BLITZ! K1 is a federal coefficient, updated annually. The value for 2021 is 2.005 . K2 is a regional coefficient; it needs to be clarified with local governments; it is different for each region. It depends both on your region (sometimes even on the municipal area) and on the type of activity you are engaged in.
Before finally choosing any tax regime, novice entrepreneurs, and even those who simply decided to switch from one tax scheme to another, should first thoroughly study the features of each of the taxation systems operating in Russia, since all of them have their own subtleties and nuances. UTII is no exception. For example, when calculating the single tax on imputed income, an accountant must take into account the special adjustment coefficients K1 and K2.
New coefficient value for 2017
From January 1, 2021, it is planned to increase the deflator coefficient K1, used for the purpose of calculating UTII. The source of the latest news about the increase in UTII from 2021 was officials of the Russian Ministry of Finance, who published the draft federal law “On Amendments to Chapters 262, 263 and 265 of Part Two of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.”
Article 2 of the bill provides for a gradual increase in the values of the deflator coefficient K1 starting next year:
- K1 for 2021 – 1.891;
- K1 for 2021 – 1.982;
- K1 for 2021 – 2.063.
What could be the impact of such an increase? Let me explain.
Later, officials decided that they would not increase the K1 coefficient for unified income for 2021 (Order of the Ministry of Economic Development dated November 3, 2016 No. 698). And they left its value as 1.798. Therefore, in 2021, the values of basic profitability and the amount of UTII payable will not increase. For more information about this, see “Deflator coefficients for UTII, simplified tax system, PSN and trade tax for 2017 have been approved.”
UTII: the special regime has been extended until 2021
This is probably the most pleasant news for all “imputed” people.
As it was in 2021. The fact is that Federal Law No. 97-FZ dated June 29, 2012 (Part 8, Article 5) set the date for the abolition of UTII - January 1, 2021. And many single tax payers were seriously alarmed. After all, I had a little more than a year left to work at the imputation.
However, Federal Law No. 178-FZ dated June 2, 2016 (Article 2) extended the validity of UTII until January 1, 2021.
How it happened in 2021. This year and the next three ( until the end of 2021 ), you can safely continue to work on the “imputation”.
How do coefficients affect the amount of UTII?
UTII is calculated from the amount of imputed income, taking into account two coefficients:
- Deflator coefficient K1;
- Correction factor K2.
These coefficients allow you to adjust the basic profitability taking into account the influence of various external conditions (factors) on the amount of income received (clause 4 of Article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Coefficient K1
K1 is a deflator coefficient. It is used to bring imputed income to the level of consumer prices for goods (work, services) of the past year. That is, to take into account inflation indicators for the past year (paragraph 5 of Article 346.27 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The value of K1 for the next calendar year is usually established by the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia and publishes its value in the Rossiyskaya Gazeta no later than November 20 of the previous year (clause 2 of the order of the Government of the Russian Federation dated December 25, 2002 No. 1834-r). That is, the K1 value for 2021, logically, should be published no later than November 20, 2021.
However, this approach is planned to be abandoned. As you can see, for 2017-2019 K1 is proposed to be approved by federal law. Accordingly, the Ministry of Economic Development, apparently, will not approve the deflator coefficient for 2021.
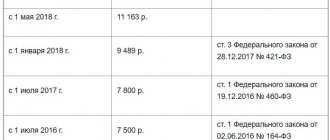
Let us recall that for 2021 the coefficient K1 was set at 1.798 (Order of the Ministry of Economic Development of Russia dated October 20, 2015 No. 772). If the commented project is accepted, the coefficient for 2017 will increase by 0.093 (1.891 - 1.798).
K2 coefficient
K2 – correction factor. With its help, factors affecting the basic profitability of various types of business activities are adjusted. For example, the range of goods, seasonality, operating hours, amount of income, features of the place of business (paragraph 6 of Article 346.27 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
K2 is established and adjusted by representative bodies of municipal districts, city districts, legislative (representative) government bodies of federal cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg (clause 3, clause 3, article 346.26, clause 6, article 346.29 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
The period during which the established K2 must be applied may not be limited in time. At the same time, local authorities may approve an adjustment factor for a particular year. That is, it is possible that local authorities may also change K2 for 2021.
Tax base: basic profitability and physical indicators
When calculating the Unified Tax on imputed income, regulators take into account the basic profitability for a particular type of activity. Basic yield is an estimated monthly income corresponding to some specific physical indicator. In turn, the unit of physical indicator can be:
- individual entrepreneurs and employees,
- shopping places,
- vehicles (cars and others),
- area of retail premises, i.e. square meters.
