Home — Articles
When goods are returned to the supplier, contract prices or delivery conditions are changed, and when discounts are provided, suppliers often issue “negative” (“minus”) invoices, on the basis of which the buyer reduces the amount of tax deductions, and the seller reduces the amount of calculated tax.
And this is not surprising, because for companies that have a large number of counterparties, the rules prescribed by law for making changes to invoices are sometimes difficult to apply. Taxpayers are required to adjust the amounts for each contract and supply for the relevant tax period, submit updated tax returns to the tax authorities and pay (submit for deduction) additional amounts of tax, and sometimes penalties. Moreover, you need to be sure that the counterparty has also adjusted its tax obligations according to the same rules. Isn't it easier to issue a “negative” invoice ?
Why do you need an invoice?
The document, which is drawn up on a standardized form that includes information required by the state, is needed by both sellers and buyers. When a trade transaction is carried out, confirmation is needed that the goods were actually shipped, services were provided, and work was done. An invoice is just such documentary evidence.
VAT and invoice
When paying for the transaction, the seller is charged value added tax. It is the document that we consider (invoice), as confirmation of VAT payment, that is registered by the buyer in a special book. Based on this document, he fills in the corresponding indicators in the VAT return. According to the law, the buyer has the right to a tax deduction under this taxation article (Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation), if everything is completed correctly and accurately.
There are situations when VAT is not charged, for example, for entrepreneurs working under the simplified tax system. But often the buyer, despite this circumstance, asks for an invoice, even without VAT. This is not the seller’s responsibility, but sometimes it is still worth meeting the buyer’s request and issuing an invoice, just indicate in the document that it is without value added tax, without filling out the corresponding line of the form.
IMPORTANT! If you are not a VAT payer, you should not indicate a 0% rate on your invoice instead. Even zero percent shows the real rate to which you are not entitled in this case. Specifying a rate that does not correspond to reality can create many problems for the recipient of the document, starting with a fine and ending with the accrual of the standard 18% rate.
Invoice under the simplified tax system (invoice with VAT and without VAT) in 2021
If an accountant decides to meet the buyer halfway and issue a document with zero VAT, the tax authorities have the right to charge it, not at a zero rate, but at a rate of 18%. This will happen because VAT is indicated in the invoice, and it is impossible to confirm that the company’s rate is zero.
- Line 1 – date of the document from the seller;
- On lines 2, 2a and 2b – data on the seller (name, address, tax identification number and checkpoint);
- On line 5 - details of payment documents (if any) for the transfer of funds by the commission agent to the seller, and by the committent to the commission agent;
- The tabular part must contain information on the quantity of products, their cost, the amount of VAT, as well as other indicators issued by the seller in the invoice.
Invoices: standard, corrected, adjustment: understanding the definitions
We have long been accustomed to invoices and do not experience any particular difficulties in preparing them. However, recently, along with the concept of “invoice”, such terms as “adjustment invoice” and “corrected invoice” have increasingly begun to be heard.
The appearance of these varieties is not accidental. In practice, any taxpayer may encounter a situation where an adjustment must be made to the invoice originally issued for the shipment of goods. At the same time, information about shipment must reliably reflect all the necessary parameters (information about the buyer and seller, natural and price indicators).
The type of invoice used (corrected or adjustment) depends on the type of information being adjusted, and the possibility of obtaining a reasonable tax deduction depends on its correct choice.
It would seem that similar concepts are adjustment and correction. In both cases, for a person in everyday life, they indicate the process of clarifying primary information - but not in a situation with an invoice.
For example, the seller made an arithmetic error in the invoice or the buyer identified a misgrading when accepting the goods - in these cases, you need to issue a corrected invoice (letters from the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 16, 2015 No. 03-07-09/13813 and 08.08.2012 No. 03 -07-15/102, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated March 12, 2012 No. ED-4-3/414). That is, the corrected document serves to correct an error made during registration.
While an adjustment invoice is drawn up when the document was initially drawn up correctly, but then changes needed to be made to it.
Negative invoices, amount differences and other innovations in VAT
In cases where an organization works on an advance payment basis, no amount differences are created, since the tax base is formed at the time of payment and the entire amount will be included in the VAT tax base. The Ministry of Finance has reported this more than once (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 05/04/2011 No. 03-03-06/2/76, dated 09/04/2008 No. 03-03-06/1/508).
Since that part of the tax that corresponds to the share of goods not subject to VAT is included in the cost of fixed assets and is subsequently depreciated, the legislator decided to change the accounting of input VAT when purchasing fixed assets in the first and second months of the VAT tax period for the convenience of recognizing the expenses of those taxpayers who pay corporate income tax monthly.
