Errors in VAT accounting
Error types can be divided into two parts:
- those related to the calculation of VAT directly
- technical, identified when filling out a VAT return.
To identify the former, you should use a tool such as an express accounting check. Essentially, this is the company's "internal auditor".
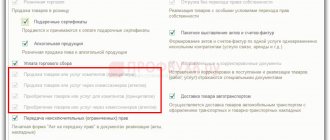
To use the tool, in the “Reports” menu in the “Accounting Analysis” section, select “Express Check”. In the window that opens, select a period, for example, the 4th quarter of 2021, and click “Show settings.”
In the settings, check the boxes “Maintain a sales ledger for value added tax” and “Maintain a purchase ledger for value added tax.” Then perform the check by pressing the button of the same name.
The program generates errors separately for the purchase book (CP) and for the sales book (KPR). By clicking on the icon next to the corresponding lines, information about the detected inaccuracies should be revealed.
The example reveals a miscalculation when analyzing the formation of advance invoices in the presence of received prepayments. Now we recommend clicking on the icon next to the line and revealing the details of the mistake made.
The result of the analysis and the cause of the error are indicated here, as well as recommendations for action. To correct this, you need to click on the hyperlink “Registration of advance invoices”.
In the window that opens, set the period, select an organization, and click “Fill.”
The table will be filled with information about unregistered documents. Click the “Run” button. A message will appear indicating that the s/f registration has been completed.
It is important to check the completeness of the personal statement; the program will show which document is missing or not posted. Such accounting errors are also possible as a result of the human factor. And as a result of incorrect data transfer, for example, from “Trade and Warehouse” to “Accounting 8.3”.
Consequently, when generating a declaration, the counterparty will have information about the document. But your company does not, which will lead to tax audits and additional assessments.
Care should be taken to identify compliance in the accounting of sales revenue with accrued tax (account 90), incl. for other income (account 91). For example, fines are not subject to VAT, however, the program mistakenly took into account fines.
Thus, using the tool in question, check how your real activity is reflected in the system.
Incorrectly formed records
Similarly, according to the CP, it is necessary to check the completeness of receipt of the tax return, the compliance of the amounts of tax taken for deduction when offsetting advances, in accounting and the VAT accounting subsystem. And also check everything related to the accounting and distribution of tax on purchases.
In our example, during an express check of LLC Trading House "Complex" for the first quarter of 2021, an error was identified in the presence of the document "Creating purchase book entries." We talked about this regulatory operation in the article about purchase and sales books.
By clicking on the icon next to the line, you can expand the details.
Do not forget that before submitting a tax return, two regulatory documents must be generated:
- generating purchase ledger entries;
- generating sales ledger entries.
In the case described above, one of the most common inaccuracies in the CP is an incorrectly formed entry.
When creating entries in the CP, the accounting employee presses the “Fill in” button while on the “Purchased Assets” tab. And he forgets to go to the “Advances Received” tab.
Accordingly, the tax on prepayments received does not fall into the CP.
To correct it, you need to go to the next tab and also click “Fill”.
In the example below, only a single entry related to tax restoration is generated according to the CPR.
A similar situation occurs, for example, when your company made an advance payment to the supplier, and according to the presented s/f, VAT was accepted for deduction. Further, when the contractor supplies goods, work or services, your organization’s accountant must restore the tax previously accepted for deduction.
Restoration is automatically carried out using the routine operation “Creating sales ledger entries”.
Accounting for tax on advances
In general, one of the common mistakes associated with this tax is the incorrect generation of invoices for advance payments. Here it is necessary to clearly understand how such operations are formalized. Upon receipt of an advance payment, an advance payment account is issued, and VAT is taken into account. Further, when goods or services are received, the document reflects the full cost, respectively, when accepting the SF for the goods or tax for accounting. To prevent this from happening, a “reverse” recording is carried out. Tax accepted for accounting from an advance payment is “returned” to the previous account.
For example, at the time the advance payment is received, entry D76.AV K68.02 is generated for the amount of VAT payable on the advance payment of RUB 15,200.
At the time of shipment, posting D62 K90.1 is generated. VAT on sales of 76,000 rubles has been assessed for payment to the Federal Tax Service. – D90.3 K68.2. And the creation of entries in the CP creates posting D68.02 K76.AV in the amount of 15,200 rubles. (restoration of VAT on advances).
