Issues discussed in the material:
- In what cases does an individual entrepreneur overpay taxes?
- What sources can you find information about overpayment of taxes by individual entrepreneurs?
- Is it possible to reconcile with the tax office and write an application for a refund of overpaid taxes for individual entrepreneurs online?
- Is it possible to return an overpayment of taxes to an individual entrepreneur if more than 3 years have already passed?
The main task of the Federal Tax Service (FTS) is to replenish the state budget and control tax contributions. This determines the primary focus of its actions - ensuring timely and full tax payments, which is achieved through various means of influence, including financial sanctions. In practice, the opposite phenomenon is often encountered, namely, excessive payments to the state treasury. What can an individual entrepreneur do in such a situation? How to return overpayment of taxes to individual entrepreneurs? Let's find out.
Why does an individual entrepreneur overpay taxes?
Of course, no one will deliberately deduct excess tax. As a rule, the cause of this phenomenon is trivial errors, for example, in calculating the tax itself or in filling out the payment order form.
In addition, overpayment is possible for other reasons:
- The entrepreneur was not aware of the special reduced rate under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses”, which is valid in the corresponding region, and paid tax at a rate of 15%.
- A declaration was submitted with clarifications for the previous period, due to which the payment was due in a smaller amount.
- Preferential conditions that were available for use, for example, from the beginning of this year, and were introduced by regional authorities later.
- Under the simplified tax system “Income minus expenses,” the entrepreneur transferred more funds in quarterly advance payments throughout the year than is required for the final tax amount for the annual period.
- Lack of awareness that a specific type of activity is subject to preferential taxation.
Top 3 articles that will be useful to every manager:
- How to choose a tax system to save on payments
- How to minimize taxes and not interest the tax authorities
- How to create an electronic signature quickly and easily
Accounting for expenses on the simplified tax system Income minus Expenses
To recognize expenses when calculating the tax base, taxpayers who have chosen this option of the simplified tax system must meet the following conditions:
1. Expenses must be included in the list given in Art. 346.16 Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Among them:
- expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets and intangible assets;
- expenses for repair and reconstruction of fixed assets;
- expenses for wages, business trips and compulsory insurance of employees;
- rental, leasing, import customs payments;
- material costs;
- expenses for accounting, auditing, notary and legal services;
- the amount of taxes and fees, except for the single tax on the simplified tax system;
- expenses for the purchase of goods intended for resale;
- transportation costs, etc.
The list of expenses is closed, i.e. does not allow the recognition of other types of expenses not specified in the list.
Important: quarterly advance payments cannot be taken into account in expenses when forming the tax base for the simplified tax system Income minus expenses. These payments can only reduce the amount of tax at the end of the year, calculated in the declaration under the simplified tax system.
2. Expenses must be economically justified and documented.
Economically justified expenses mean those expenses that are aimed at making a profit, i.e. have a clear business purpose. Here you need to be prepared to explain to the tax authorities the need for those expenses, the connection of which with a business purpose is not clearly visible. For example, why a computer with bells and whistles was purchased for the office, and not a regular one, or how a luxury company car can be associated with the formation of a circle of elite clients.
As an argument in tax disputes, you can use the legal position of the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation, expressed in Determination No. 320-O-P of 06/04/07. In this document, the Constitutional Court recognizes that expenses that were aimed at making a profit from business activities can be recognized as economically justified, even if this result was not achieved.
However, a taxpayer can spend his money without the approval of the Federal Tax Service, but in order to take these expenses into account when forming the tax base for the simplified tax system Income minus expenses, one will have to take into account the factor of the supervisory authorities’ suspicious attitude towards business. Unfortunately, the presumption of good faith of the taxpayer, approved by Art. 3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation and Art. 10 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, works little in practice.
As for documenting expenses for the simplified tax system, you must have at least two documents to confirm each expense. One of them must prove the fact of a business transaction (consignment note or acceptance certificate), and the second confirms payment of the expense. In case of non-cash payment, the expense is confirmed by a payment order, account statement, receipt, and in case of cash payment - by a KKM cash register receipt. Documents that confirm the expenses incurred for the simplified tax system, as well as the payment of tax, must be kept for four years.
3. Expenses must be paid.
All expenses under the simplified system are recognized on a cash basis, i.e. costs can only be taken into account after they have actually been paid. For example, wage expenses should be taken into account not on the day they are accrued, but on the day they are actually paid to employees. Costs associated with paying interest on loans and credits are also taken into account not on the day they are accrued, but on the day of payment.
