Estimate
| Reviews: | 0 | Views: | 4746 |
| Votes: | 0 | Updated: | n/a |
File type Text document
Document type: Statement
?
Ask a question Remember: Contract-Yurist.Ru - there are a bunch of sample documents here
Working balance (turnover sheet) for synthetic accounts +——————————————————————-+ ¦Name¦Balance at the beginning¦Turnover for the month¦ Balance at the beginning ¦ ¦ bills ¦ of the month ¦ ¦ of the next month ¦ +————+—————-+—————-+———————¦ ¦ ¦ D ¦ K ¦ D ¦ K ¦ D ¦ K ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+———+———-+———¦ ¦Cashier ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+ ———+——-+———+———-+———¦ ¦Products ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+—— —+———-+———¦ ¦Profits and ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦losses ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+—— —+———-+———¦ ¦Reserve ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦fund ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+——— +———-+———¦ ¦Settlements with ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦founders¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+——— +———-+———¦ ¦Charter ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦capital ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+———+ ———-+———¦ ¦Calculation ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦account ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+———+— ——-+———¦ ¦Loans ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦banks ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+———+—— —-+———¦ ¦Creditors ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +————+——-+———+——-+———+———-+———¦ ¦ Total ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ +———————————————————————-+
Download the document “Current balance (turnover sheet) for synthetic accounts"
Register of settlements and its details
As such, the balance sheet is one of the most common accounting registers.
The balance sheet under consideration for account 62 is a type of accounting register. It is needed for the timely reflection and accumulation of data that is in the primary accounting documents (Part 1, Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ “On Accounting”).
Let us say right away that a single form of statement for account 62, mandatory for all organizations, has not been approved by law. Therefore, each enterprise chooses and approves it itself.
At the same time, the balance sheet for account 62 as in the register must contain the following mandatory details (Part 4 of Article 10 of the Federal Law of December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ):
- Name;
- name of the organization that compiled the statement;
- the start and end date of the period for maintaining the statement or the period for which it was compiled;
- chronological or systematic grouping of accounting objects;
- the value of monetary measurement of accounting objects indicating the unit of measurement;
- names of positions of persons who are responsible for maintaining the register;
- signatures of the indicated persons, their surnames and initials.
The selected or developed form of the turnover sheet for account 62 must be approved in the accounting policy for accounting purposes. If the organization decides to use the statement form included in the accounting program, this must also be mentioned in the accounting policy.
Also see “Why is an organization’s accounting policy needed?”
The balance sheet for account 62 for a certain period usually reflects the following indicators:
- balance at the beginning of the period (Dt/Kt);
- turnover for the period (Dt/Kt);
- balance at the end of the period (Dt/Kt).
By the way, you can draw up a balance sheet for account 62 both in the context of subaccounts to account 62, and with detailed information on clients, contracts with them and payment documents.
What does a balance sheet look like (structure example)
The Soviet legacy and modern business practices have led to the emergence of 3 main types of balance sheets:
- compiled from a set of values in synthetic accounts;
- compiled according to analytical accounts;
- combined, combining the previous types of whorls.
Statements on a set of synthetic accounts compiled by different enterprises will generally be very similar to each other, since the list of relevant accounts is approved by law.
In turn, filling out SALT for analytical accounts in each organization may differ in very specific nuances. Let's consider what a typical structure of a balance sheet for analytical accounts might look like.
A typical balance sheet for an active or passive account consists of 7 columns:
- name of a specific account (sub-account);
- debit and credit balance at the beginning of the reporting period;
- turnover within the reporting period by debit and credit;
- debit and credit balance at the end of the reporting period.
Depending on which account the balance sheet reflects - active or passive, an increase in assets is recorded in the “Debit” columns and a decrease in them in the “Credit” columns (for active accounts) or, conversely, a decrease in liabilities in the “Debit” and an increase in those in the “Credit” columns (for passive accounts).
You can check whether you are preparing your accounting registers correctly using the Typical Situation from ConsultantPlus. Study the material by getting trial access to the K+ system for free.
Sample statement (download)
A sample form for the turnover sheet for account 62 could be as follows:
| Account/Counterparty/Agreement | Balance at the beginning of the period | Period transactions | balance at the end of period | |||
| Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | Debit | Credit | |
| TOTAL | ||||||
You can get free statements for account 62 from our website using the direct link here.
Also see “How to create a balance sheet for account 60: sample.”
Read also
31.08.2018
Where are the SALT fills?
You can download a sample of filling out the balance sheet on our website using the link below. Our experts have prepared for you an example of filling out a statement in Word format, reflecting transactions on account 60 (“Settlements with suppliers and contractors”).
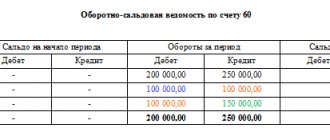
This turnover sheet reflects the following sequence of business transactions:
1. The company transferred to its counterparty an advance payment for goods under a contract in the amount of 100,000 rubles. and reflected this operation as an increase in assets in the debit of active subaccount 60.1. Posting: Dt 60.1 Kt 51 for 100,000 rubles.
2. The counterparty delivered goods to the company under a contract in the amount of 150,000 rubles, and this operation is reflected as an increase in liability in the credit of passive subaccount 60.2. Wiring: Dt 41 Kt 60.2 for RUB 150,000.
