What to show on account 71
Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 94n approved that account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” is intended to reflect transactions for the issuance and return of accountable amounts.
What is a subreport? This is a certain amount of money from the organization that is transferred to the employee for specific purposes. Moreover, the purpose of expenses and the reporting period are strictly limited. After the allotted time has passed, the subordinate must provide a report on the expenses incurred. In simple words, money is given in advance, but with the condition that the employee provides a report - this is the essence of reporting.
For example, the company secretary was given 100 rubles from the cash register to buy an envelope and send a letter. When the reporting employee sends the letter, he will be given a receipt or check at the post office. It is these payment documents that the secretary will attach to the report, which will confirm the fact that the funds were spent on purpose.
For what purposes can a report be issued:
- Advance on travel expenses. This is relevant when an employee is sent on a business trip. Travel allowances include payment for accommodation and travel, daily allowances and other expenses en route.
- Expenses for the business needs of the company. Money can be issued for any purpose, from buying a light bulb for a utility room to building materials for major repairs.
- Settlements with counterparties. For example, the issuance of money is subject to payment for the services of third-party organizations. The operation is used less and less often, since non-cash payments are much more convenient.
- Other goals fixed by the decision of the company management. The director has the right to order the issuance of a report for any purpose. For example, for the purchase of equipment, exclusive rights, software products, etc.
IMPORTANT!
Loans and advances to employees cannot be reflected in account 71. For this purpose, a separate account is provided in accounting - 73. Some companies, wanting to simplify accounting and evade taxes, issue short-term loans to employees through 71 accounts. This is a violation.
What expenses can you give money for?
The legislative framework contains instructions for what purposes accountable amounts can be issued, these include:
- Payment for business trips and similar trips;
- Payment for services or work;
- Purchase of materials and goods;
- Incurring entertainment expenses;
- Other similar expenses.
An organization can establish the areas on which accountable persons have the right to spend the amounts issued to them by issuing an Accountability Regulation.
Important! The law prohibits the issuance of accounting funds for the acquisition of fixed assets. Also, accountable amounts cannot be used to make one-time transactions with organizations and entrepreneurs, the amount of which exceeds 100 thousand rubles.
Rules for issuing money report
The organization is obliged to independently develop and approve the procedure for settlements with accountable persons. For example, by identifying uniform provisions in the annex to the accounting policies. The company calculates limits and standards on an individual basis.
Key requirements for conducting settlements with accountable persons:
- Money can only be given to an employee of the company. That is, accountable persons (account 71 is used only in this case) must be determined by a separate order of the manager.
- Funds can be transferred in cash from the cash register or by bank transfer. Which method will be used in settlements with accountable persons should be specified in the accounting policy.
- The maximum amount to be issued for reporting can be fixed by a separate order of management.
- It is recommended to approve the limits on travel expenses in the subsistence report separately.
- The deadline for submitting a report on accountable money is also fixed in the regulations or in the accounting policy.
- All settlements with accountable persons (account 71) must be documented. To do this, checks, invoices, tickets, receipts and other documentation are attached to the report.
Money is issued based on a written application from the employee or by order of management. The recipient is required to sign the cash receipt order if funds are issued in cash from the cash register. When making purchases or while on a business trip, the reporting employee must keep all receipts and checks in order to account for the advance received. Upon returning from a trip or upon completion of the purchase, the subordinate draws up an advance report. Supporting documents are attached to the report. The deadline for drawing up a report on accountable money is 3 days.
What are accountable funds
Accountable money is the amount of money that was given to the employee for solving specific tasks: a business trip, a meeting, purchasing something, and so on. Money is issued in advance for a specific period. Upon expiration, the employee reports, that is, submits an advance report, all supporting documents and returns the balance.
For example, an employee was given 1,000 rubles for production needs - purchasing a cable for repairing a compressor. Based on the results of spending money, the employee prepares a report and attaches a cash receipt. The check amount may be more or less. In the first option, the organization will return to the employee the part that he paid from his own funds. In the second, the employee hands over the unspent money to the company cash desk.
The advance report is made according to form No. AO-1, approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated 01.08.2001 No. 55.
Characteristics of account 71
71 accounting accounts are considered active-passive accounts. This means that account balances can have both a debit and a credit balance at the end of the reporting period. This means that at the end of the month the debt may be registered with the employee. For example, a subordinate has just received an advance and has not yet had time to report.
The debt may also be attributed to the company. For example, if an employee spent his own funds to provide for business needs or on a business trip. Overexpenditure is reflected in accounting after the employee has provided an advance report and documented his expenses.
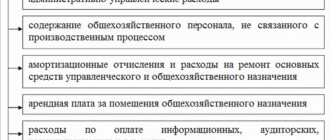
Main components of general business expenses
The main general operating expenses include the following:
- Remuneration for management staff, directorate, accounting, office (including bonuses, vacation pay, benefits at the expense of the employer).
- Amounts of insurance payments to extra-budgetary funds related to the remuneration of employees of the administrative and economic apparatus of the organization.
