The balance sheet (Form No. 1) is the main financial annual report, mandatory for preparation by all Russian organizations. The document represents systematized information about the property, finances, assets and liabilities of the company. It is submitted annually to the Federal Tax Service by March 31, along with applications.
In accordance with the requirements of Federal Law No. 402 dated December 6, 2011, all organizations are required to keep records and prepare financial (accounting) statements at the end of the year. The package, which is submitted to the Federal Tax Service at the end of the year, and throughout the year is provided by the owners of organizations upon request, includes a balance sheet. Let’s figure out what form is used to compile it for 2021, what features this report has, and what “asset” and “liability” are.
Financial statements: forms 1 and 2 - what are these reports
Data from forms 1 and 2 are the main components of financial statements:
- Form 1 – balance sheet;
- Form 2 – statement of financial results.
Starting with reporting for 2021, all enterprises use accounting forms, approved. By Order of the Ministry of Finance dated 07/02/10 No. 66n as amended by Department Order No. 61n dated 04/19/2019. In the new edition, in particular:
- OKVED code was replaced by OKVED2;
- There is only one allowed unit of measurement left - thousand rubles. (previously it was possible to indicate data in million rubles);
- OKEY code has been corrected.
Balance due dates
According to the general rules, the balance sheet - Form 1 must be submitted as part of the reporting for the past year no later than March 31 of the following year. This deadline must be observed when submitting balance sheets and other forms to the Federal Tax Service and statistics.
In addition, under certain conditions, an audit report must be sent to Rosstat as an attachment. The deadline is set for ten days, but no later than December 31 of the following year.
Some organizations need to submit financial statements and publish them due to the type of activity they carry out, or according to other criteria defined by law. For example, tour operators must send their reports to Rostrud within three months from the date of their approval.
The legislation provides for separate deadlines for organizations that registered after September 30 of the reporting year. Due to the fact that their calendar year may be determined differently in this case, the due date may be set by such organizations on March 31 of the second year after the current one. For example, Rebus LLC received an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities on October 25, 2017; the accounting report must be submitted for the first time on March 31, 2021.
Attention! Accounting statements are usually submitted based on the total for the year. However, it is possible to present it quarterly. In this case it is called intermediate. Such documentation is very often needed when applying for loans from banks, company owners, etc.
Accounting: forms 1 and 2 - who submits
All organizations maintain accounting records, and entities that maintain simplified accounting can use simplified forms of reporting forms. According to paragraph 4 of Art. 6 of Law No. 402-FZ, such enterprises include:
- small firms (including micro-enterprises) included in the SME register - these include companies with an average staff of up to 100 people. and an annual income of no more than 800 million rubles;
- non-profit organizations (NPOs);
- participants of the Skolkovo project.
Simplified Form 1 and Form 2 of the enterprise imply a generalized grouping of data, which is recommended in Appendix 5 to Order No. 66n. But subjects have the right to develop and use their own forms.
Clause 5 Art. 6 of Law No. 402-FZ provides a list of organizations for which simplified methods of accounting and reporting are not available, incl. These are enterprises whose reporting is subject to mandatory audit, public sector employees, non-profit organizations with the functions of a foreign agent, bar and notary chambers, etc.
How to use interconnection in accounting
Reporting forms, both financial and accounting, in addition to the informational relationship, also have a logical relationship. This relationship is visible when one understands the balance sheet results, because for the most important total values, a detailed explanation can be seen in other forms. When deciphering the results in detail, the arithmetic side of filling out the reports is checked, and any changes are clearly visible.
Balance of indicators is the main principle of not only accounting, but also financial reporting.
For small companies and large holdings, accounting indicators are a stimulant for moving forward. It is possible to assess the state in which the company is currently located with the help of accounting records. At the same time, it should be understood that each form of reporting can characterize the situation “in its own way.” By applying relationships in practice, you can study accounting in more depth and draw the necessary conclusions.
The logical connection of the indicators is that they complement each other and also correspond in different reporting forms. Explanations of some balance sheet items can only be found in the accompanying forms. An example is the article “Intangible assets”, the explanation of which can be found in the appendix to the balance sheet.