Purpose of a correction invoice
An adjustment invoice is issued by the seller when there is a change in the cost of goods shipped by him (work performed, services rendered, transferred property rights), if such clarification is associated with an increase or decrease in the price or quantity (volume) of products already sold (clause 1 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation ). The document indicates the old and new value of goods (work, services, property rights) and the amount of change in this value. If the cost of 2 or more delivery lots has changed, then in this case you can issue either an adjustment invoice separately for each original document, or a single adjustment invoice. If such a change is repeated, a new adjustment invoice is issued, into which data from the previous adjustment document is transferred to compare the cost (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 09/05/2012 No. 03-07-09/127, dated 12/01/2011 No. 03-07-09/ 45, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated December 10, 2012 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ).
However, it should be remembered that before issuing an adjustment invoice, the seller must notify the buyer of a change in the cost of goods shipped (work performed, services rendered, property rights transferred) and obtain his consent to such a change.
KSF form
If an error is found in the preparation of the primary shipping documentation, then it is necessary to issue a corrected invoice.
If the invoice is issued next month
Tax legislation does not provide for liability for violation of deadlines for issuing invoices. However, due to a violation of the deadline for issuing an invoice by the seller of goods (works, services), problems may arise for the taxpayer claiming to deduct VAT amounts on the basis of such an invoice.
Let us recall that a primary accounting document is a supporting document with which an organization formalizes each completed business transaction (Part 1, Article 9 of Federal Law No. 402-FZ of December 6, 2021 “On Accounting” (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 402-FZ). Primary the accounting document must be drawn up when a fact of economic life is committed, and if this is not possible, immediately after its completion (Part 3 of Article 9 of Law No. 402-FZ).
Design rules
Five days are allotted for the preparation and delivery of an adjustment invoice to the buyer from the date of the decision to make changes and its documentation. The CSF must be drawn up in two copies.
If prices or quantities change for several items of the primary document, then information for each item must be indicated separately.
The Tax Code allows you to issue one adjustment invoice for several shipping invoices issued to one buyer (clause 13, clause 5.2, article 169). In this case, information about identical goods (works, services), the shipment of which was documented in several documents at different times, can be indicated in total. This is possible if the shipment was made at the same price and the following has changed:
- delivery quantity;
- the price is the same amount compared to shipping.
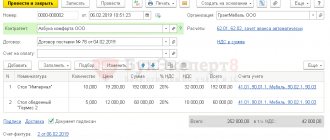
An example of compiling a CSF
On March 26, LLC "Company" shipped goods to JSC "Buyer". On May 25, it was agreed to change the price for “Colored Pencil” from 10 to 9 rubles. Also, when recalculating the delivered goods, it was discovered that “Ballpoint pen” was supplied in the amount of 202 pieces, that is, 2 more than indicated in the shipping documents. 05/28/2018 LLC "Company" exhibits KSF.
In line 1 we indicate the date and number of the CSF, and in line 1b - the details of the document being adjusted.
Lines 2–4 contain the details of the parties to the transaction, as well as the currency of the document.
In the tabular section we indicate changes for each position separately.
At the end of the form, do not forget to sign the responsible persons.
An invoice for payment
An invoice for payment is drawn up in two copies , one of which is sent to the service consumer or buyer, the second remains with the organization that issued it. You can fill out the invoice either on a regular A4 sheet or on the organization’s letterhead. The second option is more convenient, since you do not need to enter information about the company each time.
So, an invoice for payment is not a mandatory document , just like an accountable document. It cannot in any way influence the movement of financial funds, it can be suspended or not paid at any time - such phenomena occur quite often and do not have any legal consequences. However, this document is equally important for the parties to the transaction, as it allows them to enter into a kind of preliminary agreement on the transfer of funds.
What documents are the basis for drawing up the CSF?
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation refers to the existence of a contract, agreement, or other primary document confirming the consent (fact of notification) of the buyer to change the cost of shipped goods (work performed, services rendered), transferred property rights.
Changes in the requirements and obligations of the seller and buyer as a fact of economic life are subject to registration with a primary accounting document. Currently, a single unified form of document that is used to document this fact of economic life has not been established.
The seller and the buyer can formalize a change in the amount of claims and obligations in any independently determined form, provided that it contains all the mandatory details established by Part 2 of Art. 9 of Law No. 402-FZ.
Example:
The seller issues an invoice based on the delivery note and sends them to the buyer. When accepting the goods, the buyer identifies the shortage, draws up an acceptance certificate and a claim, puts the appropriate mark in the seller’s delivery note, transfers them to the seller, and the seller, based on these documents, issues an adjustment invoice to reduce the quantity and cost of the goods. The documents listed above serve as a document confirming the fact of the buyer’s consent to reduce the cost.
In letter dated December 29, 2012 No. 03-07-09/168, the Ministry of Finance of Russia explains that confirmation of the date of receipt of a document can be an envelope with the stamp of the post office through which it was received.
