Account 002 “Inventory assets accepted for safekeeping” is used to summarize information about the availability and movement of inventory items that are not the property of the enterprise. Responsible storage may mean the following situations:
- receipt from suppliers of goods and materials, the payment of which was refused on legal grounds;
- receipt of goods and materials, which, according to the rules of the contract, should not be spent before payment;
- receipt of goods and materials, for which the contract provides for a special option for transferring ownership, etc.
How to use
Account 002 is traditionally used to summarize information about the existence and movement of inventory items that are not directly owned by the company. Within the framework of responsible storage, we can talk about the following situations:
- receipt of certain goods and materials from suppliers, payment from them was extended or stopped on legal grounds;
- acquisition of valuables that cannot be spent before payment events within the framework of the current rules and regulations of the contract;
- receipt of goods and materials, for which the agreement specifies a special option for the transfer of ownership rights.
Since the account “works” behind the balance sheet, it reflects items that are not registered. It is active in nature and does not involve double entry rules.
When received, it is entered only as a debit, and when spent, it is entered exclusively as a credit.
Off-balance sheet account 002 - what is it intended for?
Off-balance sheet accounts in accounting are intended to reflect values that do not belong to the enterprise by right of ownership, that is, those that are in temporary use. These can be not only inventory items, but also conditional rights and obligations:
Account 002 in accounting is an active account; any receipt of inventory items is reflected as a debit of the account, and disposal (movement) as a credit. Valuables in accounting account 002 are accepted at the value indicated in the accompanying documents. If there is no value, then in a conditional or quantitative assessment.
Which inventory items are taken into account
As already mentioned, material values that were accepted but cannot be reflected on the balance sheet are subject to accounting in this area:
- damaged goods or items that are defective and do not comply with the set of requirements and characteristics specified in the supply agreement, subject to return measures;
- ownership rights to items that, on the basis of an agreement, are transferred not in the process of direct shipment, but upon payment arrangements;
- Inventory and materials that are subject to accounting on the basis of a pledge transaction agreement;
- commodity items that were paid for, but were not transported from the warehouse in accordance with technical or other details, i.e. are in storage only temporarily;
- products received on the basis of the relevant agreement;
- valuables that arrived at the warehouse by mistake.
Reflection of the transfer of NFA for safekeeping in “1C: Public Institution Accounting 8”
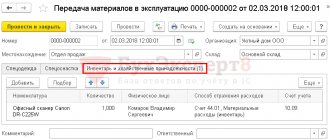
In the program “1C: Public Institution Accounting 8” this operation is reflected in the document Internal movement of fixed assets and intangible assets (see Fig. 1).
Rice. 1
In the document Internal movement of fixed assets and intangible assets, the recipient is selected from the directory Material Responsibility Centers, in which for each material responsibility center (LLC) the financially responsible person and department that are responsible for the safety of material assets (MC) are indicated.
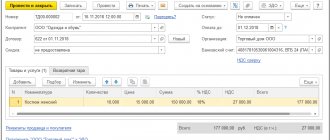
In the case of transfer of material assets (MT) for safekeeping to a third-party organization, a service element should be entered into the Material Responsibility Centers directory, in which the responsible person of the contractor is indicated as the MOL (Employee attribute), and the name of the contractor organization as the department. In the Comment line, we recommend indicating that this element is used to transfer materials to the contractor (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2
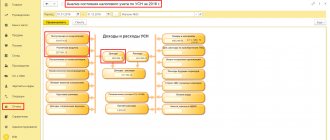
When returning the MC from safekeeping, a reverse posting is made - the document Internal movement of fixed assets and intangible assets with a change of MTs is drawn up. Only in this case, a service DMC for settlements with the custodian organization should be indicated as the sending center. As the recipient DSC, you should specify the DSC that contains the OS objects (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3
Equipment for installation is accounted for on account 0 105 04 000 “Building materials”. The transfer of materials for safekeeping is formalized by the document Internal movement of materials, which is drawn up in a similar manner. This is described in more detail in the article “Transfer of materials to the construction contractor”, posted in the ITS-budget information system, starting from the February issue.
If objects transferred for storage are accounted for as part of capital investments on account 0 106 01 000, then their transfer for safekeeping is not registered in the program, since analytical accounting is not maintained under account 0 106 00 000 “Investments in non-financial assets”, since Instruction No. 157n for this account does not provide for analytical accounting of MOL and storage locations. According to paragraph 128 of Instruction No. 157n, analytical accounting for account 0 106 00 000 “Investments in non-financial assets” is carried out in the Multigraph Card in the context of types (codes) of costs for each object of non-financial assets under construction (reconstructed, modernized), acquired (manufactured, created) .
If necessary, the list of transferred objects can be reflected in the newly introduced working off-balance sheet account.
