How are travel allowances calculated?
An employee going on a business trip must be reimbursed for all expenses associated with it, including travel, accommodation, etc.
Due to the fact that the employee is absent from the workplace to perform a work task, the employer is obliged to pay him for this work period in accordance with the average earnings. The rules for its calculation are approved by Art. 139 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation “On the specifics of the procedure for calculating the average salary” dated December 24, 2007 No. 922.
Average daily earnings are calculated as follows:
SDZ = DRP / KD,
Where:
DRP - income accrued for the billing period;
KD - the number of days worked by the employee in the pay period.
The result obtained is multiplied by the number of business trip days. This is the amount that should be paid for the employee’s work during his forced trip.
Find out in ConsultantPlus whether payment for work on weekends on a business trip is taken into account when calculating vacation pay. If you do not have access to the K+ system, get a trial online access for free.
Details are in the material “Calculating average earnings for a business trip.”
Expenses
If an employee is given leave immediately after a business trip, many enterprises do not consider it necessary to reimburse travel expenses.
Based on the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, such actions are unlawful.
Payment is due even in the event of a long delay.
Taxation
Ministry of Finance requirements:
According to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, the cost of a ticket for travel from a business trip to a permanent job is not subject to personal income tax if the employee stayed only for the weekend.
If it is returned significantly later than the date established in the order or travel certificate, income tax must be withheld.
If the cost of a ticket is recognized as employee income, insurance premiums and income tax are charged.
Amounts related to travel expenses are subject to VAT deduction. Free transfers (up to 4,000 rubles per year) formalized by a gift agreement are not subject to insurance premiums.
Example:
Manager N.I. Kulikova was on a business trip from June 14 to June 24, 2019 in Krasnoyarsk.
Upon completion of work, with the consent of management, she stayed for paid leave for:
- 2 days (weekend, June 25-26);
- 20 days (from June 25 to August 15).
Upon returning, Nadezhda Ivanovna provided an advance report. The cost of a round-trip ticket was 10,000 rubles (excluding VAT). Do I need to withhold personal income tax and in what amount?
Solution:
- Since the employee stays for a short period of time on weekends, the organization must reimburse travel costs. The amount is not subject to personal income tax, since the employee does not receive economic benefits. Kristall LLC compensates N.I. Kulikova documented travel expenses, including 10,000 rubles. for tickets.
- Since the time of absence greatly exceeds the period established in the order, compensation will be recognized as income (letters from the Ministry of Finance). Consequently, the organization withholds personal income tax. In 2021, the rate has not changed and is equal to 13%: 5000 x 13% = 650 rubles.
LLC "Crystal" pays Nadezhda Ivanovna compensation in the amount of: 5000 + (5000-650) = 9350 rubles.
Opinion of the Arbitration Court:
The authority believes that travel compensation cannot be recognized as employee income, therefore the amount is not subject to personal income tax. The reasons and duration of the delay do not matter. There is an obvious contradiction in the legislation.
Which opinion should you listen to: the Ministry of Finance or the Arbitration Court?
Practice shows that the position not to withhold personal income tax from an employee who took leave immediately after a business trip has to be defended in court.
According to experts, the letter from the Ministry of Finance is advisory in nature, so the personnel officer pays income tax.
But some organizations use a little trick:
- They agree with the employee that rest is part of the business trip. Daily allowance is paid.
- Upon return, the employee takes leave at his own expense, but actually comes to work and performs duties.
- In the future, the money is returned to the company under a legal pretext (for example, a reduction in bonuses).
How to cancel a business trip? Find out from our article.
Read about arranging a business trip at the expense of the host party.
How to properly arrange a business trip abroad? See.
The procedure for determining the amount of vacation pay
Art. 114 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation regulates the employee’s right to annual leave, during which he is guaranteed the retention of his position and payment of the average salary. The calculation of the average daily earnings in this case is in many ways similar to its calculation for business trips. The calculation period is also the last 12 months. The periods specified in paragraph 5 of Resolution No. 922 associated with payment based on average earnings and social payments are removed.
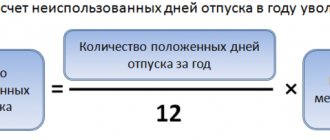
Formula for calculating average earnings per day:
SZP = DRP / 12 / 29.3,
Where:
DRP - income for the billing period;
12 - number of months;
29.3 is the average number of days in a month.
But this formula is applicable only in the absence of partially worked months. If an employee was absent from work for part of the days, the number of actual days worked is calculated separately for each partial month.
See an example of vacation calculation. Better yet, use our vacation pay calculator.