Form 1 and 2 of simplified accounting statements: basic principles of preparation
The Ministry of Finance brought to the attention of subjects information on the use of simplified reporting (Message No. PZ-3/2015), according to which:
- Information is disclosed taking into account its significance for the user. Individual significant items can be distinguished from groups in reporting forms.
- Events after the reporting date are recognized where it makes reasonable sense to do so.
- Significant errors of previous years are corrected at the expense of other income and expenses of the past year, without changing the financial result.
Answers to common questions
Question No. 1. “Is it possible to link accounting and tax reporting?”
The fact is that different principles are used to generate both reports, which indicates different compilation rules. In this regard, there is no direct correlation between tax and accounting reporting indicators.
Question No. 2. “It has been said that absolutely all companies are recommended to carry out interconnection. Does this apply to small businesses? (click to expand)
For small businesses, interconnection will not be difficult, since compared to large companies, the volume of indicators is significantly reduced. But this does not mean that verification is not important. On the contrary, it is worth conducting it in order to see the economic picture of the activities of your, albeit small, company.
Question No. 3. “Who at the enterprise should carry out interconnection? Only the chief accountant?
At each individual enterprise, this can be almost any employee of the economic or accounting department, not necessarily the chief accountant. It could even be a third party hired specifically for this purpose.
Question No. 4. “What documents should be used to document the fact of interconnection of indicators?”
Answer: There is no specially designed form for information about the completed interconnection. Organizations and entrepreneurs can independently develop this form, determine the timing and procedure for interconnection, and also consolidate this in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
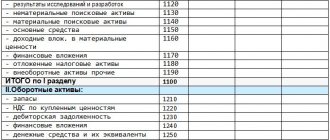
>Sections of the balance sheet
Simplified annual balance sheet in form 1 and form 2: how to fill out
When preparing a balance sheet, indicators record the state of affairs in the organization on a specific date - the end of the year or the last day of business (upon liquidation of the company), as well as on December 31 of each of the previous 2 years.
Here are the main relationships between the lines of the simplified balance sheet and the accounting accounts, the balances of which should be used when filling out the report:
| Balance sheet item | Line code | How to calculate |
| Tangible non-current assets | 1150 | The sum of balances on accounts 01, 03, 07, 08 minus the balance on account 02 |
| Intangible, financial and other non-current assets | 1170 | Account balance 04, 08 (investments in intangible assets), 09, 55 (deposits), 58, 73 (employee loans) minus the reserve on the account. 59 and balance 05 |
| Reserves | 1210 | Balances on accounts 10, 11 (minus the reserve on account 14), 15, 16, 20, 21, 23, 28, 29, 41 (minus account 42, if goods are accounted for with a markup), 43-46, 97 |
| Cash | 1250 | Sum of account balances 50, 51, 52, 55 (excluding deposits), 57 |
| Financial and other current assets | 1230 | The sum of account balances is 19, 55 (minus long-term deposits), 58 (short-term investments minus the reserve of 59), + debit balances 60, 62 (minus reserves for 63), 66-71, 73 (minus long-term loans), 75, 76 |
| Capital and reserves | 1300 | Sum of account balances 80, 82, 83, 84 |
| Long-term borrowed funds | 1410 | Balance of debt on account 67 with a repayment period of at least 1 year (interest is included in line 1510) |
| Other long-term liabilities | 1450 | Account balances 77 and 96 (reserves used for more than 12 months) |
| Short-term borrowed funds | 1510 | Account balance 66, interest on long-term borrowed funds (account 67), and account debt. 67, the maturity of which is less than 1 year left at the reporting date |
| Accounts payable | 1520 | Credit balance of accounts 60, 62, 68-71, 73, 75, 76 |
| Other current liabilities | 1550 | Balances on accounts 86, 96 (short-term reserves) and 98 |
why is a cube more convenient?
