The work of occupational safety specialists involves filling out a large number of document forms, such as, for example, logs. Despite the variety of regulatory legal acts regulating the availability of certain journals, we can identify general principles for maintaining these forms of documents.
The training logs should be:
- numbered. You can number the pages or sheets of the magazine; numbering the sheets will be less labor-intensive;
- laced. It is up to you to choose what you will use for lacing: it can be twine, linen cord, ribbon, stitched nylon thread, etc. The ends of the lacing material should be released on the cover of the magazine or on its last page and secured with a sticker so that the ends of the lacing remain visible. To avoid inconvenience when using a laced magazine, the length of the extended ends of the lacing must be at least 5 cm. drawing;
- signed by the person responsible for its maintenance. The following inscription should be placed on or next to the sticker: “The magazine contains ___ sheets numbered, laced and sealed. "date"_month_20__ Full name, position, signature_______.” The journal is signed by the person authorized to keep this journal;
- sealed with the seal of the organization. We place the seal so that its imprint is both on the sticker and on the cover/sheet of the magazine to which the ends of the lacing are glued. See picture.
- When filling out the journal, we do not leave empty lines and do not make corrections.
- Defining a journal form in a regulatory document as recommended means that we can make changes to this form, for example, adding columns.
- It is not necessary to purchase magazines printed in a printing house; you can print them in your organization yourself.
- The storage period for completed journals is 10 years (Order of the Ministry of Culture of Russia dated August 25, 2010 No. 558 “On approval of the “List of standard management archival documents generated in the process of activities of state bodies, local governments and organizations, indicating storage periods”), unless otherwise provided for by regulatory documents regulating the maintenance of relevant journals. For example, a log of accidents at work is kept for 45 years.
Let us dwell in more detail on some aspects of filling out logs related to the registration of briefings.
Induction training
Induction training is carried out with the employee immediately after he is hired. At its core, this is a story about how to comply with safety rules while at the enterprise as a whole. As a rule (but not necessarily) this type of instruction is carried out by a labor protection specialist. Sometimes it is right for several people to have the right to conduct induction training, since a specialist may get sick, quit, or go on vacation. Sometimes even hiring can take place at different addresses.
The main thing is that this employee (employees) is appointed by order of the director.
download the order appointing those responsible for conducting induction training |
An entry about the induction briefing is made in the introductory briefing registration log. Along with the magazine, a personal training card can be used.
Download the induction training log form |
As an example:
Download the induction program |
Download induction instructions |
Timing of briefings
| Type of instruction | Date |
| Introductory | During hiring. |
| Primary | On the first working day. |
| Repeated | Once a year, with workers in fire-hazardous industries - once every six months. |
| Unscheduled | Before admission or on the day of work in new conditions. |
| Target | Before performing specific work. |
On-the-job training
On-the-job training is called that because it talks about the rules for safe work performance directly at the employee’s workplace.
This responsibility rests with the immediate supervisor of the work. If, for example, several teams work in a workshop, then the task of conducting on-the-job briefings lies with the foremen, and not with the workshop manager.
download the order appointing those responsible for conducting workplace training |
The procedure for conducting briefings is determined by the relevant regulations.
provisions on conducting briefings with employees |
The safety magazine itself 2021 ()
Below is the link to find the Safety Magazine 2021 (). When printing it, be sure to use mirrored margins to ensure proper margins for duplex printing. Next, be sure to number the pages and stitch the magazine with stationery thread, and on the last format put the stamp “laced-numbered” and seal it with the manager’s visa. That's it, the magazine is ready for use!
Treat safety magazines responsibly and take care of yourself!
Initial training at the workplace
It is carried out with everyone before starting independent work. Conducting labor safety briefings includes familiarizing workers with existing hazardous or harmful production factors, studying labor safety requirements contained in the organization’s local regulations, labor safety instructions, technical and operational documentation, as well as the use of safe methods and techniques for performing work.