To make it clearer, let’s give examples: for veterinary and household services, the physical indicator will be the number of employees, for grocery chains - square meters, for transport enterprises, in turn, the number of cars involved in work, etc.
Tax base = basic profitability x physical indicators.
A separate material contains a table of the values of basic profitability and physical indicators depending on the type of business activity.
Important! It happens that during the tax period there is a change in the value of a physical indicator. In such a situation, this change must be taken into account to calculate the amount of UTII from the beginning of the month in which it occurred.
The physical indicator and basic profitability of each type of activity falling under UTII are established in the corresponding article of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
ATTENTION! It is the basic profitability that needs to be adjusted by the coefficients K1 and K2. Thanks to these coefficients, it is possible to take into account the influence of external factors on the profit received by businessmen.
By the way, since the basic income is calculated based on a monthly period, then when determining the tax base, which for UTII, as is known, is equal to a quarter, it must be increased three times (i.e. by three calendar months).
EXAMPLE OF CALCULATION
Let's compare how the tax burden of UTII payers will change with an increase in the K1 indicator. Let’s imagine that an individual entrepreneur provides shoe repair services and has 2 shoemakers working for him. The basic profitability of its activities (“household services”) per month, according to the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, will be 7,500 rubles. Let K2 be equal to 1 in a given region, and the maximum tax rate is 15%. For simplicity of calculations, we will assume that the entrepreneur does not enjoy benefits for compensation for paying insurance premiums.
Let's calculate what tax an individual entrepreneur must pay for the 1st quarter of 2018, when the K1 indicator of last year is still in effect - 1.798. First, let's calculate the tax base: (7500 × 1 × 1.798 × (2 + 2 + 2 (persons)) × 3 = 242,730 rubles. Multiply it by the tax rate: 242,730 x 15% = 36,409 rubles (with rounding, as required by the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Now let's see how this indicator changes with the growth of K1 to 1.868 - let's calculate the amount of UTII payment for the 2nd quarter. The tax base will be (7500 × 1 × 1.868 × (2 + 2 + 2 (persons)) × 3 = 252,180 rubles. We take 15% of this amount: 252,180 x 15% = 37,827 rubles.
Thus, the quarterly payment will increase by 1,418 rubles, and at the end of 2021, this individual entrepreneur will have to pay approximately 4,254 rubles more than before.
Increasing UTII from 2021: calculation example
There is a high probability that the bill of the Russian Ministry of Finance will be adopted. Let's try using examples to calculate UTII from 2021 taking into account the new coefficient and compare the indicators with 2021. So, the general formula for calculating UTII in 2021 remains the same:
Let us give examples of calculations adjusted for K1.
An example of calculating UTII in 2021
Tsvetochek LLC is engaged in retail trade through its own store with a sales area of 80 sq. m. m. In the city where trade is carried out, the use of UTII is allowed. The tax rate for retail is 15%. Alpha LLC conducted imputed activities in January, February and March. The calculation will be based on the following indicators:
- in 2021, the new value of the deflator coefficient K1 is 1.891;
- The regional authorities set the value of the correction coefficient K2 at 0.7.
- the basic profitability for retail trade in the presence of trading floors is 1800 rubles/sq.m. m.
Imputed income for February–March 2021 (that is, for the 1st quarter) will be:
571,838 rubles. = 1800 rub./sq. m × (80 sq. m + 80 sq. m + 80 sq. m) × 0.7 × 1,891.
UTII for the first quarter of 2021 with the new value of the K1 coefficient will be:
RUB 85,776 = RUB 571,838 × 15%
Comparison of calculation with 2021
Let’s assume that the bill to increase the coefficients for “imputation” is not adopted and in 2021 the K1 coefficient remains at the same level – 1.798. In this case, under the same conditions, the amount of UTII payable for the 1st quarter of 2021 will be less. In this case, the basic profitability indicator will be equal to 543,715 rubles. = 1800 rub./sq. m × (80 sq. m + 80 sq. m + 80 sq. m) × 0.7 × 1,798.
The amount of tax payable will be 81,557 rubles = 543,715 rubles. × 15%
Thus, if the new coefficient for UTII is approved, then with similar indicators, the amount of tax for the 1st quarter of 2021 will increase by 4219 rubles. (RUB 85,776 – RUB 81,557). In percentage terms, the increase in 2021 will be 5.2 percent.
