When the management of an enterprise needs to check documentation related to its activities for accuracy and compliance with the requirements specified in the legislation, an independent verification is carried out - an audit. For some companies, this is a mandatory procedure that must be completed annually.
Auditing activities in the Russian Federation are regulated by the Federal Law of December 30, 2008. No. 307 (law “On auditing activities”).
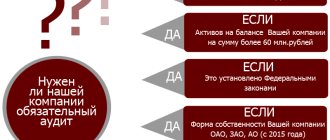
Who should undergo a mandatory audit ?
Accounting policy
One of the first documents that the auditor will ask you for is your organization's properly executed accounting policies . We remind you that the need to formulate an accounting policy and the basic requirements for its content and disclosure are enshrined in Article 8 of Federal Law 402-FZ “On Accounting”, as well as in PBU 1/2008 “Accounting Policy of the Organization”.
Key considerations regarding accounting policies generally include the following:
- The accounting policies are not properly drawn up or are out of date.
What does this mean? The accountant brings the accounting policy without a signature, just printed sheets with text, sometimes still warm from the printer. Or the other extreme: the accounting policy was properly approved, but it was so long ago that even the sheets have turned yellow, not to mention the fact that the content of such an accounting policy has long been outdated. - The accounting policies do not fully reflect the accounting methods used.
This means that you forgot to include in your accounting policies some of the actually used accounting methods. To avoid this, when preparing for the audit, check your accounting policies again for compliance with paragraph 4 of PBU 1/2008 “Accounting Policies of the Organization.” Your document must state: - working chart of accounts containing synthetic and analytical accounts necessary for maintaining accounting records in accordance with the requirements of timeliness and completeness of accounting and reporting
- procedure for conducting an inventory of the organization's assets and liabilities
- methods for assessing assets and liabilities
- document flow rules and accounting information processing technology
- procedure for monitoring business transactions
- other solutions necessary for organizing accounting
forms of primary accounting documents, accounting registers, as well as documents for internal accounting reporting
Can negativity on the Internet affect the audit process?
Direct negativity cannot become a reason for checking. The maximum is to push for closer attention. If there is a lot of negativity about a company, then this is a consequence of systemic problems.
The main thing you need to know about auditing is that it is a legally regulated procedure. Even unscheduled inspections cannot happen just like that. This also applies to the procedure itself - business activities and financial statements are studied. However, the form of the report is more democratic, so the auditor can attach screenshots of negative publications to it. After all, this is a risk to your financial condition, right?
In reality, everything is somewhat more complicated. The impact of negativity on reputation - and, as a result, sales - is difficult to imagine as a quantifiable metric. There is another concept for this - goodwill. However, it is recorded only when purchasing an operating enterprise when preparing consolidated financial statements.
A negative information background is of great importance during another check - due diligence. Most often, it is ordered by investors to assess the attractiveness of a potential asset: business, real estate, land, etc.
A Russian businessman was looking for partners to open a company in Europe. Interested parties were found, and after discussing the plans, due diligence began. Unfortunately, the joint venture did not work out. It's all about media publications where the entrepreneur appears as a trader. There is no negativity or crime in the articles. However, European investors did not want to do business with a trading partner.
Unlike an audit, due diligence is a more flexible procedure. Therefore, such failures are becoming more common.
So far, in our practice, there have been no cases where undesirable publications prevented us from passing an audit. At the same time, there are plenty of cases with due diligence - we wrote about this in detail together with experts.
Financial statements
At this step, you need to check the completeness of your reporting, the consistency of accounting and reporting data, as well as the quality of completion. The fact is that some required fields or lines are not filled in automatically in 1C or in another accounting program, and we are all too accustomed to the fact that it is enough to click the “Fill” button. For example, in the balance sheet and income statement, the “Explanations” column must be filled out independently.
In addition, please note that if you are subject to a statutory audit, the reporting set must contain all forms, including attachments, and not be limited to a set of simplified financial statements. This norm is enshrined in paragraph 5 of Article 6 of Federal Law 402-FZ “On Accounting”. As a rule, a small business, encountering a mandatory audit for the first time, mistakenly provides an incomplete set, acting in accordance with paragraph 4 of Article 6 of the above-mentioned law, which allows small businesses to use simplified accounting methods, including simplified financial statements.
Directions
Comprehensive audits of accounting statements are most common in Russia: payment documents, pay slips, and tax returns. But in a broad sense, it can also be the study of technological processes, an economic project or a separate product.
In world practice, three main directions have emerged:
- Financial . It can be carried out either by company employees (internal) or by an independent expert (external). There is also such a thing as an investment financial audit: when investors want to make sure that their funds are used legally and effectively.
- State. Most often it is carried out on its own, that is, it is internal, and is designed to solve the specific problems of a particular organization.
- Managerial (comprehensive). This is a diagnostic study aimed at increasing efficiency, optimizing enterprise costs, and ensuring transparency of management processes. It is in the field of management auditing that it is not the identification of violations that is of particular value, but the recommendations of the competent person who conducted the analysis.
It is interesting that the legislation of the Russian Federation gives a very narrow definition of this term: according to 307-FZ (as amended on April 23, 2018) “On auditing activities,” this is only called “independent verification of accounting (financial) statements.”
With this interpretation, internal measures lose legal force and acquire an unofficial character, while other non-monetary objects completely fall out of the sphere of external economic control.
Tax
It is often confused with financial or tax inspection. In fact, owners order testing when there is a need to determine the correct amount of payments, analyze specific tax problems inherent in a given area of business, and plan amounts for paying taxes in expense items.
Independent opinion and advice can be indispensable for the normal functioning of a company, especially a small one that relies on the services of one accountant. The fact is that tax legislation is very changeable, and it is incredibly difficult to keep track of all the innovations alone.
The process is usually preventive in nature: thanks to the recommendations received, the manager can prepare for the visit of the tax inspectorate, eliminate violations and avoid large fines and sanctions, including freezing and liquidation of the legal entity.
Personnel
Personnel audits are related to the use and movement of labor resources - the hiring and dismissal of employees, the vacation schedule, the amount of sick leave.
There are two types of personnel analytics: analysis of record keeping and full coverage of the management sphere, right down to the policy of rewarding and punishing employees.
Companies operating in a high-risk segment, for example, attracting foreign employees, are especially in dire need of independent labor assessments.
During the inspection, the expert not only identifies the presence of errors in the document flow, but also evaluates the completeness and compliance with the law of each package of documents filed for an employee or department. This allows the manager to receive competent recommendations and protect the organization from fines.
Reconciliation reports for counterparties
Paragraphs 73 and 74 of the Regulations on accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation state:
- settlements with debtors and creditors are reflected by each party in its financial statements in amounts arising from the accounting records and recognized by it as correct
- The amounts reflected in the financial statements for settlements with banks and the budget must be agreed upon with the relevant organizations and identical. Leaving unresolved amounts for these settlements on the balance sheet is not permitted.
Thus, the law does not establish mandatory reconciliations with counterparties when conducting an inventory of receivables and payables, with the exception of reconciliations with the bank and the budget.
In practice, the auditor, on a selective or continuous basis, will ask you for signed reconciliation reports with counterparties. The fact is that in his activities the auditor is obliged to be guided by auditing standards, which, in particular, indicate that audit evidence obtained from an independent source external to the audited entity (third-party confirmation) is more reliable. Therefore, when preparing for an audit, it is very important to check in advance, if not for all, then for the main counterparties, especially since accounting errors may be identified during the reconciliation process.
What is an audit
An audit is independent and involves the collection, evaluation and analysis of data that indicate the functioning and financial position of a public, commercial or private enterprise (the entity being audited).
You can learn more about the list of necessary documents for opening an individual entrepreneur in this article.
The results obtained make it possible to draw final conclusions (conclusion) about how correctly the accounting records are maintained and whether the financial statements are truthful and reliable.
An independent audit merely provides control over how laws and norms of economic law are observed and whether there are any violations of tax legislation.
There is a complete lack of targeted identification of errors in the work of accountants (financiers).
Inventory
In accordance with paragraphs 26 and 27 of the Regulations on maintaining accounting and financial reporting in the Russian Federation, in order to ensure the reliability of accounting data and financial reporting, organizations are required to conduct an inventory of property and liabilities, during which their presence, condition and assessment are checked and documented, in In particular, it is mandatory to do this before drawing up annual financial statements. Therefore, when preparing for an audit, make sure that your organization has carried out an inventory and its results are documented, since such a procedure as an inventory, due to its mandatory nature, cannot be ignored by the auditor. In addition, the inventory carried out in terms of receivables and payables allows us to identify doubtful or bad debts for which it is necessary to create a reserve.
Typical errors and violations
Here is a list of common violations that may be detected during an inspection:
- expenses and income are reflected incorrectly;
- the accounting details are filled out incorrectly or incompletely;
- tax amounts are calculated incorrectly;
- indicators of different reporting forms contradict each other;
- the amount of the authorized capital differs from what is stated in the charter;
- arithmetic errors in calculations;
- formal inventory taking, carrying it out with errors, etc.
Reserves
At this stage, it is necessary to check whether a reserve for doubtful debts has been formed in the accounting records and how well the formed reserve corresponds to the inventory results as of December 31. The most common mistake in this matter is completely ignoring the obligation to form a reserve for doubtful debts, despite the clear requirement of the law for its formation in accordance with paragraph 70 of the Regulations on Accounting and Financial Reporting in the Russian Federation.
Also make sure that your company has created a reserve to pay for vacations of the organization's employees, which is an estimated liability. In accordance with paragraph 3 of PBU 8/2010 “Estimated liabilities, contingent liabilities and contingent assets,” all organizations are required to reflect estimated liabilities, with the exception of those who have the right to use simplified accounting methods. I repeat once again that if your organization is a small business, but is subject to mandatory audit, then you cannot use simplified accounting methods.
Responsibility for failure to carry out
The business entities listed earlier must undergo an audit of their financial statements every year, and also send the conclusion to the statistical authorities. Submission of the report must be carried out together with the submission of reports. If you cannot send the document on time, you can submit it within 10 days from the date of issue, but no later than December 31 of the year following the reporting year. This is stated in the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402 (the Law “On Accounting”), namely in its 2nd article.
In addition, within 3 working days from the date of issue of the conclusion, the company is obliged to enter information about the results of the audit into the Unified Federal Register on the facts of the activities of legal entities.
The fact of failure to conduct an audit does not entail punishment. Administrative liability occurs in the cases described below. Punishment is possible only for those organizations that are required to undergo a mandatory audit of their financial statements.
| Initiator of the fine | Cause | Article | Fine |
| Federal Tax Service | During an on-site inspection, it was discovered that an audit report was missing for the required storage period (from 5 years). | Part 1. Art. 15.11 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | From 5 to 10 thousand rubles for officials. |
| Rosstat | If an audit report has not been provided to this body within the required period. | 19.7 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | From 300 to 500 rubles for officials and from 3 thousand to 5 thousand rubles for legal entities. |
| Bank of Russia | The audit report was not posted on the JSC website within the required period. | Part 2 art. 15.19 Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation | From 30 thousand to 50 thousand rubles or suspension from work for 1-2 years for officials. For legal entities - from 700 thousand to 1 million rubles. |
The amount of the fine may be reduced by court decision if there were any exceptional circumstances that resulted in an administrative offense.
Source documents
Of course, you won’t be able to eliminate the auditor’s possible comments regarding the primary documents in one day; this is exactly the case when it is better to do everything correctly right away, namely, keep under control not only the timeliness of receipt of original documents, but also the “quality” of your primary documentation. You will be surprised, but for the most part, auditors’ comments on primary documents refer to paragraph 2 of Article 9 of Federal Law 402-FZ “On Accounting,” which lists the mandatory details of the primary document, or to paragraph 1 of the same article, which states that Each fact of economic life is subject to registration with a primary accounting document. Thus, typical comments regarding primary documentation boil down to the following:
- the primary document was drawn up in violation of current legislation
- primary document missing
As a rule, based on the results of an audit, there are always comments on primary documents, so it would be useful to pay special attention to this issue when preparing, and it is better to start preparing a year before the audit J.
Progress of the process
During the direct study of documentation and its assessment, the auditor must adhere to the requirements and standards. The specialist carries out:
- Collection of evidence, i.e. primary documents reflecting the facts of transactions, information from third parties, etc.
- Evaluation of sample results.
- Study of reporting indicators.
- Assessment of the degree of materiality.
- Determination of audit risk.
- Assessing the compliance of completed financial transactions with legal requirements.
- Other actions necessary to formulate valid conclusions.
Tip 1: How to audit an enterprise
The activities of any enterprise are subject to mandatory audit
, which is a verification of the reliability of the financial statements of the organization, its compliance with legislation in the field of accounting.
The audit also consists of monitoring the activities of the company, as a result of which clarifications and clarifications regarding the operation of the enterprise .
Instructions
- Audits can be mandatory or proactive. In the first case, they are held annually and are regulated by Russian legislation. Joint-stock companies, credit organizations, insurance companies, commodity and stock exchanges, and investment funds are subject to mandatory audit.
- An initiative audit is a check of the accounting and reporting of a company under an agreement with an audit company. At the same time, the scope of the audit may vary from the entire accounting and reporting system to its individual part. The most important goal of a proactive audit for a company is the ability to predict bankruptcy.
- The basic principle of conducting an audit is to determine the relationship between costs and results. It is necessary to agree in advance with the company on the scope of work, the timing of the inspection, as well as the method of providing information about the company’s activities. In some cases, auditors go directly to the enterprise, sometimes the company independently submits data.
- The audit begins with a review of the enterprise's and preparation for the audit. In this case, the cost of costs is calculated, as well as an assessment of the auditor’s risk during the audit.
- Next, audit procedures are carried out directly, with the help of which the compliance of the company’s internal control system with the required standards is determined. After which an audit report is drawn up, and then it is transferred to the head of the company. At the same time, violations identified during the inspection are indicated and the level of reliability of the submitted reports is calculated.
Deadlines
The duration of the inspection period during a voluntary audit of an organization’s activities is determined in the contract. The period depends on:
- Enterprise scale.
- Availability of representative offices and branches.
- Duration of activity.
- Scope of inspection.
- Accounting quality.
If a mandatory inspection is carried out, the period is established by law and regulations. As practice shows, an audit of an organization’s reporting in this case takes on average 1-2 weeks. There are cases of longer inspections, but they rarely last more than two months.
Tip 2: How to conduct an audit
The goal of any audit should be the extent to which the audit is needed. This may be the objective state of financial activity, economic strategy and internal verification of control of one or another structural form. Improving the company's performance should be a top priority in the audit.
Typically, a mandatory audit is carried out before the annual report is submitted. If an audit is carried out in several stages, the company can achieve a number of advantages, namely:
- Rates quoted at the end of the calendar year are usually higher because this is when most firms conduct audits.
- Your company will not need to change data in accounting and tax accounting just before submitting annual reports
- Limited time will definitely lead to errors in correction
It is advisable to conduct an audit distributed over several periods. For example, six months and the subsequent third quarter. In this situation, the accounting department will have enough time to correct various shortcomings. At the end of the year, all that remains is to check the corrections based on the comments made earlier. The last quarter will not be so busy. Thus, the burden on the finance department becomes minimal, and the cost of the audit is reduced through a phased audit.