In the same way, transactions are made for prepayment and receipt of goods from the supplier.
For example, at the time of payment of the advance and receipt of the SF from the counterparty, entry D68.02 K76.AV is generated for the amount of VAT deductible 22,300 rubles.
At the moment of goods receipt, posting D41 K60 is generated. VAT on sales of 101,000 rubles has been assessed for payment to the Federal Tax Service. – D19 K60. And the creation of entries in KPR will create posting D76.AV K68.02 in the amount of 22,300 rubles. (restoration of VAT on advances).
It is the creation of entries in the books of purchases and sales that allows you to correctly take into account the tax on advances.
Rebus Company
But we looked at only one side of the coin - when our company acts as a seller of its own products.
But in order to produce these products, the enterprise buys everything necessary for production (materials, equipment, etc.) and in this case itself acts as an ordinary buyer and pays VAT upon purchase, which the sellers added to the price of their goods. And this is where the “most interesting” part comes in.
Since VAT must flow into the pocket of the state from the buyer through the pocket of the seller, then when our enterprise acts as a buyer, the state returns to it the amount of VAT that it transferred to the seller.
In order not to get confused in complex calculations, the state introduced the following procedure: 1) first, each enterprise calculates the amount of VAT that it must pay to the state directly - that is, the amount from transactions in which our enterprise acted as a seller.
This part of the VAT is reflected in the liability side of the balance sheet.
Technical errors
To identify technical errors, you should use the “VAT Accounting Data Reconciliation” service. It allows you to reconcile invoices with counterparties. It will reflect discrepancies between the other party's invoice information and your organization's.
Accordingly, it will be possible to send a message to the buyer so that he makes corrections, or to correct errors in the SF from the supplier.
To do this, go through the “Administration” menu, “Organizer” section, and follow the “System account setup” hyperlink in the Mail subsection. Here in the window that opens you need to enter your email address, password and check the appropriate boxes.
Next, in the “Purchases” or “Sales” menu, select “Reconciliation of VAT accounting data” in the calculation block.
In order to receive data from the supplier, you need to click on the “Supplier Requests” hyperlink. Next, select those with whom you plan to reconcile and click the “Request registers” button.
In order for the supplier to send the register, the employee must click on the “Customer Requests” hyperlink in his program on his part. Select your organization and click the “Reply” button. Consequently, reconciliation can only be carried out with those companies that also have 1C: Accounting 8.3 installed.
In the reconciliation window, click the “Reconcile” button to create a reconciliation of SF data between your organization and suppliers.
If everything is in order, a message will be displayed that no discrepancies were found. If there are technical inaccuracies, they will be reflected in the generated report. Let's assume that discrepancies are found in this version. According to your company, there is invoice No. 500 dated 02/02/2020 for the amount of 72,000 rubles, but according to the contractor there is no such invoice. However, your company does not have it, but the contractor displays SF No. 50 dated 02/02/2020 in the amount of 72,000 rubles. Accordingly, we can conclude that the accountant made a mistake; instead of number 50, number 500 was entered.
If you do not correct this oversight, you will receive a notification from the Federal Tax Service about a data discrepancy. Therefore, this determination of the correctness of accounting must be approached with all attention and care.
By clicking on the erroneous SF, you can make corrections to your document.
account 76.AB is not closed
IAt the end of the year there were advances from buyers on account 62.2 and, accordingly, VAT on these advances on account 76.AB. Advances from customers were transferred using the document Entering initial balances of advances received from customers. Account 76.AB was transferred by operation. In January 2021, there were sales of these advances and they are included in the document immediately, but VAT is not included, i.e. account 76.AB is not closed. What was done wrong?
Get your work in order using the 1C configuration “IT Department Management 8”
ATTENTION!
If you have lost the message input window, press
Ctrl-F5
or
Ctrl-R
or the Refresh button in your browser.
Additional “manual” check
There are often situations when no errors are found during the express check. Next, you should generate “VAT reporting” through the “Reports” menu. Set a period, select an organization and see if all regulatory operations are ticked. If this is so, then the program believes that there are no errors in tax accounting. If there is no checkmark against any of the operations, then it needs to be performed.
