Power of attorney
An employee whose authority is confirmed by a power of attorney can receive purchased goods or accept work or services.
It can be written out using standardized forms No. M-2 or No. M-2a. They were approved by Decree of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated October 30, 1997 No. 71a. The forms of these powers of attorney are essentially the same, the only difference is that form No. M-2 has a spine. It is needed to record powers of attorney in the registration journal. Whether to keep such a journal or not is up to everyone to decide for themselves. If you don’t, then it’s easier to use form No. M-2a.
Situation: is it possible to issue an M-2 power of attorney to a citizen who is not an employee of the organization?
Answer: yes, you can.
The instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated October 30, 1997 No. 71a provide that a power of attorney in form No. M-2 can only be issued to employees of the organization. However, the Resolution of the Presidium of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated August 13, 1996 No. 1792/96 states: from the moment the first part of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation came into force (from January 1, 1995), powers of attorney on behalf of a legal entity are drawn up taking into account the requirements of Article 185 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. This norm allows the right to issue a power of attorney to any person, and not just an employee (clause 1 of Article 185 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, there is no prohibition on giving cash on account to a person working under a civil contract. And the accountant needs a power of attorney to receive goods and materials.
Thus, current legislation allows the issuance of a power of attorney to receive goods and materials to people who are not employees of the organization.
Similar conclusions follow from the decision of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation dated June 6, 2011 No. GKPI11-617.
Instead of standardized ones, you can also use forms developed independently. The main thing is that the document contains all the necessary details. Whatever form you use, it is first approved by the manager with an order to the accounting policy.
This is provided for by Part 2 of Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ and paragraph 4 of PBU 1/2008.
Set the validity period of the power of attorney depending on the possibility of receiving and exporting the relevant valuables according to the order, invoice, invoice or other document replacing them. However, the maximum and minimum terms of validity of a power of attorney are not established by law. If this period is not specified in the power of attorney, then it will be valid for one year from the date of issue (clause 1 of Article 186 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Situation: is it necessary to issue a power of attorney to an accountable person in order for him to act on behalf of the organization?
Answer: no, not necessarily. The legislation does not contain such a requirement.
However, if you do not issue a power of attorney to the employee, the organization may have problems receiving an invoice. It is this document that serves as the basis for deducting VAT on goods (work, services) purchased through an employee (clause 1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Difficulty in obtaining an invoice may arise because when selling for cash, retailers have the right not to issue invoices, but to limit themselves to cash receipts (Clause 7, Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Acting without a power of attorney, an employee of an organization acts as an ordinary person purchasing things for personal use. Therefore, the seller is not obliged to issue him an invoice.
But if the employee presents a power of attorney from the organization, the supplier will have to issue an invoice. In this case, the employee will act on behalf of the organization, and the seller will have the obligation to issue the required document (Clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
This position is set out in the letter of the Ministry of Taxes and Taxes of Russia dated October 10, 2003 No. 03-1-08/2963/11-AL268.
Report on imprest amounts
Within three days from the end of the period for which the advance was issued, the employee is required to report on the money spent. To do this, he must submit an advance report to the accounting department in the unified form No. AO-1 or in a form developed by the organization independently. The main thing is that the document contains all the necessary details. Whatever form you use, it is first approved by the manager with an order to the accounting policy.
This procedure follows from paragraph 6.3 of the Bank of Russia directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014, part 2 of Article 9 of the Law dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ and paragraph 4 of PBU 1/2008.
Situation: is it possible to prepare an advance report once at the end of the month? During the month, cash is issued for reporting to the same employee several times (for example, on the 5th and 15th).
Answer: no, you can't.
You can issue cash against an account provided that the employee has accounted for the advance received previously. When drawing up one advance report for all accountable amounts issued during the month, this requirement is not met. This follows from paragraph 6.3 of the Bank of Russia Directive No. 3210-U dated March 11, 2014 and paragraph 214 of the Instructions to the Unified Chart of Accounts No. 157n.
