Posting penalties according to the Writ of Execution through Bailiffs in State Institutions
For information: If, by a court decision, the state duty is transferred by the defendant institution to the budget, then the expenses should be attributed to expense type 852 “Payment of other taxes, fees” and KOSGU code 291 “Taxes, duties and fees”.
Having considered the issue, we came to the following conclusion: Expenses associated with payments under the writ of execution in terms of reimbursement of legal expenses to the plaintiffs are subject to attribution to the expense type code 831 in conjunction with subarticle 296 “Other expenses” of article 290 “Other expenses” of the KOSGU.
Accounting for legal costs and penalties
Almost every organization in the process of economic activity has to participate in litigation. Sometimes the business entity itself sues unscrupulous contractors, and sometimes it becomes necessary to act as a defendant.
We must not forget about disputes with tax authorities, which very often end up in arbitration courts.
When participating in a lawsuit, an organization incurs certain costs.
Leonid SOMOV Tax lawyer In general, legal costs can be divided into state fees and costs associated with the consideration of the case. The Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation specifies the composition of the costs associated with the consideration of the case.
Thus, in accordance with Article 106 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, such costs include: • sums of money to be paid to experts, witnesses, translators; • costs associated with on-site inspection of evidence; • expenses for the services of lawyers and other persons providing legal assistance (representatives); • other expenses incurred by persons participating in the case in connection with the consideration of the case in the arbitration court. If the case is heard in courts of general jurisdiction, and this happens when the plaintiff or defendant is a citizen of the Russian Federation or a foreign person, then the costs associated with the consideration of the case, in accordance with Article 94 of the Civil Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, include: • amounts subject to payments to witnesses, experts, specialists and translators; • expenses for translation services incurred by foreign citizens and stateless persons, unless otherwise provided by an international treaty of the Russian Federation; • travel and accommodation expenses of the parties and third parties incurred by them in connection with their appearance in court; • expenses for the services of representatives; • costs of on-site inspection; • compensation for actual loss of time; • postal expenses incurred by the parties related to the consideration of the case; • other expenses recognized by the court as necessary.
Regarding tax disputes, let us recall that the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, in its ruling dated February 20, 2002 No. 22-O on the complaint of the open joint-stock company "Bolshevik" about the violation of constitutional rights and freedoms by the provisions of Articles 15, 16 and 1069 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, noted that all losses, related to unlawful actions of the tax inspectorate, including the costs of paying lawyers, should be included in the damages reimbursed to the winning party.
Before the definition of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, arbitration courts considered these costs not losses, but legal costs that must be compensated in a special manner.
When filing a claim with the arbitration court, you must pay a state fee (Art.
102 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). Its dimensions are established by the Law of the Russian Federation of December 9, 1991 No. 2005-1 “On State Duty”.
The amount of the state duty depends on the nature of the claim and its price. The state duty for cases considered in arbitration courts, with claims of a property nature is: • 5% of the value of the claim, but not less than one minimum wage for the value of the claim up to 10,000 rubles; • 500 rub.
Posting penalties according to the Writ of Execution through Bailiffs in State Institutions
The debt of accountable persons is reflected according to the article specified in the current legislation. It must be remembered that the tax sphere is constantly being reformed. If not all amounts have been spent, then the remainder is returned to the company's cash desk. If the amount was overspent, and there is evidence that it was necessary, then the overspending is returned to the employee. The necessity of the expenses incurred is checked and certified by the company management. If the employee received funds for travel expenses, then the advance report and the unspent amount should be submitted to the accounting department no later than 3 working days upon return. As a rule, a writ of execution comes by mail with a notification, which, after receiving it, must be sent back to the bailiffs. In this case, in the notification it is necessary to make a note about the receipt of the writ of execution, indicate its incoming number and date, the telephone number of the enterprise, signature and affix the seal of the organization. For bailiffs, this will be confirmation that the writ of execution has been received and the procedure for withholding the amounts specified in it has begun. Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
The formula for calculating deductions for claims of the same priority will be as follows: Postings on writs of execution with an example of calculating deductions In accounting, for deductions on writs of execution, account 76 is used. Let's consider an example with postings on deductions from wages on a writ of execution. Let’s say an employee receives two writs of execution for the collection of alimony. Payments under writs of execution: No. 1 – RUB 11,200.00. and No. 2 – RUB 14,200.00. Withholding according to the writ of execution of postings: Account Dt Account Ct Posting amount, rub. Description of the posting Document-basis 26 70 40 450.00 An employee of the enterprise has been paid wages Payroll statement 70 68-NDFL 5 258.50 Income tax has been withheld from the employee's wages 40,450.00 * 13% = 5,258.50 rubles.
