Procedure for submitting a VAT return
You need to submit your VAT return to the Federal Tax Service at the location of the tax agent.
Important! The declaration is submitted electronically through specialized operators. Moreover, all tax agents submit returns electronically, regardless of the number of employees.
An exception to this requirement are tax agents who are not VAT payers, including those who do not conduct intermediary activities in issuing invoices on their own behalf.
Responsibilities of a tax agent
Simply, we can say that the VAT agent is obliged to transfer the tax to the budget instead of a counterparty who cannot carry out such an operation himself, including:
- for a foreigner who is not registered with the Federal Tax Service;
- for the government body that is the lessor of the property;
- for a government agency that is the seller of state or municipal assets.
An agent is required to pay tax when carrying out any of the listed operations, regardless of whether he himself is a VAT payer or applies one of the existing special regimes. VAT payers are tax agents who withheld and paid tax to the budget when purchasing from a foreign counterparty, renting or purchasing state property from government authorities, have the right to accept it as a deduction in the future. Enterprises that use special regimes and are exempt from paying tax will not be able to reimburse the transferred VAT.
The calculated VAT must be paid to the Federal Tax Service at the agent’s location. The tax amount can be divided into 3 parts and each third can be transferred by the 25th day of each of the 3 months following the quarter in which VAT was withheld upon completion of the transaction, for example, transfer of payment for supplies/rent.
An exception is the payment of tax when purchasing work/services from a foreign company. In this situation, VAT must be paid simultaneously with the transfer of funds to the seller. For transactions carried out in which the company acts as the NA, it is necessary to prepare a declaration and submit it to the Federal Tax Service.
How to fill out a VAT return for a tax agent
In the case when the organization was only a tax agent during the tax period, then in addition to the title page, only the second section of the declaration needs to be filled out. And in the first one, dashes are simply added.
When a tax agent also carries out transactions subject to VAT, the second section must be included. If, in addition to all of the above, the organization carries out transactions exempt from VAT, then the seventh section is also included in the declaration.
Important! It should be borne in mind that the first section is filled in as the last section in the declaration, after all other data (except for the second section) has been filled out.
The VAT calculated as for the taxpayer cannot be summed up with the VAT of the tax agent. They are reflected on different lines - 040 and 050 of the first section (
Who fills out which sections?
The following table lists the sections of the VAT return, as well as the cases when entities must fill them out.
Table 2. Sections of the VAT return
| Chapter | Who fills in / What is reflected |
| Title page | All |
| Section 1 | All |
| Section 2 | Tax agents |
| Section 3 | Everyone who performed taxable transactions. The calculation of the amount of tax to be paid/refunded is reflected. |
| Section 4 | If the activity was carried out at a VAT rate of 0%, and there are documents to confirm its legality |
| Section 5 | If activities were carried out at a VAT rate of 0%, but there are no documents for confirmation |
| Section 6 | If the application of a 0% rate was previously announced, but the right to the benefit was received only in the current period |
| Section 7 | If there are transactions exempt from VAT |
| Section 8 | Everyone who performed taxable transactions. Purchase ledger data is displayed |
| Section 9 | Everyone who performed taxable transactions. Sales book data is reflected |
| Section 10 | Intermediaries reflect data on issued invoices |
| Section 11 | Intermediaries reflect data on received invoices |
| Section 12 | Non-payers of VAT when issuing invoices |
The table above shows that in most cases, organizations and individual entrepreneurs fill out the following sections of the declaration:
- Title page.
- Section 1, which indicates the amount of VAT payable.
- Section 3 in which this amount is calculated.
- Sections 8-9 containing purchase and sales ledger data.
Completing the remaining sections depends on the specifics of the activity.
Zero VAT return
VAT payers must submit reports even if there are no indicators . In particular, this is necessary if:
- in the reporting period there were no activities or were carried out only outside the Russian Federation;
- in the reporting period, only transactions not subject to VAT were carried out;
- the subject performed long-cycle operations (completion time was more than six months).