The amounts of expenses are reflected in KUDiR on the day when the money was transferred from the current account or issued from the cash register. If payment is made by bill of exchange, then the date of recognition of the expense for the simplified tax system will be the day of repayment of the bill of exchange or the day of transfer of the bill of exchange by endorsement.
4. For some types of expenses on the simplified tax system Income minus Expenses, a special recognition procedure applies
Accounting for costs of purchasing goods intended for resale
You can reduce your income by the amounts spent on purchasing goods for resale only after meeting two conditions:
- pay their cost to the supplier;
- sell the goods, i.e. transfer it to the buyer into ownership (the fact that the buyer paid for this product does not matter).
When taking into account the costs of goods purchased in batches, with a large number of assortment items, which, moreover, will be paid to the supplier in more than one amount, it will hardly be possible to do without an accountant or specialized service. Let us give a conditional example of a simple operation for the sale of a homogeneous product with stage-by-stage payment to the supplier.
✐ Example ▼
An organization using the simplified tax system received from the supplier two batches of the same toilet soap intended for further sale. The cost of soap in the second batch increased, due to inflation, by 10%.
| Batch number | date of receiving | Quantity, boxes | Unit price, rubles | Batch price, rubles | Terms of payment | Paid, rubles |
| 1 | 13.01.21 | 100 | 300 | 30 000 | 75% prepayment | 22 500 |
| 2 | 02.03.21 | 130 | 330 | 42 900 | 50% prepayment | 21 450 |
In total, as of 03/02/21, there were 230 boxes of soap in the warehouse, the cost of which at the purchase price was 72,900 rubles, of which only 43,950 rubles were paid to the supplier.
On 03/11/21, 220 boxes of soap were sold to the buyer. Debt to the supplier for the first batch in the amount of RUB 7,500. was repaid on 03/15/21. Payment of the debt for the second installment was not made by the end of the 1st quarter.
To calculate the tax base under the simplified tax system Income minus expenses, you can only take into account the cost of sold and paid for boxes of soap . The first batch of soap was paid to the supplier in full, so we can take into account the entire purchase price of this batch - 30,000 rubles.
Of the second batch of 130 boxes, 120 were sold to the buyer (220 boxes of soap sold minus 100 boxes from the first batch), but only 50% was paid to the supplier as a percentage, i.e. cost 75 boxes. When calculating the tax base, soap from the second batch can only be taken into account in the amount of 21,450 rubles, despite the fact that almost all of the second batch was sold.
In total, according to the results of the 1st quarter, only 51,450 rubles can be taken into account in the costs of purchasing goods intended for sale.
Accounting for costs of raw materials and supplies
By analogy, taking into account goods intended for sale, it can be assumed that the payer of the simplified tax system is allowed to take into account the costs of raw materials and materials only after the manufactured products are sold to the consumer. This is wrong. Moreover, to account for such costs, you don’t even need to write off raw materials and supplies to production. You just need to pay for them and receive them from the supplier. In this case, consumption is taken into account according to the latest date of fulfillment of these two conditions.
✐ Example ▼
In March 2021, the organization made an advance payment to the supplier for a batch of materials. The materials on the invoice from the supplier arrived at the warehouse in April 2021, so the prepayment amount can only be taken into account in expenses when calculating the tax base for the 2nd quarter, because this is the later date of two conditions: payment for materials and their receipt.
Accounting for expenses for the acquisition of fixed assets
Fixed assets taken into account for the simplified tax system Income minus expenses include labor equipment with a useful life of more than 12 months and a cost of more than 100 thousand rubles. These are equipment, transport, buildings and structures, land plots, etc. To account for such expenses, the cost of the fixed assets must be paid, and the fixed asset itself must be put into operation.
The cost of fixed assets is taken into account in expenses during the tax period, i.e. year, in equal shares by reporting periods, on the last day of each quarter. In this case, accounting for expenses begins from the reporting period in which the last of two conditions was met: payment of the fixed asset or its commissioning.
✐ Example ▼
In January 2021, the organization acquired and put into operation two fixed assets:
- a machine worth RUB 120,000, which was paid for on March 10, 2021;
- a vehicle worth RUB 300,000, paid for in April 2021.
Both fixed assets were put into operation in the first quarter, and payments for fixed assets were made in different quarters. The costs of purchasing a machine can be taken into account starting from the 1st quarter, so we divide its cost into 4 equal shares of 30,000 rubles each. each. Expenses for the purchase of transport can be taken into account only from the 2nd quarter, in three equal shares of 100,000 rubles each.
