General analysis of account 71
First, briefly about what 71 accounting accounts are, including for dummies.
According to the Chart of Accounts for accounting financial and economic activities of organizations and the Instructions for its application (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n), settlements with accountable persons are reflected in 71 accounts.
REFERENCE
An accountable person is an employee, including under a GPC agreement, who is given money to pay the organization’s expenses, and he must then account for this money. This follows, in particular, from the letter of the Bank of Russia dated October 2, 2014 No. 29-Р-Р-6/7859.
Thus, maintaining account 71 is necessary to summarize information on settlements with employees for the amounts issued to them on account for administrative, business and other expenses.
If we talk about the score 71, then it is active-passive. That is, the balances on it can be debit and credit.
Also see “Central Bank of the Russian Federation: new rules for issuing “on account””.
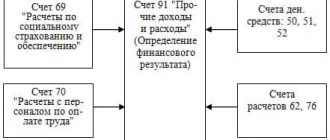
Dt 91 “Other income and expenses”
Home Favorites Random article Educational New additions Feedback FAQ⇐ PreviousPage 6 of 6
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - by writing off the amounts of travel expenses to increase other expenses, the costs of business trips related to other activities of the organization, as well as for business trips in connection with emergency circumstances or the elimination of their consequences are recorded;
Dt 50 "Cash desk"
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - for the amount of the unused balance of the accountable amount handed over by the accountable person to the organization’s cash desk;
Dt 51 “Current accounts”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - for the amount of the unused balance deposited by the accountable person upon announcement directly to the bank account;
Dt 55 “Special bank accounts”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - for the amount of the unused balance deposited by the accountable person upon announcement directly to a special bank account. The same posting reflects the return of an unused letter of credit;
Dt 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” - for the amount of the unused balance of the accountable amount withheld from the salary of the accountable person.
In addition, under certain conditions, permanent tax liabilities may arise in connection with the recording of travel expenses. A similar situation may occur if the employment contract provides for the possibility of paying business trip expenses in excess of the norms established by law. In this case, the following entry is made in accounting:
Dt 99 “Profits and losses”
Kt 68 , subaccount “Organizational Income Tax” - for the amount of permanent tax liability.
Example.
The employee is sent on a business trip for five days to purchase supplies. Based on the calculation, he was given 100,000 rubles on account, including 1,000 rubles. – daily allowance for a business trip, 19,000 rubles. – to pay the cost of travel, 5000 rubles. – to pay for accommodation, 70,000 rubles. - to pay for purchased materials.
Upon returning from a business trip, the employee submitted an advance report for a total amount of 85,000 rubles, including the cost of purchased materials - 60,000 rubles, travel documents - 9,000 rubles, payment for accommodation at the place of business trip - 5,000 rubles, daily allowance - 1,000 rubles. (in accordance with the collective labor agreement). The business trip is directly related to the acquisition of materials. In accordance with the accounting policy of the organization, the actual cost of materials is formed on account 15. The unused balance is not returned to the cash desk.
The following entries were made in the accounting records:
Dt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”
Kt 50 “Cash desk” – 100,000 rubles. – the amount of cash issued on account;
Dt 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” – 60,000 rubles. – the amount of the cost of purchased materials;
Dt 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” – 9,000 rubles. – the amount of payment for the cost of travel to the place of business trip and back;
Dt 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” – 5000 rubles. – the amount of payment for the cost of living;
Dt 15 “Procurement and acquisition of material assets”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” – 1000 rubles. – the amount of accrued daily allowance;
Dt 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages”
Kt 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” – 15,000 rubles. – for the amount of the unused balance of the accountable amount withheld from the accrued wages of the posted employee;
Dt 99 “Profits and losses”
Kt 68 “Calculations for taxes and fees” – 120 rubles. – for the amount of permanent tax liability based on the amount of the difference between the actually accrued daily allowances and their standard amount. The amount of the cost of purchased materials in tax accounting, in our opinion, should subsequently be written off in the amount of their actual cost formed in accounting, that is, without taking into account permanent tax obligations, since the amount of profit in excess of the actual amount of daily allowance (included in the cost of materials) is already accrued.
The actual cost of materials is written off from the credit of account 15 to the debit of account 10 upon completion of all necessary operations related to bringing them to a state in which they are suitable for use for the planned purposes, and accordingly accounting for all additional expenses.
Travel expenses are included in production and distribution costs in the amount actually incurred. For tax purposes, business travel expenses are accepted within the established norms. Travel expenses in excess of the norms increase the tax base. VAT on excess costs is not presented to the budget as a credit, but is written off from the enterprise’s own funds.
Daily allowances issued in excess of the norms are included in the total annual income of the reporting person and are subject to personal income tax. Insurance premiums under the Unified Social Tax are not charged on daily allowances issued in excess of the norms.
Persons who received cash on account are required to submit to the accounting department a report on the amounts spent with supporting documents attached, return unspent amounts or receive overspent amounts from the cash register.