In this case, only the Title Page and Section 1 are completed. Dashes are placed in the lines intended to indicate tax amounts.
Filling out the Declaration Cover Page
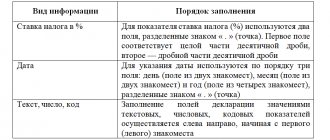
The TIN and KPP of the organization are filled out on the title page. The data can be found in the registration certificate received upon registration. You need to fill out the TIN from the first cell, if the organization's TIN has only 10 digits, the last two cells do not need to be filled in, dashes are placed in them.
The “adjustment number” depends on what kind of declaration the organization submits: primary or updated. When submitting an initial declaration, you need to enter “0–”, and when submitting an updated declaration, indicate the adjustment number, that is, “1–” for the first clarification and “2–” for the second.
The “tax period” is set depending on the quarter for which the declaration is submitted, that is, 21 – the first quarter, 22 – the second quarter, 23 – the third quarter, 24 – the fourth quarter.
“Reporting year” – enter the year of the quarter for which the declaration is submitted. For the 3rd quarter of 2021 – “Reporting year” should be entered as 2021.
“Submitted to the tax authority” - enter the code of the Federal Tax Service that registered the tax agent. This code can be found in the same certificate as the TIN, or at the address of the Federal Tax Service on the official website.
“At the location (registration)” it is indicated that the declaration is submitted at the place of registration of the organization. For this, the code “214” is indicated.
“Taxpayer” – indicate the full name of the organization, or the full last name, first name and patronymic of the entrepreneur. It should be indicated in the same way as written in the registration certificate.
“Code of the type of economic activity according to the OKVED classifier” - it should be borne in mind that from 2021 the code is indicated in accordance with the OKVED2 classifier.
“Contact telephone number” – indicate a landline or cell phone number, including the area code.
Let's review the basics
VAT returns are submitted by payers of this tax, and sometimes by persons who do not pay it. For example, if a VAT evader has issued an invoice with an allocated tax amount or, by virtue of law, has acquired the duty of a tax agent.
Note! From 2021, all entities on the Unified Agricultural Tax must pay VAT, unless they have received an exemption under Article 145 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. They fill out the declaration in the general manner.
The report is submitted electronically by all taxpayers. On paper, VAT returns will only be accepted from tax agents who do not pay their own VAT.
The form is submitted to the Federal Tax Service four times a year, for each quarter . The filing deadline is the 25th day of the month following the reporting quarter. The reporting deadlines for 2021 are shown in the following table:
Table 1. Deadlines for filing a VAT return in 2021
| Period | Deadline for submission |
| VI quarter 2020 | January 25, 2021 |
| I quarter 2021 | April 25, 2021 |
| II quarter 2021 | July 25, 2021 |
| III quarter 2021 | October 25, 2021 |
For reporting for the fourth quarter of 2021, the declaration form approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated October 29, 2014 No. ММВ-7-3/558 (hereinafter referred to as the Order) is valid, but with adjustments made by Orders dated December 28, 2018 No. SA-7-3/ 853 and dated August 19, 2020 No. ED-7-3/591 . The form includes 12 sections with attachments, but not all need to be filled out.
