Issues discussed in the material:
- Why destroy accounting documents?
- What are the storage periods for accounting documents?
- How to document the destruction of documents
- What are the most reliable methods for destroying accounting documents?
- Is it necessary to destroy accounting documents electronically?
At some point, every accountant begins to be interested in such a question as the procedure for destroying accounting documents. This happens because over time the volume of accounting papers begins to exceed all imaginable sizes. And due to age, there is no longer any need to store some of them. Our article today is devoted to the issue of organizing the storage of documents and the procedure for their liquidation.
Documents have accumulated: what to do with them so as not to break the law
Our life is closely connected with a huge amount of papers.
Even in an ordinary apartment you can find deposits of various types of waste paper (for example, invoices or copies of personal documents). In companies and institutions, paper waste is generated in incomparably large volumes (administrative, administrative, economic, accounting, personnel and other documents). An ordinary citizen can get rid of unnecessary papers without any problems - do a general cleaning and throw away all the unnecessary paper trash. There is no need to follow any special procedures - even if something valuable is accidentally destroyed, no punishment will follow. True, in such a situation you will have to spend time and money to restore the lost document.
Completely different requirements apply to the destruction of documents generated during the activities of various companies. It will not be possible to get rid of orders, instructions, personnel and primary accounting documents, as well as many other documents without following a special procedure. In addition, documents can be destroyed only after the expiration of the legally established storage periods.
IMPORTANT! The responsibility for preserving archival documents (including personnel) during their storage periods is assigned to state bodies, local governments, organizations and citizens engaged in commercial activities, in accordance with paragraph 1 of Art. 17 of the Law “On Archiving in the Russian Federation” dated October 22, 2004 No. 125-FZ.
In case of non-compliance with this law, various types of liability are provided (Article 27 of Law No. 125-FZ).
What to do if the document is lost
There are times when for some reason a document may be lost or lost.
This may occur in the following force majeure situations:
- Fire;
- An earthquake, with the complete destruction of the building where the archive is stored;
- Flood;
- Robbery.
In this case, the documents should be restored to the extent possible, although such a procedure is difficult and in some cases impossible.
In the event of natural disasters and damage to document flow information media, it is necessary to record this precedent in writing. Such written registration will extend the time for information recovery.
If damage or loss occurred due to the fault of an employee, then what to do in this situation? The culprit must be given a written explanation of the fact and reason for the loss, with the help of which the boss will decide what measures to take against the employee.
Such measures are regulated by Art. 193 Labor Code. A penalty or other disciplinary measure against the perpetrator is formalized by personnel orders, followed by dismissal.
Description of the destruction procedure - is it possible to do it with one act?
What is the procedure for destroying documents with expired storage periods?
For any documents (no matter administrative, accounting or personnel) there is a uniform procedure for their destruction. It is as follows:
- It is necessary to check whether the storage period for documents has expired, as well as the presence of documents that have lost their practical significance.
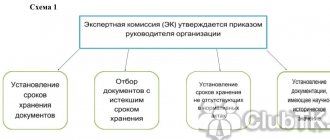
- An Expert Commission (EC), the composition of which is approved by the head of the company, must conduct an examination of the value of the documents (documented in the minutes of the EC meeting).
- An act for the destruction of documents is drawn up, approved by the head of the enterprise.
- The cases reflected in the act are destroyed, which is documented in a separate document.
To learn about the storage periods for documents, read the article “Retention period for accounting documents in an organization.”
You can’t do this with just one act, and you won’t be able to get rid of the documents alone. The role of the expert commission should not be underestimated in this case. For example, if during the examination it is revealed that in one case documents with an expired storage period are filed simultaneously with papers that have permanent or long storage periods, then such a set of documents will need to be expanded and disassembled. Documents that are not subject to destruction by a certain date are registered as separate files.
Or another example: if an examination of permanent storage documents reveals the presence of both originals, copies or their duplicates (that is, duplicate information), then the originals are subject to further storage, and the remaining documents are destroyed. All this is decided by an expert commission.
Her responsibilities also include determining whether the text of damaged documents can be recovered. Documents may be selected for destruction if most of the text is unreadable and cannot be restored. If text restoration is possible, the damaged document is not destroyed, but is subsequently restored or photocopied.
The results of the examination of documents must be reflected in the EC protocol, the form of which is not regulated by law. And when drawing up an act for the destruction of documents, it is better to use the form given in Appendix No. 4 to the Basic Rules for the Operation of Organizational Archives, approved by the decision of the Rosarkhiv Board of 02/06/2002.