Let's assume that all operations are completed and the express check is passed, however, manual analysis will be able to find additional distortions. Therefore, when checking VAT, we recommend that you independently reconcile the indicators for accounts 76.AB and 62.02, for example.
You need to create a balance sheet for account 19, click in the “Reports” menu, in the “Standard Reports” section, on the “Account balance sheet” hyperlink. Set the quarter, in our example this is the 1st quarter of 2021. Select account 19 and the name of the organization. In the settings, set the details for invoices received and check the “By subaccounts” checkbox.
Account 19 is value added tax on purchased assets. If account 19 reflects the balance at the end of the period, it means that your organization did not accept some part of the VAT for deduction. Consequently, there is input tax, but it is not accepted for deduction.
Compliance with accounts 76.AB and 62.02
The topic has not been updated for a long time and has been marked as archived. Adding messages is not possible.
But you can create a new thread and they will definitely answer you!
Every hour there are more than 2000
people on the Magic Forum.
1. Credit turnover on account 90.01 (in the absence of sales at a rate of 0% and transactions not subject to VAT) * 18/118. It should be equal to the debit turnover on account 90.03 in correspondence with account 68.02.
2. Credit turnover on account 91.01 in correspondence with account 62 *18/118. It should be equal to the debit turnover on account 91.02 in correspondence with account 68.02.
3. Check whether there were any gratuitous transfers or gifts.
Reasons for inaccuracies under Article 19
This may be done on purpose in order to apply deductions later, in the next reporting period, or it may simply be a miscalculation. For example, when posting a receipt, there is no invoice information. If indeed it has not yet been received, then everything is in order. There is no original, but it will appear in the future, for example, in the next quarter. In the same period, the tax will be deducted.
Sometimes it happens that you forgot to register an invoice. In this case, looking at the balance on account 19 in the context of documents, you need to open the document and see what inaccuracies it contains. If the invoice is not registered, but came from the contractor, then you need to enter the information into the system.
It happens that the operator who prepares documents from companies delivering goods or providing services does not understand the difference between the date of issue and the date of receipt. Accordingly, the SF could be issued in the reporting period, but received in the next one.
For example, the date SF is 03/28/2020, but it was received on 04/05/2020, while the operator o.
Indeed, the date of receipt may differ from the date of the invoice. This happens, for example, with a late “primary”. Let's assume that the report is generated when the s/f has already been received. Then, you need to decide whether it is worth leaving a reflection of the deduction by the date of receipt or not. If the company is not going to transfer the deduction to the next period, then this miscalculation needs to be corrected. For example, set the receipt date to 03/31/2020.
As you can see, errors occur that cannot be detected when automatically detected, so you should check the reflection of data on account 19, identify inaccuracies and correct them manually.
Account 76 av
The critical closing date for advances received is:
3.6.1. If the advance payment was received according to the “Buyer’s Order” - the date specified in the “Shipment” field;
3.6.2. If the advance payment was received without a “Buyer’s Order”, or the date is not specified in the “Shipment” field, then the date of receipt of the advance payment plus 30 days is taken.
3.7. To monitor the timeliness of closing accounts receivable from customers, the report “Register of accounts receivable and payable by customers” is used.
3.8. Accounts receivable managers are responsible for the timely use of the buyer's advance to close its receivables.
3.9. The report “Register of accounts receivable and payable by customers” with comments on overdue debts is provided by e-mail (Excel format) to the financial director weekly, on Thursdays until 14-00.
The developed register of receivables and payables of customers allows you to simultaneously group both receivables and payables of customers in the context of different divisions and legal entities of the company:
Moreover, if the advance payment is overdue, then the closing date of the advance payment is highlighted in red.
The report grouped in this way allowed us to see in one place the picture of mutual settlements for all buyer contracts. Working with this report made it easier to find information about unclosed sales documents and immediately eliminated questions about the timeliness of incoming payments for them. Since the report allows you to see information in the context of all legal entities of the company, it has become much easier to prepare documents for offset of counter obligations.
Regulations for the control of advances allowed the company's accountants to more accurately and unambiguously classify the incoming payment: now the accounting department accounts for excessively transferred funds in a separate subaccount to account 76 and does not charge VAT payable on them, which allows us not to divert funds to pay VAT or the single tax ( under the simplified tax system) according to them. And this is especially true in conditions of a shortage of free funds.