Initial instruction on labor protection sampleAttention! Important note! Initial instruction is provided by profession and type of work. We bring to your attention general instructions for all employees. Despite its versatility, it cannot always replace the others. |
The labor safety briefing ends with an oral assessment of the employee’s acquired knowledge and skills in safe work practices by the person conducting the briefing.
All types of briefings are recorded in the briefing log.
Download the workplace briefing log form |
Not all employees are required to undergo on-the-job training. If the responsibility to instruct lies with the boss, then who will instruct the director? Or why instruct people who themselves have the right to instruct employees?
Employees may be exempt from undergoing initial training at the workplace. The list of professions and positions of employees exempt from undergoing initial training at the workplace is approved by the employer.
list of those exempt from workplace training |
Who is assigned responsibility and who keeps the log
In accordance with the law, the safety manager and engineer must have valid certificates that they have been trained in specialized institutions. At the same time, it is necessary to remember that the manager must be trained once every 5 years, because only he is responsible for organizing safety and health at the enterprise.
Re-briefing
All workers undergo repeated training at least once every six months. Drivers are given briefings every quarter.
Repeated instruction is carried out according to the initial instruction program at the workplace in full.
Initial training program
This is a document issued for each profession. It indicates the topics of the briefing and the time required to study them. And most importantly, the numbers of instructions according to which workers of a particular profession are instructed.
initial training programs |
If an enterprise treats training formally, then sometimes you can see in a magazine how on the same day a dozen people in one department were trained, and according to different instructions. If at least one hour is allotted for each person in the program, then the instructor would have to have a ten-hour working day. This can only mean that in fact people were given to sign in a pre-filled journal.
At the same time, you can conduct briefings with employees who have the same training programs.
document
To make it easier to work with instructions and document them, a sample filling is below.
Download: Workplace briefing log (form)
Download: Workplace briefing log (filling sample)
Unscheduled briefing
Unscheduled briefing is carried out by:
- upon the introduction of new or revised standards, rules, instructions on labor protection, as well as amendments to them;
- when changing the technological process, replacing or upgrading equipment, devices and tools, raw materials, materials and other factors affecting labor safety;
- in case of violation by workers and students of labor safety requirements, which can lead or have led to injury, accident, explosion or fire, poisoning;
- at the request of supervisory authorities;
- during breaks in work - for work for which additional (increased) labor safety requirements are imposed for more than 30 calendar days, and for other work - 60 days.
Procedure for keeping a TB journal and sample filling
The safety briefing log must be kept continuously at the enterprise in a standard form in compliance with the mandatory details provided for by GOST 12.0.004-90. This document can be supplemented by the company depending on the type of activity performed. As a rule, these magazines can be purchased from printing houses in ready-made form. It is advisable to create a separate register for each type of instruction. The safety log must be laced, numbered, sealed with the company seal and endorsed with the signature of the manager.
During training, the employee is provided with safety instructions, which he studies. The safety officer explains the main points and answers all the employee’s questions. After this, the engineer checks the knowledge gained and enters the relevant data into the safety briefing log.
The title page contains the name of the organization and its structural unit. The following is the name of this register. In the lines “Started” and “Ended” you must write down the corresponding dates.
The tabular part of the document indicates the date of training, full name, year of birth of the person being instructed, his profession or position, and the structural unit where the employee is going to work. Then fill in information about the type of instruction provided, full name. instructing. As soon as the employee becomes familiar with the safety rules, the log is signed by the person responsible for the instruction and the employee himself.
When a mandatory internship is provided, it is necessary to fill out the appropriate columns with the number of shifts, signatures of the intern and the person who conducted it.
In the case of unscheduled training, in the line with the type of training, you must indicate the reasons that caused it.
In addition to this magazine, the organization can use personal training cards, which are compiled for each employee.