In total, in the 1st quarter the organization can take into account only 30,000 rubles in the costs of purchasing the OS, and all subsequent quarters - 130,000 rubles each. (30,000 rubles per machine and 100,000 rubles per transport). At the end of 2021, expenses will take into account the amount of costs for both fixed assets in the amount of 420,000 rubles.
If a fixed asset is purchased in installments, then the expenses for the simplified tax system Income minus expenses can include the amounts of partial payments, even if the fixed asset is not paid in full during the tax period.
✐ Example ▼
In March 2021, a simplified organization purchased production premises worth 6 million rubles on an installment plan. In the same month, the facility was put into operation, and the first payment in the amount of 1 million rubles. was introduced in April 2021. According to the terms of the agreement, the remaining amount is 5 million rubles. must be repaid in equal installments of RUB 500,000. per month for 10 months, starting from May 2021.
Based on the results of the 2nd quarter, 2 million rubles can be taken into account in the expenses associated with the purchase of premises. (1 million rubles in April and 500 thousand rubles each in May and June). In the 3rd and 4th quarters, expenses include payments of 1.5 million rubles. in everyone. In total, when calculating the tax for 2021, 5 million rubles will be taken into account, and the remaining amount of 1 million rubles. will be taken into account next year.
5. You need to check your business partner
Unfortunately, even expenses that are correctly completed and included in the closed list for the simplified tax system Income minus expenses may not be taken into account in calculating the tax base if the tax inspectorate considers that the counterparty who provided you with the documents for the transaction is dishonest.
The taxpayer’s obligation to check his counterparty is not legislated anywhere; moreover, the Constitutional Court of the Russian Federation of October 16, 2003 N 329-O emphasizes that “... the taxpayer is not responsible for the actions of all organizations participating in the multi-stage process of paying and transferring taxes to the budget.”
Along with this Decree of the Constitutional Court, Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 53 of October 12, 2006 is in effect, paragraph 10 of which states that “A tax benefit may be recognized as unjustified if the tax authority proves that the taxpayer acted without due diligence and caution, and he should have been is aware of violations committed by the counterparty.”
Tax benefit is a reduction in the tax burden, including when expenses incurred on the simplified tax system are taken into account in the tax base. Thus, in order to increase the tax base for the simplified tax system Income minus expenses and, accordingly, the amount of tax payable, it is enough for the tax inspectorate to accuse the taxpayer of acting without due diligence and caution when choosing a counterparty.
Probably, tax officials are not embarrassed by the fact that such accusations occur against the background of the declared good faith of the participants in tax legal relations, and “... all irremovable doubts, contradictions and ambiguities of acts of legislation on taxes and fees are interpreted in favor of the taxpayer.”
What violations committed by the counterparty should the taxpayer be aware of? Among the main ones: activities without state registration, registration using lost or forged documents, non-existent TIN, lack of counterparty data in the state register (Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs), absence from their location or legal address, violation of deadlines for submitting reports and paying taxes.
The Federal Tax Service website allows you to check the registration data of the counterparty, and also offers to find out whether your business is at risk. At a minimum, the dossier on the counterparty must contain copies of state registration and tax registration certificates, constituent documents and an extract from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities or Unified State Register of Individual Entrepreneurs.
How to find out about overpayment of taxes as an individual entrepreneur
There are two ways to clarify this issue: receive a notification from the Federal Tax Service or deal with it yourself (through the taxpayer’s personal account).
- Notification from the Federal Tax Service
May take the form of a telephone call. For example, at the Federal Tax Service they found an overpayment and call you on your mobile, introducing themselves something like this: “Hello, this is the tax office.” In this case, be sure to write down which branch you are calling from and what tax was paid in excess. Pay special attention to recording the phone number or address of the branch where your overpayment was detected.
If excess tax is detected, the Federal Tax Service may require documentation, such as acts, contracts, invoices and even a cash register for double-checking. There is no point in obstructing, because these measures serve your interests, and, moreover, refusal to implement them can result in a fine of about 10,000 rubles. And the sooner you provide the data and allow the tax inspectorate to clarify everything, the sooner you can return the erroneously transferred funds.
- Taxpayer personal account
You can use your personal account on the official website of the Federal Tax Service; Among other things, it helps to find out whether overpayments exist and monitor the progress of applications for their return. If you have an EDS (electronic digital signature), you will be able to transfer your reporting and contacts with the tax office into digital format, giving up paper documents and personal visits.
Just register on the Federal Tax Service website and you will be able to track the entire progress of your tax payments in your personal account.
