Requirements for OS accounting registers
Registration of OS accounting registers occurs in compliance with uniform requirements for the creation of these documents. Accounting registers are consolidated forms for displaying accounting data, formed on the basis of information contained in primary documents (clause 19 of Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 29, 1998 No. 34n). As a rule, they are formed so that each of them reflects a group of homogeneous information that falls into a certain accounting account (for example, about fixed assets, about capital investments, about inventories or about calculations). The use of this document is mandatory for all persons conducting accounting in Russia (Article 2 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Accounting” dated December 6, 2011 No. 402-FZ).
The fundamental requirements for registers are contained in Art. 10 of the same law:
- The data included in them must be shown in accounting in a timely manner (clause 1) without any distortion (clause 2).
- Information in registers is reflected in the double entry method, unless the possibility of using a different method is established by law (clause 3).
- If there are details required for this document (clause 4), the forms of the applied registers are developed and approved by the person in which the accounting is maintained (clause 5), attaching them to its accounting policies. An exception is public sector organizations that are required to use the forms approved for them by Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2015 No. 52n.
- Registers can exist both on paper and in electronic form (clause 6). To transfer them at the request of other persons, the electronic document is transferred to paper (clause 7). At the same time, corrections in them that are not agreed upon with the person responsible for maintaining the registers are not allowed (clause 8).
- In its meaning, the register is equivalent to an accounting document (clause 9).
The required details for the register include:
- the name of the register and the person in which this register is used;
- the period for which the register is compiled or its start/end dates;
- principle of formation: chronological or systemic;
- quantitative accounting indicators indicating the units in which they are expressed;
- signatures of responsible persons containing their transcript and indication of position.
All these rules are directly related to OS accounting registers.
For more information about existing types of accounting registers and their application for certain accounting data, read the material “Accounting registers (forms, samples)”.
The influence of the accounting form on OS registers
The principles outlined above for the formation of accounting registers are valid for all persons engaged in accounting, but for some of them, namely for small enterprises, non-profit organizations and participants in the Skolkovo project, the possibility of maintaining records in simplified ways is acceptable (clause 4 of article 6 of the Russian Federation law dated 06.12.2011 No. 402-FZ).
Simplification of accounting can follow the following path (clause 4.1 of the information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. PZ-3/2015):
- Simplifying registers and reducing their number. Recommended forms of such registers are given in Appendices 2–11 to Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 1998 No. 64n.
- Refusal to use registers. In this case, they will be replaced by one document - a book of accounting facts of economic activity, the form of which is given in Appendix 1 to the order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 1998 No. 64n. Micro-enterprises are given the opportunity to maintain this book without using the double entry method (clause 2.1 of the information of the Ministry of Finance of Russia No. PZ-3/2015).
In terms of fixed assets, the simplified register provides for combining in one document information about each fixed asset and the depreciation related to it.
Calculation of depreciation in 1C 8.3 Accounting - step-by-step instructions
Fixed assets (FPE) are means of labor that are repeatedly used in the process of manufacturing products, the useful life of which is more than 12 months, the cost of which exceeds 40,000 rubles. (as of 2021). Let's look at step-by-step instructions on how to calculate depreciation in 1C 8.3. This instruction is also suitable for 1C 8.2, the only difference is a different program interface.
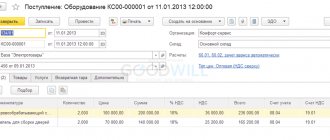
To generate depreciation charges in 1C 8.3 (Accounting), it is necessary to record the following business transactions:
OS data entering registers
Fixed assets are an accounting unit for which an incomparably greater amount of information is entered into accounting than for all other accounting units:
- method of admission;
- manufacturer data, date of issue and passport data;
- inventory number;
- the accounting group to which the product belongs;
- date of acceptance for accounting (commissioning);
- place of operation;
- financially responsible person;
- initial cost;
- depreciation group;
- depreciation calculation parameters;
- change in cost during modernization (reconstruction);
- revaluation results (ratio and resulting value);
- conservation data;
- information about movements between departments;
- information about renting or receiving;
- information on disposal indicating the residual value as of its date.