Note! Since transactions for transfer for storage (return from storage) and the procedure for their documentation are not reflected in the accounting instructions, the procedure you have adopted for their execution and reflection in accounting should be approved by the manager (chief manager of funds), and also enshrined in the accounting policy of the institution .
Basic postings
The principle of double entry is not necessary here, therefore, in the process of compiling transactions, only the number of the account in question appears. Let's study the main transactions for 002 for debit and credit.
By debit
An approximate list of transactions that are widely used in the process of processing transactions:
- Dt 002 Kt (-). Receipt for safekeeping of valuables that were found to be defective, of poor quality, of the wrong assortment position, or other violations of contractual obligations.
- Dt 002 Kt (-). Product units have arrived at the warehouse, which imply special conditions for the transfer of ownership (not after actual shipment, but during the payment process).
- Dt 002 Kt (-). The items have been paid for, but the buyer has yet to withdraw them, so they are being held in-house.
- Dt 002 Kt (-). The receipt of inventory items occurred on the basis of a storage agreement.
- Dt 002 Kt (-). If the pledgor has not fulfilled the requirements described in the pledge agreement.
By loan
- Dt (-) Kt 002. Goods that were returned to the supplier were written off.
- Dt (-) Kt 002. Write-off for the reason that the valuables became the property of the buyer, who paid for them in good faith and removed them.
- Dt (-) Kt 002. Write-off of funds that were left by the buyer in the warehouse for the purpose of safekeeping.
- Dt (-) Kt 002. Return of commodity items to their legal owner in accordance with the norms of the drawn up storage agreement.
- Dt (-) Kt 002. Sale of positions that were received on the basis of a valid collateral agreement.
Results
Reflection of the receipt and write-off of materials using off-balance sheet accounts is carried out both to control one’s own property (low-value materials) and to reflect values received for a time and not becoming the property of the organization (raw materials supplied by customers; goods and materials accepted for safekeeping; goods taken on commission ).
You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Regulatory regulation
Operations and actions regarding goods that were transferred as inventory for temporary storage are regulated by the norms of current legislation (Orders, Resolutions, acts), as well as accounting documents:
- invoice TORG-12;
- form 1-T;
- uniform M-15;
- an act related to the occurrence of a shortage of goods;
- certificate from the accounting department;
- Bank statement;
- act of acceptance and transfer of inventory items;
- collateral agreement.
This is not the entire list of documents by which activities in this area are regulated, but it is basic.
Tell me how to spend and write off a purchased computer
here is a thread about decommissioning of equipment (so, to the heap)
if everything was purchased in parts, then it must be capitalized as materials, and then transferred to production as ordinary consumables) if not the budget, then 1C will tolerate it) and it’s certainly not worth making a fixed asset out of these spare parts
(2) krcsrgi, I don’t see the thread about writing off, maybe it’s not attached?! Everything was purchased on one invoice, that is, 1 receipt of goods and services. The total amount is 39990, including delivery of 390 rubles.
I credited the components to the accounting account at 10.6, and VAT as usual at 19.03, I’m wondering how to transfer these components to production (to which account should I put them)? And maybe there is an opportunity to somehow do without production by writing off these components?
Enterprise Accounting 8.2 edition 3.0
I support, sir. 26, services))
(7) You are equally happy - they haven’t told you anything about the case yet.
(12) -1 This is not a question of the requirements of specific individuals, but a question of legal requirements.
(14) +1 Ideally true, but. Rarely does anyone keep a count of 15 - only big ones. Small businesses, as a rule, do not use this scheme.
(0) Firstly, I recommend doing as the 1C company itself recommends: an OS costing up to 40,000 rubles. be taken into account when capitalizing on account 10.09 as materials, and not as fixed assets, and after write-off - on the off-balance sheet account MTs.04. In this case, account 08 is not used for capitalization purposes, i.e. reclassification of property - depreciable or not - occurs at the time of capitalization. Secondly, since the computer assembly needs to be done somewhere, but there is no account 08, it needs to be replaced with another account. I recommend using account 10.09 for assembly.
Then the wiring will be as follows:
Operation 1. Capitalization of components, document “Receipt of goods and for the amount of components 39,600 rubles, tab “Services” for the amount of delivery 390 rubles: Dt 10.01 - Kt 60.01
Operation 2. Assembling the computer: Dt 10.09 - Tt 10.01 I don’t immediately remember the document.
Operation 3. Write-off of the computer by amount, but the quantity continues to be accounted for on the off-balance sheet account, document “Transfer of materials for operation”, tab “Inventory and household supplies”: Dt 20/26/44 - Kt 10.09 Dt MTs.04
Accounting examples
Accounting actions are carried out directly on the account with the supplier and buyer.
Provider
It is carried out only in situations where the right of ownership is transferred to the buyer's side.
Let's look at an example. The organization ODO "Rus" shipped goods worth 50,000 rubles. The buyer side does not accept it due to insufficient quantity. Instead, it only accepts it for safekeeping and sends the corresponding act.