However, the question remains: are travel allowances included in the calculation of vacation pay or should they be excluded from the calculation period?
Vacation after a work trip
When an employee plans to go on a business trip followed by vacation (in the same area), he must submit a written application in advance. A signature is required.
What documents are required for registration:
- Service assignment. Issued and signed by the head of the structural unit. The second part is filled out by the employee upon return. Form No. T-10a or a template established by the organization is used.
- Application from an employee to postpone the main vacation. Based on it, you can change the date approved in the schedule. The document must indicate: the reason for postponing the vacation, the number of days for which the employee plans to stay.
- Order on granting leave. In practice, an established form or the organization's own template is used. The document contains: type and duration of rest; the period of work for which it is provided; start and end date; signature of the manager and employee. If the vacation is extended, there is no need to issue a new order; it is enough to make adjustments to the relevant sections of the document.
- Time sheet. The period during which a subordinate is on a business trip is marked with the letter code “K” or the number “06”. Based on the letter from the Ministry of Labor, the number of hours actually worked is not indicated, so the cell is left empty or “0”.
- Personal card. Contains all vacation periods used by the employee, helping to keep accurate records. It is filled out according to the unified form No. 2, but the company has the right to use its own template.
Examples and forms of these documents are presented below:
Service assignment
Employee personal card (form T-2)
Application for transfer of vacation
Leave order
Calculation of vacation pay for business trips
The calculation of vacation pay should not include periods of absence of an employee from the workplace, paid according to average earnings (clause 5 of Resolution No. 922). As we have already found out, payment for the time spent on a business trip is based on the average salary. But is a business trip the same as being away from work?
The definition of a business trip is given in Art. 166 Labor Code of the Russian Federation. This is a trip carried out by an employee by order of his manager for a certain period of time for the purpose of performing an official task outside his place of permanent work. That is, the employee leaves his workplace, albeit for official reasons. Thus, the business trip meets the criteria of paragraph 5 of Resolution No. 922 and is a period excluded from the calculation of vacation pay. The Ministry of Labor came to the same conclusion in letter dated August 13, 2015 No. 14-1/B-608. Thus, the amount of travel allowances paid to an employee during a business trip is not taken into account in calculating average earnings.
Separately, it is necessary to mention the additional payments made by the employer if the average earnings paid during a business trip do not correspond to the employee’s salary. In letter dated March 16, 2016 No. 14-1/B-226, the Ministry of Labor classifies this additional payment as part of the salary accrued for the pay period, and it must be taken into account when calculating the amount of vacation pay.
For the most common mistakes accountants make when calculating vacation pay, see ConsultantPlus. Get trial access to the system and access the material for free.
Procedure for processing documents
If a business trip during vacation is not properly documented, then the employer may have problems - the Code of Administrative Offenses provides for punishment under Article 5.27. To avoid penalties and problems with employees, you need to carry out the registration as correctly and correctly as possible, as well as accurately calculate daily allowances and vacation pay.
Employee consent
Consent on the part of the employee is mandatory; without it, further registration will simply be impossible. Accordingly, you first need to secure it, however, it does not have to be drawn up immediately in the form of a separate document.
Employer decisions
The entire procedure is usually initiated by a statement from the head of the department to his management that it is necessary to recall the employee and send him on a business trip.
At the same time, it should be clarified that this particular employee is required for certain reasons. It can be oral, but more often they prefer to put it in writing, like a memo.
Then the employee is asked to interrupt his vacation. Again, although the law does not specify that this can only be done in writing, it never hurts to document it. If there is a corresponding document, then the employee will only have to sign and indicate that he agrees, or disagrees and asks not to be disturbed until the end of his vacation.
If agreement on the issue of business travel on vacation is reached, an order is drawn up indicating:
- the reasons why the vacation was interrupted;
- the period for which it was interrupted;
- duration of the business trip (does not always coincide exactly with the previous point);
- what happens to the rest of the vacation after the work trip ends.
The order must also be signed by the employee himself. After this, a service assignment, an order to be sent on a business trip, as well as a travel certificate are drawn up. Changes are made to the vacation schedule to reflect the fact that the employee is called to work; changes are also saved in his personal card, in the “Vacation” section.
Nuances by type of vacation
Depending on what kind of vacation the employee is on, the review will have to be formatted slightly differently. Let's look at the main differences:
- Study leave - if you study at the same time as work, a certain period is allotted for passing the exam. The educational institution indicates this period in the call sent to the employer. In turn, the company cannot recall an employee while he is taking the exam, however, if the exams are passed ahead of schedule, such an opportunity arises.