There is another way. You can clarify the existence of an overpayment and return it through a personal visit to the tax office and the Russian Post. If it is more convenient for you to personally ask for information and have all relationships fixed on paper, you can choose this path. Just while reading the article, replace “electronic appeals” with “visiting the tax office at the place of registration” and “letter with a list of attachments” - in general, the algorithm is common.
Reasons for overpayment
Overpayments in a taxpayer’s personal account appear for three main reasons. Moreover, the type of collection does not matter, which means that all factors are relevant for both individuals and individual entrepreneurs.
No. 1. The tax has not yet been “written off”
After the funds are accrued, the payer, as a rule, has a certain period of time to pay budget contributions. During this period, there is virtually no debt and is formed only when deadlines are violated. By transferring funds at this time, an individual or individual entrepreneur is subject to a so-called “overpayment”, because the payment date has not yet arrived and, therefore, the payer does not owe anything.
No. 2. The Federal Tax Service is checking documents
This applies to both individual entrepreneurs and individuals. The payer makes the payment on time, its deadline passes, but the Federal Tax Service is still checking the declaration. Legally, this may take 3–6 months, depending on the type of tax report (3-personal income tax, simplified tax system declaration, unified income tax).
No. 3. The fee is written off in full, and an excess balance is recorded on the balance sheet (“excess payment”)
There are several reasons for excessive payment of budget charges:
- Error in details. If the BCC is incorrectly indicated in the payment order or receipt, then the money is sent to pay for a completely different fee. At the same time, arrears (debt) appear on the primary tax. In this case, you can submit an application to the Federal Tax Service to clarify the amount and indicate the correct BCC, then the mutual settlements will become correct.
- Submitting an updated declaration or information about the right to benefits after payment. After recalculation, the amount payable may be reduced, leaving a surplus in the account.
- Incorrect payment to the budget. A simple situation when the payer mistakenly overestimated the amount and transferred more than required.
How to return overpayment of taxes to individual entrepreneurs: step-by-step instructions
We provide step-by-step instructions to help you, which will tell you how an individual entrepreneur can return an overpayment for the simplified tax system, UTII and in other cases.
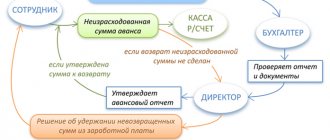
Step 1. Reconciliation with the Federal Tax Service
Determine the amount of overpaid funds. This is carried out through reconciliation of mutual settlements (and execution of the appropriate act).
The act of reconciliation with the tax service has a regulated form. To obtain such a document, the taxpayer needs to write an application and submit it to his Federal Tax Service office.
The application can be drawn up in free form; make sure that it contains the main elements:
- full designation of the Federal Tax Service body, its address;
- information about the tax payer (last name, first name and patronymic, TIN, address, contact telephone number);
- reconciliation parameters (period subject to reconciliation; type of taxation – UTII, simplified tax system, etc.);
- method of receiving the reconciliation report (by mail or in person at the tax office);
- date of writing the application.
Having submitted such an application, the entrepreneur will receive a reconciliation report within five working days. The document will be provided in 2 copies and completed by the Federal Tax Service. Enter your part of the data into it (in accordance with how payments were actually accrued and made), sign. Provide one copy to the tax office, the second remains for you.
The amount of tax overpayment can be seen in the line called “Positive Balance”.
The calculations will be reconciled, the data on them will be agreed upon, and the amount to be returned will be confirmed when the positive balance indicators from both the tax service and the entrepreneur are the same.
Base
There are several types of situations that lead to the state owing to the taxpayer, and not vice versa:
- if the tax budget received a larger amount than necessary (Article 78 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the decision on the previously collected tax is canceled in court (Article 79 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if a citizen is entitled to a tax deduction (Article 219 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if the court decided to return the previously paid state duty (Article 333.40 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- if you have the right to other tax refunds, for example, excise taxes (Article 203 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation) or VAT refund (Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Each of these cases has its own article of the Tax Code, therefore the refund procedure has its own characteristics. In general, this right is the basis of tax legislation on taxpayer rights: Art. 21 clause 5 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, which also contains an indication of the timeliness of execution of such a procedure.
Attention! Not only the taxpayer may be charged penalties for late payment of taxes, but also the tax authority itself. This can happen if there is a delay in returning overpaid amounts. The amount of the penalty is calculated as standard at the Central Bank refinancing rate.
