balance sheet. The amount is usually calculated for each item number or name, and sometimes for groups of similar values.
Reserve amount = (US - TS) * CMC, where
US – accounting value indicator, TC – current value, KMC – number of material assets.
Reserves are not created if the actual cost is high at the reporting date. The account is active-passive. The formation of the reserve is subject to reflection on the credit of the account. Below are the main transactions for this account:
- Dt 91 Kt 14 – formation of a reserve. The basis for regulation is an accounting certificate and an order from the manager.
- Dt 14 Kt 91. The invoice is generated on the basis of the same types of documentation. The operation means writing off and restoring the reserve amount for inventories.
- Dt 60 Kt 41 – acceptance of commodity items for accounting. Actions are carried out on the basis of the consignment note.
- Dt 91 Kt 14 – creation of a reserve. It is carried out on the basis of the manager’s order and certificate.
- Dt 99 Kt 68. Permanent tax liability.
- Dt 62 Kt 90 – reflection of revenue received during the sale of commodity items.
- Dt 90 Kt 68. The operation is traditionally regulated by an invoice and involves the accrual of VAT on sales.
- Dt 90 Kt 41. Interim operation, which reflects the write-off of cost. The consignment note serves as an indicative regulatory document.
- Dt 14 Kt 91 – the reserve amount is written off.
- Dt 68 Kt 99 – introduction of a tax asset on an ongoing basis.
Example of creating a reserve fund
Let’s imagine that at the end of 2021, a certain Invest LLC has 37,000 bricks on its balance sheet, the actual cost of which is 9.0 rubles per piece. Thus, the total cost was 333,000 rubles. During the year, the market price fell slightly and, in accordance with the results of trading on the commodity and raw materials exchange, at the end of the reporting period it amounted to 7.0 rubles. As a result, the total market price was 259,000 rubles. At the beginning of 2021, the company sold 15,000 units. bricks
Thus, due to disposal, part of the created reserve must be written off: 74,000: 37,000 * 15,000 = 30,000 rubles.
Accounting entries for account 14 as a result of a decrease in the market value of inventory items will look like this:
- Dt 91.02 - Kt 14 - 74,000 rubles, a fund has been formed to cover losses resulting from a decrease in value;
- Dt 14 - Kt 91.01 - 30,000 rubles, write-off of part of the reserve fund.
Accounting Features
The net realizable value of inventories is subject to revision in each subsequent period. If the net realizable value of inventories that were previously marked down subsequently becomes greater, the amount that was previously written off is reversed to the extent of the initial markdown so that the new cost corresponds to the minimum actual cost.
At the end of the reporting year, in the process of writing off materials, the reserved value is restored, and the entry Dt 14 Kt 99 appears in accounting. As for the restoration of the reserve value in the process of disposal of inventories, it is reflected through the operation Dt 14 Kt 90.
Formation of reserve
Accounting for reserves for impairment of inventories is carried out in accordance with the standards specified in regulatory legal acts in the field of accounting. At the same time, many aspects of the procedure for creating and accounting for such reserves are not clearly regulated by the current provisions. Therefore, the procedure for creating a reserve for reducing the value of inventories must be provided for in the accounting policies of the organization.
>> Full text is available to subscribers. Get access. >>
Example 1. No reserve is created
As of the date of assessment of the reserve for a decrease in the value of valuables (March 31, 2021), fabric inventories in the organization’s clothing production amounted to RUB 850,000. (residue D-t 41).
It was established that the market value of the fabric on this date decreased to 700,000 rubles. At the same time, all finished products in the production of which it is used remain profitable.
>> Full text is available to subscribers. Get access. >>
Example 2. Determining the size of the reserve
As of June 30, 2021, the trading organization has 30 pairs of women's boots of an outdated model (2012) with signs of scuffs and scratches. The actual cost of the boots was 80 rubles. for a couple. The organization's accounting policy establishes that the provision is assessed at the last reporting date of each quarter (hereinafter referred to as the assessment date), and impairment exceeding 20% is significant.
In the accounting records of the organization, the cost of the boots is listed as D-t 41, the balance is 2,400 rubles. (80 rub. × 30).
>> Full text is available to subscribers. Get access. >>
Example 3. Write-off (restoration) of reserve
Performed in the event that inventories are written off from the balance sheet due to their direction into production, sale, or transfer on a free basis. Write-offs are made to other income.
Let's use the data from example 2.
At the beginning of the fourth quarter of 2021, a reserve was created to reduce the value of inventories in the amount of RUB 1,500. (50 rubles × 30 pairs of shoes).
>> Full text is available to subscribers. Get access. >>
Example 4: Provision adjustment
Performed if the value of inventory has increased. The difference between actual and market value decreases. The reserve must be reduced.
Let's use the data from example 3.
For 2021, the organization has adopted similar provisions regarding reserve accounting.
>> Full text is available to subscribers. Get access. >>
Calculation of the final balance for account 14
The formula for calculating the final balance on account 14 = Beginning balance on the loan + Turnover on the loan 14 - turnover on the debit 14.
Let's use the previous example and draw an airplane:
Balance at the end = Balance at the beginning CT + Credit turnover - debit turnover = 1000 + 200-100 = 1100 rubles. Debit turnover is shown (200 rubles) for the amount of reserves created for the period. Credit turnover (100 rubles) is the amount of the reserve written off. The closing balance (1100 rubles) shows how much reserves we have in account 14 at the end of the reporting period. 1100 rubles are not reflected in the balance sheet but are subtracted from the amount of INVENTORIES in the balance sheet asset. Let's say we have INVENTORIES in the amount of 10,000 rubles in the balance sheet on the INVENTORIES line there will be 8900 rubles (10000-1100)
Instructions 14 count
Instructions for using the chart of accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations in accordance with Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000:
Account 14 “Reserves for reduction in the cost of material assets” is intended to summarize information about reserves for deviations in the cost of raw materials, supplies, fuel, etc. values determined on the accounting accounts, from the market value (reserves for a decrease in the value of material assets). This account is also used to summarize information about reserves for reducing the value of other assets in circulation: work in progress, finished products, goods, etc.
The formation of a reserve for a decrease in the value of material assets is reflected in accounting as a credit to account 14 “Reserves for a decrease in the value of material assets” and a debit to account 91 “Other income and expenses.” In the next reporting period, as the material assets for which the reserve was formed are written off, the reserved amount is restored: an entry is made in the accounting to the debit of account 14 “Reserves for reduction in the value of material assets” and the credit of account 91 “Other income and expenses”. A similar entry is made when the market value of material assets for which corresponding reserves were previously created increases.
Analytical accounting for account 14 “Reserves for reduction in the value of material assets” is carried out for each reserve.
Account 14 Creation of reserves for reducing the value of material assets
Reserves for a decrease in the value of material assets are created if the current market value of material assets is lower than their actual cost.
This situation occurs if:
- material assets on the balance sheet are physically or morally obsolete;
- market prices for material assets have decreased.
Provisions are usually created before preparing the annual balance sheet. The amount of the created reserve is included in other expenses of the organization.
Debit 91-2 Credit 14 - a reserve has been created for reducing the value of material assets.
The amount of the reserve for a decrease in the value of material assets does not reduce the taxable profit of the organization.
The amount of the reserve is determined separately for each item (nomenclature number), and in some cases - for groups of homogeneous material assets, by the product of the accounting value minus the current market value and the number of material assets.
It is impossible to create a reserve for enlarged groups of inventories (for example, for all materials or goods).