How critical is it in this situation to comply with the established clause 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation for a period of 5 days from the date of drawing up the act?
For the buyer, an adjustment invoice in such a situation is not so important, since we are talking about reducing the quantity of goods. In order not to restore VAT later, he can deduct VAT on the original invoice, only not in full, but within the limits of the goods actually accepted for registration. In order for the seller not to delay the deduction and reduce the amount of VAT calculated on shipped goods, it is better to still issue the CSF within the period established by law.
However, missing the deadline is not a critical mistake, and the taxpayer-seller will have a chance to defend his right to deduct VAT
. The Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation has repeatedly explained that violation of the deadline established by clause 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation is not a basis for refusing to deduct VAT; tax authorities are obliged to be guided by this position (see letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated January 25, 2016 N 03-07-11/2722, letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia for Moscow dated March 29, 2016 N16- 15/031787). There are positive examples in judicial practice, Resolution of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Volga Region dated April 15, 2014 N A65-11811/2013.)
The taxpayer retains the right to deduct on an adjustment invoice no later than three years from the date of drawing up the adjustment invoice (clause 13 of article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, clause 10 of article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
It does not matter in what period the shipment occurred
, the period for deduction is counted from the date of compilation of the CSF (letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated 08/15/2012 N 03-07-09/116, Federal Tax Service dated 06/17/2015 N ГД-4-3/ [email protected] ).
But if we were talking about an increase in price or cost, then for the seller a delay in drawing up the CSF could result in trouble.
Example:
The fact of the price increase for the shipped goods was agreed upon in the 1st quarter, and the CSF was issued in the 2nd quarter.
An adjustment invoice drawn up by the seller upon an increase in the cost of goods (work, services, property rights) shipped (performed, rendered, transferred) in the expired tax period is subject to registration in the sales book for the tax period in which the documents that are the basis for issuing adjustment invoices
in accordance with clause 10 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
We are reducing not the tax, but the tax base!
Yes, current legislation does not provide for “negative” invoices. But it doesn’t prohibit them!
Arbitration courts pay attention to this. Thus, there are court decisions in which the issuance of a “negative” invoice is recognized as lawful (Resolutions of the Federal Antimonopoly Service of the Moscow District dated September 11, 2008 N KA-A41/8495-08-P, dated June 25, 2008 N KA-A40/ 5284-08).
The judges noted that providing a discount to its customers is a separate business transaction, which, in terms of the time of its completion, does not coincide with the time of the transaction for the transfer of goods.
At the time of a business transaction (and if this is not possible, immediately after its completion), a primary accounting document must be drawn up (Clause 4, Article 9 of the Federal Law “On Accounting”, hereinafter referred to as the Law on Accounting). A unified form of the primary document for registering the provision of discounts is not provided, therefore the taxpayer has the right to develop and use it to reflect transactions in accounting.
As such documents, as a rule, invoices (credit notes) are used, which reflect the amount of the discount, as well as the amount attributable to this discount. In this case, credit notes must contain all the mandatory details provided for by the Accounting Law.
Thus, a “negative” invoice is not a document on the basis of which tax is deducted . It becomes documentary evidence of a decrease in the tax base , which leads to a change in the amount of calculated tax and does not affect tax deductions (Articles 171, 172, paragraph 1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Therefore, the tax inspectorate’s conclusion about a violation of the norms of paragraphs 5 and 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code on the illegality of issuing “negative” invoices is not substantiated.
When is the document related to the adjustment issued?
The seller undertakes to issue an adjustment form in the following situations:
- When prices for products, services or work change. For example, if the price has decreased due to a decision to provide a discount to the buyer, which was made after the invoice was issued. Or vice versa - the tariff has increased when the cost is based on regulated prices. Fluctuation is also possible in agreements containing preliminary prices with the option of further clarification.
- In the case of specifying the quantity of goods supplied upon detection of defective products, mismatches, underdeliveries or surpluses that were not discussed in the contract.
- With simultaneous changes in supply volumes and tariff schedules.
For more information about when an adjustment invoice is needed and how to issue it correctly, read this material.
Important! The legislation indicates the need for mutual agreement of the parties with the changes that have occurred (clause 3 of Article 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This must be confirmed by primary documentation - contracts and agreements.
If the counterparties to the transaction have reached a consensus on the necessary adjustments, an invoice is created strictly within 5 working days from the moment the agreement is verified (clause 10 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). You can also issue a generalized adjustment invoice for several shipments of one product at an identical price (Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The form is created in two copies - for the supplier and the buyer. They must be drawn up in accordance with Appendix No. 2 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1137 of December 26, 2011 (as amended by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 981 of August 19, 2017).
If the enterprise chose to develop its own document, it is necessary to make sure that it contains all the points specified in clause 5.2 and clause 6 of Art. 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, - otherwise, presenting the tax difference for withholding will be impossible.
