Work time
Natalya Vasilyeva
Certified Tax Advisor
Current as of September 27, 2019
The production calendar for 2021 was compiled taking into account the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 10, 2019 No. 875, which approved the postponement of some days off in 2021. The calendar contains up-to-date information on the number of working days, weekends and holidays, standard working hours, and transfers of weekends.
The concept of a six-day working week, legislative framework
Chapter 16 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation provides for the establishment of working hours. There is no precise definition of this concept in the legislation, however, Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that the working time regime must take into account the following nuances:
- length of the work week (five-day work week with two days off, six-day work week with one day off, or work on a rotating schedule);
- irregular working hours for certain categories of workers;
- time of arrival and departure from work, including breaks;
- change of working days and days off in accordance with labor legislation, collective and labor agreements.
Regardless of work mode, the working week should not exceed 40 hours in total. However, there is an exception when a summary recording of working time is carried out - the norm of working time for a certain period (month, quarter, year) is observed.
This option is used if it is impossible to comply with the stipulated daily or monthly working hours. An organization can use a single operating mode (a five-day work week) or simultaneously use several modes (for example, one group works a five-day week with sliding days off, another group works a six-day week with one day off).
Where do the discrepancies come from?
In practice, such a “shift” of the working time norm from a five-day week to a six-day week leads to deviations. Simply put, with a six-day work week, the monthly norm calculated according to Order No. 588n may differ from the norm obtained by adding up the hours worked for the month. After all, the standard working time for a month during a six-day work week, according to the order, is determined by multiplying the number of working days on a five-day calendar by eight working hours. But the number of working Saturdays per month may not coincide with the number of working weeks on the five-day calendar. As a result, we have a strange situation - employees worked all month, as expected, 40 hours a week, but the total number of hours does not match the production calendar. And this happens quite often.
For example, in 2011 such a situation will occur in April, August and October. So, in August, during a six-day workday, employees cannot work more than 181 hours (23 working days of 7 hours and 4 Saturdays of 5 hours), while the norm according to the calendar for this month is as much as 184 hours. That is, it turns out that the employees did not meet the standard and they seem to need to reduce their salaries.
In October, we have the opposite situation: the norm according to the calendar is 168 hours, and because of the “extra” Saturdays, the actual time is much more - 172 hours (21 working days of 7 hours and 5 working Saturdays of 5 hours). That is, suddenly, out of nowhere, recycling appeared! This means you have to pay overtime. Agree, there is something to doubt.
Features of a six-day work week compared to a five-day schedule
Article 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation states that with a five-day working week there are two days off, and with a six-day week - one. The second day off during a five-day week is established in a collective agreement or in accordance with internal regulations, and Sunday is considered a general day off.
According to the rules, the length of the working day before a holiday is reduced by one hour. According to Article 95 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, with a six-day working week, the duration of work on such days cannot exceed five hours.
It is worth noting that if a weekend and a non-working holiday coincide, the first is transferred to the next working day after the holiday. Exceptions to this rule are the New Year holidays and Christmas (Part 2 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, two days off that coincided with these holidays are transferred to other days in the next calendar year.
This rule of transferring a day off that coincides with a holiday to the next working day also applies to regional holidays (Minutes No. 1 of 06/02/2014)
It is worth mentioning the length of a typical working day. With a five-day working week, it is eight hours; with a six-day working week, the number of hours per day is not clearly established, however, in practice, five days of seven hours are often set, and the sixth is five.
The nuances of work on a six-day schedule under different working conditions
Irregular working hours, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, provide that, by order of the employer, individual employees may be involved in performing their job duties beyond the established working hours. However, such a regime can only be applied to those employees whose collective bargaining agreement or agreement contains a list of job descriptions adopted taking into account the representative body of employees.
The employee's consent to the use of such a regime is not required.
A flexible work schedule, according to Part 1 of Article 102 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, is an organization of working time when the beginning, end or duration of working time is established by agreement of the parties to the employment contract. In this mode, daily or monthly working hours cannot be met, so summarized working time recording is used.