Attention: if tax inspectors discover that an organization has unlawfully issued money on account (an employee has not yet reported on previously issued amounts), then they may try to fine it for violating the Rules for Conducting Cash Transactions.
However, liability for this offense occurs in strictly limited cases. They are specified in Article 15.1 of the Code of the Russian Federation on Administrative Offenses. Failure to comply with the rules for issuing imprest amounts does not apply to them. It turns out that there is no fine for such an offense. This is confirmed by arbitration practice (see, for example, decisions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the North-Western District dated February 21, 2005 No. A56-33543/04 and dated February 9, 2005 No. A21-8287/04-C1).
On the front side of the report, the employee indicates his last name and initials, profession (position), purpose of the advance, etc. On the back side, he must reflect all expenses incurred by him. The employee attaches the received supporting documents to the advance report and numbers them in the order in which they are recorded in the report.
Situation: should an employee issue an advance report if he has returned the entire accountable amount received?
Answer: no, you shouldn't.
The advance report serves as the basis for writing off expenses that the organization incurred through an employee (instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 1, 2001 No. 55).
If the employee has returned the entire amount given to him on account, no expenses arise.
For the amount received, draw up a cash receipt order, form No. KO-1. In the “Base” line of this document, write: “Return of unused accountable amounts.”
Issuance of money against reporting for the purchase of fixed assets
It is better to entrust the preparation of an advance report (AO) to certain employees and record this in an order.
You will find a sample order approving the list of accountable persons entitled to receive funds in ConsultantPlus. If you do not already have access to this legal system, a full access trial is available for free.
Legislative norms do not establish the amount of amounts to be reported; the enterprise can approve this independently.
See what has changed in sub-reporting and cash transactions since November 30, 2020.
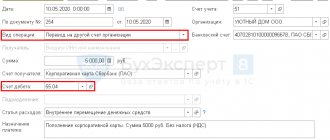
OS is an expensive item, so it is easier to transfer money to an employee’s salary card - this is legally permitted (letter of the Ministry of Finance dated August 25, 2014 No. 03-11-11/42288). This way you can avoid the restrictions on the maximum amount of cash payments in the amount of 100,000 rubles. between legal entities (LEs) and entrepreneurs (IP) under one agreement (clause 6 of the instructions of the Bank of the Russian Federation “On cash payments” dated 10/07/2013 No. 3073-U).
Important! Tip from ConsultantPlus If an employee spent his money for business purposes, he has the right to compensation for his expenses. Find out how compensation is processed and whether you need to prepare an advance report at K+. Trial access is available for free.
Checking the expense report
When you receive an advance report, fill out a receipt (a detachable part of the report) and give it to the employee. It is needed to confirm that the report has been accepted for verification. And the check is as follows.
First, control the targeted spending of money. To do this, look at the purposes for which the employee received money from the organization. These data are indicated in the document that served as the basis for issuing accountable amounts. For example, in a cash receipt order, order, statement, etc. Then compare the goal with the result according to the documents that the employee attached to his report. If they match, it means the money was used for its intended purpose.
Secondly, make sure that you have supporting documents that confirm the expenses, and also check that they are correctly prepared and the amounts are calculated.
If the employee paid in cash, proof of expenses may be a cash receipt, a receipt for a cash receipt order, or a strict reporting form. And when making payments by bank card - original slips, receipts from electronic ATMs and terminals. The amounts spent by the employee according to the report must correspond to the amounts indicated in the payment documents.
Situation: is it possible to accept only a receipt for a cash receipt order (without a cash register receipt) as confirmation of expenses of an accountable person?
Answer: yes, you can.
The employee can attach to the advance report a receipt for the cash receipt order issued by the counterparty (without a cash register receipt). Such a document also confirms that the employee incurred out-of-pocket expenses.