The adjustment invoice is certified by the head and chief accountant of the company (or their representatives who perform similar actions on the basis of a power of attorney). An individual entrepreneur personally signs the document, indicating the details of the state registration certificate (clause 6 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
When is a correction invoice needed?
The seller of goods (works, services) must issue an adjustment invoice in the following cases:
- after shipment of goods (transfer of works, services) when clarifying the price, if the shipment of products was carried out at a preliminary price, and there was an agreement with the buyer that the final price would be determined later (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated January 31, 2013 No. 03-07-09/1894, dated January 28, 2013 No. 03-03-06/1/39);
- when returning to the seller goods that were not accepted for registration by the buyer, for example, low-quality goods or when a defect is discovered (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/10/2012 No. 03-07-11/280, dated 08/07/2012 No. 03-07-09/109, dated 02.03.2012 No. 03-07-09/17, dated 02.27.2012 No. 03-07-09/11, dated 20.02.2012 No. 03-07-09/08, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 05.07.2012 No. AS-4-3 / [email protected] );
- upon disposal of low-quality goods by the buyer, agreed with the seller, even if the goods have been capitalized (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 13, 2012 No. 03-07-09/66);
- when returning goods from a buyer who is not a value added tax payer, if the goods have already been accepted by him for registration (letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 31, 2012 No. 03-07-09/96, dated July 24, 2012 No. 03-07-09/ 89, dated 07/03/2012 No. 03-07-09/64, dated 05/16/2012 No. 03-07-09/56);
- if the buyer discovers a discrepancy between the quantity of goods received and the quantity indicated by the seller in invoices and invoices, for example, a shortage (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated May 12, 2012 No. 03-07-09/48, dated March 12, 2012 No. 03-07-09/22 , Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01.02.2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] , dated 12.03.2012 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] );
- if there is a discrepancy in the volume of services (work) accepted by the customer compared to the quantity specified by the contractor in acts and invoices when the cost of these services (work) changes as a result of clarification of the quantity (letter of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 01.02.2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ).
When an adjustment invoice is not needed
An adjustment invoice is not required when the seller provides bonuses or incentives to the buyer. Such bonuses do not affect the cost of products sold (work performed, services rendered, property rights), i.e., the tax base does not change and no adjustment is required (clause 2.1 of Article 154 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition, there are situations when it is necessary to make corrections to the original invoice rather than issue an adjustment:
- If the change in cost is associated with the correction of an arithmetic or technical error that arose due to incorrect entry of the price or quantity of goods shipped (work performed, services provided) (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated 08/23/2012 No. 03-07-09/125, dated 08/15/2012 No. 03-07-09/119, dated 08.08.2012 No. 03-07-15/102, dated 07.31.2012 No. 03-07-09/95, dated 04.16.2012 No. 03-07-09/36, dated 05.12 .2011 No. 03-07-09/46, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated 08.23.2012 No. AS-4-3/ [email protected] ). For example, it is necessary to correct an invoice if the error occurred due to incorrect data entry into programs designed for accounting and tax accounting (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 30, 2011 No. 03-07-09/44, Federal Tax Service of Russia dated February 1, 2013 No. ED-4-3/ [email protected] ). However, in practice it is very difficult to determine whether there is a technical (arithmetic) error or whether there are grounds for issuing a correction invoice.
- When the final price of a consignment of goods is determined after shipment based on quotes. In this case, corrections are also made to the “shipping” invoice, drawn up indicating the planned prices, since the calculation of the price of goods does not change (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 1, 2011 No. 03-07-09/45).
Sometimes, when the price (tariff) or quantity (volume) of goods (work, services), property rights changes, neither an adjustment nor a corrected invoice needs to be drawn up. So, if the seller knows that the price and quantity of shipped products will be updated within 5 days from the date of sale, then he just needs to wait for these changes and issue an invoice taking into account the new prices or the updated quantity. After all, according to paragraph 3 of Art. 168 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, when selling goods (work, services), transferring property rights, invoices are issued no later than 5 calendar days, counting from the day of shipment of goods (performance of work, provision of services), from the date of transfer of property rights.
In what cases does negative VAT arise? Who will reimburse it?
Value added tax (VAT) is a very unique tax.
It is wound up, roughly speaking, on gross revenue - any income from the sale of products, goods, works or services (naturally, subject to the use of a general taxation system). The longer the chain from initial materials to the finished product a product (service or work) goes through, the greater the amount of VAT will be included in its price (after all, each participant in the chain will do this at its own stage). However, manufacturers and sellers have some “bonus”. It's called a tax deduction. To put it very simply: manufacturers and sellers have the right to reduce the amount of tax they must pay by the amount of tax that was included in the price of purchased raw materials, goods, services, equipment, i.e. everything that had to be purchased, to produce your product (or resell it, which also happens).