Cash issuance on account is subject to a complete report on previously issued amounts.
CONCLUSION
Based on the above, we can conclude that in the life of any enterprise, calculations occupy one of the main places in the accounting system. It is no coincidence that in the Chart of Accounts of the total number of accounting accounts, settlement transactions account for almost 1/5 of their total number.
Mastering the methodology for accounting for settlements with accountable persons is important in the entire accounting system, since the mobility of funds makes this area of the economic activity of an economic entity the most vulnerable from the point of view of various violations and abuses.
A scientifically based system of organizing accounting contributes to effective control over the availability and flow of funds of an enterprise, timely prevention of negative facts in business activities, obtaining complete and reliable information about business processes, performance results and financial condition of the organization.
In the course of their financial and economic activities, enterprises and organizations often make cash settlements (not related to the payment of wages) with both legal entities and individuals. Funds for these purposes are usually issued on account.
Accountable persons are employees of the organization (including part-time workers) who were given cash from the cash register with the condition of submitting a report on their use (hence the term “on account”).
The organization can issue funds to accountable persons: for travel expenses; for economic needs; for payment of entertainment expenses. The reporting form for amounts issued to accountable persons is an advance report.
To summarize information on settlements for accountable amounts in accordance with the Chart of Accounts for accounting the financial and economic activities of organizations, approved by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 N 94n, active account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons” is used.
In the accounting of the enterprise, the issuance of funds is recorded as the debit of account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”. Account 71 is credited for amounts spent by accountable persons in correspondence with accounts that record expenses and acquired values, as well as other accounts depending on the nature of the expenses incurred. Analytical accounting for account 71 is carried out for each amount issued for reporting.
Expenses incurred by accountable persons may be included in the cost of products (works, services), increase the actual costs of acquiring fixed assets, intangible assets, inventories, or be covered by the net profit of the enterprise.
This paper examines the basics of accounting for settlements with accountable persons, identifies the main directions for spending accountable amounts, and examines the main primary documents and regulations used in the preparation of settlements with accountable persons in accounting.
To summarize information on settlements with employees on the amounts issued to them for reporting on administrative, economic and operating expenses, the Chart of Accounts for accounting of financial and economic activities of organizations provides for account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”. This is an active-passive account, the balance of which reflects the amount of debt of accountable persons to the enterprise or the amount of unreimbursed overexpenditure. On the debit side of the account, the amounts of reimbursed overexpenditures and again issued for reporting on the basis of cash outgoing orders are recorded, on the credit side - the amounts used according to advance reports and handed over under incoming cash orders (unused).
Accountable amounts to control their expenditure are taken into account for each employee of the enterprise in account 71 “Settlements with accountable persons”. The basis for filling out these documents are cash receipts and expenditure orders - when issuing funds for reporting and returning them to the cash register, as well as an advance report - when writing off spent amounts.
Properly organized accounting of settlements with accountable persons at the enterprise will ensure control over the use of funds and will not create problems with taxation and audit.
⇐ Previous6
Rules for accounting entries with account 71
For the amounts issued for reporting, account 71 is debited in correspondence with the cash accounting accounts.
And vice versa, the credit of account 71 in correspondence is adjusted for the amounts spent by accountable persons:
- with accounts that record costs and acquired values;
- other accounts depending on the nature of the expenses incurred.
Accountable amounts not returned by employees on time are reflected in the credit of account 71 and the debit of account 94 “Shortages and losses from damage to valuables.” Subsequently, these amounts are written off from account 94 in:
- Dt 70 “Settlements with personnel for wages” (if they can be withheld from the employee’s wages);
- Dt 73 “Settlements with personnel for other operations” (when they cannot be deducted from the employee’s salary).
Reportable amounts for other transactions
In addition to travel expenses, the company can issue funds to the employee as an account for the purpose of paying for:
- business and operating expenses;
- purchases of small wholesale goods;
- entertainment expenses.
Business and operating expenses involve the purchase of goods, payment for fuel and lubricants and services. Entertainment expenses are classified as general business expenses and include the costs of receiving foreign representatives, buffet services, translation services, etc. They do not include expenses for entertainment events and recreation in health resorts.
Examples of postings to account 71
Next, using the example of several standard transactions, we show how we write off 71 accounts and what happens to the account balance 71.
| On the day of issue of money for reporting | |
| Issuing money against a report from the cash register | Dt 71 – Kt 50-1 |
| Transferring money to an employee’s bank card for reporting | Dt 71 – Kt 51 |
| As of the date of approval of the advance report | |
| Payment made by an accountable person for goods, work, services | Dt 60, etc. – Kt 1 |
| Daily allowances for the time spent on a business trip are recognized as an expense | Dt 20 (91-2, etc.) – Kt 71 |
| As of the date of final settlement of outstanding amounts issued | |
| The overexpenditure was paid according to the advance report from the cash register | Dt 71 – Kt 50-1 |
| Overspending on the advance report is transferred to the accountant’s bank card | Dt 71 – Kt 51 |
| The unspent balance of accountable amounts was returned to the cash desk | Dt 50-1 – Kt 71 |
| The unspent balance of accountable amounts is transferred from the accountable person’s bank card to the organization’s current account | Dt 51 – Kt 71 |
The procedure for receiving money on account
The procedure for issuing finance for reporting is regulated by a special regulatory document approved by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, which reflects the rules for conducting cash transactions by business entities.