It turns out that the seller places these product items on account 41 in order to reflect the goods transferred for storage. Once returned, they will be entered into warehouse inventory and will remain the property of the seller. In this case, 002 will not be used.
To study the intricacies of using the account in question, it is worth considering another example.
The organization ODO "Rus" sold goods worth 100,000 rubles. On this occasion, a deed of sale was drawn up, payment was made, i.e., ownership was transferred to the buyer, but he did not remove the goods from the warehouse, although he managed to pay for it.
In this case, the seller’s accountant records the goods sold in 002. After the buyers’ purchased goods are removed, a debit will occur from this account.
Buyer
In practice, there are situations in which the buyer is not able to capitalize commodity items within the framework of accounting. For example, when a delay in payment makes itself felt, the delivered goods are of inappropriate quality, defective, or missing in quantity.
So the transaction is “frozen” until funds are deposited as payment. In this situation, as in many others, account 002 comes to the rescue.
A furniture organization sent 10 chairs to a retail facility for a total amount of 5,000 rubles, including VAT of 500 rubles. According to the provisions of the agreement, the store takes ownership of the goods after they have been paid for, and a week later it finally paid for them.
In this case, until the goods were paid for, but were in safekeeping, they were reflected in the debit of account 002. After payment, they were written off.
Thus, account 002 is widely used in modern accounting practice and allows for a large number of transactions.
Accounting for transactions on account 002 using an example
Romashka LLC shipped products worth RUB 59,000 to the buyer. The item had not been paid for on the date of shipment. According to the contract, ownership passes to the buyer upon payment.
In the buyer’s accounting, we will reflect the received goods on off-balance sheet account 002 with the following entries:
| Account Dt | Kt account | Transaction amount, rub. | Wiring Description |
| 002 | — | 50 000 | The goods are accepted for off-balance sheet accounting |
| 19 | 60 | 9 000 | VAT presented by the supplier is reflected |
| On the date of payment: | |||
| 60 | 51 | 59 000 | Payment made to supplier |
| — | 002 | 50 000 | Goods written off balance sheet |
| 41 | 60 | 50 000 | The goods are accepted for balance sheet accounting at the time of transfer of ownership |
| Dt 68/VAT | 19 | 9 000 | Accepted for deduction of VAT presented by the supplier |
Today there is a promotion - consultation of lawyers and advocates 0 - rubles.
hurry to get an answer for free→
This Personal Data Privacy Policy (hereinafter referred to as the Privacy Policy) applies to all information that the website https://online-sovetnik.ru, (hereinafter referred to as Online Advisor) located on the domain name https://online-sovetnik.ru (and also its subdomains), can obtain information about the User while using the site https://online-sovetnik.ru (as well as its subdomains), its programs and its products.1.
Definition of Terms 1.1 The following terms are used in this Privacy Policy: 1.1.1.
“Site Administration” (hereinafter referred to as the Administration) - authorized employees to manage the site https://online-sovetnik.ru, who organize and (or) carry out the processing of personal data, and also determine the purposes of processing personal data, the composition of personal data to be processed , actions (operations) performed with personal data.1.1.2. “Personal data” - any information relating to a directly or indirectly identified or identifiable individual (subject of personal data). 1.1.3.
“Processing of personal data” - any action (operation) or set of actions (operations) performed using automation tools or without the use of such means with personal data, including collection, recording, systematization, accumulation, storage, clarification (updating, changing), extraction, use, transfer (distribution, provision, access), depersonalization, blocking, deletion, destruction of personal data.1.1.4.
Off-balance sheet accounting: who needs it and what happens if done incorrectly
The annual report has been compiled and submitted, the first quarter is closed. It's time to catch up and improve those areas of accounting that remain on the to-do list.
Most chief accountants ignore or very sparingly reflect information on off-balance sheet accounts. Of course, any accounting is a labor-intensive process that requires time, effort and other resources (including money). And accounting should not turn into accounting for the sake of accounting in companies.
The main task is to control the company’s property/liabilities and provide information on them to managers. In this case, the main rule must be observed - the costs of accounting should not be greater than the benefits from it. The establishment and maintenance of off-balance sheet accounting in a company must be carried out primarily taking into account this rule.
Since the end of 2000, there have been no changes in the accounting of commercial organizations in off-balance sheet accounts. According to the standard chart of accounts, there were 11 accounts and remain so. But for colleagues working in the public sector, this section of accounting changes every year and grows before our eyes.
Today, public sector employees use accounts from 01 to 42 to maintain off-balance sheet accounting. By the way, it is in budget accounting that you can look at the methodology for some areas for your company.
For example, if the operating rules are not defined for commercial accounting and are left to the chief accountant when drawing up accounting policies.
You probably have a question: why does the chief accountant of a commercial company need this?