This is interesting: Monthly allowance for single mothers for children aged 3 to 18 years Yekaterinburg
Accounting in non-profit organizations
Non-profit organizations are required to keep accounting records in accordance with generally accepted standards, in accordance with Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n. So, accumulate all accrued remunerations for labor in accounting account 70 “Settlements with personnel for remuneration”.
IMPORTANT!
Regardless of the type of organization (non-profit, budgetary, commercial), keep records of accruals separately for each employee. It is not allowed to enter generalized information on the enterprise as a whole or entries by workshop, section, department, shift.
It is permissible to open corresponding sub-accounts to account 70. For example, to detail information on workshops, departments and other structural divisions of the enterprise.
To reflect the accruals, an entry is made on the credit of account 70 in correspondence with the production cost accounts. For example, to reflect the earnings of core personnel, account 20 “Main production” is used, for support personnel - account 23.
Postings for deduction from wages according to the writ of execution
- Alimony for minor children;
- Alimony for elderly relatives;
- Compensation for harm caused to both physical and moral health of a person;
- Reimbursement of loans, borrowings and accrued interest;
- Compensation for damage caused to the organization.
The object of withholding is wages after taxation, that is, minus income tax. Payments under the writ of execution are transferred within 3 days from the date of payment of wages.
Which entries should be used to reflect payroll transactions?
Thus, in accordance with these regulations, public sector employees are required to use account 0 302 10 000 “Calculations for wages and accruals for wage payments” to reflect accruals in favor of their employees.
- Code “1” or 0 302 11 000 - is intended to reflect operations for directly calculating wages. For example, on this accounting account reflect the accrued salary, incentives, and compensation payments. If a territorial (district) coefficient is applied to earnings, then also reflect these amounts with code “1”. Also include in the group the amounts of accrued vacation pay and sick leave benefits at the expense of the employer.
- Code “2” or 0 302 12 000 - information on other payments in favor of employees is accumulated. For example, this group includes accruals in favor of women receiving benefits for children under three years of age. Currently, the amount of such payment is 50 rubles. If there is a regional coefficient in your region, then also include it in the group with code “2”.
- Code “3” or 0 302 13 000 - this group includes all calculations for calculating benefits for illness, pregnancy and childbirth, one-time payments from the Social Insurance Fund. That is, code “3” is intended to reflect charges for wage payments.
Reflection in accounting of collection under a writ of execution
How to reflect in the accounting of a state-owned institution a writ of execution, according to which a debt is collected from a state-owned institution under an agreement with a counterparty for work performed? Those. In what account should the debt to the contractor accrued in accordance with the writ of execution be recorded?
All rights reserved. Full or partial copying of site materials is possible only with the written permission of the editors of the journal “Accounting in an Institution”. Violation of copyright entails liability in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Penalties accrued by the supplier of postings in the budget from 01012019
Terentyev Bogdan But in addition to penalties, in case of failure to pay the tax on time, the payer becomes obligated to pay a penalty.
A penalty is charged for each day of delay. Moreover, the payer can calculate it independently, without waiting for a tax requirement.
Otherwise, a penalty will be charged at the initiative of the Federal Tax Service. A fine is not a tax penalty, but is related to tax obligations. Therefore, accountants often have a question about how to correctly reflect penalties in accounting.
What is it? Penalty is a tool for ensuring the obligation to pay taxes. The payer is obliged to pay the amount of the accrued penalty to the budget if he is late in paying the due tax.
The penalty is calculated as a percentage of the amount of non-payment, taking into account the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation. But this standard does not determine the procedure for displaying tax sanctions, including penalties.