Convenient online invoicing
Instantly send invoices by e-mail to your buyer
Debt control for each customer
Management reporting
Organized storage of all your documents
20% discount on accounting services from your accountant
Have you changed your mind about downloading document templates online?
With the KUB service you can save 29 minutes on issuing documents without a single error, and that’s not all. Get KUB - an online service for automating invoicing and other documents.
Start using the CUBE right now 14 days FREE ACCESS
Do you need help filling out documents or advice?
Get help from expert accountants to prepare documents
+7
[email protected] kub-24
Accounting report: form 1 and 2 - how to fill out a simplified statement of financial results
Form 2 is compiled based on the turnover of the accounts and reflects the summarized indicators for the reporting and preceding years:
| Article form 2 | Line code | How to calculate |
| Revenue (net of VAT and excise taxes) | 2110 | Credit turnover of account 90.1 minus debit turnover 90.3 (VAT) and 90.4 (excise taxes) |
| Expenses for ordinary activities | 2120 | Debit turnover by account. 90.2 (cost of sales) |
| Percentage to be paid | 2330 | Debit turnover 91.2 (in relation to interest on all types of obligations) |
| Other income | 2340 | Loan turnover 91.1 |
| other expenses | 2350 | Debit turnover 91.2 (except interest) |
| Income tax | 2410 | Account loan turnover 68 (accrual according to the declaration) |
| Profit Loss) | 2400 | Calculation by lines: 2110 – 2120 – 2330 + 2340 – 2350 – 2410 |
Form 1 and 2 of financial statements: example
The small enterprise Pekar LLC produces bakery and confectionery products. As of December 31, 2021, according to the accounting accounts, the enterprise draws up simplified Form 1 and Form 2:
| Index | Accounting data | Amount, thousand rubles | Form 1 and 2 line codes | Total per line, thousand rubles. |
| Equipment | Debit balance 01 | 1150 | 1150 | 794 (1150 – 356) |
| Accumulated depreciation | Loan balance 02 | 356 | ||
| Cost of a registered trademark (depreciation is calculated without using account 05) | Debit balance 04 | 100 | 1170 | 100 |
| Raw materials | Debit balance 10 | 214 | 1210 | 229 (214 + 15) |
| Finished products | Debit balance 41 | 15 | ||
| Cash in hand | Balance debit 50 | 17 | 1250 | 1002 (17 + 985) |
| Funds in the current account | Balance debit 51 | 985 | ||
| Buyers' debts | Debit balance 62 | 576 | 1230 | 576 |
| Authorized capital | Balance credit 80 | 980 | 1300 | 980 |
| Long-term loan | Loan balance 67 minus interest | 752 | 1410 | 752 |
| Loan with a repayment period of 6 months and interest on it | Loan balance 66 | 321 | 1510 | 396 (321 + 75) |
| Interest on long-term loan | Loan balance 67 (interest) | 75 | ||
| Debt to suppliers | Credit balance 60 | 573 | 1520 | 573 |
| Revenue | Credit turnover 90.1 | 2389 | 2110 | 2078 (2389 — 311) |
| VAT | Debit turnover 90.3 | 311 | ||
| Cost price | Debit turnover for 90.2 in correspondence with 20, 23 | 1256 | 2120 | 1472 (1256 + 216) |
| Business expenses | Debit turnover for 90.2 in correspondence with 44 | 216 | ||
| Interest on loans and borrowings | Debit turnover 91.2 (based on interest paid) | 89 | 2330 | 89 |
| Income from equipment rental | Loan turnover 91.1 | 60 | 2340 | 60 |
| Payment of mandatory payments | Turnover by debit 91.2 (taxes) | 98 | 2350 | 98 |
| Profit tax accrued | Credit turnover at 68 | 102 | 2410 | 102 |
At the end of 2021, the profit of Pekar LLC was (line 2400):
2078 – 1472 – 89 + 60 – 98 – 102 = 377 thousand rubles.
You can check the correctness of filling out the reports using the control ratios given in the Letter of the Federal Tax Service dated July 31, 2019 No. BA-4-1/ [email protected] (as amended on March 10, 2020).