Targeted briefing
Targeted instruction is carried out when performing one-time work not related to direct responsibilities in the specialty (loading, unloading, cleaning the territory, one-time work outside the enterprise, workshop, etc.); liquidation of consequences of accidents, natural disasters and catastrophes; production of work for which a permit, permit and other documents are issued; conducting excursions at the enterprise, organizing public events (excursions, hikes, sports competitions, etc.).
Targeted briefing with employees carrying out work according to work permit, order, etc. recorded in the work permit or other documentation authorizing the execution of work.
How to make occupational safety instructions
The procedure for developing, approving, revising and taking into account labor protection instructions for employees is described in the Methodological Recommendations for the development of state regulatory requirements for labor protection (approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 17, 2002 No. 80).
Instructions for workers by profession and for certain types of work are developed in accordance with the list compiled by the head of the labor protection service.
General provisions
In accordance with Order No. 645, management (owners of organizations) are obliged to:
- organize fire safety training according to the program developed by the administration;
- train personnel in fire safety;
- check the level of acquired knowledge;
- record the fact of conducting classes and testing in a special journal.
All workers in fire-hazardous industries and employees who work in buildings with crowds of more than 50 people must be able to act in the event of a fire and use primary fire extinguishing equipment.
What occupational safety logs should be kept at the enterprise?
Occupational safety logs must be kept in every organization. How many magazines an organization should have depends on the scope of the enterprise. The recommendations include which occupational safety logs are required to be prepared in each organization, how to fill out and register the logs, and how much an organization that does not keep occupational safety logs will be fined.
An organization, regardless of its field of activity and the number of employees, must have a log of introductory briefings, a log of registration of workplace briefings and a log of accidents. This is indicated in paragraph 2.1.3 of the Procedure for training in labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations, which was approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29 (hereinafter referred to as the Training Procedure), and in paragraph 33 of the regulations on the specifics of the investigation accidents at work in certain industries and organizations, which was approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated October 24, 2002 No. 73.
Logbooks for recording and issuing instructions on labor protection and a logbook for three-stage control are drawn up at the request of the employer. With their help, it is convenient to monitor compliance with labor protection requirements in the organization.
WORTH PAYING ATTENTION
Carrying out three-stage control and keeping a log is mandatory for organizations that carry out general construction and special construction work.
Also, the journal must be kept during new construction, expansion, reconstruction, technical re-equipment, current and major repairs of buildings and structures. This is the requirement of paragraph 19 of the Rules on labor protection in construction, approved by Order of the Ministry of Labor dated 06/01/2015 No. 336.
In organizations that carry out hazardous work under a permit, it is necessary to draw up a journal for recording the issuance of permits. If the organization employs employees who, according to standard standards, need to be issued special clothing and PPE, you can create a journal for recording the issuance of special clothing and PPE.
How to fill out the induction log
Conduct induction training for employees upon hiring, business travelers, employees of other organizations who perform work at the enterprise, trainees and other persons who participate in the production activities of the organization.
The recommended form of the journal is specified in GOST.
Make entries in the introductory briefing log after the introductory briefing and testing of the employee’s knowledge (clause 2.1.3 of the Training Procedure).
In column 1
“Date” indicate the actual date of the training. The date must coincide with the date the employee was hired, since the employer must conduct induction training for the employee on the day he is hired. If an employee who is authorized to provide instructions is absent from work, the instruction is carried out by the employee who replaces him or by the director of the enterprise.
In column 2
"F. I.O. of the person being instructed,” write down the last name, first name, and patronymic of the employee who was instructed.
In column 3
“Profession, position of the person being instructed”, indicate the position that is indicated in the employment contract of the employee who was instructed.
In column 4
“Name of the production unit to which the person being instructed is sent” indicate the name of the unit, department, workshop in which the employee will work.
In column 5
"F. Acting instructor” write down the last name, first name, patronymic of the employee who conducted the instruction.
In columns 6, 7
The employee who conducted the instruction and the employee who received the instruction put their signatures after the instruction.