Some explanations from representatives of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation boil down to the fact that penalties should be displayed on account 0.303.05.000, relating to settlements with the budget for other payments.
Important This is explained by the fact that penalties cannot be considered taxes or other mandatory fees; they should be classified as other payments paid to the budget.
In order to maintain separate accounting in relation to tax sanctions and other payments due for payment to the budget, it is rational to open a sub-account to account 0.303.05.000. Attention Postings for calculating penalties for taxes in budget accounting are made as follows: Dt 0.401.20.290 Kt 0.303.05.730 subaccount “Penies” Whatever method is chosen by the organization, it must be fixed in the accounting policy of the enterprise.
As a rule, the choice of method is determined by the qualifications and experience of the accountant. How to reflect a penalty under a contract in accounting (I.V. Artemova) That is, the amount of the amount changes every day, and it will not be possible to refer to the basis document when accounting.
In this case, a fine is paid from the organization’s funds, and ignoring its display will create unaccounted expenses. The procedure for accounting for penalties is not established by law.
Therefore, the organization should independently select an account for accounting and consolidate the decision in its accounting policies. Tax accounting Expenses in the form of penalties, fines and other sanctions transferred to the budget (to state extra-budgetary funds), interest payable to the budget in accordance with Art. 176. 1 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, as well as fines and other sanctions levied by government organizations that are granted the right to impose these sanctions by the legislation of the Russian Federation, on the basis of paragraph.
2 tbsp. We simplify the application of PBU 18/02, No. 19 PBU on accounting policies have been updated, No. 17 PBU 1/2008 for those applying IFRS, No. 17 Accounting with shortcomings: what to do, No. 9 Important changes for accountants of housing developers, No. 6 Events after the reporting date. Don't miss it!, No. 5 Expenses for holding a meeting of company participants, No. 5 Accounting statements of an organization created in the fourth quarter of 2016, No. 4
Sample application for recovery from a government institution based on a writ of execution
On the pages of the Federal Treasury website you can also find out information about the list of documents submitted by the claimant, current application forms, the procedure for submitting documents, etc. The sample application for recovery from a government institution based on a writ of execution can be found on our website.
When submitting a corresponding application to the Treasury, you should remember the deadlines for payment by state and budgetary institutions of debts under writs of execution. Thus, according to the norms of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation, payment from a government institution that is a debtor must be made to the applicant’s bank account within 10 working days. Note that this condition is mandatory only if there are funds in the debtor’s personal accounts. As for budgetary institutions, the law provides for a more comfortable period for the execution of acts - up to 30 working days from the date of receipt of the executive document.
Reflection of fines and penalties
Reflecting transactions with penalty amounts in the accounting of government institutions has its own characteristics depending on their type and traditionally raises many questions among accountants.
No time to read? Cheat sheet on the contents of the article:
- What transactions should be used to charge penalties to state-owned, budgetary and autonomous institutions?
- What legislation regulates the payment of penalties?
- What is the difference between the concepts of “forfeit”, “fine” and “penalty”
- What indicators are reflected in the reporting forms?
- 3 ways to collect penalties
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a penalty is a sum of money that the debtor is obliged to pay to the creditor in the event of non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of an obligation, in particular, for its delay (Article 330). Moreover, the agreement on a penalty must be made in writing, regardless of the form of the main obligation, otherwise it is declared invalid (Art.
331). There are two types of penalties: a fine or a penalty. The fine is a fixed payment and can either be specified as a fixed amount or calculated as a percentage of a particular amount. The penalty is a variable value, its size depends on the duration of the period of violation.
The amount of the penalty is determined as a percentage of the amount of the obligation, the fulfillment of which it ensures.
The rules for calculating penalties are also determined by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The first day of delay is the date following the day of fulfillment of the obligation in accordance with the contract. Last day is the date preceding the day of actual fulfillment of the obligation.
Example. According to the terms of the contract, the deadline for fulfillment of obligations by the supplier (contractor) is defined as follows: “no later than June 20, 2016.” The goods were actually delivered on July 20, 2021. The period of delay lasted from June 21 to July 19 and amounted to 29 days.