If the value examination is carried out for the first time
The first assessment of value is always a large-scale event. It is necessary to review all the documents that have accumulated over the years of the organization’s existence. The expert commission must act consistently.
■ Step 1: select the documents for which the value assessment will be carried out.
At this stage of the examination, members of the EC do not participate. This is the area of responsibility of the archivist (clerk, secretary) and employees of the company’s structural divisions. They separate documents that were completed before the beginning of the current year from those that are still in progress.
■ Step 2: divide the documents by year. This stage is relevant during the first EC, when absolutely everything that has been completed in office work has to be reviewed.
The first thing to do to put things in order is to separate the documents by year. Perhaps the employees who were responsible for these documents have done this before. If not, you'll have to do it now. The archivist and department employees are still responsible; it is too early to involve EC members.
■ Step 3: we conduct an examination. At this stage, the main role in the examination is played by the members of the EC, who review the documents prepared for assessment and divided by year and make a verdict: whether they represent practical (scientific, historical) value or not. After this, the part of the documents that has received the status “may be destroyed” is checked by the archivist. He finds out whether the storage periods for these documents have expired.
■ Step 4: we formalize the results of the examination. The results of the examination of value are recorded, firstly, in the inventory of cases and documents, and secondly, in the act of allocating documents for destruction.
■ Step 5: we coordinate and approve inventories and acts. After the documents that record the results of the value assessment have been drawn up, a meeting of the expert commission is held. On it, members of the EC agree on the inventory and act, after which they are approved by the General Director.
■ Step 6: we prepare documents for storage and destruction. Those files and documents that remain in the organization are registered for storage. For those that are decided to be destroyed, a recycling process is organized.
How to draw up an act for the destruction of documents
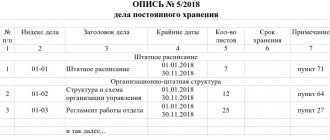
Until documents with an expired storage period are destroyed, those responsible for their destruction will have to work hard. Firstly, the selected documents must be organized and described - this is what the act “On the allocation for destruction of documents not subject to storage” is intended for.
The act does not need to describe each case - it is enough to indicate their total number and deadlines for completing the paperwork. For example, in an act regarding orders for administrative and economic activities, it is enough to provide the following information:
In addition to filling out the tabular part of the act, it is required to indicate other important information: the total numbers of storage units to be destroyed, indicating the time period of the cases; a note confirming the agreement of the information given in the act with the expert commission (including the date and number of the EC protocol on the approval of inventories of permanent storage files). The act is approved by the head of the company. A special place in it is given to the date of compilation - this detail deserves special attention. We'll talk about this further.
The act has been drawn up, what next?
The act is drawn up, signed by the main expert commission and agreed upon by its members, and endorsed by management.
ATTENTION! If it is customary to transfer part of the company’s documentation for storage to the funds of the state archive, then the acts must be agreed upon with the archival expert commission.
Preparing for destruction:
- removal of relevant documents from their storage location;
- freeing papers from staples, stitching, and other types of connections;
- packaging for transportation to the place of destruction (it can also be produced on the premises of the company itself).
IT IS FORBIDDEN! It is strictly prohibited to use documents “condemned” for disposal for other purposes, for example, as drafts, etc.
How not to make a mistake with the act date
In order not to violate the requirements of the law and not to accidentally get rid of documents whose storage period has not yet expired, it is necessary to correctly calculate these periods. The following must be taken into account:
- Before destroying files with a registration date of 2010 or later, their storage periods must be checked against the list approved by Order No. 236 of the Federal Archive of Russia dated December 20, 2019, or Order No. 558 of the Ministry of Culture dated August 25, 2010.
- Documents created before 2009 (inclusive) can be destroyed only if the storage period specified in the List of standard management documents approved by Rosarkhiv on 10/06/2000 has expired. This is due to the fact that Order No. 558, which put the 2010 list into effect, does not have retroactive force, that is, it does not apply to previously established relationships - otherwise it is not directly stated in it. And the individual terms of the 2000 list and the 2010 list do not coincide for the same types of documents.
When specifying the date of destruction of documents, it should be remembered that the destruction act is allowed to include those documents whose storage period has expired by January 1 of the year the act was drawn up. For example, a case from 2015 with a storage period of 5 years can be included in the act no earlier than 2021.
When to draw up an act if the storage periods for documents are unknown
In the course of business activities, an organization may acquire documents that are not listed in legally defined lists. Sooner or later the question of their destruction also arises.