QUESTION ANSWER
How to make corrections to the induction log
The legislation does not provide for the procedure for making corrections in the logs of registration of labor safety briefings.
If an error was made in the briefing log, you can make an entry: “The entry number... was entered erroneously” - and repeat the correct entry below. At the same time, you should not cross out or cover up the erroneous entry with correction fluid.
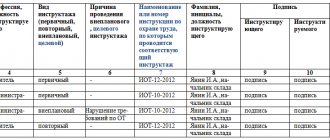
How to fill out a workplace briefing log
Instruction at the workplace is carried out by the immediate supervisor of the work - foreman, foreman, teacher, etc., who has undergone training in labor protection and testing of knowledge of labor protection requirements. The recommended form of the journal is specified in GOST.
Make entries in the briefing log after completing the briefing and testing your knowledge (clause 2.1.3 of the Training Procedure).
In column 1
“Date” indicate the actual date of the training.
In column 2
"F. I.O. of the person being instructed,” write down the last name, first name, and patronymic of the employee who was instructed.
In column 3
“Profession, position of the person being instructed”, indicate the position that is indicated in the employment contract of the employee who was instructed.
In column 4
“Type of briefing” indicate the type of briefing that was provided to the employee: primary, repeated, unscheduled or targeted.
Column 5
“Reason for unscheduled briefing” must be completed only when conducting an unscheduled briefing. In the column, indicate the name, number and date of the document on the basis of which the unscheduled briefing was conducted.
In column 6
"F. Acting instructor" indicate the last name, first name, and patronymic of the employee who conducted the instruction. The briefing is carried out by the supervisor of the instructed employee or the head of the department to which the employee is assigned to work.
In columns 7, 8
The employee who conducted the instruction and the employee who received the instruction put their signatures after the instruction.
Columns 9, 10, 11
filled out when the employee is assigned to an internship.
In column 9
“Number of shifts” indicate the number of shifts or working days of the internship and indicate the start and end dates of the internship.
In column 10
“Completed the internship” is signed by the employee who completed the internship.
In column 11
“Knowledge checked, permission to work issued”, the internship supervisor, after completing the internship, testing the employee’s knowledge and permission to work, puts a date and signature.
QUESTION ANSWER
How many logs of occupational safety briefings should there be at an enterprise?
The employer decides how many logs of labor safety briefings to keep. The main thing is that these logs record all five types of briefings: introductory, primary, repeated, unscheduled and targeted.
Training Procedure No. 1/29 has no requirements for the number of briefing logs; it states that all types of briefings are registered in the appropriate briefing logs, indicating the signature of the person being instructed and the signature of the instructing person, as well as the date of the briefing (clause 2.1.3 of the Training Procedure , approved by resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29).
The number of briefing logs is specified in GOST 12.0.004-2015 - three logs: registration of introductory briefing
,
registration of workplace briefing
and
registration of targeted briefing
. However, GOST 12.0.004-2015 is not a mandatory document, unlike Training Procedure No. 1/29.
Therefore, each enterprise independently determines the number of briefing logs; you can keep only one log, you can follow GOST 12.0.004-2015 and keep three logs, or you can keep five logs for each briefing, if that is more convenient.
QUESTION ANSWER
Is it possible to keep briefing logs electronically?
No you can not.
The conduct of briefings must be recorded in a journal entry with the signatures of the person being instructed and the person instructing. This is indicated in the Procedure for training on labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Ministry of Education dated January 13, 2003 No. 1/29. There is no information in the document about maintaining journals in electronic form and using electronic signatures.
QUESTION ANSWER
What is the shelf life of labor safety briefing logs?
Instruction logs are kept for 45 years. This follows from subparagraph “a” of paragraph 423 of the List, approved by order of Rosarkhiv dated December 20, 2019 No. 236
.
How to fill out a work accident log
Record all cases of work-related injuries at the enterprise in the accident register. Make entries in the journal after you have approved the investigation report. When filling out the journal, use Form 9, approved by Decree of the Ministry of Labor dated October 24, 2002 No. 73.