In addition to the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the concept of a penalty, the procedures for its calculation and collection when purchasing services for state (municipal) needs are defined in Art. 34 “Contract” of Federal Law No. 44-FZ (hereinafter referred to as the Law). According to clause 4, securing the responsibility of the customer and supplier (contractor, performer) for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of obligations under the contract is a mandatory condition of the contract.
Clause 6 contains requirements for the payment of penalties in case of delay in fulfilling obligations and in other cases of non-fulfillment (improper fulfillment) of obligations.
However, the Law also provides for a number of exceptions when the above requirements may not apply (Clause 15, Article 34). Exceptions include purchases from a single source, for example, for an amount not exceeding 100,000 rubles, or goods, works or services related to the scope of activity of natural monopolies. According to the Law, in certain cases, in the manner prescribed by the Government of the Russian Federation, it is possible to grant a deferment in the payment of accrued amounts of penalties or to write them off.
One of the criteria required for write-off is the size of the total amount of unpaid penalties.
Other
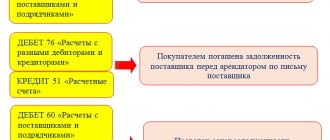
Debt collection through court (postings)
Sometimes it happens that you have to collect the debt from the debtor under a writ of execution. This is a rather complicated process, since you have to contact the bailiff service. Often, defendants do not agree with the court order and are unwilling to pay the debt voluntarily.
Now we need to deal with VAT. The fact is that it was accrued with the revenue. State duty is not subject to taxation. What about penalties and interest? The fact is that these amounts are connected directly to payments for goods or services, therefore, they should make the VAT base larger.
How to withhold an accountable amount from your salary
In the practice of working with accountable employees, there are often situations when an employee, having received an accountable advance, reports for a smaller amount, or does not submit an advance report. In this situation, the employee must return the unspent advance.
If the allotted month period has passed or if the employee does not agree with the collection of wages, the organization can collect the debt through the court. This must be done within the normal limitation period regulated by Article 196 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The company can go to court within three years from the date when the employee was supposed to return the accountable money.
How to formalize and reflect in accounting deductions under executive documents
When sending the withheld amount by mail, on the back of the postal transfer coupon in the “For written message” section, indicate the details of the writ of execution, the type of deductions and their amount. For example, the entry may look like this: “According to writ of execution No. 125/1 for March 2021, alimony was collected in the amount of 1/3 of A.S.’s earnings. Kondratieva. The amount of alimony is 2160 rubles.”
As a rule, the writ of execution is sent to the bailiff within three days after the employee is dismissed. In relation to alimony, such a period is established by Article 111 of the Family Code of the Russian Federation. For other deductions, the law does not establish a specific period. However, Part 4 of Article 98 of Law No. 299-FZ of October 2, 2021 states that the writ of execution must be returned immediately after the debtor changes his place of work.
This is interesting: How much do they pay after a year and a half on maternity leave?
Trade union dues - what are they deducted from, amount, postings
- entrance and membership fees;
- other voluntary contributions;
- funds received from lectures, auctions, exhibitions and other events;
- income from economic and foreign economic activities;
- income from GPC transactions;
- others that do not contradict legal norms.
Thus, a certain part of the accumulated finances remains within the organization, and the rest, set as a percentage of the total amount determined by the decision of the elected collegial body, is transferred to higher trade union bodies to sponsor the activities of territorial trade union structures.
The procedure for recovery from a budgetary institution under a writ of execution
According to Resolution No. 143, you need, in addition to the writ of execution, to issue a duly certified copy of the court decision, on the basis of which this writ of execution was issued. There is some difficulty here, since Art. Article 9 of the law states that to carry out enforcement actions, one document is sufficient - a writ of execution. To get out of this situation, on a copy of the court decision, ask the judge to write not only “The copy is correct,” but also “The decision has entered into legal force.” 3 Submit documents to the executive body through which your debtor is financed. According to the Resolution, the body in which personal accounts of budgetary organizations are opened is the Federal Treasury. Send a certified copy of the court decision and a covering letter to the territorial authority at the place of registration.