The service, which is carried out when there is a change of owner, chief accountant, or during reorganization, is called a proactive audit. The main thing in such an audit is to assess the efficiency of the enterprise and the state of accounting. With this form of audit, the manager can check any departments where cost calculations were made and the correctness of taxation. As a result, your company will be able to pass all tax audits.
Express audit is carried out in cases of brief analysis. This may be a reporting period of a certain time associated with a change in the chief accountant or various personnel changes in departments.
The expert auditor's recommendation usually contains a number of explanations for the analysis of the client's financial activities. Based on any results of the audit, the auditor must issue documents to the customer-client with a detailed report on the work done and a conclusion that determines the correctness of the financial statements.
Recently, the services of audit firms have become widely used. Right now, many enterprises, even those for which annual inspections are not mandatory, are asking for inspections more and more often. Responsible selection of auditors and the goals set by the company are the key to a competent commercial strategy.
Instructions for auditors
The reporting can be verified by specialized organizations or private specialists. The latter are subject to a number of requirements. A private auditor must, firstly, be a member of an accredited self-regulatory organization. In addition, they must have:
- higher legal or economic education;
- work experience as an assistant auditor or chief accountant for at least three years;
- auditor certificate (issued based on the results of passing a special exam).
The legislation also establishes a number of requirements for audit firms. The organization must, firstly, be commercial, and secondly, be formed in any form, with the exception of an OJSC. Such a company must have at least three specialists on staff. At the same time, at least 51% of its authorized capital must belong to auditors or other similar organizations.
Tip 3: How to conduct an internal audit
Internal audit is carried out in order to obtain truthful information about the financial and material condition of the organization. It evaluates the methods and procedures of the business system for their productivity and effectiveness.
Instructions
- Before conducting an internal audit, you need to decide on the purpose and objectives that you would like to see as a result of the auditors’ work. The creation of your own audit may be negatively accepted by the employees of the enterprise, which may negatively affect the work of the organization. Therefore, it is necessary to convey to all services and departments of the enterprise that the audit is intended to control not employees, but the work process, identifying shortcomings and deviations in work, thereby helping to achieve better results.
- At the board of directors or at a meeting of founders, a decision is made to create an internal audit; such a decision is recorded in the relevant documents.
- The rules and powers of internal audit are formalized in a written document, which is signed by the board of directors or founders of the company.
- Before conducting an audit, auditors write a plan that specifies the method of carrying out procedures and the scope of work. The plan is signed by the head of the organization. If necessary, the manager gives written explanations about the work of the enterprise.
- If, when auditing a production process or similar operation, a specialist with specific knowledge is needed, then an outside professional is hired for such an audit and an appropriate agreement is signed with him.
- After conducting its own audit, the department issues a report in which the responsible auditor expresses an opinion on all material relationships and makes detailed recommendations. When expressing an opinion, the auditor is guided by the standards in accordance with the professional code of ethics for auditors.
- The audit department must conduct an internal audit on one assigned task until all errors and deviations are corrected.
- Remember that the auditor is independent of the company's management. This is the only way to ensure the reliability of the data provided in the auditor’s final report.
Key terms
Proper organization of an audit at an enterprise is impossible without implementing a set of measures, including:
- Drawing up projects for organizing internal audits by industry and area of work. They must clearly indicate the specific functions of the responsible persons, the rules for their interaction with other departments and the management of the enterprise, the status of internal auditors, their responsibilities, duties, and rights.
- Establishment of qualification requirements for audit service employees.
- Development and determination of rules for introducing standards, guidelines, and norms into the activities of the audit department.
- Drawing up programs for advanced training and training of internal auditors.
- Forecasting staffing needs.