Tax inspectors often require that a cash receipt be attached to the advance report as the main supporting document (see, for example, letter of the Department of Tax Administration of Russia for Moscow dated August 12, 2003 No. 29-12/44158). But this requirement is not confirmed by legal norms. Cash order form No. KO-1 is one of the forms of primary accounting documentation. Therefore, the receipt issued for it is the same supporting document as a cash receipt. This conclusion is confirmed by arbitration practice (see, for example, Resolution of the FAS Moscow District dated December 9, 2005 No. KA-A40/12227–05).
Documentary proof of purchases
In addition to payment documents, the employee must attach documents confirming the purchase to the advance report. For example, these could be sales receipts, invoices, certificates of work performed (services rendered), etc.
If an employee acquired property (fixed assets, materials, goods), work or services for the organization, then the fact of their receipt (like any other fact of economic life) must be confirmed by a primary accounting document (Part 1 of Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ). This document must come from the supplier.
If there is no such document, then draw it up yourself (for example, when receiving materials without documents, draw up a report in free form or in form No. M-7 (Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated October 30, 1997 No. 71a)). It should be borne in mind that a document drawn up in any form must contain all the mandatory details provided for in Part 2 of Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ.
Situation: is it possible to accept an employee’s advance report for the purchase of materials if only a cash receipt is attached to it (without a sales receipt or invoice)?
Answer: yes, you can.
But to do this, you need to independently draw up an additional document confirming the receipt of valuables (see, for example, the resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the West Siberian District dated February 25, 2004 No. F04/953-206/A45-2004).
For example, upon receipt of materials, you can draw up an act of acceptance of materials in a form approved by the head of the organization, for example, in form No. M-7 (Part 4 of Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated 30 October 1997 No. 71a).
It is necessary to draw up such a document, since a cash receipt confirms only the amount that the employee spent. On its basis, it is impossible to take into account values acquired through an employee. The cash receipt does not contain such mandatory details of the primary document as the signatures of the responsible persons (Part 2 of Article 9 of the Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ, Clause 7 of the Instructions to the Unified Chart of Accounts No. 157n).
Situation: is it possible to accept an employee’s advance report for the purchase of materials if only a sales receipt is attached to it (without a cash receipt)? The employee bought materials from the organization on UTII.
Answer: yes, you can. But only if the sales receipt contains the required details.
Organizations on UTII have the right not to use CCP. Instead of cash receipts, they give customers sales receipts, receipts, or other documents confirming the sale of goods. In this case, these documents must contain a number of mandatory details:
– name, serial number and date of issue of the document;
– name of the organization (full name of the entrepreneur), TIN;
– name and quantity of paid goods (works, services);
– payment amount;
– position, surname and initials of the seller, his personal signature.
This is provided for in paragraph 2.1 of Article 2 of the Law of May 22, 2003 No. 54-FZ.
If the sales receipt contains all this data, the advance report can be accepted. The organization will be able to take such expenses into account when calculating income tax. Otherwise, the cost of materials cannot be recognized as expenses.
Such clarifications are contained in letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 19, 2010 No. 03-03-06/4/2, dated November 11, 2009 No. 03-01-15/10-499, dated October 22, 2009 No. 03- 01-15/9-470.
Answers to frequently asked questions
Question N1: Good afternoon! My subordinate purchased a fixed asset with accountable money abroad, therefore all supporting documents are in a foreign language. Can our accountant accept them as supporting documents for the expense report?
Answer: All foreign documents, including shipping documentation, receipts and checks, can be accepted for accounting in Russia. However, in your case, as in most others, it is necessary to make an official translation of the document and have it certified. In this case, the translation must be carried out line by line.
Question N2: Hello! Should an employee of an organization, when purchasing a fixed asset for it, have with him, in addition to cash, any other documents.
Answer: Not always. In some cases, the purchase of a fixed asset for cash using an advance report may require the authorized person to have certain documents. So, in some cases, you may need a power of attorney to remove inventory items from the supplier and transfer funds to him. In this situation, the reporting person may need a document proving his identity, for example, a passport of a citizen of the Russian Federation or his driver’s license.
