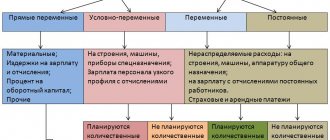
The mere fact of violation of job descriptions and failure to fulfill official duties already implies the possibility of bringing the cashier to disciplinary action within the framework of the law. Impacts related specifically to the area of disciplinary responsibility can be called a reprimand, reprimand or dismissal of the worker.
Disciplinary responsibility.- Financial responsibility. If, during the discovery of surpluses in the cash register, due to the actions of the cashier, the company suffered some kind of actual damage, the employee may be brought not only to disciplinary, but also to financial liability. Compensation may be demanded from him, which the employer, by law, can withdraw, including through deductions from wages.
- Administrative responsibility. The appearance of surpluses in the cash register is direct evidence of a violation of administrative legislation in the field of conducting various cash transactions. Therefore, if such a situation arises, both the enterprise itself and the cashier may be held administratively liable and will have to pay a fine.
- Criminal liability. If surpluses in the cash register arose as a result of unlawful actions of an employee, misappropriation, embezzlement or theft of employer funds, then the employee may also face criminal liability if the amount of damage caused and its nature allow criminal law standards to be applied to such a worker.
It must also be remembered that the final decision to hold the worker accountable for the presence of surpluses in the company's cash register in almost all cases is made by the employer. Thus, he may decide not to resort to bringing the employee to disciplinary, financial or criminal liability, either in whole or in part. However, administrative responsibility for surpluses in the cash register, revealed during inspections and control activities by representatives of government bodies, may imply the involvement of an employee without the employer’s desire.
What to do if excess funds are identified during inventory?
Cash surplus means that the real amount of available cash of the enterprise, confirmed by the results of the audit performed, exceeds the amount of cash recorded in the cash accounting registers.
Excess cash in a company is often detected by the inventory commission based on the results of a cash audit.
When such facts are discovered, members of the commission carrying out the inventory of the cash register study the accounting documentation.
The commission’s tasks are to document this fact, establish the causes of the cash surplus, determine the culprit of the detected violations, and correctly eliminate the identified discrepancies in accounting.
Cash audit rules
The cash register inventory is carried out at a frequency established by order of management and enshrined in the accounting policy of the enterprise. The same regulations establish the inventory procedure. The cashier is recognized as the financially responsible person for the cash register.
Before the inventory, the manager (director) issues an order (order), which indicates the start date and composition of the inspection commission.
The commission must include at least three people. The presence of the MOL on the commission's list is mandatory. In addition, the presence of security and internal audit employees (if available) is desirable. If there is no signature of even one of the commission members, the inventory is considered invalid.
Before checking, the cashier stops all operations and generates a cash report.
Example of a cash report
This report reflects all incoming and outgoing orders, which, in addition, must comply with the approved forms. Identified missing or excess amounts are reflected in accounting during the audit period.
During the inventory the following is also checked:
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
- Free video tutorial on 1C Accounting 8.3 and 8.2;
- Tutorial on the new version of 1C ZUP 3.0;
- Good course on 1C Trade Management 11.
- Setting a limit on the balance of DS at the cash desk;
- Inconsistency between the dates of cash receipts and the actual issuance of money;
- Correctness of correspondence of cash document accounts;
- Whether unpaid wages were deposited on time.
Based on the results of the inventory, an inventory report INV-15 is drawn up. In commercial organizations, surpluses and shortages are written off to the financial result.
Example of an inventory report
Unscheduled audit of the cash register
The cash register inventory can be carried out unscheduled, suddenly and without warning, in order to control the responsibility of the MOL. The timing and procedure for unscheduled inventory are also established by the regulations of the enterprise.
Possible reasons for the detected money
The discovery of excess cash in an organization's cash register is often perceived ambiguously by the employer.
This makes management's reaction to the facts of cash surpluses significantly different from the typical consequences of identifying cash shortages, in which embezzlement/theft usually becomes the priority version.
Thus, the presence of excess, unaccounted cash in the cash register can be caused, for example, by the sale of goods at an erroneously indicated (inflated) price or, alternatively, underweight.
Although, of course, such situations rarely arise by chance with modern control and transaction systems.