The updated declaration form contains new barcodes on each page. The table shows the changes:
| Declaration page | Old barcode | New barcode |
| Title page | 00311014 | 00312011 |
| Section 2 | 00311038 | 00312035 |
| Section 3 | 00311045 | 00312042 |
| Second page of section 3 | 00311052 | 00312059 |
| Appendix 1 to section 3 | 00311069 | 00312066 |
| Appendix 2 to section 3 | 00311076 | 00312073 |
| Section 4 | 00311083 | 00312080 |
| Section 5 | 00311090 | 00312097 |
| Section 6 | 00311106 | 00312103 |
| Section 7 | 00311113 | 00312110 |
| Section 8 | 00311120 | 00312127 |
| Second page of section 8 | 00311137 | 00312134 |
| Appendix 1 to section 8 | 00311144 | 00312141 |
| Second page of Appendix 1 to Section 8 | 00311151 | 00312158 |
| Section 9 | 00311168 | 00312165 |
| Second page of section 9 | 00311175 | 00312172 |
| Third page of section 9 | 00311182 | 00312189 |
| Appendix 1 to section 9 | 00311199 | 00312196 |
| Second page of Appendix 1 to Section 9 | 00311205 | 00312202 |
| Third page of Appendix 1 to Section 9 | 00311212 | 00312219 |
| Fourth page of Appendix 1 to Section 9 | 00311229 | 00312226 |
| Section 10 | 00311236 | 00312233 |
| Second page of section 10 | 00311243 | 00312240 |
| Section 11 | 00311250 | 00312257 |
| Second page of section 11 | 00311267 | 00312264 |
| Section 12 | 00311274 | 00312271 |
Filling out the second section of the declaration
If the organization performed transactions with several counterparties, then section 2 should be filled out for each of them; to do this, you need to add additional pages of the second section.
For one counterparty, one page of the second section is filled out, regardless of how many contracts of the same type are concluded with him. If the type of agreement for each transaction with a counterparty is different, then you will still have to add additional pages. Moreover, each page must contain information on contracts of the same type.
In line 020, the counterparty is indicated if it relates to:
- To the government agency leasing the property;
- To the seller selling treasury property;
- To a foreign organization that is not registered with the tax authority of the Russian Federation;
- To a bankrupt debtor, and the tax agent acquires property from him.
In line 020, dashes are added if the organization purchased a vessel that is not registered in the Russian Register of Ships within 45 days from the date of purchase, or when the organization sells:
- Property in accordance with a court decision or confiscated;
- Confiscated property;
- Ownerless or purchased assets;
- Treasures;
- Values that were transferred to the state by right of inheritance.
Line 040 “Budget classification code” – is entered by KBK VAT 182 1 0300 110.
Line 050 – indicated by OKTMO according to the registration of the organization. You can find out OKTMO on the official website of the Federal Tax Service.
Line 070 – indicates the transaction code where the organization was a tax agent. You can find the required code in Appendix No. 1 to the Procedure, approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service No. ММВ-7-3 / [email protected] dated 10.29.2014.
Line 060 - before filling it out, the need to fill in lines 080, 090, and 100 is checked. They are filled in in cases where dashes are placed in line 020, or if the organization acted as an intermediary in the sale of goods by foreign companies. In all other cases, dashes are placed in these lines.
Line 080 – VAT on shipment is indicated.
Line 090 – VAT on prepayment of the reporting period is indicated.
Line 100 – VAT is indicated on prepayments of the current and previous quarters, against which the shipment was made in the reporting period.
Line 060 – indicates the amount of VAT payable. When 080-100 lines are filled in, the amounts are calculated using the formula:
Line 060 = line 080 + line 090 – line 100.
If lines 080-100 contain dashes, then VAT is calculated on transactions in line 070.
When an enterprise becomes a tax agent
A company or individual entrepreneur acquires the status of a VAT agent if (Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- Buys goods/services in Russia from foreign companies that are not registered with the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation;
- Acts as an agent (intermediary) and participates in settlements when selling goods of foreign companies on the territory of our country that are not taken into account by the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation;
- Leases property from government agencies and municipalities;
- Acquires state property from state and municipal bodies that does not belong to them;
- Buys (except for those exempt from VAT) raw hides, waste paper, scrap ferrous/non-ferrous metals;
- Sells confiscated goods in the Russian Federation, as well as property sold under court decisions (except for situations where the debtor is declared bankrupt), treasures, valuables inherited by the state;
- Buys a vessel that is not named in the international registry of Russia within 45 days from the date of transfer of ownership;
- Provides rolling stock and containers for operation under mediation agreements (except for international transportation of exported goods), if the points of departure/destination are located in the Russian Federation.