As a result of the implementation of this regulation, the measures taken to inventory accounts payable and return excessively transferred amounts previously taken into account in advances on account 62, made it possible to simultaneously reduce VAT payments to the budget by almost 70 thousand rubles.
Altai Financial Consulting Center
| IamAlexy | |
| bazvan | (0) There is an explanation about this on the closed forum |
| shuhard | (0) oxy, every time the balance sheet structure changes, you must reduce it to previous periods, otherwise it is not possible to compare rows |
| bazvan | https://partners.v8.1c.ru/forum/thread.jsp?id=1121701 like this. Thus, we comply with clause 10 of PBU 4/99: 10. For each numerical indicator of the financial statements, except for the report prepared for the first reporting period, data must be provided for at least two years - the reporting year and the one preceding the reporting one. If the data for the period preceding the reporting period are not comparable with the data for the reporting period, then the first of these data are subject to adjustment based on the rules established by regulatory acts on accounting. Each material adjustment must be disclosed in the notes to the balance sheet and income statement along with the reasons for the adjustment. |
| IamAlexy | chic and shine.. I wonder how many users who do not have access to the affiliate program corrected the balance manually by correcting, I quote, “behind this crude and buggy Adine” the balance, in particular the columns of 2011 and 2010? |
| IamAlexy | (3) thank you, good man, may your flocks be fat and your wives reward you with mighty sons... |
| Irbis | bazvan Where do the stars go? Are you drinking or what? |
| bazvan | (6):)))) |
| bazvan | (4) why have access to the affiliate program?? Finally, users should know the hardware. |
| IamAlexy | (8) waaah haaaa haaaaa made me laugh... you know.. 1C does EVERYTHING to ensure that cooks work in their programs with a work book in which “accountant” is written, what the hell is the equipment? |
| bazvan | (9) well, then in ZhPO, everything is clear and understandable |
Subconto analysis
If routine operations have been completed, an express check has been carried out, everything is in order with account 19, you can look in the “Subconto Analysis” report in the “Reports” menu.
In the window that opens, you need to set the period. Click the “Show settings” button in the “Grouping” tab. In the “Types of subconto” tab, select “Counterparties and “Agreements”. Generate a report by clicking on the button of the same name.
It is necessary to check whether there is a cross-balance for any clients, primarily for account 62. In the example presented, it can be seen that the receipt was made under the agreement “With the buyer” (account 62.01), and the payment was made under the agreement “Untitled” (account 62.02) . Accordingly, at the end of the period, the balance is reflected in both debit and credit, that is, we have both prepayment and debt under different agreements.
In such cases, the program registers invoices for advance payments and takes into account VAT on prepayments. Then the sale takes place and the tax payable is calculated again. If these are really two different agreements under which mutual settlements are carried out, then everything is in order. If this is a mistake, and judging by the name of the agreement “Untitled”, this is what it is, then adjustments need to be made.
Most likely, the wrong contract was selected when entering the document. Or, when downloading a bank statement, the program automatically entered the wrong agreement. Accordingly, mutual settlements are currently reflected incorrectly.
Having indicated the agreement “With the buyer” in the bank statement, it is clear that the cross-balance for the store has disappeared.
Next, after the changes have been made, it is necessary to re-carry out the regulatory operations for generating records of purchase and sales books, depending on what was corrected.
Balance and 76.AB
IActually there is an innovation: https://www.buh.ru/qaDescr-935
“Why did the algorithm for automatically filling out financial statements for 2012 change? The balance of account 76АВ “VAT on advances and prepayments” and 76ВА “VAT on advances and prepayments” began to be taken into account in lines 1230 (account balance 76АВ) and 1520 (account balance 76АВ), while in the explanations of section 5 to the financial statements the accounts receivable (+76АВ) and accounts payable (+76АВ) are entered taking into account these balances. In the reporting for the first quarter, half of the year, 9 months of 2012, these balances were entered on lines 1260 and 1550.
These changes were made on the basis of the Methodological Recommendations for Auditors on Reporting for 2012 dated January 9, 2013 (see https://www.minfin.ru/common/img/uploaded/library/2013/01/Rekomendatsii_auditorskim_organizatsiyam_za_2012_god.doc).”
ok, let's say.