Speaking about possible reasons, we cannot exclude the fact that cashiers of trade organizations sometimes report their own money to the cash register.
This is often done when there is a shortage of change bills in order to freely give change to customers.
Sometimes employees forget about this, which causes excess cash to appear in the cash drawer.
One way or another, these facts can be regarded as violations of cash discipline, which is not acceptable from the point of view of conducting cash transactions.
Determining the culprit
In order to find out the reasons for the situation and correctly record cash surpluses in accounting, the inventory commission sends appropriate requests to financially responsible entities - the organization's cashiers.
Employees of the company who are personally responsible for the correct management of the cash register provide written explanations regarding excess cash.
Explanatory notes from responsible persons make it possible to identify the entities responsible for the appearance of cash surpluses.
In addition, the solution of this problem is effectively facilitated by reconciling factual information with accounting information.
How is an explanatory note drawn up by the cashier of an organization?
If an audit reveals a cash surplus at an enterprise, the responsible cashier is obliged to provide his employer with an explanatory note regarding this fact.
Current legislation provides that the head of a business entity must require the cashier to provide the necessary explanations in writing within 2 (two) days.
Being a financially responsible entity, the cashier does not have the right to refuse to write an explanatory note.
This paper is an official document.
It can be compiled manually or as a computer printout. One way or another, the explanatory note is written on the official form (form) of the business entity and signed by the cashier (with a transcript).
The explanatory document drawn up by the cashier regarding the detected excess cash contains two key sections:
- Description of facts/circumstances. The prerequisites for the situation that arose or the real events that led to its occurrence are indicated.
- A statement of specific reasons for the appearance of excess (unaccounted for) cash in the cash register. As a rule, there are several such reasons. They should be correctly identified to minimize the degree of guilt and mitigate future liability.
In addition, the explanatory paper, presented in two copies, must contain the following mandatory details:
- name of the business entity (employing company);
- Full name, position of the manager;
- the name of the paper itself (“Explanatory”);
- Full name, position of the responsible employee (cashier);
- date of preparation of the document, signature of the originator.
When the document is fully drawn up and signed by the cashier, it should be provided to the employer. The manager signs the paper (both copies) with the registration number. One copy must remain with the compiler (cashier).
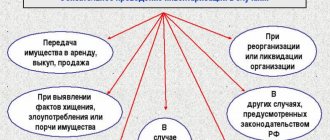
What documents need to be completed?
The work of the inventory commission to identify and investigate cash irregularities in the organization is necessarily recorded by maintaining a special protocol, which reflects the following:
- detailing the results of the cash audit;
- description of methods used to identify cash surpluses;
- expert conclusions regarding the discovery of excess cash in the company's cash register.
The results of the activities of the inventory commission in the prescribed form are provided to the head of the organization, who authorizes the acceptance of excess cash into the cash desk by issuing a special administrative act.
The documentary basis for drawing up such an order is the cash inventory report, drawn up by the audit commission according to the INV-15 standard and containing the following information:
- basic details of the company;
- number and date of the inventory order (documentary basis for verification);
- number and date of formation of the INV-15 act;
- date of execution of the cash audit regulated by management order;
- financially responsible entity (full name, position) with signature;
- detailing of factual information and accounting data on the state of cash;
- determination of the total - the amount of the detected surplus;
- numbers of the latest cash orders (receipt / expense);
- Full name, position, signatures of all commission members;
- confirmation by the cashier of responsibility for the available cash in the cash register;
- the reason for the detected excess;
- signature of the financially responsible entity (with transcript);
- the manager's verdict regarding the discovered surplus;
- signature of the manager (with transcript and date).
The shortage is attributed to the person at fault
To perform an operation, you must create an Operation document.
Creating and filling out the “Operation” document (Fig. 3):
1. Menu: Transactions - Accounting - Transactions entered manually.
2. “Create” button.
3. Select the document type “Operation”.
4. In the “from” field, enter the inventory date.
5. In the “Content” field, enter the content of the operation.
6. To create a new transaction in the tabular section, click the “Add” button.
7. In the “Debit” field, select account 73.02 “Calculations for compensation of material damage.” Next, fill out the “Subconto1 Debit” field by selecting from the “Individuals” directory the person found guilty of the shortage.