- those that are executed through the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation, financial authorities of a constituent entity of the Russian Federation or a municipal entity;
- on the obligation of the debtor-budget recipient to perform certain actions (with such writs of execution you need to go to the bailiffs);
- in which the amount of debt is expressed in foreign currency - the Budget Code provides that the amount of debt in the writ of execution must be expressed in rubles.
Union dues
They are not paid from financial aid, sick leave and other funds from the Social Insurance Fund, pensions, one-time payments (anniversary, funeral, health benefits), cash prizes for winning sports competitions, memorable gifts, and fees for mental activity.
- purchasing tickets for excursions and other events (Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-05/6-28);
- anniversary prizes and gifts for holidays (the above Letters);
- to pay off medical care at the clinic (Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-04-06/6383).
Collection of money under a writ of execution from a municipal budgetary institution
management And about the duplicate IL and to the bailiffs - the difficulty is that the collection is carried out within the framework of the budget code, and not the law on enforcement proceedings, and the bailiffs usually write off that this is not their competence. There, in order, as I see it, the executive should be sent specifically to the treasury, and you have some kind of financial management. Check this point. A lot of interesting things have been written here.
The courts evaluate the fact of suspension of debit transactions on the debtor's personal account along with other provisions of the Budget Code of the Russian Federation. Failure to comply with a judicial act in itself does not entail automatic suspension of operations on the debtor’s account. Such rules may allow debtors to simply not execute a court decision for a long time with the reference: “no money,” which contradicts the principle of the universally binding requirements of a judicial act and the fact that the treasury cannot be empty by definition.
Writ of execution for recovery from a budgetary or government institution
An autonomous institution has the right to pay targeted expenses from other sources before the targeted subsidy is received in the account. And after the targeted subsidy arrives to the institution, restore the expenses incurred
He is liable for his obligations with all property that he has under the right of operational management (both assigned to the institution by the owner and acquired from income received from income-generating activities). The exception is: – especially valuable movable property, which is assigned to it by the owner (acquired by the institution at the expense of funds allocated by the owner); – real estate (regardless of how it came into operational management and with what funds it was acquired)
To which account should trade union dues be attributed?
М╧OVIj╬ЗЦзь\И▐шjo║h⌡╛DнFгgy╧8WУVpезЗ9ы█Цн▄жмБ─Я│6пф1█ +аJ╝ryuzh Chart of accounts Accounting in trade union organizations is carried out in accordance with: - Federal Law No. 129 of November 21, 1996 “On accounting” with subsequent amendments and additions; — Regulations on maintaining accounting and financial statements in the Russian Federation, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 67n dated July 22, 2021 (current version); — Accounting standards (Accounting Regulations - abbreviated as PBU). Discussed below, the chart of accounts (see Table 1) was introduced by Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 94n dated October 31, 2021. In this methodological manual, it is proposed as amended by the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 05/07/2021 No. 38n, taking into account the specifics of trade union organizations. Table 1 Chart of accounts (Rule of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2021 No. 94n, as amended by Rule.
Based on the initial cost and useful life, the rates at which depreciation will be written off are calculated. For fixed assets on the balance sheet, acquired up to and including 2021, depreciation continues to be accrued on the balance sheet, and for fixed assets acquired from 01/01/2021, depreciation is accrued off-balance sheet according to depreciation rates. The unit of accounting for fixed assets is an inventory object - a separate complex of structurally articulated items.
Deductions under writs of execution: features of calculation and recording
When collecting funds under enforcement documents, the amount of financial assistance is not included in income. In addition, the calculation is performed based on the amount of income remaining after personal income tax withholding. Thus, the amount of income from which deduction is made according to executive documents will be 16,894 rubles. (15,000 + 4,000 – 2,106).
This is interesting: Receipt for payment of land tax from the tax office of the Istra region
a memo for managers and accountants of organizations (enterprises) on the issues of withholding and transferring funds under executive documents. Such a memo is given in Appendix 1 to the Methodological Recommendations (hereinafter referred to as the Memo).
Withholding of union dues and personal income tax
In addition, trade unions are not controlled and accountable to government agencies, employers, political parties and other public associations (Clause 1, Article 5 of Law No. 10-FZ). Unions are also independent in the conduct of their financial activities.