Information about accounting entries when calculating and paying insurance premiums can be found in the material “Insurance premiums accrued (accounting entry)” .
- Accrued depreciation on fixed assets and intangible assets that were acquired to serve administrative and business personnel.
- Expenses for repairs of fixed assets not related to production.
- Expenses for renting premises used for management staff and other non-production purposes.
- Expenses for information and consulting services.
- Expenses for materials used for administrative needs.
- Entertainment expenses.
- Expenses for retraining of personnel.
- Expenses for paying for the services of security organizations.
- Recruitment costs.
- Expenses for subscription to periodicals.
- Software costs.
- Expenses for telephone calls and Internet services.
- Travel expenses.
ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to take into account administrative expenses when calculating taxable profit. To do everything correctly, get trial access to the system and go to the Ready solution. It's free.
You can familiarize yourself with all the nuances of documenting travel expenses in the article “Procedure for accounting for travel expenses in 2020-2021”.
Debit and credit of account 71: what to reflect
| What we reflect on the debit of account 71 | What do we indicate in the credit of accounting account 71 |
| 71 debit account is the amount that was provided to the company employee in advance for specific expenses. That is, this is the money that the employee received as an account. For example, a cashier dispenses cash from a cash register. The balance of account 50 “Cash” decreases - the turnover to the credit account is reflected. 50. And at the same time the debit turnover on the account is reflected. 71 - the employee received accountable funds. Before the subordinate provides an advance report, he will be credited with an advance - a debit balance on the account. 71. Or a debit balance is formed if the employee reported less than the amount received in advance. The remainder should be returned to the organization's cash desk. | In the credit of the account we reflect the expenses of the accountable person, supported by documents. That is, the employee submitted an advance report, and the manager checked and approved it. Then the accountant accepts the transactions for accounting and accrues expenses according to the report. The expenditure of funds is reflected in the credit of accounting account 71. At the same time, the debit balance of the account decreases. The result of the operation may be the loan balance if the reporting employee spent his money on company expenses. The company must repay this debt. That is, pay the amount of the credit balance to the accountable person. |
Correspondence
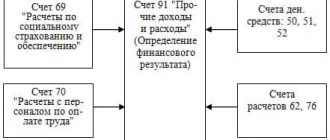
Account 71 can participate in transactions with many accounts.
According to the debit of account 71, he can correspond to the credit of accounts:
- Account 50 - when issuing imprest amounts from the cash register;
- Account 51 - when transferring accountable amounts from a current account to a card;
- Account 52 - when issuing accountable amounts in foreign currency (for example, when traveling abroad);
- Account 55 - when issuing a report from special accounts;
- Account 76 - when issuing money, reporting according to the bank register;
- Account 79 - when issuing the account at the expense of the branch, separate division;
- Account 91 - when writing off exchange rate differences if the funds were issued in foreign currency.
By crediting the account, it can enter into transactions with the debit of the following accounts:
- Account 07 - when registering equipment for further installation purchased through accountable amounts;
- Account 08 - when reflecting costs (business trips, other costs) associated with the acquisition of non-current assets;
- Account 10 - when purchasing materials using imprest amounts;
- Account 11 - when purchasing animals for fattening using accountable amounts;
- Account 15 - when purchasing materials, if the accounting policy stipulates accounting using account 15;
- Account 20 - when writing off accountable amounts for the main production;
- Account 23 - when writing off accountable amounts for auxiliary production;
- Account 25 - when writing off accountable amounts for general production expenses;
- Account 26 - when writing off accountable amounts for administrative expenses;
- Account 28 - when writing off accountable amounts to correct a previously committed defect;
- Account 29 - when writing off accountable amounts for the costs of service and subsidiary farms;
- Account 41 - when reflecting the acquisition of goods through reporting;
- Account 44 - when writing off accountable amounts for the costs of selling products;
- Account 45 - when writing off accountable amounts for the purchase of goods that have not yet arrived at the organization;
- Account 50 - when returning unused imprest amounts to the cash desk;
- Account 51 – when returning unused imprest amounts to the current account;
- Account 52 – when returning unused imprest amounts to a foreign currency account;
- Account 55 – when returning unused imprest amounts to a special bank account;
- Account 70 - when deducting unreturned accountable amounts from wages (one-time deduction);
- Account 73 – when deducting unreturned accountable amounts from wages (multiple deduction);
- Account 76 - when closing a debt to a supplier for previously written off work or services;
- Account 79 - when transferring debt between branches and parent organizations;
- Account 91 - when reflecting a shortage of purchased materials within the limits of natural loss, when reflecting exchange rate differences when issuing a report in foreign currency;
- Account 94 - when reflecting a shortage, if the expenditure of the accountable amount is not confirmed by documents and it is not returned to the cash desk;
- Account 97 - when reflecting accountable costs that will be written off in future periods;
- Account 99 - when writing off accountable funds for liquidation of emergency situations and natural disasters.