Example
Continent LLC is an intermediary in the sale of goods by a foreign company that is not registered for tax purposes in the Russian Federation. Continent LLC enters into an agreement for the amount of 1,250 thousand rubles for the supply of goods with Federation LLC.
On March 20, 2021, Federation LLC made an advance payment to Continent LLC of 850 thousand rubles, including VAT.
On May 20, Continent LLC shipped goods to Federation LLC for 625 thousand rubles.
On July 20, Continent LLC made a second shipment to Federation LLC for 625 thousand rubles.
On July 25, Federation LLC paid the remaining amount of the contract - 400 thousand rubles.
Filling out a VAT return.
First quarter:
Line 090 – RUB 129,661, based on 18% VAT on the prepayment amount.
Line 080 is not filled in.
Line 060 – 129,661 rub.
Second quarter:
Line 080 – RUB 112,500, based on 18% VAT on shipment.
Line 100 – 112,500 rubles, since VAT on prepayment is higher than VAT on shipment;
Line 060 – 0 rub.
Third quarter:
Line 080 – 112,500, based on 18% VAT on shipment.
Line 090 – put a dash.
Line 100 – 17,161 rubles, based on the calculation of 129,661 – 112,500.
Line 060 – 95,339 rubles, based on 112,500 – 17,161.
Receipt of scrap metal
To reflect the receipt document, offset the advance payment to the supplier and account for incoming VAT, we use the document “Receipt (act, invoice)” with the transaction type “Goods (invoice)”. The document can be prepared in the “Purchases”/subsection “Purchases”/”Receipts (acts, invoices)”.
Fig. 24 Receipt of scrap metal
Let's create a new document and fill it out according to the data received from the supplier. When posting a document in the accounting register, entries are reflected to offset the advance payment to the supplier, the cost of scrap metal received from the supplier and the VAT amounts calculated by the tax agent for the seller, based on the amount of delivery.
Fig.25 Creating and filling out a new document
Entries for the type of movement “Receipt” will be added to the “VAT presented” register. In this case, the value “Product (tax agent)” will be reflected in the “Type of value” field.
Fig. 26 “Type of value” the value “Product (tax agent)” will be displayed
According to Art. 168 (clause 5) of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the supplier-VAT payer when shipping scrap non-ferrous metals is obliged to issue an invoice to the buyer.
Fig.27 Operation type code
We indicate the number and date of the received invoice at the bottom of the receipt document and click the “Register” button.
Fig.28 Document movements
After recording the invoice received, transactions are generated on account 76.NA - for the amount of VAT calculated by the buyer-tax agent for the supplier on the cost of the supply, and in the “VAT Sales” register an entry will appear indicating the type of value “Goods (tax agent)” and event “VAT accrued for payment”.
Fig.29 Specifying the type of value and event
Scrap metal is accepted for accounting. Now the buyer-tax agent has the right to a tax deduction for VAT:
- According to paragraph 15 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - VAT deduction after shipment of goods - for the seller;
- According to paragraph 3 of Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation - deduction of VAT from the cost of purchased scrap - for yourself.
Filling out sections 8 and 9 of the declaration
Section 8 should contain information from the purchase book. Only transactions for which the right to deduction arose during the reporting period are reflected. The section is completed by all tax agents, with the exception of organizations selling seized property by court decision, or goods of foreign companies.
Section 9 should contain information from the sales book. The section is filled in by all tax agents for transactions that resulted in an obligation to pay VAT to the budget (
Advance payment to the supplier
Postings for prepayment transactions are generated in the system by documents written off from the current account in the “Bank and Cash Office” section/subsection “Bank”/journal “Bank Statements”.
Fig. 18 Prepayment to supplier
The document “Write-off from the current account” generates a posting to the debit of account 60.02 and the credit of account 51 for the amount of the advance payment transferred to the supplier.