And then nuances arise.
Firstly, the often and habitually mentioned tax rate of 18% is far from the only one. Simply the most common.
In addition, there is a rate of 10%. It is used for food products, goods for children, medical products, and printed materials. The list is quite extensive.
It’s easy to understand that if you yourself use a rate of 10%, and purchase raw materials, materials, services, the price of which includes VAT at a rate of 18%, it may well turn out that the tax you have charged is clearly less than what has already been paid to suppliers. The calculated amount is less than the deduction - that’s why negative VAT results.
There is also a 0% rate. Yeah, that’s exactly it—zero. This “exotic” is used when selling for export, including when transporting goods abroad or providing services for storing or loading such export goods, and also by those who mine and sell precious metals. For such “zero” workers, the calculated tax is naturally zero, but the deduction (tax included in the price of what was purchased from suppliers) is. Again VAT is negative.
Finally, the timing of tax assessment matters. For VAT, the “by shipment” method is used, i.e., the goods were shipped (the transfer deed was signed, the rights were transferred) and the tax was calculated. And the deduction can be claimed immediately as soon as the raw materials, supplies, fuel have been received (the service or work has been accepted). Whether they are used in production immediately in whole or in part is not important.
So if there was no production or there was, but small, or if the purchases were large (for example, for stocks for the future), or if something very expensive was purchased (say, a machine tool, loader or truck), the amount of VAT “to be deducted » will easily exceed VAT “to be charged”.
So, “negative” VAT is obtained quite naturally in the following cases:
- if there is a difference in the rates applied by those who calculate VAT and the one used by the supplier (for example, a manufacturer of canned fish - after all, its rate is 10%, and the rate of suppliers is mostly 18%);
- when using a zero VAT rate (for example, for an exporter);
- when there are significant expenses (for example, when purchasing equipment, forming inventories, or during the initial stages, when there is no production (sales) yet or they are insignificant, but costs already exist).
This VAT is called “recoverable tax”.
Who will reimburse it? Naturally, budget! In this case, the one that receives this type of tax is federal.
The decision on compensation is made by the Federal Tax Service of Russia (logically - it is this service that controls taxes), of course - in the person of its tax inspectorates. VAT refunds have their own rules, prescribed in Article 176 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (and with a bunch of reservations and details).
Where are reduction adjustment invoices recorded?
The CSF for reduction is subject to registration by both the seller and the buyer.
Seller's actions
By reducing the cost of shipped goods, the seller:
- draws up a CSF or consolidated CSF;
- transfers data from the KSF (consolidated KSF) to the purchase book (clause 13 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- takes for deduction the difference between the VAT amount on the PSF and the reduced tax amount calculated after making adjustments.
The seller has the following rules regarding CSF for reduction:
- VAT clarification for the period when the shipment occurred does not need to be submitted;
- It is possible to claim a deduction within 3 years from the date the CSF is set for reduction (clause 10 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Buyer actions
The buyer upon receipt from the seller of CSF for reduction:
- registers it in the sales book;
- restores the portion of VAT previously accepted for deduction.
He will not have to submit an updated declaration and pay penalties.
Invoice with minus from supplier 2021
Attention! According to officials, issuing an invoice with negative values is illegal, therefore, on the basis of such a document, tax amounts cannot be reduced. Officials have issued a number of letters, which define in detail the procedure for accounting and documenting transactions for the provision of retrospective discounts by the seller for the purpose of calculating VAT (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated November 14, 2005.
They indicate: if the discount is provided by changing the price of the goods after transferring it to the buyer, then the seller: - sends the buyer a corrected invoice and invoice indicating the reduced cost of the goods and the amount of VAT; — documents the fulfillment of the conditions for granting a discount by the buyer (achievement of the required volume of purchases). Supporting documents are invoices for the release of goods, approved by the Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of Russia dated December 25, 1998, and payment and settlement documents confirming the buyer’s fulfillment of certain deadlines for payment for goods; — draws up an additional sheet of the sales book for the period in which the goods were sold.
How not to lose a deduction on an adjustment invoice for a reduction?
The CSF for reduction is a document on the basis of which a taxpayer can claim a VAT deduction. You can use the right to deduction only if the CSF does not contain significant errors.
For example, controllers may refuse a deduction if in the CSF:
- goods not specified in the PSF are listed;
- negative values are indicated (all numbers in the CSF must be positive, even when adjusting the cost of the product downward).
K+ experts explained in detail how to correct errors in an adjustment invoice. You can find out the procedure by getting free trial access to the system.
The supplier sent us an invoice with minuses
— I believe that your company does not have the right to deduct VAT. To clarify the price for the discount amount, the supplier must issue an adjustment invoice rather than include the difference in the original invoice. Even individual lines in this document cannot be reflected with a minus. Negative amounts prevent identification of the VAT amount and the cost of the goods. This means that the invoice for April was issued in violation. The basis is paragraph 2 of Article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Therefore, it is necessary to require the supplier to make corrections to the invoice for April. And receive adjustment invoices for the discount amount.