In any case, before issuing a destruction certificate, it is necessary to specify the storage period for such documents. In accordance with clause 2.2.5 of the Basic Rules for the Operation of Organizational Archives, to determine the storage periods for documents not provided for in the lists, the organization's EC has the right to make a request to the specialists of the archival institution.
Only after the storage period has been determined can the future fate of such documents be decided (destroyed or continued to be stored).
Expert commission: composition and functions
EC appears in the organization immediately after management decides to create an archive. The secretary of the EC is always an archivist, and the chairman is either a top manager to whom the clerks report (for example, the administrative director), or, as in our example, the director for general affairs. If one is not found - the general director himself, who signs the order to create a commission (Example 1). The same order can approve the regulations on the new collegial body and request a plan for its work. If the date of creation of the EC is not indicated in the order, it is considered that the commission operates from the date of signing the order.
1Not shown.
The EC is a collegial advisory body under the general director of the organization. “Collegial” means that the commission includes several officials from among the organization’s employees, “deliberative” - the officials do not make a decision, but only recommend to the general director to carry out this or that operation on documents and approve it.
A clerk or archivist knows management documents well, but in the organization’s archive there is also a huge layer of personnel records, accounting and tax reporting, and documents accompanying the organization’s core activities. Since these are independent documentation systems, only specialists can evaluate them. For this purpose, an expert commission is created - a meeting of competent (each in their own field) officials.
The main function of the EC in an organization that is not a source of acquisition of the state (municipal) archive is to organize the annual selection of files for storage and destruction.
In organizations that are sources of acquisition of the state archive, the functionality of the EC is broader: the commission actively interacts with the expert verification commission of the archival institution, submits to them for approval draft nomenclatures of files, archival inventories, and makes proposals for changing the storage periods of documents.
Regardless of the company’s field of activity, the EC must include:
• head of the HR department;
• chief accountant;
• head of the legal department;
• an official in the company's profile (production manager, construction manager, chief technologist, etc.), whose task is to evaluate documents on the main activities of the organization.
Each EC meeting is documented in minutes (Example 2).
Nuances of drawing up an act for the destruction of accounting documents
It is necessary to dwell separately on the features of destruction of accounting documents. Despite the fact that their storage periods are also established by the 2010 list and they are subject to the general procedure for storing and destroying documents in accordance with Law No. 125-FZ, there are still a number of regulatory documents whose requirements must be taken into account.
So, in Art. 23 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the taxpayer is obliged to retain accounting data and other papers necessary for the calculation and payment of taxes for 4 years. A Art. 29 of the Law “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ establishes a retention period of 5 years for primary accounting documents, accounting registers, accounting policies, accounting records and other documents related to the organization and maintenance of accounting.
For more information about the period for which documents such as invoices must be stored, read the material “What is the storage period for invoices?” .
That is, if the accounting register, certificate or other paper in any way belongs to the accounting category, it is impossible to issue a destruction act before the expiration of the 5-year period. If this happens, the head of the company will be held liable for unlawful destruction.
However, that's not all. The above applied to those companies and enterprises whose activities during the entire period of their existence were break-even. If a loss is received and it is transferred to subsequent periods, all documents confirming the amount of such loss are prohibited from being destroyed during the entire period of transfer (Article 283 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When all legally established storage periods have expired, a destruction certificate is issued in the usual manner.
The act has been completed - how to get rid of waste paper
The law does not define specific methods for destroying documents with an expired storage period. Since at the time of drawing up the act, these documents no longer represent any value for the company and, in fact, are waste paper, any way to get rid of them is possible. For example, you can:
- send documents for processing (disposal) to a specialized organization;
- get rid of unnecessary papers using a special shredder (office shredder, paper shredder, etc.);
- burn (however, this may cause problems with firefighters).
The first method can result in significant material costs for the company to pay for disposal services, and the transfer of documents will have to be formalized with an acceptance certificate or invoice indicating the number of cases and their weight. To ensure confidentiality, you will need to send your employee to a special organization to monitor the document destruction procedure.
In all other cases, you also cannot do without completing additional documents - we’ll talk about this in the next section.
Features of the destruction of secret documentation
In addition to ordinary papers, organizations also encounter documentation with special stamps—secret. In 2021, instructions for destroying secret documents consist of the following steps:
- Papers classified as confidential for liquidation are formed into a separate act.
- Disposal is carried out in an area where unauthorized persons have no access.
- The preferred method of destroying such papers is burning.