You can dispose of overpaid tax not only by way of a refund, but also by making an offset against upcoming payments. But this also has its own peculiarities, since all taxes are divided into several levels:
- federal (personal income tax, VAT, mineral extraction tax, water tax, simplified tax system, UTII, unified agricultural tax, PSN);
- regional (for transport);
- local (for property and land).
There is a rule according to which offsets are made only between taxes of the same level. For example, if a businessman has an overpayment of the simplified tax system, then he can direct it towards the upcoming payment of other taxes at the same federal level, the same simplified tax system in the future, but he cannot pay with it for his personal property or transport.
How to return overpayment of taxes to an individual entrepreneur through a tax agent (in terms of personal income tax)
If a tax agent withholds excess personal income tax from your income, it is this agent who must return it himself (grounds: clause 14 of article 78, clause 1 of article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; clause 34 of the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated July 30, 2013 No. 57). This refers to the return of personal income tax collected incorrectly as a result of an error. For example, the accountant withheld the appropriate percentage of earnings from income that is not subject to taxation.
What should your actions be in this case? Here's an algorithm to help.
Stage 1. Submitting an application to the tax agent.
There is no regulated form, write freely. Be sure to indicate the bank account number where your funds should be transferred. The employer, by law, has the right to return overpaid taxes only by non-cash means (Clause 1, Article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Application deadlines are limited: an application can be submitted within three years from the date of transfer of the excessively collected amount to the state budget.
Please note that your ability to get your money back will not be affected by whether you are still employed by the company or have already left.
Stage 2. Receipt of erroneously withheld personal income tax (to the designated account).
The employer is obliged to return the funds no later than three months from the receipt of the application by the employer. If after the specified period the money has not been received into the account, you are additionally entitled to a certain percentage for each overdue calendar day. The size of this percentage will be determined by the current refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (basis: paragraph 3, 5, paragraph 1 of Article 231 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Accounting entries
Despite the fact that entrepreneurs have the right not to keep accounting records, no one forbids organizing them. Some consider it necessary for an effective business entity.
Let's consider 1C postings if an employee applied to the head of an individual entrepreneur, who acts as a tax agent, for a personal income tax refund in the amount of 30 thousand rubles. The employee submitted all the necessary documents, including a notification from the tax authority about the right to provide a tax deduction.
The amount will be returned from the withheld personal income tax:
Debit 70 (73) Credit 68-4 (sub-account “Personal Income Tax Payments”)
RUB 30,000 reversed
Debit 70 (73) Credit 51
300,000 rubles were transferred. employee.
Let's look at specific examples of how the amount of refund from the budget is calculated under various circumstances.
Nuances of refunding overpayments on taxes for individual entrepreneurs
1. First of all, find out which Federal Tax Service you need to contact.
This will depend on your place of registration, the region where you operate, and the type of taxation you prefer.
For the most part, taxes are paid at the place of registration of the individual entrepreneur, which is based on his registration. For example, a person is registered in the Tver region, which means that his registration as an individual entrepreneur will be attached to this region. At the same time, he can carry out activities in the Nizhny Novgorod region, but he will still fulfill tax obligations in Tverskaya.
Registration of an individual entrepreneur at the place of his official residence does not at all limit the field of his activities - it can be freely carried out within the entire Russian Federation. You will not need to change your place of registration for this.
An entrepreneur's tax obligations correspond to the rate of the region where he is registered. For example, an individual entrepreneur chose the simplified tax system and registered in Crimea, where he is registered. He runs his business in Moscow. The tax rate in Crimea is 3%, and in Moscow 6%. Tax payments are subject to a rate of 3%. If they are carried out at the place of business (6%), the individual entrepreneur pays them in error and in excess.
However, some entrepreneurs are entitled to tax binding to another region. When are there exceptions?
- Patent applies. In this case, the individual entrepreneur is subordinated to the tax inspectorate at the place where the patent was acquired. In addition, there cannot be an overpayment here, because tax obligations in this option are fixed and are included in the initial cost. At the same time, all other taxes continue to be paid in accordance with the region of residence of the individual entrepreneur.
- UTII is applied. Here you will need to register only with the tax office whose jurisdiction is indicated first in your application to conduct business. However, you will need to submit reports to different inspectorates - according to the regions of the country or intra-city territories that have separate tax authorities where you conduct your business.
- The simplified tax system is applied, commercial real estate has been purchased where the activity is carried out. In this situation, registration is required at the place of purchase - there you will pay taxes on the real estate itself, and others - as before, at the place of your registration.
The taxation system that applies in your case can be clarified in the taxpayer’s personal account.