For most of this data, it may be necessary to create an appropriate accounting register. This requires broad capabilities in the formation of accounting registers related to the OS, allowing the creation of registers with an emphasis on certain parameters. To the greatest extent, these tasks are met by automated accounting, which, when entering complete information on a fixed asset and specifying it correctly, makes it possible to generate a wide variety of reports, including the required set of information for a certain period of time, thanks to the available selection function according to specified parameters.
Organization of tax accounting
The basic requirements for tax accounting of depreciable property are given in Article 323 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation. Accounting for income and expenses on depreciable property is carried out object by object. The exception is depreciation when using the non-linear method.
The tax accounting system developed in the organization must contain information:
- about the initial cost of the property;
- about the useful life;
- on the date of acquisition and commissioning;
- on depreciation of fixed assets (intangible assets) accrued for the entire period of operation of the facilities - using the straight-line method of calculating depreciation;
- about depreciation and the total balance of each depreciation group (subgroup) - with a non-linear method of calculating depreciation;
- on the residual value of depreciable property upon its disposal from the depreciation group;
- about sales (date, sales price and sales costs), etc.
A complete list of information that analytical accounting of depreciable property should provide is given in Article 323 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
The Tax Code of the Russian Federation provides for two options for maintaining tax accounting:
- use of accounting registers;
- use of tax accounting registers specially developed by the organization.
This is stated in Article 313 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
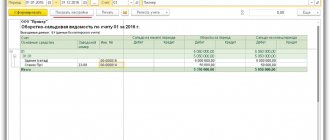
Basic OS registers
The main accounting registers of OS are:
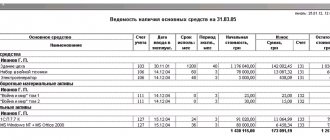
- an inventory card that contains all information about an object or group of objects;
- turnover balance sheet.
It is these 2 documents that Order No. 52n of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2015 obliges to use in public sector organizations to account for fixed assets. Also, based on the balance sheet principle, a simplified register for accounting for fixed assets and their depreciation (Form B-1) was created, given in Appendix 2 to Order No. 64n of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated December 21, 1998.
Other persons using the usual form of accounting form balance sheets relating to fixed assets in 2 accounts: 01, which provides information about the presence and movement of fixed assets themselves, indicating their accounting value, and 02, which reflects data on accrued depreciation. As an inventory card, they, having the right to independently develop such a document, most often use those forms approved by Resolution of the State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation dated January 21, 2003 No. 7:
- OS-6 - for one object;
- OS-6a - for a group of objects;
- OS-6b (inventory book) - for all objects of a division or the entire legal entity (IP).
Read more about these forms in the articles:
- “Unified form No. OS-6 - form and sample”;
- “Unified form No. OS-6a - form and sample”;
- “Unified form No. OS-6b - form and sample.”
Depreciation calculation in 1C 8.3
To perform an operation for calculating depreciation in 1C 8.2 or 8.3, you need to create a document “Routine operation”, the type of operation of which is “Depreciation and depreciation of fixed assets”.
Operations -> Period closure -> Regular operations -> Create
You can also more clearly see this regulatory operation in the form of month closure.
Operations -> Closing the period -> Closing the month
By clicking on the hyperlink “Depreciation and amortization of fixed assets”, you must select “Perform operation”:
The result of the routine operation in 1C will be the following depreciation transactions:
Now we have the opportunity to create a printed form “Help for depreciation calculation”:
Operations -> Closing the period -> Certificates and calculations
Select “Period”, our organization and click “Generate”:
Video on calculating depreciation in 1C 8.3:
Unfortunately, we are physically unable to provide free consultations to everyone, but our team will be happy to provide services for the implementation and maintenance of 1C. You can find out more about our services on the 1C Services page or just call +7 (499) 350 29 00. We work in Moscow and the region.
Other OS registers
In addition, a number of additional registers are convenient to use, making it possible to more clearly obtain any specific accounting information about the OS. For example, the 1C program provides for the formation of:
- a consolidated balance sheet, from which data for calculating property tax can be easily determined;
- analysis of the account, showing the turnover on it in relation to the corresponding accounts for the period;
- account cards, in which all transactions on the account are reflected in chronological order, indicating account correspondence;
- a report on transactions, which makes it possible to select transactions that have specified criteria;
- subconto analysis, which allows you to see in one report data related to one accounting unit, but accounted for in different accounting accounts;
- revolutions between subcontos, in which you can see the revolutions between the subcontos selected for its construction;
- subconto cards, formed similarly to an account card, but according to subconto;
- a calculation certificate showing the amount of accrued depreciation for each of the objects for the period;
- fixed asset depreciation sheet, which reflects all the components that affect the book value of each fixed asset.