Fig. 19 Document “Write-off from current account”
At the time the supplier receives payment for the upcoming supply of scrap metal, the buyer must fulfill the duties of a tax agent for calculating VAT, and the seller must issue an invoice for the received advance without taking into account VAT amounts with the note “VAT is calculated by the tax agent.”
To register this operation, you must enter the document “Invoice received” based on the document “Write-off from the current account”. The document will reflect:
- The amount of the advance payment transferred to the supplier, taking into account VAT amounts (in our example, this is 50,000 rubles + 50,000 * 18% (VAT rate as of the current date)) - 59,000 rubles;
- The estimated VAT rate is 18/118;
- VAT amount - 9,000 rubles. (RUB 59,000 * 18/118).
Fig.20 Invoice received
Postings are generated for accounts 76.AB and 76.VA:
- The amount of VAT calculated by the buyer-tax agent on the amount of the advance payment (for the seller);
- The amount of VAT on prepayment accepted for deduction, in accordance with Art. 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the buyer-tax agent (for himself).
Fig. 21 Postings are generated for accounts 76.AB and 76.BA
Please note that for this operation, the VAT of the tax agent is taken into account in account 68.52 “VAT of the tax agent for certain types of goods” (clause 8 of Article 161 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, entries are made in the registers “Invoice Log”, “VAT Sales” and “VAT Purchases” to store information about the received invoice, indicating the type of value and event.
Fig.22 VAT Purchases
Fig.23 VAT Sales
Preparation of invoices
In accordance with paragraph 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, upon the sale of goods (work, services), transfer of property rights, as well as upon receipt of payment amounts, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights, appropriate invoices are issued - invoices no later than five calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), from the date of transfer of property rights or from the date of receipt of payment amounts, partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services), transfer of property rights right
As noted in the letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated August 12, 2009 No. ШС-22-3/ [email protected] , tax agents, as well as VAT taxpayers, are required to issue invoices. However, the procedure for issuing such invoices will differ from the generally accepted one. Table No. 1 discusses the features of issuing invoices by tax agents when purchasing goods (work, services) from foreign organizations that are not registered in the Russian Federation, as well as when leasing state or municipal property.
Table 1.
| Invoice Line | Category of the payer filling out this line | |
| Tax agents leasing state (municipal) property | Tax agents purchasing goods (work, services) from foreign organizations that are not tax registered in Russia | |
| Line 2 (seller) | Provide the full or abbreviated name of the seller (specified in the agreement with the tax agent) for whom the tax agent fulfills the obligation to pay tax | |
| Line 2a (address) | The location of the seller (specified in the agreement with the tax agent) for whom the tax agent fulfills the obligation to pay tax is given. | |
| Line 2b (TIN/KPP of the seller) | The identification number and reason code for registering the seller (specified in the agreement with the tax agent) are provided. | A dash is placed |
| Line 3 (shipper and address) | A dash is placed (for purchased works or services) | |
| Line 4 (consignee and his address) | A dash is placed (for purchased works or services) | |
| Line 5 (to payment and settlement document No. _from__) | The number and date of the payment and settlement document indicating payment for purchased services and (or) property is indicated. | Indicate the number and date of the payment and settlement document indicating the transfer of the tax amount to the budget (when purchasing works, services) Indicate the number and date of the payment and settlement document indicating payment for purchased goods (when purchasing goods) |
Additionally, it is necessary to pay attention that dashes are also placed on line 5 of the invoice when using a non-cash form of payment.
With regard to filling out individual columns of invoices, it is worth considering that in column 7 “Tax rate” you should indicate the tax rate determined by paragraph 4 of Article 164 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (10/110 or 18/118).
In 1C: Accounting 8, an invoice is entered based on a payment document or by processing Registration of tax agent invoices. In this case, the payment document means the document that registers the payment to the supplier.
The document Invoice issued (see Fig. 1) generates a posting
Debit 76.NA Credit 68.32.
Rice. 1