The powers of the commission members for the disposal of papers with special stamps are determined by a special order of the head of the organization.
We formalize the fact of destruction of documents
The act “On the allocation for destruction of documents that are not subject to storage” is not the only document that needs to be drawn up in such a situation. Another document (usually also called an act) is drawn up to confirm the very fact of destruction of documents that have lost practical significance and are outdated. There is no standard form for this act, so it is drawn up in any form. It is important to include all the necessary information.
To ensure that there are no complaints about this document later, it must reflect the following:
- the name of the document and the name of the company on behalf of which it is drawn up;
- date of execution of the act;
- description of the fact of destruction of documents (indicating the volume or quantity, as well as the method of destruction);
- signatures with transcripts, full names of responsible persons.
A sample document destruction act was developed by ConsultantPlus experts. Get a free trial of K+ and proceed to the sample.
If there is no expert commission
It happens that there is no EC in the organization. For various reasons: officials (potential participants) do not see the need to create this collegial body, and they managed to convince the director of this, or the director himself does not consider it necessary. However, the secretary is tasked with organizing the destruction of the accumulated documents.
Thus, in the absence of an EC, the secretary, performing the task of destroying documents, acts exactly according to the algorithm described above, but in the act of destruction on the spot of the approval visa, he indicates the data not of the protocol, but of all officials with whom the act is approved. Documents cannot be destroyed without approval. However, even if the heads of the departments you need have a negative attitude towards archiving, they will reluctantly review the documents allocated for destruction. Because they know very well which documents from those that are under their control should be stored in the organization, and therefore should not be destroyed. And the secretary will kindly inform them about liability for violating legal requirements for storing documents.
Documents were destroyed according to the act - can the manager be punished?
If the act of allocating documents for destruction is formed correctly (in compliance with the entire procedure for organizing and conducting the examination of documents and recording the results of the EC’s work), the manager can still be held accountable if the documents were destroyed prematurely and their storage periods were not respected .
IMPORTANT! In accordance with Art. 15.11 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation for gross violation of the terms of storage of accounting documents, a fine in the amount of 5,000 to 10,000 rubles is possible.
If a legal entity does not have the funds to organize and maintain a separate archival service, but does not want to be punished, it is necessary to appoint responsible employees whose functions will include continuous monitoring of the storage of documents and the timely destruction of files with expired storage periods.
How to draw up an act if you need to destroy documents in electronic form
In accordance with Art. 5 of Law No. 125-FZ, the reflection of documents in the archival fund does not depend on the method of creation and type of media.
In paragraph 2 of Art. 29 of Law No. 402-FZ states that documents and means that reproduce electronic media, as well as verify the authenticity of digital signatures, must be stored for at least 5 years after the year in which they were last used to prepare accounting reports.
Currently, huge volumes of documentation can be stored in a company in electronic form, as well as on special media (disks, flash cards, etc.). If the EC determines that electronic documents have no practical significance and (or) their storage period has expired, the information must be destroyed along with the media. In this case, the same destruction methods can be used as for paper documents (shredding, burning, changing shape, etc.).
In addition, special methods can be used - erasing or overwriting files (paragraph 2, section 9.9 of GOST 15489-1-2007, approved by order of Rostekhregulirovaniya dated March 12, 2007 No. 28-st).
The law does not provide for a special procedure (including for drawing up an act), so it is necessary to adhere to the general procedure described earlier for paper documents. However, we should not forget the following:
- It is prohibited to get rid of unnecessary files and documents without authorization and without drawing up an act;
- documents related to legal proceedings (ongoing or upcoming) must not be destroyed;
- the requirement for confidentiality of information contained in destroyed documents and their copies cannot be ignored;
- it is necessary to destroy all copies of documents (including personal and backup ones), if such duplicates are permitted for destruction.
For information on how seals are destroyed, read the article “Procedure for writing off and destroying seals (nuances).”
Results
The destruction of documents with expired storage periods occurs after the completion of the work of the expert commission with the mandatory execution of a report. Then, in relation to all documents reflected in the act, a physical liquidation procedure is carried out - this action is also formalized in a separate act.
Methods for getting rid of documents may be different; this point is not regulated by law. It is permissible to hand them over for recycling to a specialized company, use an office shredder, or use another method.
Sources:
- Basic Rules for the Operation of Organizational Archives
- Tax Code of the Russian Federation
- Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ
- Code of Administrative Offenses of the Russian Federation
- Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated August 25, 2010 No. 558
- Order of Rosarkhiv dated December 20, 2019 No. 236
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.