The employer, in this case, must ensure that the employee works the total number of working hours during a certain accounting period.
Shift work is established when the duration of the production process is higher than the permissible norm. This mode is used for more rational use of equipment, as well as increasing the volume of products or services provided. In accordance with Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, each group of workers must perform their labor duties during the time established in the shift schedule.
In some types of production with unequal intensity of work throughout the working day, according to Article 105 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the working day can be divided into parts. Labor legislation does not regulate their duration and quantity. The only condition remains compliance with the limits of the total working time and the prescribed duration of daily work.
Internal labor regulations are a local regulatory act that regulates hiring, dismissal, rights, duties and responsibilities of the parties, work and rest hours, types of incentives and penalties applied to the employee, as well as other issues regulating labor relations (Article 189 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation) .
Solving the problem
In fact, the situation is resolved quite simply - you just need to carefully read the definitions contained in the Labor Code. The Labor Code is a document of direct effect, its legal force is higher than that of the order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development (issued, by the way, on the basis of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
So, how to solve the problem that will arise for organizations working six days a day in August, when employees do not formally work out the norm? To answer, you need to refer to Article 129 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which defines salary. It is understood as a value depending on the performance of job duties of a certain complexity for a calendar month. Job responsibilities are fixed in employment contracts and (or) job descriptions. This means the following: if employees performed their duties for a month in full accordance with the employment contract and instructions, there is no reason to reduce the salary. And a formal discrepancy between the figures of actually worked time and a certain standard, calculated according to the rules of Order No. 588n, cannot be such a basis for reducing wages.
Now let's move on to October, when "extra" Saturdays will provide "extra" hours. Do I need to pay overtime? Here we need to carefully study Article 99 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, which defines overtime work. It refers to work performed by an employee at the initiative of the employer outside the working hours established for the employee: daily work (shift). The duration of working hours is again fixed in the employment contract and (or) internal labor regulations. This means that if the duration of each work shift during a month does not exceed what is stated in the employment contract (and in Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation), then overtime work cannot occur. So the employer is not required to make any additional payments.
Thus, it can be stated that in both cases under consideration we are talking only about a mathematical discrepancy in the norm of working time, caused by the imperfection of the mechanism for calculating this norm, enshrined in order No. 588n. Accordingly, this imperfection cannot lead to any negative consequences for the organization, but it is necessary to know about it, precisely in order to correctly calculate the standard working time for “six-day workers.”
*Let us note in passing that this norm is far from new - previously a similar provision was contained in the clarification of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 29, 1992 No. 5, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 29, 1992 No. 65. However, now the status of this norm has increased significantly - it is contained in the order issued by virtue of direct instructions in Part 3 of Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Standard hours for a six-day work week
According to Article 100 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, one day off is established for enterprises and organizations with a six-day working week. The general day off is Sunday (Article 111 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The normal duration of a six-day working week, like a five-day one, cannot be more than 40 hours (Article 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
The standard working time for a six-day work week is calculated according to the calculated schedule of a five-day work week. Thus, the standard working hours in both cases are the same.
Calculation of working time standards in 2021 is carried out depending on the duration of the work shift:
- with a 40-hour work week – 8 hours;
- if the working week is less than 40 hours - the number of hours that is obtained by dividing the established working week by five.
The absence of postponements of weekends due to holidays does not in any way affect the procedure for calculating time standards, since they are calculated based on a five-day week.
Therefore, the working time standards for a six-day working week are:
- at 40 hours – 1970 hours (40 hours: 5 days × 247 days – 6 hours);
- at 36 hours – 1772.4 hours (36 hours: 5 days × 247 days – 6 hours);
- at 24 hours – 1179.6 hours (24 hours: 5 days × 247 days – 6 hours).
Production calendar for 2021 (6-day work week)
The following non-working holidays are established in Russia (Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation):
- January 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 8 — New Year holidays;
- January 7—Christmas Day;
- February 23 - Defender of the Fatherland Day;
- March 8—International Women's Day;
- May 1 - Spring and Labor Day;
- May 9 - Victory Day;
- June 12—Russia Day;
- November 4 is National Unity Day.