Important Note:
If there was an overpayment, and you registered with several inspectorates, to get the money back, contact exactly the one where the excess payment was sent.
2. Be sure to assist the Federal Tax Service in establishing the overpayment.
Reconciliation with the budget (as well as a certificate of the status of settlements) will help with this. These measures are not mandatory, but help confirm the excess tax payment and return it sooner.
Reconciliation of your calculations with the budget is information about how much money you were supposed to transfer over a certain period and how much was actually paid. For example, in 2021, tax liabilities amounted to 25,000 rubles - and you (let’s say, by mistake) sent 250,000 rubles. All this will be reflected.
It is convenient to carry out such a verification procedure from your personal account. In the “Calculations with the budget” section, select “Submit an application to initiate the procedure...”, and then follow the algorithm that will be proposed.
3. Reconciliation will take 10-15 business days.
You can request a certificate about the status of your payments to the budget. It is not related to the reconciliation process and may well be issued in parallel. This document reflects overpayments and debts as of a specific calendar date. You can also request it from your personal account: in the “Get a certificate” section, click “Get a certificate on the status of tax payments...”, then follow the instructions.
4. Preparation of the certificate takes approximately 5 working days.
Don't agree to re-apply. It may happen that an individual entrepreneur submits an application for a refund of the overpayment, then an act of reconciliation of mutual settlements with the Federal Tax Service - and at this moment he is sent to write a new application. Refuse: according to the law, one is enough.
The timing of the decision on the refund of funds will depend on whether you submitted your application immediately with a reconciliation report or initially without it, that is, in two stages.
- If both documents are submitted at once (and also if the tax office does not find it necessary to check), the decision will be made within 10 days.
- If the tax office conducts an audit, the result will take 20–25 days.
When talking about the three-year allowable period within which an overpayment can be returned, the starting point does not mean the date of discovery of the tax surplus or submission of the application, but the date of submission of the declaration.
The result of your request, as well as the status of its consideration, can be tracked through your personal account.
Let us remind you once again: the refunded funds will arrive approximately a month after a positive decision.
If this period has expired and the money has not arrived in the current account, the Federal Tax Service will pay you interest for each overdue day. The percentage will depend on the current refinancing rate of the Central Bank (for example, 7.75% per annum).
Examples:
Individual entrepreneur Sidorova M. bought an apartment for 2.5 million rubles. in 2021. Is she entitled to a refund from the 2017 budget if she used the simplified tax system?
Art. 219 of the Tax Code indicates that a tax deduction is made on income taxed at a rate of 13% (personal income tax). The simplified tax system for individual entrepreneurs does not require the payment of this tax, so Sidorova M. will not be able to return the tax from the budget for this year. If a citizen were on the general taxation system, she would have the right to count on a refund. For further examples, we will keep in mind that the citizen is a personal income tax payer.
Citizen Kuznetsov A. had surgery in 2021 at a cost of 40 thousand rubles. His total income for this year was 280 thousand rubles. He will calculate the amount of refund that Kuznetsov A. has the right to receive in 2021 after presenting all the necessary documents (3-NDFL declaration, 2-NDFL certificate, certificate of payment for medical services, agreement with a medical institution, copy of the license, checks).
280000*0.13=36400 rub. – the tax transferred by the employer for Kuznetsov A.;
280000-40000=240000 rub. – tax base minus the amount of the transaction (funds spent on the operation are not subject to personal income tax);
240000*0.13=31200 rub. – personal income tax amount for 2021;
36400-31200=5200 rub. – the difference between the accrued and paid personal income tax amount, which can be returned from the budget.
Citizen Makarova S. is studying at a university on a correspondence course and works officially in the organization. For 2021, her earnings amounted to 310 thousand rubles; for the year of study she paid 130 thousand rubles. Let's calculate its return:
310000*0.13=40300 rub. – paid personal income tax;
310000-120000=190000 rub. – tax base (Makarova paid 130,000 rubles, but there is a restriction under clause 2 of Article 219 of the Tax Code: the deduction cannot exceed 120,000 per year);
190000*0.13=24700 rub. – calculated tax;
40300-24700=15600 rub. - return.
Individual entrepreneur Semenov P., located at OSNO, bought an apartment in 2021 for 2.2 million rubles. His income according to the 3-NDFL declaration amounted to 350 thousand rubles. Let's calculate how much money he can return from the budget for this year.