WORTH PAYING ATTENTION
A log of accidents must be registered in the organization, even if there were no accidents (clause 1 of the resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated October 24, 2002 No. 73).
When you make a journal entry, use the information from the accident investigation report. The dates in the eighth column of the journal must be in order, so make entries in the order in which you receive the investigation reports. A record of a serious accident that occurred earlier may follow a record of a minor accident that occurred later because fewer days were spent investigating the minor accident.
In column 1
indicate the serial number of the journal entry.
In column 2
write the date and time of the accident from paragraph 1 of the investigation report.
In column 3
indicate the employee’s full name and total length of service, which is indicated in the work book.
In column 4
write the employee's position. If the employee’s position has changed during the investigation, you need to write the one indicated in paragraph 5 of the act.
To column 5
Enter the information from paragraph 7 of the investigation report.
In column 5.1
write the individual workplace number. It is listed in section II of the SOUTH report. If the workplace is similar, add the letter "A" after the number. The column is filled out only if a special assessment has been carried out at the workplace.
In column 6
write down the type of incident. It is indicated in paragraph 8.1 of the investigation report.
In column 7
Enter the information from paragraph 8 of the investigation report.
In column 8
indicate the act number and the date of its approval.
In column 9
write the number of days on sick leave, if the loss of ability to work was temporary, if the employee received permanent loss of ability to work, indicate the disability group and the degree of loss. If an employee dies, write “fatal.”
In column 10
provide information from paragraph 11 of the investigation report.
QUESTION ANSWER
What is the retention period for an accident log?
The register of accidents at work is kept for 45 years. This is indicated in paragraph 424 of the List, approved by order of the Federal Archives of December 20, 2019 No. 236
.
How to fill out a log of occupational safety instructions
The legislation does not stipulate the employer’s obligation to keep a log of labor safety instructions (letter of the Ministry of Labor dated September 15, 2016 No. 15-2/OOG-3318). A journal can be designed to systematize work with instructions in the organization.
The recommended form of the journal is indicated in Appendix 2 to the Methodological Recommendations for the Development of Labor Safety Instructions, which were approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated May 13, 2004.
In column 1
write the serial number of the entry.
In column 2
indicate the date of registration of the instruction.
In column 3
write down the full name of the instruction.
In column 4
indicate the date of approval of the instructions by the head of the organization.
In column 5
write the serial number of the instruction and the date of approval.
In column 6
indicate the planned deadline for revising the instructions.
In column 7
Write down the details of the employee who registered the instruction with the organization.
In column 8
sign the employee who made the accounting.
Usually the log is filled out by a labor protection specialist.
How to fill out a journal for issuing instructions
There is no mandatory requirement in the legislation to keep a log of the issuance of occupational safety instructions (letter of the Ministry of Labor dated September 15, 2016 No. 15-2/OOG-3318). A log can be issued to document the issuance of instructions to employees. The recommended form of the journal is indicated in Appendix 3 to the Methodological Recommendations for the development of labor protection instructions, which were approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated May 13, 2004.
In column 1
indicate the serial number of the entry.
In column 2
record the date the instruction was issued to the employee.
In column 3
indicate the designation of the instruction, which is indicated in column 5 of the instruction log.
In column 4
write the full name of the instruction, which is indicated in column 4 of the instruction log.
In column 5
indicate the number of instruction copies issued.
In column 6
write the full name and profession of the employee to whom the instructions were issued.
In column 7
the employee who was given the instruction signs.
Typically, the log is kept by heads of structural units who conduct on-the-job training.
How to fill out a three-stage control log
There are no direct requirements for maintaining a three-stage control log in the legislation, but the log is convenient to use in organizations where three-stage control of compliance with labor protection requirements is used to systematize and confirm inspections.