Reasons for adjusting the K2 coefficient
Under some circumstances, the value of the K2 coefficient for some specific enterprises or individual entrepreneurs may be changed. In particular, this is possible if:
- the work of the enterprise or individual entrepreneur was carried out for less than the tax period (for example, only two months out of three quarterly months). Moreover, if such an adjustment is not specified in local legislative norms, this cannot serve as a basis for its cancellation;
- the company’s activities did not occur every day, for example, due to sanitary days and weekends, or according to a schedule approved within the organization;
- there was a forced suspension of activities caused by objective reasons. These include force majeure, cases of accidents and repair work, temporary disability of employees, suspension of activities by court decision, etc.
To ensure that tax officials do not suspect a desire to evade paying taxes, these facts must be supported by relevant documents.
IMPORTANT! If for some time an individual entrepreneur or an enterprise located on UTII for some reason did not have contracts and transactions, but, nevertheless, actually carried out commercial activities, then this cannot serve as a legal basis for non-payment of the Unified Tax on imputed income.
In other words, if there are no valid explanations for the lack of income, you will still have to pay this tax.
How will an increase in UTII affect individual entrepreneurs?
It is worth noting that the increase in UTII from 2021 may have a special impact on individual entrepreneurs. The fact is that individual entrepreneurs pay insurance contributions to the Pension Fund and the Federal Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund in fixed amounts (Parts 1.1 and 1.2 of Article 14 of the Federal Law of July 24, 2009 No. 212-FZ). Moreover, they pay “for themselves” contributions for themselves, regardless of whether they have employees. If the minimum wage increases from 2021, then the amount of insurance premiums for individual entrepreneurs in 2017 will also increase (See “Will the minimum wage be increased in 2021”).
However, only individual entrepreneurs without employees have the right to reduce UTII by the amount of insurance premiums “for themselves” (clause 2.1 of Article 346.32 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Individual entrepreneurs - “imputed” providers who make payments and other rewards to individuals do not have the right to reduce UTII by insurance premiums paid “for themselves” (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 17, 2015 No. 03-11-11/41339.
In this regard, some individual entrepreneurs (without employees) will be able to reduce insurance premiums for UTII in 2021, and some will not. Taking this into account, some media outlets have already provided calculations of the tax burden on various categories of individual entrepreneurs in connection with the increase in UTII and insurance premiums from 2021.
So, for example, RKB provides the following calculations.
| IP business in 2021 | Calculations |
| Retail store (SP) with an area of 50 sq. m in the regional (regional) center, without employees. | — in 2021, the individual entrepreneur will pay 39.5 thousand rubles. contributions and 251.7 thousand rubles. UTII tax; – in 2021 – 45.4 thousand rubles. contributions and 261 thousand rubles. UTII. |
| The same retail store, but with an employee whose monthly salary is 30 thousand rubles. | – in 2021 – 148.5 thousand rubles. contributions (39.5 + 109) and 182.2 thousand rubles. UTII; – in 2021 – 154.4 thousand rubles. contributions (45.4 + 109) and 153.17 thousand rubles. UTII. |
| Shop (IP) with an area of 10 sq. m (conditional pavilion), without employees. | – in 2021 will pay 24 thousand rubles. contributions and 34.2 thousand rubles. UTII tax; – in 2021 – 29 thousand rubles. contributions and 32.2 thousand rubles. UTII. |
| The same store, but with an employee whose salary is 30 thousand rubles. per month. | – in 2021 – 133 thousand rubles. contributions (24 + 109) and 29.1 thousand rubles. UTII; – in 2021 – 138 thousand rubles. contributions (29 + 109) and 30.6 thousand rubles. UTII. |
| Individual entrepreneur providing household services, without employees: | – in 2021 pays 23.2 thousand rubles. contributions and 1.1 thousand rubles. UTII tax; – in 2021 – 28 thousand rubles. contributions and 0 (zero) rub. UTII. |
| The same individual entrepreneur with one employee with a salary of 30 thousand rubles. | – in 2021 – 132.2 thousand rubles. contributions (23.2 + 109) and 24.3 thousand rubles. UTII; – in 2021 – 137 thousand rubles. contributions (28 + 109) and 25.5 thousand rubles. UTII. |
The RBC website does not provide the source data on the basis of which these calculations were made. Therefore, it is not possible to check them. However, the general trend associated with the increase in UTII and insurance premiums from 2021 can still be discerned.
