An agreement on collective liability allows you to protect the interests of the employer. But it can be concluded only with those employees who perform work included in the “List of positions and work replaced or performed by employees with whom the employer can enter into written agreements on full individual or collective (team) financial responsibility for shortages of entrusted property,” approved Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85.
For example, such an agreement can be concluded with a team of warehouse workers, since they perform the work provided for in the specified List: acceptance for storage, processing (manufacturing), storage, accounting, release (issue) of material assets.
The standard form of such an agreement is provided for by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85.
Sample agreement on collective liability 2020, standard form
Order No. 169 of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated August 19, 1982 approved the “Instructions on the procedure for applying in state trade the legislation regulating the financial liability of workers and employees for damage caused to an enterprise, institution, or organization.” According to clause 3.7 of the Instructions, an agreement on full collective brigade financial responsibility cannot be concluded with the following persons:
- with employees of the small retail network (delivery and distribution trade, trade in tents, kiosks, etc., including those located separately in the sales area), as well as other persons with whom an individual agreement on full financial responsibility has been concluded;
- hired on a part-time or part-time basis, if they, together with other employees, do not manage commodity assets (these persons can be sent to independent areas of work with full individual financial responsibility);
- workers of auxiliary professions (ironers, cutters, etc.);
- junior service personnel, loaders, auxiliary (transport) workers, watchmen;
- persons under 18 years of age;
- trainees of educational institutions, students studying directly at trade enterprises;
- graduates of higher and secondary specialized educational institutions and vocational education institutions who do not have experience working with material assets, as well as persons who have undergone industrial training during the first year of work. These employees are prohibited from entrusting independent work on servicing material assets outside the enterprise (delivery and distribution trade, trade in tents, stalls, etc.).
IMPORTANT!
The guidelines continue to apply to this day, but the order in which they will be applied has not been determined. In this regard, this document can be used as a recommendation, since the mandatory nature of its norms is not established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other Federal laws.
However, this regulatory act contains important clarifications that are not reflected in the current legislation. So, for example, according to clause 2.6 of the Guidelines, group responsibility for valuables located on the sales floor (in production) and in the utility room can be established if:
- the utility room is used by only one group, all its members have free access to material assets located both in the sales area and in the utility room, and participate in all trade, warehouse and production operations;
- all commodity operations of production, auxiliary warehouse premises, commodity-money transactions of the trading floor constitute a single process of the group’s work and are controlled by all its participants.
The employer can use these provisions when organizing the safety of property entrusted to the team.
Sample collective liability agreement for a store
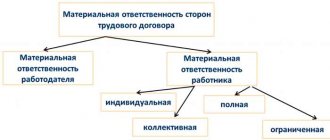
When is a collective financial responsibility agreement needed?
In accordance with Article 244 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, an employer can enter into financial liability agreements with employees in cases where it is impossible to differentiate the responsibility of each employee for causing harm.
Agreements on full collective (team) financial responsibility can be concluded only with those employees who perform work included in the List of Positions and Works, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 31, 2002 No. 85.
Such an agreement can be concluded, for example, with a team of warehouse workers, since they perform the work provided for in the specified List, namely: acceptance for storage, processing (manufacturing), storage, accounting, release (issuance) of material assets. However, remember that you cannot prepare a sample agreement on collective financial liability of the seller; in this case, you will need an agreement on individual financial liability.
Grounds for prosecution
The use of this type of responsibility is typical for companies operating in a certain direction. For example, this is catering or sales, construction work, accepting payments, taking measures aimed at protecting documentation, etc.
The conditions for the application of liability in its financial manifestation are specified in Article 243 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The list includes:
- availability of evidence from the company management that items were used in a smaller volume than indicated in the documentation, items were damaged during the working period;
- presence of intent to carry out this violation;
- the cause of the damage was non-compliance with commercial secrets;
- damage to members of the enterprise committed during non-working hours.
An important condition for the use of this type of measure is the presence of evidence of harm.
Who can you enter into an agreement with?
Order of the USSR Ministry of Trade dated August 19, 1982 No. 169 approved “Instructions on the procedure for applying in state trade the legislation regulating the financial liability of workers and employees for damage caused to an enterprise, institution, or organization.” According to clause 3.7 of the Guidelines, agreements on full collective responsibility cannot be concluded with the following persons:
- employees of a small retail network (delivery and distribution trade, trade in tents, kiosks, etc., including those located separately in the sales area), as well as with other persons with whom an individual agreement on full responsibility has been concluded;
- persons hired on a part-time or part-time basis, if they, together with other employees, do not manage commodity assets (these persons can be sent to independent areas of work with full individual financial responsibility);
- workers of auxiliary professions (ironers, cutters, etc.);
- junior service personnel, loaders, auxiliary (transport) workers, watchmen;
- persons under 18 years of age;
- trainees of educational institutions, students studying directly at trade enterprises;
- graduates of higher and secondary specialized educational institutions and vocational education institutions who do not have experience working with material assets, as well as persons who have undergone industrial training during the first year of work. These employees are prohibited from entrusting independent work on servicing material assets outside the enterprise (delivery and distribution trade, trade in tents, stalls, etc.).
IMPORTANT!
The guidelines continue to apply to this day, but the order in which they will be applied has not been determined. In this regard, this document can be used as a recommendation, since the mandatory nature of its norms is not established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal laws.
However, this regulatory act contains important clarifications that are not reflected in the current legislation. So, for example, according to clause 2.6 of the Instructions, the financial responsibility of the team for valuables located on the sales floor (in production) and in the utility room can be established if:
- the utility room is used by only one group of workers, all of them have free access to material assets located both in the sales area and in the utility room, and participate in all trade, warehouse and production operations;
- all commodity operations of production, auxiliary warehouse premises, commodity-money transactions of the trading floor constitute a single work process and are controlled by all its members.
The employer can use these provisions when organizing the safety of property entrusted to the team.
What types of work fall under this form of relationship?
All work that involves general access to goods or funds falls under this type of liability. This is justified by the fact that goods or other items that are available to the entire group of employees may be subject to theft or damage due to the fault of any of the employees .
After a precedent of damage arises, the entire team working on the site is subject to the possibility of obtaining recovery in the form of deducting the amount of damage from earnings .
Important! On behalf of the team or team, a representative - the foreman or the head of the unit - acts as a party to the contract.
This type of liability primarily imposed on the following employees:
- sales team;
- employees of some credit institutions;
- warehouse and storage workers;
- public service providers;
- other persons who have full access to the property.
The main rule is the absence of a reliable opportunity to identify who is responsible for the damage .
The remaining employees put their signatures on the agreement indicating their agreement.
A complete list of positions falling under responsibility can be found in this article.
How to conclude an agreement on collective liability
The employer's decision to establish full collective (team) financial liability is formalized by order or directive. Team members must be familiarized with the document and signed.
Since there is no unified form of the order, the employer has the right to develop it independently. The order (instruction) should reflect the following information:
- on the formation of a team (team);
- on the appointment of its leader;
- on concluding an agreement on full collective material liability.
General and mandatory points of the DKMO
General (managerial) aspects of the operation of the DKMO are reflected in a separate section and include the following:
- compliance with the principle of voluntariness when forming a team;
- appointment of a foreman taking into account the opinion of the team;
- assignment of duties to a temporarily absent foreman;
- an unconditional requirement to re-conclude the DKMO when the team changes by 50%;
- entering additional information into the DKMO, which does not lead to its re-conclusion, upon the admission or departure of its members from the brigade.
An important part of the DKMO is the section on the rights and obligations of the parties to the agreement. The team and the employer are subject to a set of mandatory procedures, which can be grouped into 3 groups:
- the team is obliged to ensure the safety of the entrusted property, and the employer is obliged to organize the necessary conditions for this;
- the team is obliged to promptly inform management about cases that threaten the safety of property, and the employer is also obliged to promptly influence their elimination;
- the foreman must monitor the movement and take into account the balances of the entrusted assets, as well as report on this, and the employer must provide appropriate conditions for this.
In addition to those indicated, the employer is assigned 2 additional groups of responsibilities:
- provide the team with up-to-date information about current legislation in the field of liability, regulatory nuances of the procedure for storage and other operations with property;
- take into account the opinion of the brigade in various issues related to the formation of the brigade, or when considering the validity of requests for an inventory of assets entrusted to the brigade.
Learn the nuances of conducting and registering an inventory in the materials posted on our website:
- “Inventory order - sample filling”;
- “Unified form No. INV-3 - form and sample”.
The same section of the DKMO establishes the rights of the brigade - we’ll talk about this later.
The procedure for collecting damages under a collective liability agreement
If damage is identified that is subject to compensation by the team, the employer is obliged to:
- Document the amount of damage.
- Request an explanation from all team members regarding the existence of damage.
- Establish a cause-and-effect relationship between damage and the performance/non-performance of job duties by employees.
Damage to be compensated by the team is distributed among team members in proportion to the monthly tariff rate (official salary) and the time actually worked for the period from the last inventory to the day the damage was discovered (clause 7.3 of the Instructions). Judicial practice recognizes this method of calculating damages as logical and lawful (clause 14 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of November 16, 2006 No. 52, Determination of the Moscow City Court of June 29, 2010 in case No. 33-16601).
IMPORTANT!
It should be taken into account that, according to Part 4 of Art. 245 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, the degree of guilt of each team member is determined by agreement between all members of the team and the employer. Therefore, the employer must draw up an agreement with the employees, which will specify the amount of compensation for each of them.
The very amount of damage to be paid by a specific employee, in accordance with clause 7.3 of the Instructions, can be determined using the following formula:
Р1= С x З1/ (З1+ З2+…+ Зn),
Where:
- P1 - the amount of compensation for damage by the first member of the team;
- C - amount of damage;
- Z1, Z2, Z3, ... Zn - wages of team members for the inter-inventory period based on salaries taking into account the time worked.
When calculating the amount of damages, wages do not include bonuses received by team members, as well as severance pay, compensation and other payments, which, according to the law, are not subject to recovery.
Accordingly, after determining the amount of compensation for damage, a written agreement is drawn up on the amount and procedure for its repayment. The agreement is drawn up by all team members and signed by them and the employer.
If damage is recovered in court, the degree of guilt of each member (of the team) is determined by the court (Part 4 of Article 245 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Current legislation does not provide for joint liability of employees with whom an agreement on collective financial liability has been concluded in case of harm to the employer.
How to determine the amount of damage caused
To determine the amount of damage, you will need to use the provisions of Art. 246 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This rule reflects that when damage is caused to objects belonging to a particular enterprise, the amount of damage is reflected according to the actual losses. Market prices should be taken into account. They are established on the day when the harm occurred. Financial accounting data can be taken into account.
The provisions of the definition, developed by the highest judicial body of our country in 2009, indicate that a company employee is obligated to pay compensation only for the damage that was actually caused. There is no obligation to realize compensation for lost profits of the organization.