Methods for calculating depreciation
Accounting has four options for calculating depreciation. You can learn more about the methods for calculating depreciation in PBU 6/01.
Depreciation should be calculated from the month following the month in which the asset was registered. Let’s say the computer was capitalized in October 2018, the accountant will begin calculating depreciation from November 1, 2018.
Depreciation calculation methods:
- Linear.
- Reducing balance method.
- A method of writing off cost based on the sum of the numbers of years of useful life.
- The method of writing off the cost is proportional to the volume of products (works).
Please note that the listed methods relate to depreciation of fixed assets in accounting. In tax accounting, there are only two ways to calculate depreciation charges - linear and non-linear.
Linear method
Most often, practicing accountants use this method. It is very simple and clear.
To find out the amount of monthly depreciation, you should find the product of the original cost of the asset and the depreciation rate.
Depreciation rate = 1/SPI (months) x 100%.
Example. Funtik LLC registered a Samsung computer. The initial cost is 49,320 rubles. SPI - 5 years (60 months).
The depreciation rate for a Samsung computer = 1/60 * 100% = 1.67.
Monthly depreciation = 49,320 x 1.67% = 823.64 rubles.
Due to rounding, the amount of depreciation in the first months will differ from the amount of depreciation in the last month (the total amount of depreciation for the entire period should not be more than the original cost).
In practice, it is customary to calculate depreciation in a simpler and more accurate way.
Monthly depreciation = 49,320: 60 = 822 rubles.
Tax reporting on time and without errors! We are giving access for 3 months to Kontur.Ektern!
Try it
Reducing balance method
To find out the required amount, you will need the residual value of the fixed assets at the beginning of the year, SPI. Companies also have the right to use an acceleration factor from 1 to 3.
Example. Funtik LLC uses OS in production, the residual value of which as of 01/01/2018 is 49,320 rubles (the same amount is the initial cost). SPI - 60 months. The coefficient is set at 1.3.
2018
49,320: 60 x 1.3 = 1068.60 rubles per month
The amount of depreciation for 2021 will be 12,823.20 rubles (1068.60 x 12).
2019
Residual value as of 01/01/2019 = 49,320 - 12,823.20 = 36,496.80 rubles.
36,496.80: 60 x 1.3 = 790.76 rubles per month.
Depreciation in subsequent years is also calculated in this way. The residual value of the operating system is always taken as a basis. Thus, every year depreciation charges decrease.
Method of writing off cost based on the sum of the numbers of years of useful life
The calculation is based on the initial cost and the sum of the number of years remaining until the end of the investment project.
Example. Funtik LLC uses OS in production, the initial cost of which is 49,320 rubles. SPI - 48 months (4 years). Depreciation is accrued from 01/01/2017.
First, let's determine depreciation rates.
2017 = 4 / (1 + 2 + 3 + 4) x 100% = 40%.
2018 = 3 / (1 + 2 + 3 + 4) x 100% = 30%.
Results
OS accounting registers are formed according to the same rules as all other accounting registers, and have 2 main forms (inventory card and balance sheet), which exist in different versions.
For more convenient work with accounting information, other reports are also used, each of which allows you to effectively solve a specific problem. You can find more complete information on the topic in ConsultantPlus. Free trial access to the system for 2 days.
conclusions
If you follow all the rules for filling out Form B-1 or sample statements developed by yourself, the enterprise will be able to see and evaluate the existing fixed assets, their total capitalization and analyze the process of depreciation (depreciation) of fixed assets, adjusting the company’s behavior towards increasing fixed assets or getting rid of surpluses, and also a correct reflection of the tax base.
Accounting statement indicators have a direct impact on the final cost of fixed assets, which, if calculated incorrectly, leads to a large number of difficulties, both in the field of tax and accounting, and can lead to direct losses for the organization.
The article describes typical situations. To solve your problem , write to our consultant or call for free:
+7 (499) 938-43-28 - Moscow - CALL
+7 - St. Petersburg - CALL
+7 — Other regions — CALL