In column 1
indicate the production control level number. Level I – control carried out by employees, level II – control carried out by managers, Level III – control carried out by the employer.
In column 2
write the date of inspection.
In column 3
indicate the identified shortcomings and violations of labor protection requirements. In the same column, it is advisable to indicate the place where the violations were discovered. For example, office number or workshop name.
In column 4
indicate the full name and position of the employee who must eliminate the violations.
In column 5
write down what measures need to be taken to eliminate the violations.
In column 6
indicate the full name of the employees who monitor the elimination of violations. Their signatures are placed in the same column.
In column 7
After the violations are eliminated, the employee responsible for the elimination signs.
The log is filled out by employees who are appointed responsible for conducting inspections.
How to fill out a logbook for issuing permits for high-risk work
Draw up a journal for recording the issuance of work permits if the organization carries out work with increased danger according to the work permit (clause 3.2 of POT RO 14000-005-98).
The recommended form of the journal is specified in Appendix 4 to POT RO 14000-005-98.
In column 1
indicate the work permit number.
In column 2
Write down the date the permit was issued.
In column 3
Briefly describe the work that workers will perform under the work permit.
In column 4
indicate the period for which the permit was issued.
In column 5
signed by the employee who issued the permit.
In column 6
the employee who was issued the work permit signs.
In column 7
puts the full name and signature of the employee who accepted the closed work permit after completing the work.
In the journal, record only the initial permission of employees to work.
How to fill out a logbook for issuing protective clothing and personal protective equipment
Draw up a log if the organization has employees who are supposed to be issued protective clothing and PPE. There are no legal requirements to keep a log, but it will help organize accounting and control of the issuance of PPE.
In column 1
indicate the serial number of the entry.
In column 2
write the name of the protective clothing or PPE, which is indicated in the issuance standards.
In column 3
indicate the date of issue.
In column 4
write down the service life of the workwear or PPE, which is indicated in the issuance standards.
In column 5
indicate the full name and position of the employee who was issued special clothing or PPE.
In column 6
The employee who received special clothing or PPE puts his signature.
In column 7
indicate the full name and position of the employee who issued the protective clothing or PPE.
In column 8
The employee who issued the PPE or workwear signs.
In column 9
You can indicate the standard standards according to which the workwear or PPE was issued, the number of the certificate or declaration of conformity.
Typically, the journal is kept by the head of a department or a housekeeping employee.
What are the fines for lack of occupational safety magazines?
If the enterprise does not have logs for recording training and accidents at work, they will be held accountable under paragraph 1 of Article 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses, issued a warning or imposed a fine:
- for officials - from 2000 to 5000 rubles;
- Individual entrepreneur – from 2000 to 5000 rubles;
- legal entities – from 50,000 to 80,000 rubles.
Our services
Training Expert provides services for the development of documents on labor protection, filling out logs and briefings, preparing all necessary documentation, organizing a labor protection service at the enterprise.
CONTACTS
Phone E-mail
Internal numbers of specialists
Leading occupational safety specialist Alexander Vladimirovich Kudryavtsev
tel:+7 (ext. 605) mob:+7
E-mail
The material was created with the support of the Occupational Safety and Health System.
clause 2.1.3 of the Procedure for training on labor protection and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements for employees of organizations
2.1.3. In addition to introductory briefing on labor protection, initial briefing in the workplace, repeated, unscheduled and targeted briefings are carried out.
Initial briefing at the workplace, repeated, unscheduled and targeted briefings are carried out by the immediate supervisor (producer) of the work (foreman, foreman, teacher, etc.), who has undergone occupational safety training in the prescribed manner and tested knowledge of labor safety requirements.
Conducting labor safety briefings includes familiarizing workers with existing hazardous or harmful production factors, studying labor safety requirements contained in the organization’s local regulations, labor safety instructions, technical and operational documentation, as well as the use of safe methods and techniques for performing work.
The labor safety briefing ends with an oral assessment of the employee’s acquired knowledge and skills in safe work practices by the person conducting the briefing.