8. In the “Credit” field, select account, select account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.”
9. In the “Amount” field, you must fill in the amount of the shortfall attributed to the guilty party.
10. In the “Content” field, indicate the content of the operation.
11. The fields “Amount Dt” and “Amount Kt” in the “NU” line are automatically filled in with the value specified in the “Amount” column.
12. “Record” button.
13. To call up a printed form of an accounting certificate, use the “Accounting certificate” button.
Rice. 3
Accounting and posting - postings
A copy of the INV-15 act is sent to the accounting department to perform the necessary accounting actions. The accountant makes the necessary postings (account correspondence).
Cash surpluses are recorded by accounting in the month of completion of the relevant check and, if an inventory was carried out, are accounted for on the date of acceptance of the detected cash.
If an annual audit was carried out, its results are reflected in the annual reports.
Identified excess cash in the cash register is reflected in accounting entries using the following entries:
| Operation (description) | Debit | Credit |
| Reflects cash revenue identified upon verification of cash register systems. | 50 | 90 |
| Cash surplus is capitalized as other income of the organization | 50 | 91 |
Reflection of surpluses discovered as a result of the cash register inventory
Excess cash and other assets identified during the inventory are accepted for accounting. However, they will be taken into account at the current market value, and not at the prices of the previous period. As a result, on the date of discovery of the surplus, its value may be either higher or lower (which happens more often) than its price at the time of its occurrence.
Important!
When taking inventory, the difference between the actual availability and the data indicated in the accounting records must be recorded precisely in the reporting period in which the audit was carried out.
Thus, other income appears in accounting, which must be indicated on the credit of account 91 (Other income and expenses) in subaccount 91-1 (Other income).
These operations are shown in the table.
conclusions
Like cash shortages, cash surpluses detected during an audit require certain actions on the part of the inventory commission, management, and the responsible cashier.
Everything is carefully documented by the protocol, an inventory act is necessarily drawn up, and the financially responsible entity prepares an explanatory document regarding the cash surplus.
The reasons for the appearance of unaccounted cash are clarified, the guilty party is determined, the employer issues a verdict on accepting the cash surplus for accounting and imposing sanctions on the culprit, and appropriate orders are issued.
How to write an explanatory note
Within the framework of current legislation, when surpluses are discovered during inventory, the employer is obliged to require an explanatory note from the cashier.
Important!
The employee does not have the right to refuse and must provide the required document within two working days.
The explanatory note is written on a computer or manually on the organization’s official letterhead. The signature and its transcript are written by hand. If a surplus is detected, a work completion report is drawn up, and a note from the responsible employee is attached to it.
The explanatory note contains two sections:
- The factual section describes the events and conditions that led to the situation described in the document. For example, this can be done like this: “Yesterday, March 20, an inventory was taken at the Ulybka cafe. As a result of the inspection, excess funds were discovered in the cash register.”
- The causal section indicates why extra funds appeared in the cash register. There are usually several reasons, and they need to be properly explained in order to reduce the degree of your guilt or future liability.
When writing an explanatory statement, the facts must be clearly indicated, but there is no place for speculation and reasoning in it. The document conveys to management only what the employee knows and has seen—data and facts.
Mobile online ModuleKassa
You can add up to 50 thousand goods and services to its catalog
Online stores
- You can connect trade and internet acquiring to our cash register to accept card payments. A convenient solution for online stores with courier delivery or pick-up point
- The cash register works with platforms that support Yandex.Kassa or Moneta.ru. For stores on 1C-Bitrix there is a separate application “ModuleFiscalization”
The shops
- Price tags for the store are generated automatically in your personal account.
You can edit and print them - The built-in scanner reads 2D barcodes from a box, product or screen. If the barcode is not in the catalog, ModulKassa will turn to Rate&Goods - a worldwide barcode database
- Gift cards can be entered into the product directory. The sales receipt is issued in accordance with 54-FZ with the necessary tags
Cafe and street food
- Cash register
Basic rules of cash discipline: briefly
In order to avoid administrative punishment in the form of financial liability and fines, it is sufficient that the management of the cash register meets at least some criteria.