350000*0.13=45500 rub. – paid tax;
the maximum deduction amount is 2 million rubles (although the cost of housing is 2.2 million rubles), so you can only return 13% of this amount (260 thousand rubles). For the year, individual entrepreneur P. Semenov paid 45,500 rubles, this is the refund amount. The rest (260,000-45,500 = 214,500 rubles) can be returned in subsequent years, subject to payment of personal income tax.
How to return overpayment of taxes to an individual entrepreneur if it is closed
If you sent an excess payment before the termination of your activity, again try to return the funds through an application to the Federal Tax Service. The tax surplus will be transferred according to the details that you provide in this application. In this case, a debit card will also work.
In this case, the reconciliation should be ordered through the tax service using a separate document flow system.
How to return overpayment of taxes to an individual entrepreneur after closure? You can also use your taxpayer account. However, in case of termination of activity, the entrepreneur will still need to personally visit the Federal Tax Service to reconcile mutual settlements. Do not forget that the application must be filled out and printed in duplicate.
One of them is handed over personally to the authorized inspector, and the other serves to confirm the acceptance of the first - it must be returned with a special mark with the date. It is mandatory to have your passport with you. The inspection will prepare a reconciliation report within five days.
The document will be sent to you by mail, or you will be notified that it is ready for personal receipt. It happens that the tax reconciliation result is given on the day of application. If he confirms the absence of both debt and overpayment, everything is in order. If a debt is discovered, you can calmly pay it off; it will be registered with you as an individual outside of entrepreneurial activity.
If you find out that you overpaid, the news is also good: most likely, with simple steps you will return the funds back. Send the received reconciliation report to the Federal Tax Service along with a separate application for a refund of overpaid tax. Overpayment will be refunded.
An application of this type can be submitted within three years from the date of transfer of the excess payment. For example, the overpayment occurred in 2021, and the termination of activity in 2019. You can request a refund until 2021.
So, how to return the overpayment of taxes to an individual entrepreneur when he closes his activities? The application is fully prepared, duplicated, both copies are submitted to the tax office at your place of residence, one is immediately returned to you (with a stamp of acceptance and date). Refusal is not allowed.
The Tax Office will review your application within 10 days and provide a decision. If the overpayment is confirmed, it must be returned to you within one month. In practice, however, things may be different.
Delays in returning overpaid taxes for individual entrepreneurs
The tax office may not provide you with a decision on time for various reasons: the application was lost, it was not possible to consider it within the required period, there was a glitch in the program, etc. Not 10, but 15 days have passed - no response has been received? Submit another application with a request to issue you a decision from the Federal Tax Service (this is done through the same taxpayer account).
Do they unmotivatedly refuse to return your funds or leave you without an answer even after the second application? File a complaint with the Federal Tax Service, which manages all territorial divisions. Your personal account on the website will again help with this: find the “Contact the tax authority” section, where you click “Write a request” and follow the instructions.
If this measure does not bring results, you should contact the Arbitration Court. This can be done no later than three years from the date the overpayment was established.
How much can I get back?
The entire tax surplus must be returned by law. However, if you have a parallel debt, the tax office can pay it off with overpayments and, accordingly, deduct this amount from the refund.
At the same time, keep in mind that both issues can be resolved with such a convenient offset only with taxes of the same type. For example, in 2019 you overpaid income tax, but for 2021 you still owe the same - the tax office will make a offset and send a notification about this within 5 days (track it in your personal account).
The situation is completely different if the overpayment occurred for income tax, and the debt was for property tax. Here you cannot cover one with the other. The overpayment can be returned, but the debt will remain and will be supplemented by penalties. It will have to be repaid separately.
Do you want to speed up the offset or cover the debt for one tax with the excess paid from another? Write this when you apply for a refund: just add in free form that you are asking to use the overpayment to pay off debts. If the latter exceeds the overpayment, specify what debts you are asking for it to be used to repay.
Thus, the entire excess payment may be used to cover the existing tax debt, and nothing will be transferred to you. But the size of the debt will decrease.
Recommendations
Tax overpayment can arise for various reasons. The taxpayer can dispose of it at his own discretion, return it, keep it for future payments, or offset it against another tax. To detect an overpayment, you can periodically check your calculations with the tax office, or you can simply register your personal account. The most current data from the tax base will be reflected there.
Based on the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, business entities recognized as tax payers under the simplified system (STS) are exempt from paying a number of taxes, but at the same time acquire tax obligations for personal income tax. In this article we will look at what the payer should do if there is an overpayment under the simplified tax system: how to return it, what are the features of the return for individual entrepreneurs and legal entities, and in what cases is it impossible to return the overpayment under personal income tax.