Conducting all types of briefings is registered in the relevant logs of briefings (in established cases - in the work permit) indicating the signature of the person being instructed and the signature of the instructing person, as well as the date of the briefing.
paragraph 33 of the resolution of the Ministry of Labor dated October 24, 2002 No. 73
33. Every industrial accident registered in accordance with the established procedure, including industrial accidents that occurred with employees who have entered into an employment contract for a period of up to two months or are employed in seasonal work, as well as persons who have entered into an agreement to perform work from home (homeworkers) , are registered by the employer (legal entity or individual), who, in accordance with the decision of the commission, records it in the register of industrial accidents in accordance with Form 9, provided for in Appendix No. 1 to this Resolution.
Industrial accidents that occur with employees of religious organizations are registered by the relevant religious organizations (associations), which have undergone state registration in the prescribed manner and act as an employer in relation to the victim.
All industrial accidents registered in an organization (with an employer - an individual) are included in the annual form of the federal state statistical surveillance of industrial injuries, approved by the State Committee of the Russian Federation on Statistics and sent to the statistical authorities in the prescribed manner.
clause 19 of the Rules on labor protection in construction, approved by order of the Ministry of Labor dated 06/01/2015 No. 336
19. Employers, in accordance with the specifics of the work performed, must organize control over the state of labor conditions and safety:
1) constant monitoring of the serviceability of the equipment, devices, tools used, the presence and integrity of fences, protective grounding and other means of protection before and during work at their workplaces, carried out by employees (first level);
2) operational control over the state of labor conditions and safety, carried out by managers (manufacturers) of work together with authorized representatives of workers (second level);
3) periodic monitoring of the state of labor conditions and safety in structural divisions and construction production sites, carried out by the employer (his authorized representatives, including labor safety service specialists) jointly with representatives of the primary trade union organization or other representative body of workers in accordance with approved plans (third level) .
If violations of labor safety requirements are detected, workers must take measures to eliminate them on their own, and if this is impossible, stop work and inform their immediate supervisor (work performer).
In the event of a threat to the safety and health of workers, immediate managers (work performers) are obliged to stop work and take measures to eliminate the danger, and, if necessary, ensure the evacuation of people to a safe place.
When carrying out construction work on a separate site, taking measures to ensure the safety and labor protection of workers and organizations, fire safety measures is entrusted to the person carrying out the construction work.
Letter of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation dated September 15, 2016 No. 15-2/ОOG-3318 On maintaining log books and issuing instructions on labor protection for workers
Question: About keeping logs and issuing instructions on labor protection for workers.
Answer: The Department of Labor Conditions and Safety reviewed, within its competence, the appeal received on the official website of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Russian Federation on the issue related to maintaining log books and issuing instructions on labor protection, and reports the following.
Article 212 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (hereinafter referred to as the Code) stipulates that the responsibility for ensuring safe conditions and labor protection rests with the employer.
In accordance with Article 212 of the Code, the employer is obliged to ensure, among other things:
development and approval of rules and instructions on labor protection for employees, taking into account the opinion of the elected body of the primary trade union organization or other body authorized by employees in the manner established by Article 372 of the Code for the adoption of local regulations;
the presence of a set of regulatory legal acts containing labor protection requirements in accordance with the specifics of their activities.
Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of Russia dated December 17, 2002 No. 80 approved Methodological Recommendations for the development of state regulatory requirements for labor protection (hereinafter referred to as the Recommendations).
In accordance with paragraph 5.10 of the Recommendations, the recommended forms for registering labor protection instructions for workers and recording the issuance of labor protection instructions for employees of the organization's divisions are given in Appendices No. 9 and 10 to these Recommendations.
It should be noted that these Recommendations are not a normative legal act, since they are not registered by the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation and are advisory in nature, therefore, the requirement for full compliance with the above Recommendations does not have sufficient legal justification.