- The first thing you need to do is create a cash book. It must necessarily reflect all monetary transactions;
- To perform cash transactions, the management of the enterprise needs to purchase a cash register. However, in some cases it can be replaced by the issuance of sales receipts and strict reporting forms;
- The accountant or cashier of the enterprise must strictly ensure that the maximum permitted cash limit is not exceeded under any circumstances.
It is these three parameters that must invariably be observed at the enterprise in order to avoid punishment from regulatory structures.
Documents such as cash outflow orders and cash inflow orders, journals and certificates from the cashier-operator are not strictly mandatory, and therefore, as a rule, are not subject to careful scrutiny by tax authorities and are not grounds for the application of administrative sanctions.
Checking bank accounts
An inventory must be carried out before submitting annual reports. Since an organization can open accounts in different banks, before checking it should study in detail all banking agreements, check the legality and feasibility of opening an account.
To summarize the movement of funds in non-cash form, accounts 51 “bank account in rubles” and 52 “Currency accounts” are used in the balance sheet. To detail the information, you can use subaccounts 52-1 “Currency account in the Russian Federation” and 52-2 “Currency account abroad”.
What is cash discipline and why is it important to observe it?
In simple and understandable language, cash discipline is usually understood as a number of rules, norms, and restrictions on the receipt, issuance, and storage of cash at an enterprise, as well as, in the case of non-cash payments, their accounting as part of cash transactions. All operations in which cash is present, including the issuance of salaries and vacation pay, acceptance of payment for goods and services, as well as their timely documentation, are called cash transactions in the language of accountants.
As a rule, the cash desk is handled by either a cashier, a staff accountant, or, in more rare cases, the director and founder of the organization himself.
Any enterprise, be it an individual entrepreneur or an LLC, when carrying out any operations related to the circulation of cash finance, is obliged to keep a cash register and observe cash discipline.
Important! The set of rules by which it is customary to operate a cash register is not determined by internal private regulations of the organization, but is established at the level of Russian legislation.
Systematization of accounting
In accordance with paragraph.
3.3 Provisions when an organization conducts cash transactions using cash register equipment, upon completion of their implementation, based on the control tape removed from the cash register equipment, a cash receipt order (form 0310001) is issued for the total amount of cash received.
Note that based on the cited norm and other provisions of Chapter 3 “Procedure for accepting cash” of the Regulations, we can come to the conclusion that a cash receipt order is applied only when received from a specific depositor. The use of this document when identifying the fact of excess funds in the cash register is not provided.
Who checks cash discipline and what threatens violators?
Just from the fact that cash discipline is regulated by the Law of the Russian Federation, it is clear that it is controlled by government agencies. Impeccable compliance with cash discipline is monitored by the tax office and sometimes by the bank in which the organization's current accounts are opened.
- check of cash discipline by representatives of the tax office. Each territorial branch of the Federal Tax Service has a special Operational Control Department. Its employees go out to inspect enterprises and organizations regarding accounting and compliance with cash discipline.
The slightest flaws and shortcomings in cash management invariably lead to administrative sanctions.The most common of these violations are neglect of the availability and maintenance of a cash book, exceeding the limit of cash-related settlements, and incorrect calculation of cash balances.
- checking cash discipline by representatives of the servicing bank.
Every two years, employees of the servicing bank are required by law to check cash accounting at the enterprise. Typically the review period is one quarter. Banking specialists, as a rule, check the organization for the cash limit in the cash register, as well as for the correctness and completeness of the cash book. After carrying out the control, the bank specialist writes a certificate, which will subsequently need to be presented to the tax inspector during a tax audit, if one follows. If the violations identified by the bank representative are not corrected, the tax authority may impose a fine.
Recalculation of forms
The actual availability of Central Bank forms and reporting documents is carried out by name, type and category of forms. For example, shares can be registered, bearer, interest-bearing and ordinary. During check
The starting and ending numbers of the forms, their series and cost are also recorded.
All these monetary documents are registered based on the results of the inventory in the amount of expenses for their acquisition. The balance of the forms is determined based on the data in the cash book or report. If a shortage of forms is detected, the shortage is registered at the cash desk. Accounting entries are made according to analytical and synthetic accounting accounts. Examples of registration of such operations will be presented below.