How to return overpayment of taxes to individual entrepreneurs if more than 3 years have passed
Option 1. Go to court
If the excess payment is determined after the 3-year refund period has already expired, try the following to resolve the problem:
Step 1: Prepare evidence of when the overpayment was discovered (specific date).
Step 2. Submit a motivated application to the tax office to return or offset the overpaid funds.
Step 3. File a claim with the court within three months. This period is counted:
- or from the moment when they received a refusal from the Federal Tax Service to return or offset the funds;
- or from the moment when 10 days have elapsed from your submission of the application, and no official response has been received.
If you want to get back money you overpaid due to an incorrect withholding by the IRS rather than your own error, the process is the same.
Option 2. Write off the debt amount
If the court legally refused to return the overdue tax surplus due to the expiration of the statute of limitations (or the entrepreneur simply decided not to initiate legal proceedings), the existing overpayment can be used to pay off the current income tax. An individual entrepreneur’s application is not necessary for this.
The Federal Tax Service does not have the right to write off an outdated overpayment, at least for those taxpayers who did not request this, but continue to conduct their business and submit reports on it on time (grounds: Letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated November 1, 2013 No. ND-4-8/ [ email protected] ).
What taxes are paid under the simplified tax system?
Operating business entities, whether legal entities or entrepreneurs, have the right to independently choose the applicable taxation system.
If the approved conditions for income level and the number of employees are met, organizations and individual entrepreneurs can switch to a simplified taxation system (STS), which provides for the following procedure for paying taxes:
Please note that the use of the simplified tax system does not exempt business entities from paying insurance contributions to the Social Insurance Fund and the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation.
Possible consequences for unrefunded overpayment of taxes for individual entrepreneurs
What happens if you do not file the excess tax refund? No penalties will be charged and no penalties will follow.
Most likely, your inspectorate will take this excess into account in a future period of the same tax. For example, in 2021 you overpaid transport tax; You did not submit an application to return it. In this case, the Federal Tax Service will simply reduce your transport tax for 2021 by this amount.
If you stopped using corporate transport and, accordingly, paying tax on it, and did not return the overpayment, the tax office will not take any action against it in the new period. Here you have three years from the date of payment of the excess to return it or take it into account in another form of tax. If you don't do this, the money will simply disappear.
Is that exactly what happened? Then it is better to write off the outdated overpayment under the guise of a “bad debt.” This is the name of the amount that cannot be returned for objective reasons, such as the bankruptcy of the debtor company or the expiration of the permissible statute of limitations.
In accounting, a written-off debt is treated as an expense that is covered by income, resulting in the convergence of debits and credits. As a result, the amount of income subject to taxes decreases. The Federal Tax Service perceives debt write-off as a reduction in tax payments, so it carefully checks (sometimes more than once) cases of loss write-off.
The order of the Ministry of Finance on accounting allows you to write off a non-refundable overpayment as a bad debt, but in a real situation of this kind you may be refused. Here the actions will depend on the amount in question and whether it would be beneficial for you to have it written off. If the answer is yes, enlist the help of qualified lawyers and accountants who will bring this issue to a victorious conclusion.
How to return an overpayment of taxes to an individual entrepreneur if the tax office refuses to issue a refund
If the inspection delays its response, which is why you cannot return the funds, do not waste time - act.
First, check what payment details you provided on your application. You still have one copy, you can easily check this information for errors. If they simply did not accept your application during a personal visit, this is illegal action. Send it to the tax office anyway, for which you have two ways: a registered letter (with notification of delivery to the sender) and an online application (available only with a qualified digital signature).
If you are not given a decision, in a dialogue with a representative of the Federal Tax Service, mention the period indicated in the Tax Code of the Russian Federation within which the overpayment is supposed to be returned - 1 month from the date of receipt of the application. This period has expired and the situation has not changed? Write complaints to a higher authority. Please submit this only by letter (with acknowledgment of delivery).
The Federal Tax Service should answer you in the same way, in writing. It will not be possible to return the funds more quickly by calling by phone: these dialogues will not be recorded, you may be given false information, and you will not be able to attach the result of such an appeal to court proceedings.
All the deadlines have passed, but you don’t have a definite answer, and you also couldn’t get your money back? You will have to draw up a statement of claim and send it to the court. This document includes a requirement to pay the tax surplus with interest for late payments.
Note that such lawsuits are usually won by taxpayers. As a rule, the court takes the side of the Federal Tax Service only in cases of incorrectly completed documents that were submitted for the return of overpayments.