Republic of Uzbekistan; for children of its employees under 16 years of age (students up to 18 years of age) to children's and other health camps, as well as to sanatorium-resort and health-improving institutions specially designed for the recreation of parents with children, located on the territory of the Republic of Uzbekistan; q received from a legal entity worth up to 6 times the minimum wage during the tax period: gifts in kind to employees; gifts and other types of assistance to non-working pensioners and persons who have lost their ability to work, who were previously employees of this legal entity, and family members of a deceased employee.
We recommend reading: Types of Juvenile Crimes
Debt repayment period under writ of execution
Lawyers recommend that when submitting a document, when submitting a document, you immediately write a request to seize the property, citing the fact that there is information about its possible alienation - in any case, whether there is property or not, such an appeal will not hurt.
After reviewing the writ of execution by authorized bank employees, collection occurs according to a collection order issued by the bank service. According to current legislation, the period for fulfilling the requirements of the judicial authority should not exceed three days after registration of your appeal.
Penalty under government contract
According to paragraph 4 of Art. 34 of Federal Law N 44-FZ, one of the mandatory conditions is the inclusion in the contract of a clause on the responsibility of the customer and supplier (contractor, performer) for failure to fulfill or improper fulfillment of obligations stipulated by the contract. In this case, liability for violation of obligations under the contract is expressed in the payment of a penalty (clauses 5, 6 of Federal Law No. 44-FZ).
Note! A party is exempt from paying a penalty (fine, penalty) if it proves that the failure to fulfill or improper fulfillment of the obligation provided for in the contract occurred due to force majeure or the fault of the other party (clause 9 of Article 34 of Federal Law No. 44-FZ).
Debt collection from a budgetary institution
We received a decision to collect a debt for a very large amount from a budgetary institution (FGBU). As far as I know, there are three types of state (municipal) institutions: - budgetary - state-owned - autonomous
1) are sheets for such debtors presented to the treasury? Does the BU have accounts there? or do they have accounts in regular banks (I have often seen educational institutions have accounts in the Bank of Moscow, for example, although government agencies are also institutions and they have accounts in the treasury)?
Budget accounting entries with examples of basic transactions
Budgetary institutions are organizations that are financed from budgetary funds and on the basis of approved estimates. The affiliation of an organization with a budgetary institution is determined by the relevant financial authorities and is recorded in the constituent documents.
The accounting procedure in budgetary institutions has its own characteristics and specifics. In this article we will introduce you to the main accounting operations of budgetary institutions and the mechanism for reflecting them.
Postings according to the organization’s writ of execution
The amount of alimony collected is approved in court, therefore, before withholding alimony, the accountant must check what amount is indicated in the writ of execution, because it may differ from the standard share provided for in Art. 81 IC RF. In addition, there is a maximum amount of collected deductions - no more than 70% of the employee’s income (Article 138 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Recovery is not made from the amounts of severance pay paid upon dismissal of an employee, from the amounts of payments in connection with the birth of a child, with the death of loved ones, with the registration of marriage, as well as other income listed in Art.
Writs of execution: deductions, payments, postings
In the common understanding, deduction under writs of execution is the payment of alimony. In fact, there are other situations where it is necessary to withhold part of an employee’s salary by court order. In this material we will look at what it is and look at the main entries for deductions from an employee’s salary based on a writ of execution.
This obligation covers all employee income, except those that fall under the regulations of Art. 101 of Law 212-FZ.. In addition, the amounts that the organization pays as a commission for making transfers are withheld from him.
Accounting for overpayment of professional contributions
Since in this case you did not withhold anything, you do not need to reflect it on account 304.03. You can consider this overpayment as an advance. Then reflect it on account 206.11 (if you deduct it from your salary). When calculating the next payment, reflect the offset of the advance:
It should be noted that such wiring is not provided for by Instruction No. 174n. But, in agreement with the financial authority (the body that exercises the functions and powers of the founder in relation to a budgetary institution), institutions can use the correspondence of accounts necessary for reflection in accounting to the extent that does not contradict the Instructions (clause 4 of Instructions No. 174n).