So, before issuing money on account, the accounting department must check whether the employee in question has any debt for previously received resources. If this is the case, then additional funds cannot be issued.
Once it has become clear that there is no such debt, the employee must write a statement addressed to management, indicating the required amount and period.
Now, if there is an application signed by management, an expense cash order is issued, which must be endorsed by the chief accountant, cashier and manager when the accountant is not present.
After completing the designated document and handing it over to the cashier, the cashier checks the correctness of its preparation and the presence of the appropriate signatures of officials. Only after completing all of the above actions, the cashier gives the employee cash resources for reporting.
What's a corporate party without a banquet?
Costs for corporate events can vary greatly. Only imagination and a wallet can stop it. A small company will have a modest evening at the office, a larger company will order dinner at a restaurant, the very rich will take their employees to a boarding house or even a hotel abroad.
But the more spent on a corporate event, the more carefully the regulatory authorities will check these expenses.
You can find out how to arrange a corporate event in our publication “Order for a corporate event.”
Personal income tax
Employees at a holiday usually not only have fun, but also eat. That is, the company pays for food for employees. Here a situation may arise when the employer is recognized as a tax agent in relation to income in kind in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 226 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
However, in practice this usually does not happen, since the employer does not have the opportunity to personify and evaluate the economic benefit (the number of meals eaten and drinks drunk) received by each employee at the corporate event.
As a tax agent, the company must keep records of income received from it by individuals, on the basis of clause 1 of Art. 230 Tax Code of the Russian Federation. But due to the fact that it is not possible to evaluate and take into account the income of each employee separately, there is no . This position is confirmed by letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/03/2018 No. 03-04-06/55047, dated 08/14/2013 No. 03-04-06/33039, dated 03/06/2013 No. 03-04-06/6715, dated 01/30/2013 No. 03-04-06/6-29.
Also, paragraph 5 of the Review of the practice of courts considering cases related to the application of Ch. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, approved by the Presidium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation on October 21, 2015, indicates that the material benefit received is subject to personal income tax only if it is not of an impersonal nature and is subject to determination in relation to each taxpayer.
there is no need to charge personal income tax on corporate event expenses .
basic information
Data on special accounts is collected on account 55. Sub-accounts are created for it:
- 1 – letters of credit;
- 2 – check books;
- 3 – deposit.
Account 55 is needed to summarize information about the movement of funds in different currencies, presented in special payment documents (for example, letters of credit). These can also be means of targeted financing that require separate storage.
Settlements for letters of credit and checks are carried out in accordance with Regulation No. 2-P on non-cash payments established by the Central Bank of October 3, 2002.
Insurance premiums
Deductions are made only in the month to which they relate, made by their employer. They go to subaccount 69 in:
- Pension Fund.
- FFOMS.
- To a temporary disability fund, which is created to pay sick leave.
- Into a fund intended for payments for disability due to maternity.
To create an accounting entry, a credit to account 69 and a debit to accounts 20, 26, 29, 44 , since insurance premiums are not deducted from wages, but are included in the cost of production. For example:
- Debit 20 Credit 69.
How to correctly calculate the financial stability ratio - see this material. How to prepare an extract from the minutes of the general meeting - read here.
Accrual
The accrual of monetary compensation earned by the employee during the reporting period (usually for a month) is carried out on the credit of the 70th account . How to choose an account corresponding to it depends on where the employee to whom the amount of money is credited works. If production is primary (maintenance or support functions), then this will be the 20th debit account .
When making transfers to management personnel, you need to post to account 25 or 26 . For sellers of finished products and other people who are engaged in the sale of goods or services, you need to use the 44th account .
An entry must be made to the debit account “08” in the case when workers are engaged in construction or in the construction of any other objects.
For example, the construction of a two-story residential building is underway, for which wages were accrued in the amount of 520,000 rubles, of which:
- 340,000 rubles are allocated for specialists employed in the main production. Posting: Debit 20 Credit 70;
- An amount of 100,000 rubles was received to pay management personnel. Posting: Debit 26 Credit 70;
- managers from the finished product sales department need to allocate 36,000 rubles. Posting: Debit 44 Credit 70;
- workers involved in the construction of an auxiliary warehouse are paid 44,000 rubles. Posting: Debit 08 Credit 70.
Other income from the “other” section is formalized as follows: Debit 91-2 Credit 70. By the way, deductions can be made to this account intended for reserve funds for subsequent salary payments from them.
The procedure for completing earnings transactions in a specialized program is discussed in detail in the following video: