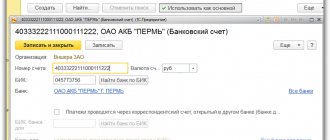
Very few people, looking at the details of an organization, are interested in the meaning of the current account numbers. Although the information encrypted in them may be of considerable interest. The account number says a lot more about the organization than its name.
Deciphering a bank account, for a prudent businessman and his accountant, should become a mandatory procedure when meeting with a new counterparty. At least as a protective measure against various kinds of intruders. And healthy curiosity will be satisfied to some extent.
The concept of “Current account” and its purpose
In practice, every business entity is faced with the need to make non-cash payments. Settlements of the enterprise with suppliers for purchased materials (services); with buyers for products sold; with credit institutions for loans; settlements for mandatory payments to the budget, payments to extra-budgetary funds and others are most often carried out through a current account. Conceptual help!
A current account is an account opened by an enterprise with a bank in ruble currency and intended for storing the organization’s funds and making non-cash payments.
The current account is the main account of the organization through which monetary transactions are carried out. In this case, the organization independently determines the required number of current accounts. Each open account is assigned a 20-digit number, with this indicated in the charter of the enterprise. In the future, this number is indicated in all documents related to the movement of funds through the current account. Banking settlement and cash services are carried out on the basis of a concluded agreement between the organization and the bank. Operations on the current account are carried out in chronological order according to the relevant order of the account owner (organization), as well as without the owner’s order in cases specified by law. If there is a shortage of funds, debits from the account are carried out in the following order:
Compliance with this queue is regulated by Art. 855 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
A current account is opened in credit institutions (banks), which the enterprise chooses for itself independently.
The bank manager puts a “permissive” signature on the Account Opening Application and the business entity opening the account is assigned a current account number consisting of 20 characters. All non-cash payments of the enterprise are carried out through the current account (only with the help of documents).
From May 1, 2014, organizations and individual entrepreneurs who pay insurance premiums are exempt from the obligation to report information on the opening and closing of bank accounts to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation. These changes were introduced by Federal Law dated April 2, 2014. No. 59-FZ.
From May 2, 2014, the obligation of organizations and individual entrepreneurs to report to the tax office information on opening and closing accounts has been abolished, in accordance with the Federal Law of April 2, 2014. No. 52-FZ.
Procedure for opening a current account
To open a current account in a bank, a legal entity must provide the following documents to the bank:
- Application for opening an account in rubles, signed by the head and chief accountant of the organization;
- Bank account agreement (two copies) in rubles, signed on each sheet;
- Certificate of state registration of a legal entity;
- A copy of an extract from the unified state register of legal entities certified by a notary or the authority that issued the document with an issue date not exceeding 1 month before the submission of documents;
- A copy of the duly approved charter (regulations) with amendments and additions, certified by a notary or the body that registered the document;
- A copy of the constituent agreement, certified by a notary or a higher authority;
- Minutes of the founders' meeting;
- A copy of the employment contract with the head of the organization;
- A copy of the order on assuming the position of the head and the appointment of the chief accountant, certified by the seal and signature of the head of the organization;
- A card with sample signatures and a seal from the head of the enterprise and the chief accountant, certified by a notary;
- A photocopy of the passports of the persons stated in the sample signature card;
- Original certificate of registration with the tax authority and its notarized copy;
- A copy of the information letter from the territorial body of state statistics with assigned codes and confirming registration with the state territorial statistical body, certified by a seal and signatures of officials of the organization (optional);
- Copies of licenses for activities that require licenses.
The list of required documents is fixed by Bank of Russia Instruction No. 153-I dated May 30, 2014 (as amended on December 24, 2018) “On opening and closing bank accounts, deposit accounts, deposit accounts” (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on June 19, 2014 N 32813).
International account number IBAN
Many countries use a single IBAN standard to designate bank account numbers - International Bank Account Number, which contains all the necessary information to identify the country, the bank in this country, and the account in this bank. Some post-Soviet countries have already switched to the international standard. The IBAN code can contain up to 34 characters, both letters and numbers.
It is applied in accordance with the requirements of the European Union Directive No. 2560/2001 “On the mandatory indication of IBAN codes in payment instructions.” And from January 1, 2007, the IBAN code (International Bank Account Number) became the only beneficiary account identifier for payments in any currency in favor of bank clients in member countries of the European Union and the European Economic Area (ES/EEZ).
Synthetic and analytical accounting of current account transactions
In the chart of accounts, information on cash flows in current accounts with the bank is taken into account in active account 51 “Current accounts”. The debit of the account reflects the receipt of funds into the current account, and the credit reflects their write-off. The account balance can only be debit or zero.
Analytical accounting of cash flows is maintained in Bank Statements. The bank compiles and provides statements to the organization in accordance with the bank's document flow. The statement is drawn up from the bank's perspective, and it is provided with all primary documents attached. The frequency of providing statements is determined by the turnover of cash flows in the current account, but usually daily.
Bank statement
| Debit (Dt) | Credit (Kt) |
| Balance as of 02/01/2020 | 1 000 000,00 |
| The buyer received revenue for sold products | 200 000,00 |
| Calculated the budget for personal income tax | 80 000,00 |
| Balance as of 02/02/2020 | 1 120 000,00 |
The bank statement is the basis for compiling correspondence of accounts for account 51 “Current accounts”.
It is important to pay attention to the fact that, as mentioned earlier, the statement is drawn up from the bank’s position. And this, in turn, means that the amounts reflected in the loan statement in accounting must be reflected in the debit of account 51 and vice versa, those amounts that are in the debit statement are an expense in account 51 and the company must reflect them in credit turnover . Based on this, the balance in the statement can only be a credit balance, because There cannot be a negative account balance.
If an enterprise has several current accounts, analytical accounting for account 51 “Current accounts” must be maintained in the context of each account.
Synthetic accounting of cash flows on the current account using the journal-order form of accounting is carried out in the journal-order No. 2, statement No. 2 and, accordingly, in the General Ledger. In the automated form of accounting, the registers systematizing primary accounting data are: SALT, account analysis, account card, SALT for the account.
Table with transcript
The table provides a brief description of all synthetic accounts from the standard Plan, divided by sections.
| Number | Name | View | Purpose |
| Section I. _ Fixed assets | |||
| 01 | Fixed assets | Active | Provides information about the presence and movement of OS |
| 02 | Depreciation of fixed assets | Passive | Accrued depreciation of fixed assets is reflected |
| 03 | Profitable investments in material assets | Active | Assets subject to transfer for temporary use to other persons are taken into account |
| 04 | Intangible assets | Active | Provides information on the availability and movement of intangible assets |
| 05 | Amortization of intangible assets | Passive | The accrued depreciation of intangible assets is reflected |
| 07 | Equipment for installation | Active | Equipment that is installed in facilities under construction and that requires preliminary installation work is taken into account |
| 08 | Investments in non-current assets | Active | Collection of expenses associated with the receipt and creation of fixed assets and intangible assets |
| 09 | Deferred tax assets | Active | SHE is taken into account - part of the income tax, which in subsequent periods will lead to a decrease in the tax amount |
| Section II . Productive reserves | |||
| 10 | Materials | Active | Material assets on hand and their movement (receipt and release) are taken into account - materials, supplies, raw materials, semi-finished products, fuel, etc. |
| 11 | Animals being raised and fattened | Active | Provides summary data on young animals for agricultural enterprises |
| 14 | Reserves for reduction in the value of material assets | Active-passive | Determining the difference between the market value of material assets and their cost |
| 15 | Procurement and acquisition of material assets | Active-passive | Collection of costs upon receipt of material assets before their arrival |
| 16 | Deviation in the cost of material assets | Active-passive | Determining the difference between the accounting and actual prices of material assets |
| 19 | VAT on purchased assets | Active | Allocation of VAT on incoming values |
Continuation of the table of accounts with explanation » » » » »
Regulatory accounting basis for account 51 “Settlement accounts”, documentation of settlements
Regulatory regulation of accounting for settlements under account 51 “Current Accounts” is primarily determined by: Federal Law “On Accounting” No. 402-FZ dated December 6, 2011, as well as the Chart of Accounts and instructions for its application, approved by the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation by Order No. 94n dated October 31, 2000
In addition, as mentioned earlier, the following act as a regulatory framework:
- Civil Code of the Russian Federation;
- Instruction of the Bank of Russia dated May 30, 2014 N 153-I (as amended on December 24, 2018) “On opening and closing bank accounts, deposit accounts, and deposit accounts”;
- Regulation of the Bank of Russia dated June 19, 2012 N 383-P (as amended on October 11, 2018) “On the rules for transferring funds”;
- and etc.
The primary documents for accounting for cash flows on a current account are:
- Payment order;
- Collection payment order;
- Payment request;
- Announcement for cash contribution;
- Cash check.
Conceptual help!
A payment order is a document that represents an order to the bank to transfer funds from the owner’s account to the recipient’s account.
Collection payment order is a requirement to write off funds in an indisputable manner in cases specified by law. When writing off funds on the basis of executive documents, the collection order must indicate a reference to the date, the executive document and the authority that issued it (For example, writing off penalties and non-payment of taxes to the Federal Tax Service).
A payment request is a document representing the supplier’s demand to the buyer and the buyer’s order to his bank to pay for the goods, works and services supplied. In this case, the supplier sends the payment request directly to the buyer's bank.
Announcement for cash deposit – issued when cash is deposited into the current account. The bank issues a receipt as a document confirming receipt of money.
Cash check is a document that acts as an order to the bank to issue cash in a specified amount. Check books are issued by the bank on the basis of a special application and are strictly accountable documents. Damaged checks are not deleted; they must be kept by the drawer for at least three years. When closing the account, the drawer must return the remaining unused check counterfoils to the bank.
Typical transactions for account 51 “Current accounts”
Business transactions on the debit of account 51 “Current accounts”
| № | Contents of business transactions | Source documents | Corresponding accounts | |
| Debit | Credit | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1 | Cash received from the cash register to the account | Bank statements, announcement for cash deposit, bank receipt for accepting cash | 51 | 50 |
| 2 | Received funds from foreign currency accounts | Bank statement for a foreign currency account, bank statement for a current account | 51 | 52 |
| 3 | Unused amounts of letters of credit, checks, bank cards, deposits were returned to the current account | Bank statement for current account, bank statement for special accounts | 51 | 55 |
| 4 | Received funds in transit (money transfers, collection of proceeds) | Bank account statement | 51 | 57 |
| 5 | In order to repay the provided long-term and short-term loans to another organization, funds were transferred to the current account | Bank account statement | 51 | 58 |
| 6 | Receipts from suppliers and contractors (refund of prepayments, advance transfers, overpayment amounts) | Bank account statement and payment order | 51 | 60 |
| 7 | Reflects revenue from buyers and customers for supplied finished products, work performed, services rendered | Bank statement on current account, payment order, payment request | 51 | 62 |
| 8 | Funds were received from bank loans and other loans: A) short-term B) long-term | Bank account statement, documents for obtaining short-term and long-term loans and borrowings | A) 51 B) 51 | A) 66 B) 67 |
| 9 | Amounts of overpayments on taxes and fees were returned from the budget based on the results of recalculation | Bank statement on current account, payment order | 51 | 68 |
| 10 | The organization was reimbursed by the social insurance fund for the costs of paying various benefits | Bank statement on current account, payment order | 51 | 69/1 |
| 11 | The amount of overpayments based on the results of the recalculation was returned from extra-budgetary funds | Bank statement on current account, payment order | 51 | 69 |
| 12 | Revenues for sold products and goods are credited to the account listed by accountable persons | Bank account statement, postal transfer receipts | 51 | 71 |
| 13 | Reflects amounts received from employees of the organization, loan repayment, compensation for material damage | Bank account statement, postal transfer receipts | 51 | 73 |
| 14 | Funds for the contribution to the authorized capital were transferred to the current account | Bank statement on current account, payment orders | 51 | 75 |
| 15 | Funds were received into the current account from various organizations and individuals to pay off accounts receivable; credited are the amounts of satisfied claims, dividends on securities, interest on debt obligations of other organizations, income from participation in the authorized capital of other organizations, distributed profits from joint activities, funds from subsidiaries | Bank statement on current account, payment orders | 51 | 76 |
| 16 | The amounts of insurance compensation received by the organization from insurance companies are credited | Bank statement on current account, payment orders | 51 | 76 |
| 17 | Received funds for targeted financing | Bank statement on current account, payment orders | 51 | 86 |
| 18 | Funds received as emergency revenues as a result of an emergency situation | Bank account statement | 51 | 99/4 |
| 19 | The parent organization's account received funds from a structural unit accounted for on a separate balance sheet | Bank account statement | 51 | 79 |
| 20 | Cash received as deferred income | Bank account statement | 51 | 98/1 |
Account 55 Special bank accounts
Letters of credit
A letter of credit is a special bank account in which funds can be reserved for settlements with a supplier. Opens for each supplier (contractor) with whom settlements are made. Letters of credit are divided into covered and uncovered.
Account 55 “Special accounts in banks” is used to reflect only covered letters of credit - when funds are debited from the buyer’s current account and deposited by the bank for subsequent payments to the supplier. The buyer cannot dispose of money held in covered letters of credit.
Debit 55 Credit 51 (52) - funds were transferred from the current (currency) account to the letter of credit.
Debit 60 (76) Credit 55 - the transfer of funds to the supplier’s account is reflected.
Bank commissions for servicing a letter of credit are written off to increase the cost of purchased material assets - to accounts 08,10,41 and others, if a letter of credit was used for their purchase. If not, then the commission is charged to operating expenses.
To account for an uncovered letter of credit, off-balance sheet account 009 “Securities for obligations and payments issued” is used.
Checks
A check is a security document containing an order to the bank to issue a certain amount of money to the person who presents the check for payment.
On account 55, settlement checks intended for non-cash payments with suppliers are taken into account; for this, a subaccount 55-2 “Check books” is opened. Cash checks used to withdraw cash for salaries and business needs are not taken into account in account 55.
Checks are strict reporting forms (SSR) and are accounted for in off-balance sheet account 006 “Strict reporting forms”. Checks are written off from account 006 as they are used.
Debit 006 subaccount “Checkbooks” - checkbooks received from the bank are accepted for accounting.
To use settlement checks, an organization must first deposit the required amount in a special bank account.
Debit 55-2 Credit 51 - funds deposited for check settlements.
Debit 60 (70,71,76,..) Credit 55-2 - funds were written off from checks presented for payment.
Unused deposited funds are credited to the current account.
Debit 51 (52) Credit 55-2 – unused funds previously deposited for payment of checks are credited to the current (currency) account.
Credit 006 - used checks are written off.
Deposits
If an organization opens a bank deposit (deposit) and places free money in deposit accounts, their accounting is kept in account 55, subaccount 55-3 “Deposit accounts”. The debit reflects the receipt of funds, and the credit reflects the write-off (reverse entry).
Debit 55-3 Credit 51 (52) - funds were transferred from the current (currency) account to the deposit.
Debit 51 (52) Credit 55-3 - funds from the deposit account are credited to the current (currency) account.
Interest received from the bank for the use of funds of your organization is subject to income tax and is included in other income.
Debit 76 Credit 91-1 - interest accrued on the deposit.
Debit 51 (52) Credit 76 - interest received for placing funds on deposit in a current (currency) account. The posting is made at the time of actual receipt of interest on the deposit.
Electronic wallets
To account for funds in electronic wallets (Yandex.Money, WebMoney, Qivi, PayPal and others), a separate subaccount 55-4 “Electronic wallet” is opened for account 55. Currency wallets are accounted for separately from ruble wallets.
Electronic transfers are prohibited between legal entities and entrepreneurs; one party must always be an individual. Businesses use electronic wallets for fast and convenient online payments for goods and services by citizens, as well as for transferring remuneration to individuals for services or work provided by them.
Debit 55-4 Credit 62 - payment received from the buyer to an electronic wallet.
Debit 60 (70, 73, 76...) Credit 55 – electronic money is transferred to the recipient
You can top up electronic wallets or withdraw funds from them only using a current bank account linked to the wallet.
Debit 55-4 Credit 50 (52) - funds were transferred from the current account to the bank account.
The maximum balance in the electronic wallet at the end of the day is 600 thousand rubles. The balance above the limit is automatically transferred to the current account.
Debit 51 (52) - Credit 55-4 - amounts of money were withdrawn to the current account.
All transactions in the wallet are subject to commissions, which are included in other expenses.
Debit 76 Credit 55-4 - the operator’s commission is reflected.
Debit 91-2 Credit 76 - commission charged to other expenses.
Electronic wallets