- To care for a child - unlike pregnant women, it is allowed to send a woman on maternity leave on a business trip. However, before this, you should definitely familiarize her with the right to refuse a call to work in general and travel in particular. Violation of this norm will result in administrative liability. Notification of refusal can be issued either in the form of a separate document or a note in the order; it may also be reflected in the statement of the employee herself, indicating that she agrees to the work trip.
- Annual – the employee’s written consent to the business trip is also required; in addition, the issue of the remaining days of rest must be resolved.
- Without pay - most often this kind of leave is provided by the company at the request of the employee himself at the end of a business trip if he wants to stay in the place to which he was sent. Only the company management can decide whether to provide such leave, or whether the employee is needed at his workplace. He can report on the completion of tasks and expenses incurred upon arrival, if the issue is not urgent. Note that the costs of the ticket and travel in general are still taken into account in the tax summary, since they would have to be borne in any case, and the fact that the employee returns while no longer on a business trip, but on vacation, does not play a role here. But at the same time, personal income tax will also be deducted from the price of the ticket, since at the same time its purchase is considered by the tax authorities as not directly related to the business trip - such a paradox. Please note: provision of leave at one’s own expense at the employee’s request is mandatory for working disabled people, combatants and pensioners.
- Part-time - such an employee can also be sent on a trip on vacation, however, it must be taken into account that the employer at the main job will not be obliged to pay anything. Therefore, the possibility remains exclusively theoretical - after all, for a part-time worker, the exit will be categorically unprofitable or he will have to pay much more than usual.
- Vacation of military personnel - if a citizen is serving under a contract, he can also be recalled from vacation on a business trip.
Results
The issue of excluding business travel expenses from the calculation of vacation pay causes so much controversy because many consider it unfair to equate a business trip with absence from work.
However, legal norms are the main argument here, and according to the instructions of the Government and the Ministry of Labor of the Russian Federation, it is the exclusion of travel allowances from the base when calculating vacation pay that is the only correct one. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
Is it possible to take a vacation during a business trip?
The design is based on the algorithm discussed above.
To take leave at his own expense during a business trip, the employee draws up a signed application indicating the reason.
The manager evaluates:
- how respectful she is;
- is it possible to postpone until the completion of orders;
- whether the employee has the right to take additional rest.
If the decision is positive, the document is signed and an order is issued to grant leave at your own expense.
The following marks are placed on the report card:
- “K” or “06” - days the employee is on a business trip;
- “UP TO” or “16” - days of leave without pay, granted with the permission of the manager.
Since the employee does not carry out official assignments during vacation, the employer is not obliged to compensate expenses for this period.
Excess amounts paid will be withheld.
According to the Labor Code, the period of business trip is not extended and is determined by order.
Now you know how to book a vacation during and after a business trip. The employer is recommended to agree in advance with subordinates whether they plan to stay behind after completing their official duties. This makes it much easier to avoid many mistakes.
Average earnings for vacation pay, business trips, severance pay: calculation nuances
: You do not need to determine the number of working days per billing period. After all, regardless of the operating mode, calendar days are used to calculate vacation pay. For all employees, vacation pay for full months of the pay period is calculated based on the average monthly number of calendar days. And for incomplete months, it is necessary to determine the number of calendar, and not working days, falling on the non-excludable time of clause 10 of the Regulations.
: Since your employee has a summarized record of working time, you had to determine his average hourly earnings for the billing period (12 months before dismissal) clause 13 of the Regulations. After dismissal, a work schedule for the employee is not drawn up. Therefore, when calculating severance pay, it is necessary to take the standard working time in hours for this employee in accordance with the production calendar, and not according to his work schedule. That is, you had to multiply the employee’s average hourly earnings by 80 hours (the number of working hours according to the production calendar with a 40-hour work week for the period from 07/29/2014 to 08/11/2014 (10 days x 8 hours)).
ConsultantPlus: Forums
Did I miss something?
What are the new interpretations of Proposition 922? See point 10! If the days when the employee retains his average earnings are excluded from the calculation period, the denominator for the average will be determined as follows: calendar days falling on days worked (that is, calendar days - a business trip is also in calendar days) * 29.4 / number of calendar days in a month . Due to errors, this value will differ from what it would be if the employee did not go on a business trip, but not by much. Did I miss something? What are the new interpretations of Proposition 922? See point 10! If the days when the employee retains his average earnings are excluded from the calculation period, the denominator for the average will be determined as follows: calendar days falling on days worked (that is, calendar days - a business trip is also in calendar days) * 29.4 / number of calendar days in a month . Due to errors, this value will differ from what it would be if the employee did not go on a business trip, but not by much