Read also
29.09.2016
UTII: established a new list of household services
As you know, certain types of business activities listed in clause 2 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation are transferred to UTII. In particular, local authorities can introduce “imputation” on their territory in relation to household services (clause 1, clause 2 and clause 3 of Article 346.26 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). But the Tax Code does not specify which types of services are classified as household services. Therefore, a special list is used for these purposes.
By the way, this list is also necessary for regions that are introducing a zero tax rate on their territory for newly registered individual entrepreneurs. The so-called tax holidays. But notice! They do not apply to UTII, only to the simplified tax system and PSN.
As it was in 2021. Last year, types of household services were determined according to the All-Russian Classifier of Services to the Population OK 002-93 (OKUN).
How it happened in 2021. As of this year, OKUN OK 002-93 is no longer valid. Instead, new classifiers were put into operation, approved by order of Rosstandart dated January 31, 2014 No. 14-ST:
- All-Russian Classifier of Types of Economic Activities (OKVED2) OK 029-2014 (NACE Rev. 2);
- All-Russian classifier of products by type of economic activity (OKPD2) OK 034-2014 (KPES 2008).
But they do not include household services in a separate section.
In order for the taxpayer to know exactly whether he has the right to apply UTII for the line of business being carried out, the Government of the Russian Federation, in Order No. 2496-r dated November 24, 2016, listed all activity codes according to OKVED2 and service codes according to OKPD2, which are classified as household.
UTII: online cash registers
Let's tell you a little about the upcoming changes for retailers on UTII.
As it was in 2021. In July 2021, Federal Law No. 290-FZ dated July 3, 2016 (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 290-FZ) came into force, obliging all companies and individual entrepreneurs carrying out cash payments with the population to switch to online cash register systems. The transition date is set for July 1, 2021. If before this date it is still possible to use “old” cash registers, then after it it is necessary to use only modern technology.
For sellers on the “imputation”, Law No. 290-FZ provides for a different transition procedure.
How it will be in 2021. UTII payers currently working without cash register equipment on the basis of Federal Law No. 54-FZ of May 22, 2003 (hereinafter referred to as Law No. 54-FZ) will have to switch to online cash register equipment a year later - from July 1, 2018 ( Clause 7 and Clause 9 of Article 7 of Law No. 290-FZ). An exception is provided for “imputed” persons who:
- are engaged in the types of activities named in paragraph 2 of Article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ (for example, trading in retail markets, fairs, and exhibition complexes);
- are located in remote or hard-to-reach places, the list of which is approved by regional authorities (clause 3 of article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ);
- are pharmacy organizations located in paramedic stations in rural areas (clause 5 of article 2 of Law No. 54-FZ).
They may no longer use cash registers.
Note! From 03/31/2017, all retailers on UTII selling beer and other alcoholic products must work only with the use of cash registers, regardless of the form of sale: store or public catering (clause 10, article 16 of the Federal Law of 07/03/2016 No. 261 -FZ).
By the way, back in 2021, the Russian Ministry of Finance prepared a list of goods that cannot be sold without a cash register at fairs, exhibitions and retail markets. These include:
- carpets and carpet products;
- electrical equipment;
- furniture;
- motor vehicles, trailers and semi-trailers;
- etc.
In total, there are 17 items on the list. However, to date, his fate has not been finally determined.
This year (2017), legislators proposed allowing taxpayers on UTII to work without cash registers until 2021. Currently, the corresponding Draft Law No. 110014-7 is under consideration in the State Duma. We will also monitor the fate of this document.
This might also be useful:
- Do I need to take the zero SZV-M in 2021?
- UST in 2021
- How to make a Z-report at the cash register?
- How to reduce the simplified tax system for insurance premiums?
- Examples of calculating UTII in 2021
- Payment of 1% on income over 300,000 rubles
Is the information useful? Tell your friends and colleagues
Dear readers! The materials on the TBis.ru website are devoted to typical ways to resolve tax and legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific issue, please contact the online consultant form. It's fast and free!
When can you keep separate records?
The Tax Code (Chapter 26.3) provides for separate accounting. The reasons for this may be the following:
- conducting activities in various areas that fall under UTII;
- conducting several types of activities, when one or some of them are taxed under a different system;
- conducting activities in different regions;
- conducting activities in conditions where different adjustment factors are applied.
The procedure for separate accounting is developed by the taxpayer himself. It is recorded by a document certified by the signature of the entrepreneur.
back to menu ↑