Weekends may be transferred to other days by federal law or a regulatory legal act of the Government of the Russian Federation (Part 5 of Article 112 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
In 2021, the following transfers of weekends are provided (Government Decree No. 1250 dated October 14, 2017):
- from Saturday 6 January to Friday 9 March;
- from Sunday January 7 to Wednesday May 2;
- from Saturday 28 April to Monday 30 April;
- from Saturday 9 June to Monday 11 June;
- from Saturday 29 December to Monday 31 December.
At the same time, Saturdays April 28, June 9 and December 29 will be shortened by 1 hour according to the “pre-holiday” principle. If, in accordance with a government decision, a day off is transferred to a working day, the duration of work on this day (in this case, Saturday) must correspond to the duration of the working day to which the day off was transferred (clause 1 of the Procedure for calculating working time norms, approved by order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated August 13, 2009 No. 588n).
Taking this into account, we rest like this:
- The New Year holidays will last 10 days - from December 30, 2021 to January 8, 2021;
- On Defender of the Fatherland Day we will rest for 3 days - from February 23 to 25;
- on International Women's Day 4 days - from March 8 to 11;
- in May we will rest for 4 days in honor of the Spring and Labor Festival - from April 29 to May 2;
- there will be another day off on May 9 in honor of Victory Day;
- Russia Day will be marked by three weekends - from June 10 to 12;
- On National Unity Day we will also have a 3-day holiday - from November 3 to 5;
- Saturday, December 29th will have to be worked, but Monday, December 31st will be a day off.
In the Republic of Crimea, by special resolution of the head of Crimea, additional days off were approved:
- March 18 is the Day of the reunification of Crimea with Russia;
- April 17, 2021 - Easter;
- May 28, 2021 - Trinity;
- June 15, 2021 - Eid al-Adha;
- August 22, 2021 – Eid al-Adha
Calculation of standard working hours
The standard working time for certain periods (month, quarter, year) is calculated as required by Art. 91 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and in accordance with Order No. 588n.
So, the norm for a particular month is calculated as follows:
the length of the working week (40, 36, 24, other number of hours) is divided by 5, multiplied by the number of working days according to the calendar of the 5-day working week of this month and from the resulting number of hours the number of hours in this month for which work is carried out is subtracted reduction of working hours on the eve of non-working holidays.
Important! The standard working time calculated in this manner applies to a 6-day working week.
Thus, when drawing up a monthly schedule for a 6-day week, it is necessary to ensure that not only the weekly limit (40-, 36-, 24-hour) is observed, but also that the total number of working hours does not exceed the monthly norm calculated in the specified above order.
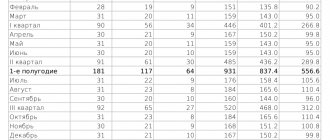
Number of days in 2021 by month: workdays, weekends, holidays
January:
- working days - 20;
- days off - 3;
- non-working holidays - 8.
February:
- working days - 24 (1 pre-holiday);
- days off - 4;
- non-working holiday - 1.
March:
- working days - 25 (1 pre-holiday);
- days off - 5;
- non-working holiday - 1.
April:
- working days - 26 (1 pre-holiday);
- days off - 4.
May:
- working days - 23 (1 pre-holiday);
- days off - 5;
- non-working holidays - 3.
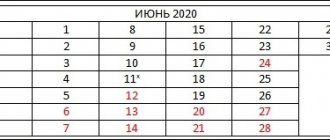
June:
- working days - 25 (1 pre-holiday);
- days off - 4;
- non-working holiday - 1.
July:
- working days - 27;
- days off - 4.
August:
- working days - 26;
- days off - 5.
September:
- working days - 26;
- days off - 4.
October:
- working days - 27;
- days off - 4.
November:
- working days - 24 (1 pre-holiday);
- days off - 5;
- non-working holiday - 1.
December:
- working days - 27 (1 pre-holiday);
- days off - 4.