— It’s safer to ask the supplier to reissue the invoice with a minus. Otherwise, there will probably be disputes with inspectors. Officials unanimously speak out against negative invoices, even if only individual lines are recorded with a minus, and not the total amount for the document. After all, neither the code nor the rules for issuing invoices provide for any disadvantages.
Also read: Application template for leave at your own expense
How is an invoice corrected?
After approval of Resolution No. 1137, correction of the invoice represents the execution of a document identical to the previously issued one, taking into account the following points:
- In paragraph 1 - the number and date of the invoice in which the incorrect data is established;
- In paragraph 1a - the number and date of amendments (the number is sequential, for the first correction - 1, for the second - 2, and so on in order);
- In the remaining fields, data is transferred from the source document with changes made to the incorrectly specified indicators.
Before the introduction of the new procedure for changing an invoice, the document had to be corrected by carefully crossing out incorrectly reflected information. The correct indicators were written next to them, the correction was certified with a signature and date.
Is it allowed to issue - negative - invoices (art.
According to the author, the established procedure for filling out invoices does not provide for issuing a “negative” invoice. Therefore, the organization must reflect the discounts provided to customers at the end of the year by making corrections to already issued invoices.
The author argues that the issue of the legality of issuing “negative” invoices is controversial. Taking into account the position of the Russian Ministry of Finance, as well as arbitration practice, the possibility of reducing the tax base by issuing a “negative” invoice will obviously have to be proven in court. To reduce tax risks, the author recommends making changes to already issued invoices instead of issuing “negative” invoices.
Corrected invoice
A corrected invoice is drawn up in cases where errors were made in the original invoice that prevent the tax authorities from identifying the seller, buyer, name of goods (work, services, property rights), their value, as well as the tax rate and amount of tax (para. . “second” clause 2 of article 169 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
In what cases is an invoice correction required?
So in what cases is a corrected invoice issued? It is needed when it becomes necessary to correct a technical error in the source document. For example, you may need to create a corrected invoice if there is an error:
- in the date, if the original document was mistakenly issued in a different month, year;
- details of the supplier or buyer, if they are written not just with a typo, but do not correspond to them at all (incorrect TIN, address, name, etc.);
- indication of the shipper and consignee, if they do not belong to the persons who actually sent and received the goods;
- details of the document for the transfer of the advance;
- name and currency code of the document;
- indicating the name of the product (work, service);
- indicating an incorrect price or quantity of goods;
- in the rate and, as a consequence, in the amount of VAT and the final amount of the document;
- or in the absence of data required to be filled in for imported goods (country of origin and registration number of the customs declaration).
It should be noted that most taxpayers, if an error is discovered in a timely manner and has not yet been identified by the tax authorities, prefer not to make a corrected invoice, but simply replace the defective document.
Features of filling out an amended invoice
In both forms of the corrected invoice, under the main heading of the document containing its number and date, a line (or lines) is provided for entering the number and date of the correction:
- there is only one line in the invoice, and it is located directly under the heading;
- in the adjustment invoice—2: one is intended for information about the correction of the adjustment invoice itself, and the second is for indicating the details of the original invoice for which the adjustment invoice was drawn up.
There are no other features in the design of the corrected invoice. It is formatted in the same way as a regular one, only incorrect data in it is replaced with correct ones.
Features of registering an amended invoice
If the correction invoice is issued in the same quarter as the original invoice (adjustment invoice), then in the same quarter:
- The seller must register the corrected invoice in the sales book and re-register the erroneous invoice, but reflect all its numerical indicators with a minus sign.
- The buyer, if he has reflected an erroneous invoice in the purchase book, must register a corrected invoice in the purchase book and re-register the erroneous invoice, but reflect all its numerical indicators with a minus sign. If the buyer has not shown an erroneous invoice in the purchase ledger, he only records the corrective invoice.
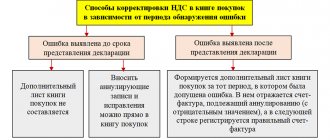
In the diagram, we showed the procedure for the seller and buyer when the data in the invoice changes or if there are errors in it.
If the corrective invoice was drawn up in another (next) quarter:
- The seller must record the corrected invoice on an additional sheet of the sales ledger for the quarter in which the erroneous invoice was recorded. In the same additional sheet of the sales book, register the erroneous invoice, indicating all its numerical indicators with a minus sign.
- The buyer must draw up an additional sheet to the purchase book for the quarter in which he registered the erroneous invoice and, in the same additional sheet to the sales book, register the erroneous invoice, indicating all its numerical indicators with a minus sign. If the buyer initially did not reflect the invoice issued with errors in the purchase book, then the corrected one must register the corrected invoice only in the purchase book of the quarter in which this document was received.