Taking into account the above, we clarify that keeping logs of labor protection instructions for employees and records of the issuance of labor protection instructions for employees of the organization’s departments is advisory in nature.
It should be noted that the issuance of instructions to employees must be recorded against signature, while the procedure and form for issuing instructions is determined by the employer.
Deputy Director of the Department of Labor Conditions and Safety of the Ministry of Labor of Russia
TM Zhigastova
clause 3 POT R O-14000-005-98 Regulations. Work with increased danger. Organization of the event
3.2. The work permit should be issued in the department where high-risk work will be performed. The issuance of a permit must be recorded in a special journal.
The registration form for issuing permits is given in Appendix 4.
Reviews
Certificates and accreditations
Development and approval of the program
The organization independently develops and approves the 2021 occupational safety induction program; this occurs on the basis of legislative and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation. The program takes into account the specifics of the organization's activities. An approximate list of questions for drawing up a program is contained in Appendix B to GOST 12.0.004-2015. The worker should be informed how to avoid hazards during the work process. For this purpose he is informed:
- about the specifics of the organization;
- work and rest schedule;
- rules of behavior in the workplace and in other areas of the organization;
- storage locations and procedure for using protective equipment;
- first aid procedures.
Taking into account the coronavirus pandemic in 2021, employers were required to instruct employees on measures to prevent coronavirus infection and what to do if there are signs of the disease.
It just seems that the instructions for conducting induction training are something complicated. In fact, this is simply a list of questions that are brought to the person being instructed, and the time allotted for their consideration. The sample program looks like this:
The sample shows that the instructions for conducting introductory training on labor protection are an appendix to the order. The form of the regulatory act on the approval of the program is not defined in any way. The employer usually approves such a program with an order, for example, this:
The order must be familiarized with the authorized person who is assigned the relevant responsibilities. Such a specialist puts a signature and date of review in the journal.
Fines if training is not carried out and a log is not kept
The absence of a log of safety training, as well as its non-conduct, is interpreted by the competent authorities as an employee’s permission to perform work duties without undergoing training in the prescribed manner and testing knowledge of labor protection requirements. Art. 5.27.1 of the Code of Administrative Offenses of Russia determines that an administrative penalty may be imposed on a legal entity in the form of a fine from 110,000 to 130,000 rubles, and on its officials - from 15,000 to 25,000 rubles.
Repeated violation of these norms (as well as failure to eliminate this fact earlier) leads to the imposition of a fine on the organization from 100,000 to 200,000 rubles or suspension of its activities for 90 days. In this case, the official is subject to penalties in the form of a fine from 35,000 to 40,000 rubles or disqualification from 1 to 3 years.
When is it held?
Initial briefing should be carried out with employees before starting independent activities:
- newly hired by the organization, regardless of the nature of the work;
- temporarily working for a period of business trip or internship;
- transferred to another area of work associated with harmful, dangerous working conditions, or other significantly changing work within the framework of labor protection.
Instruction is required for every employee hired on a permanent or temporary basis. The manager has the right to approve the list of persons who do not have to undergo it. This often applies to office workers, whose work does not involve exposure to negative factors. However, if they violate labor safety rules, responsibility rests with the employer.
Employer's liability
It is prohibited to allow employees to undergo internships and subsequently to work independently without undergoing initial training, because, in addition to moral responsibility in the event of an emergency, otherwise a fine for each employee is possible:
- for officials in the amount of fifteen thousand to twenty-five thousand rubles;
- for persons carrying out entrepreneurial activities without forming a legal entity - from fifteen thousand to twenty-five thousand rubles;
- for legal entities - from one hundred ten thousand to one hundred thirty thousand rubles.
Results
Organizing initial training for a new employee before starting work is the responsibility of the employer and is aimed at ensuring that the employee complies with the rules of conduct aimed at preventing the occurrence of situations that are dangerous both to the life and health of the employee and to the safety of the employer’s property.
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.