Approval of the advance report
The verified expense report is approved by the head of the organization or an authorized employee (for example, the head of a department).
An example of preparing an advance report for an employee of a commercial organization
On March 30, Secretary E.V. Ivanova was given 2,000 rubles. for the purchase of stationery for the organization.
On April 1, Ivanova brought the purchased stationery to the organization. On the same day, the employee submitted an advance report to the accounting department in the amount of 1,580 rubles. (with primary documents attached to it), and also returned the unspent balance of the accountable amount to the cashier - 420 rubles. (2000 rub. – 1580 rub.).
Accountant Zaitseva gave Ivanova a receipt stating that the report had been accepted for verification.
On the same day, the head of the organization approved Ivanova’s advance report.
The stated procedure for preparing, checking and approving an advance report is established by instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 1, 2001 No. 55.
Accounting
Expenses incurred through an accountable person should be reflected in accounting on the day the advance report is approved. At this moment, the employee who received the money on account is written off his debt (instructions approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated August 1, 2001 No. 55).
Depending on the purposes for which the money was spent, write off the costs to different accounts.
If an employee only paid the organization’s expenses (without receiving the property itself), for example, made an advance payment for communication services, reflect it like this:
Debit 60 Credit 71
– prepayment for goods (work, services) has been made through an accountable person.
An example of making an advance payment through an accountable person
On April 3, the manager of Alpha CJSC A.S. Kondratyev was given 4,000 rubles. to make an advance payment at the corporate rate for cellular communication services.
On April 5, Kondratyev paid money to the mobile operator and provided an advance report to the accounting department. On the same day, the head of Alpha approved the report.
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in accounting.
April 3:
Debit 71 Credit 50 – 4000 rub. - money was issued for reporting to Kondratiev.
5th of April:
Debit 60 Credit 71 – 4000 rub. – prepayment for cellular communication services was made through an accountable person.
If an employee purchased property for the organization (fixed assets, materials, goods), then reflect its value by posting:
Debit 08 (10, 41) Credit 71
– property acquired through an accountable person has been capitalized.
Example of purchasing goods through an accountable person
On April 3, the secretary of Alfa CJSC E.V. Ivanova was given 2,000 rubles. for the purchase of stationery for the organization.
On April 5, Ivanova bought stationery for this entire amount. (The purchase was not subject to VAT, since the seller applied a simplified procedure.) On the same day, the head of Alpha approved the employee’s advance report, and the accountant accepted the received materials for accounting.
Alpha's accountant made the following entries in accounting.
April 3:
Debit 71 Credit 50 – 2000 rub. – money was issued against Ivanova’s report.
5th of April:
Debit 10 Credit 71 – 2000 rub. – stationery purchased through an employee has been received.
If the accountable person accepted work or services (for example, an employee repaired a company car), then make the following entry for their cost:
Debit 20 (23, 25, 26, 29, 44) Credit 71
– services were provided (work performed) purchased through an accountable entity.
If the accountable person paid for work (services) of a non-productive nature, then document it with the following entry:
Debit 91-2 Credit 71
– non-production expenses are reflected.
Terminology
| Designation | Term |
| Simplified taxation system | simplified tax system |
| General taxation system | OSN |
| Fixed assets | OS |
| Value added tax | VAT |
| Debit | D |
| Credit | TO |
| Outgoing payment order | PP outgoing |
| A journal that reflects the arrival of OS | Purchase Invoice |
| A log that reflects the commissioning of the OS | OS input |
| A journal that reflects the monthly depreciation of fixed assets | Depreciation |
| Invoice invoice | SF incoming |
| Journal that reflects the write-off of the OS | Decommissioning of OS |
| A journal that reflects the receipt of fixed assets through an accountable person | JSC |
| A log that reflects the implementation of the OS | Sales Invoice |