How to issue an invoice for payment in an organization? Billing Rules
In some cases, large companies require the supplier to issue them an invoice with zero VAT. Simplified companies have the right to issue zero invoices and this does not serve as a basis for filing VAT reports or transferring tax to the budget.
- name of the seller (contractor);
- its details: INN and KPP (for companies only), legal and actual address;
- supplier contact details: phone, fact and email;
- serial number and date of issue - this will make it easier to understand why exactly the money was received on the account (usually the buyer writes in the purpose section of the payment order something like the following phrase “Payment of invoice No.... dated ... 2021 for construction materials”); bank details of the supplier: name of the bank and its BIC, bank address, correspondent account and current account;
- the name of the services provided or goods shipped, their quantity, unit price and total cost.
How is one document different from another?
If incorrect information is found in the invoice, accounting staff may have doubts about whether an adjustment or correction is needed, or which document to issue. Key features that will help you make your choice are presented in Table 1.
| Adjustment invoice | Corrected invoice | |
| The main reasons for issuing the form | Changes in tariffs, prices and supply volumes (discounts, retro discounts, shortages or surpluses of goods, defects). | Arithmetically incorrect calculations, technical errors, typos in the Taxpayer Identification Number, names of goods and services, parties to the transaction, tax rate and amount. |
| Mandatory agreement between counterparties | Exhibition occurs only after the buyer’s documented written consent, which is confirmed by the relevant agreement. | There is no need for confirmation from the buyer. |
| Deadlines | No later than 5 calendar days after the conclusion of the agreement on changes. | Strict deadlines are not defined. The right to issue is retained for a period of 3 years, during which time VAT can be deducted. |
| Regulatory act regulating the registration | Appendix No. 2 to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 1137 of December 26, 2011. | Clause 7 of the Rules for filling out invoices, clause 6 of the Rules for filling out adjustment invoices. |
| Type of form | Special format for adjustment invoice. | Regular invoice form. |
| Number and date | There is no need for separate numbering - the number is assigned according to the standard sequence of serial numbers. | The number and date of the primary document are indicated. |
| Filling out the column | From the original form, the name (column 1) and units of measurement (column 2) of those goods, works or services for which there has been a change in volumes or prices are transferred to the adjustment form. Next, the changed data and the difference between the new and primary indicators are entered into the appropriate paragraphs. | A new copy is issued: in line 1 it contains the number and date of the original one, and in paragraph 1a - the serial number and the number of corrections made. The remaining fields remain unchanged. |
Read more about the features of filling out an adjustment invoice using a sample here, and find out more about the timing of issuing adjustment invoices in this material.
Thus, adjustment and corrected invoices are different concepts from the perspective of changes in VAT obligations. Knowing their differences and competent use of documents will allow the enterprise to avoid conflicts with inspection authorities by eliminating all critical inconsistencies in a timely manner.
Reasons for applying adjustments and corrections
| Adjustment invoice | Corrected invoice |
| Changes in the price of goods as agreed upon by the buyer and seller | Typos in the indication of price, cost |
| Conscious change in the quantity of goods | Incorrectly entered details of the participating parties (seller, buyer, consignor, consignee) |
| Shortage, surplus | A mistake in the date due to carelessness |
| Returning goods of inadequate quality | Incorrect reflection of item names |
| Disposal of defective goods by the buyer | Incorrect VAT rate |
| Blank mandatory lines - currency, country, customs declaration number are not indicated (if the situation requires it) | |
| Incorrectly calculated tax or item cost | |
| Incorrectly indicated number of positions, units of goods |
Submission deadlines
As required by the provisions of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the selling party has 5 calendar days to issue the designated document:
- if advance funds were received from the customer for future performance of work or provision of a service, but this service or product was not shipped or delivered. In this case, the date of payment of the advance is considered to be the date of crediting the funds to the seller’s current account;
- if the products have already been shipped, then the countdown of 5 calendar days starts from the moment of their shipment, indicated in the delivery note. When providing services, the designated period is counted from the period specified in the work completion certificate.
How to simplify the process of filling out an adjustment invoice
Modern tools allow us to quickly find the necessary information, including filling out an adjustment invoice. However, it is important to understand that no matter how you formulate the request, the computer will produce many answers that will be difficult to navigate.
Will you enter into the search engine a general phrase like “adjustment invoice sample filling” (the option is incorrect, since the word “invoice” is masculine, but common) or a more precise “adjustment invoice sample fill 2021 (or 2021)” - it is not a fact that even the files proudly called “sample adjustment invoice 2019” obtained as a result will be reliable, especially in light of the fact that the form of the document has changed several times. As a result, the process of filling out an adjustment invoice may take longer.