3. The company partially pays the counterparty for the goods, and we reflect this transaction as a decrease in liabilities by 100,000 rubles. in the debit of the passive subaccount 60.2 and as a decrease in assets in the credit of subaccount 60.1. Posting: Dt 60.2 Kt 60.1 for 100,000 rubles.
4. As a result, the company owes the counterparty 50,000 rubles, and we record this in the credit of the passive subaccount 60.2, in the credit of the active-passive account 60 as a whole, and also in the final line - as of the end of the reporting period.
Similar statements can be compiled for any accounting account.
Details of the statement of account 51
The bank provides the owner with a daily cash flow report, confirming each transaction with an official document. This is a payment request or order, a receipt and debit order.
From a bank statement you can find out to whom, on what basis (application, agreement) and in what amount the money was written off. What receipts were credited and the balance at the beginning and end of the operating day.
SALT for account 51 consists of the total turnover for the day, month and any necessary period. Since it is active, the balance on the report can only be debit or positive. The generation of turnover records occurs as follows:
Figure 1. Scheme of entries in OSV
All transactions reflected in the bank statement must be carefully checked.
Only then enter into the journal entry or journal order No. 2, which is intended to create entries on the balance sheet of account 51. The journal form has a tabular form. Table 1. Journal - order
| Wiring no. | Date of operation | Debit | Credit | Amount of payment | Contents of operation |
| 1 | 21.02.2018 | 51.1 | 62.2 | 65 000 | Payment received from the buyer under the contract |
| 2 | 01.03.2018 | 60.2 | 51.1 | 36 000 | The advance payment to the supplier for the goods is written off |
| 3 | 03.03.2018 | 91.2 | 51.1 | 1550 | Bank commission for conducting transactions has been written off |
The log may have a significant number of lines. At the end of each day, the records are summarized and entered into a reverse table. To see the finished report. Movements in different banks are accounted for separately. Why is detailing by subaccounts provided?
Analysis of turnover for account 51
Externally, the back looks like a table consisting of rows and columns. Movements in debit increase the balance, and movements in credit reduce it.
Figure 2. SALT for 51 accounts
In the table you can read which bank the organization works with. The balance at the beginning of the month was 322,327 rubles. During the month, 9,191,259.75 rubles were received. After paying current expenses, the organization had 779,525.84 rubles left at its disposal. It moves to a future period.
If the data is stored on paper, then for detailed analysis you need to refer to the transaction log. Select the desired payment day and amount. Automation allows you to quickly and error-free generate reports for any periods and monetary transactions.
The video will tell you more about this
Characteristic
Movement on account 51 begins immediately as soon as this account was opened at the bank. Funds entering the account will create debit turnover, and the expenditure of funds will be reflected in credit transactions.
Account 51 is active. This means that the opening and closing balances can only be debit. The results of account 51 are reflected in the asset balance sheet of the organization, since it is active.
Operations carried out on account 51 must be carried out only in ruble currency. REFERENCE! Each movement of funds through account 51 must be accompanied by supporting documentation.
Such documents include:
- Bank statements for any open account. Account 51 refers to synthetic accounts, so it is logical to open subaccounts on it. They separately reflect movements for each open account and each bank.
- Outgoing payment requests or instructions that served as the basis for carrying out debit transactions. Credit 51 accounts show not only money transfers, but also cash withdrawals. Then the basis is the counterfoil of the check.
- The debit of account 51 reflects the receipt of revenue when it was deposited by representatives of the organization. This fact is recorded in the bank order.
- Account 51 in the accounting department is debited when money arrives from buyers and other debtors. In this case, the basis is an incoming payment order from the counterparty.
Users of the turnover sheet for account 51
Accountants rarely use such a list in their work. In most cases, a turnover is required to disclose specific transactions for the required transaction. If money is received from the buyer, then the amount is reflected in the journal of settlements with customers. There, work is already underway on the generation of primary documents: invoice, delivery note or act.
To prepare a balance sheet, such a report contains all the necessary information. Turnover indicators are included in reporting for both ruble and foreign currency accounts.
The financier works with a statement and a detailed list of transactions by counterparties. In particular, when planning expenses and assessing income for the required period. Credit organizations also analyze cash flow movements if an application for lending or leasing is received.
Necessity
As already mentioned above, SALT allows you to analyze factors influencing the quantitative and qualitative changes in balance sheet items: thus, relying on this type of report and comparing the information received with other facts of economic activity, you can draw conclusions about the reasons for the change in financial results, and, after comparing all the facts, take the necessary measures.
Such a term as a balance sheet is not enshrined in the regulations of the Russian Federation, and therefore, in fact, this document is used unofficially. However, in practice it is quite widespread and is used by most accountants.
Only indirectly the application of this document is predetermined by Federal Law No. 402 “On Accounting”. As a result, this regulatory act provides that:
- Information recorded in primary documents is displayed in accounting registers, and then accumulated here.
- For government organizations, the form of the document is approved by regulations, and for private organizations - by management.
Another significant factor that predetermines the use of a balance sheet by modern organizations is Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 119n, which approves instructions regarding the accounting of inventories of Russian enterprises. Several concepts are used:
- A turnover sheet is a source that records the amounts of expenses and income, balances at the end and beginning of the reporting period, as well as the amounts in the accounts that correspond to them.
- A balance sheet, in turn, is a document that corresponds to a circulating source, but at the same time it does not reflect the consumption and receipt of products in any way.
There is another factor in favor of working with the balance sheet. Thus, the Federal Tax Service often requires this document during inspections, both for tax monitoring and for classical interaction with persons paying taxes.