Accounting entries for account 71
Let's look at how to correctly make transactions for 71 accounts. Here are typical transactions and correspondence of accounts. Let us indicate which documents to draw up during the operation.
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Foundation documents |
| Money issued in cash report | 71 | 50 | A cashier's report and an expense order were drawn up |
| Funds are credited to the bank card account | 71 | 51 | Bank statement, payment order for transfer |
| Funds are credited to the report on the organization’s corporate card | 71 | 55 | Bank statement from special company accounts |
| The purchase of fixed assets is reflected in the advance report | 08 | 71 | Certificate of acceptance of works and services |
| Materials and raw materials purchased by the accountable person were capitalized | 10 | 71 | Invoices, sales receipts, transportation documents, acceptance certificate |
| The amount of expenses according to the advance report for production and economic needs is reflected | 20, 26, 44 | 71 | Advance report, invoices |
| Return to the cash desk of funds unspent by the accountable person | 50 | 71 | Cashier's report, receipt order |
| Debt accrued for amounts not returned on time by the accountable person | 73 | 71 | Advance report |
Now let's look at examples of posting entries for various situations.
***
Account 71 reflects settlements between the organization and its accountable persons. The debit of the account shows the amounts issued to pay for the needs of the company, and the credit of the account shows paid goods, works, and services. To clearly monitor the movement of amounts in an account, a balance sheet is used.
Even more materials on the topic can be found in the “Accounting” section.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Example No. 1. Overspending - debt in favor of an accountable employee
Vesna LLC issued in June to secretary P.P. Karandashikov. 3000 rubles for the purchase of pencils. The funds were issued from the cash register. The employee made a purchase in the amount of 3,150 rubles. An advance report was drawn up on the costs incurred, a fiscal receipt and a delivery note were attached to the documents.
Postings:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The report was issued from the cash register | 71 | 50 | 3000 |
| The advance report has been approved, the expenses for the purchase of pencils have been taken into account | 10 | 71 | 3150 |
| The overspending was transferred to the secretary's bank card | 71 | 51 | 150 |
Procedure for carrying out accountable transactions
An accountable person is an employee who has received funds to use for the business needs of the enterprise.
The basis for issuing funds against the report is an application filled out by the employee and approved by the signature of the manager. The application records the amount and purpose of the funds (purchase of materials, payment to suppliers, etc.). The form of application for the issuance of accountable amounts is not established by law; the document is drawn up in any form.
Upon completion of a business transaction, the employee submits to the accounting department an advance report and documents confirming the expenses incurred by him (receipts, invoices, certificates of work performed, invoices, etc.). These documents are the basis for recording business expenses in accounting.
If the amount of funds previously received by an employee exceeds his actual expenses, then the amount of the difference is deposited by the employee at the cash desk. In case of overspending and its documentary confirmation, the amount of excess expenses is reimbursed to the employee through the cash desk or in non-cash form.
It should be emphasized that an employee who has not reported on previously received amounts cannot be given funds to carry out new business operations. Whether the funds were issued in cash or to a bank card in this case does not matter.
Example No. 2. The balance is the debt of the accountable person
To purchase a laptop for Vesna LLC specialist K.K. Barankin. 35,000 rubles were transferred to the card. A computer hardware store provided Barankin with a 10% discount on the cost of the laptop (3,500 rubles). The total purchase amounted to 31,500 rubles. Barankin provided an advance report and returned the balance to the cashier.
Postings:
| Operation | Debit | Credit | Amount, rub. |
| The sub-report is listed on the Barankin map | 71 | 51 | 35 000 |
| The advance report has been approved, the expenses for the purchase of a laptop have been taken into account | 08 | 71 | 31 150 |
| The balance was returned to the cash desk of Vesna LLC | 50 | 71 | 3500 |
Description and use of account 26
Account 26 “General business expenses” is used to collect information about costs for management needs not directly related to the production of products, performance of work, or provision of services.
Agents, brokers, dealers, forwarders, that is, organizations not related to production, use account 26 as the main one in conducting their activities, summarizing information on all their expenses on it and writing them off to the sales account.
Trading companies do not use account 26 in their activities and all expenses, without exception, are attributed directly to account 44 “Sales expenses”.
For information on the main components of costs accounted for in account 44 “Sales expenses”, read the article “Accounting entries for business expenses”.
Analytical accounting for account 26 is carried out directly by expense items and places of their occurrence.
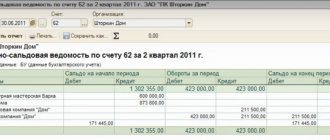
Turnover balance sheet
There are also certain features in filling out the SALT for accounting for advance reporting. It may have a balance on the debit side when the accounting policy of the enterprise is to issue advances for expenses stipulated by law. A credit balance is used in final settlements with “accountants” according to the following scheme: expense – advance report – payment of money.
Due to the nature of operations, expense reports are usually handled by an experienced accountant or financial manager.
The formation of OSV in 1C is presented below.