Attention! When making changes to an invoice, you should use the form that was in effect on the date the original document was drawn up. For example, if the initial invoice was issued in September 2021, then to correct it you should use the form that was valid before 10/01/2017.
In order not to waste extra time searching for the necessary information related to issuing an adjustment invoice, it is better to follow the following algorithm:
- Study the current text of the main regulatory document regarding adjustment invoices (Resolution No. 1137).
- Download the current adjustment invoice form (for example, on our website).
- View a sample of filling out an adjustment invoice (also available in our document database).
- Create your own adjustment invoice based on them.
This procedure when preparing an adjustment invoice will allow you to take into account the requirements of the law and use the correct form of the adjustment invoice that is relevant for the given moment when filling it out.
The invoice was issued later than 5 days from the date of sale: what are the consequences?
In particular, to close the contract, company A must provide the books and arrange delivery, that is, the transfer of books is documented by a bill of lading, and the delivery is documented by an act upon delivery, that is, more than 5 days after the bill of lading. The invoice is issued for the total amount with the date of the act.
Is this legal? Or, due to the fact that 5 days are given for issuing an invoice, the delivery note must be dated no earlier than 09/09/2021? Is it possible to accept a delivery note, document and invoice with current data or is it possible to accept some of the documents and the dates must be changed?
Reflection of corrections in the books of purchases and sales
Correction in the same quarter
Seller actions:
- An incorrect document must be entered into the sales book a second time, while the data in columns 13a to 19 is indicated with a “-” sign; this procedure cancels a previously registered invoice containing erroneous data;
- The ISF is registered in the usual way in the same quarter.
Buyer actions:
- The incorrect form is entered into the purchase book a second time, with the data in columns 15 and 16 indicated with a “-” sign, thus canceling the erroneous invoice;
- The corrected document is re-registered in the same quarter.
Correction in another quarter
Seller actions:
- An additional sheet is created that relates to the quarter in which the original invoice was prepared.
- A negative entry for the erroneous document is made on this sheet of the purchase ledger;
- The corrected form is also registered here.
Buyer actions:
- In a similar way, an additional sheet is generated for the quarter in which the original invoice was generated.
- A negative registration entry about the erroneous document is made on this sheet;
- The ISF should be registered in another quarter of the purchase book in which it was received.
What are the tax consequences of VAT for the buyer and seller when registering a CFS?
Changes have been agreed upon for previously registered goods (agreement on changes in the value of goods, fact of notification).
Changes have been agreed upon for previously registered goods (agreement on changes in the value of goods, fact of notification).
| Adjustment invoices for increasing the cost of goods | Adjustment invoices to reduce the cost of goods | |
| BUYER | KSF registers in the purchase book and has the right to deduction. The CSF deduction can be claimed no later than three years from the date of drawing up the adjustment invoice | Restores VAT accepted for deduction on goods on the earlier of the dates: receipt of the primary document to reduce the value of the goods, or receipt of the CSF (clause 4, clause 3, article 170 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). On the date of receipt, the document or KSF is registered in the sales book (clause 14 of the Rules for maintaining the sales book) |
| SALESMAN | KSF registers in the sales book in the quarter of compilation of KSF | KSF registers in the purchase book. The difference in VAT is deducted (Clause 13, Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The CSF deduction can be claimed no later than three years from the date of drawing up the adjustment invoice |
Results
After a shipment has already been made, it may be necessary to adjust the data on the quantity or price of goods sold in connection with reaching an agreement to change 1 of these indicators. In this case, an adjustment document is drawn up reflecting the original shipment data, their new value and the amount of change. Such a document is not used to correct errors made during registration.
Sources
- https://assistentus.ru/forma/schet-faktura/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/nds/schetfaktura/obrazec_zapolneniya_korrektirovochnogo_scheta-faktury/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/nds/schetfaktura/chto_takoe_korrektirovochnyj_schetfaktura_i_kogda_on_nuzhen/
- https://ppt.ru/forms/bolnichniy/korrektir-schet-factura
- https://pravovest-audit.ru/nashi-statii-nalogi-i-buhuchet/korrektirovochnyy-ili-ispravlennyy-schet-faktura-v-2018-godu-kak-ne-promahnutsya/
- https://101million.com/buhuchet/otchetnost/deklaratsii/nds/schet-faktura/korrektirovochnyj/korr-i-ispravitelnyj.html
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/nds/schetfaktura/kak_otrazit_korrektirovochnyj_schetfakturu_na_umenshenie/
- https://online-buhuchet.ru/kogda-ispolzuetsya-ispravlennyj-schet-faktura/
- https://www.klerk.ru/buh/articles/464542/
- https://nalog-nalog.ru/nds/schetfaktura/v_kakih_sluchayah_ispolzuetsya_ispravlennyj_schetfaktura/