- home
- About company
- Articles
- Advances / Settlement of advances in 1C: Accounting 8
September 17, 2019
From July 1, 2021, owners of online cash registers are required to punch checks not only for the advance payment, but also for offset of the advance payment. For a number of configurations there are already brief instructions on .
At the time of writing this instruction, there is no data regarding 1C: Accounting on the ITS website. Therefore, we will analyze the procedure on the demo base. As an example we will use:
| Platform | 8.3.15.1565 |
| Configuration | Enterprise accounting 3.0.72.66 Prof. |
| KKT model | ATOL FPrint-22PTK |
This instruction is current as of September 11, 2019.
Offsetting advances received in 1C 8.3: step-by-step instructions
Attention! The VAT rate has been changed from 01/01/2019 from 18% to 20% and from 18/118 to 20/120.
The organization entered into an agreement with the buyer LLC Architectural Workshop for the supply of office furniture in the amount of 354,000 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
On September 30, a 100% advance payment from the buyer was received into the bank account.
On October 11, office furniture was sold to the buyer:
- MIKKE desk – 15 pcs. at a price of 5,900 rubles. (including VAT 18%);
- Chair MARCUS – 15 pcs. at a price of 11,800 rubles. (including VAT 18%);
- File cabinet ERIC – 10 pcs. at a price of 8,850 rubles. (including VAT 18%).
Let's look at step-by-step instructions for creating an example. PDF
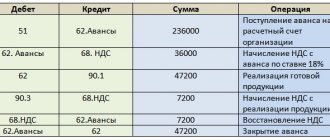
| date | Debit | Credit | Accounting amount | Amount NU | the name of the operation | Documents (reports) in 1C | |
| Dt | CT | ||||||
| Sales of goods | |||||||
| October 11 | 62.01 | 90.01.1 | 354 000 | 354 000 | 300 000 | Revenue from sales of goods | Sales (act, invoice) - Goods (invoice) |
| 90.02 | 41.01 | 245 000 | 245 000 | 245 000 | Write-off of the cost of goods | ||
| 90.03 | 68.02 | 54 000 | VAT accrual on revenue | ||||
| 62.02 | 62.01 | 354 000 | 354 000 | 354 000 | Advance offset | ||
| Issuance of SF for shipment to the buyer | |||||||
| October 11 | — | — | 354 000 | Issuing SF for shipment | Invoice issued for sales | ||
| — | — | 54 000 | Reflection of VAT in the Sales Book | Sales book report | |||
| Acceptance of VAT for deduction when offsetting the buyer's advance payment | |||||||
| 31th of December | 68.02 | 76.AB | 54 000 | Acceptance of VAT for deduction | Generating purchase ledger entries | ||
| — | — | 54 000 | Reflection of VAT deduction in the Purchase Book | Purchase Book report | |||
For the beginning of the example, see the publications:
- Issuing an invoice to the buyer and receiving an advance from him
- Calculation of VAT on advances
- Sales of goods
Crediting of advance and prepayment via online cash register
When the buyer has received what he paid for in advance, the seller issues a second check. It also uses the “calculation method attribute” attribute.
When registering an advance or prepayment at an online checkout, you should always indicate “full payment” in the “payment method indication” column. If the final payment amount differs from the preliminary payment, there will be problems with making additional payments in other ways. When issuing a check, the prepayment made is debited against the completed shipment.
Further, the check indicates that the payment was made against an advance payment (prepayment), and not in cash or non-cash.
Sales of goods
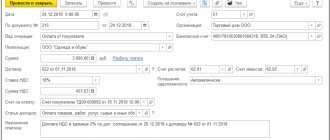
The sale of goods and the simultaneous offset of the advance received from the buyer is reflected in the document Sales (act, invoice) transaction type Goods (invoice) in the section Sales – Sales – Sales (acts, invoices) – Goods (invoice).
Please note that when offsetting advances received in 1s 8.3, when filling out the Calculations , indicate:
- Method of offset of advance payment – Automatically , it starts automatic offset of advance payment in the context of the Counterparty and the Agreement when posting a document.
See also the key points for registering the sale of goods in wholesale trade
Offsetting the buyer's advance in 1C 8.3 - postings
When posting a document, the advance previously received from the buyer is offset in the amount of the advance payment under the contract, but not more than the total amount under the document:
- Dt 62.02 Kt 62.01 – offset of the buyer’s advance in 1s 8.3.
What is the difference between an advance and a prepayment?
The difference between an advance payment and an advance payment is the ability to determine what exactly the buyer paid the seller for. This nuance affects the choice of the cash receipt attribute “payment method attribute”.
If it is possible to count the number of goods (or services) for which money was paid, then this is an advance payment. For example, a client paid in advance for 5 visits to the gym or swimming pool. Each visit is tied to a date and time and has a fixed cost. This means that an advance payment has been made.
There are situations when it is impossible to clearly determine what exactly the money was received for. For example, a buyer entered into an agreement with a store to purchase kitchen furniture with built-in appliances, with delivery and assembly. According to the agreement, he paid 50% of the cost of the entire order. For what exactly is not clear. This means an advance has been made.
When issuing a check for an advance or prepayment, you must indicate the “payment method indicator”. There are several options (see Appendix No. 2 to the order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated March 21, 2017 No. MMV-7-20 / [email protected] ).
If, when paying, you can determine the list of goods, works or services, then this is an advance payment. If you make a 100% prepayment, we will indicate in the check “Full prepayment until the item of payment is transferred.” If the prepayment is partial, then we enter “Partial prepayment until the goods are transferred or the service is provided.”
If during payment it is impossible to determine the list of goods, works or services to be transferred, then an advance has been made. In the check we indicate “Partial or full prepayment of goods or services.”
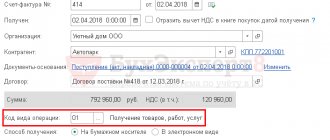
Issuing an invoice for shipment to the buyer
An invoice for shipped goods is issued using the Issue invoice , located at the bottom of the Sales document (act, invoice) .
Invoice document is automatically filled with data from the Sales document (act, invoice) .
- Operation type code – “” Sale of goods, works, services...”
Please note that the tabular section Payment documents is automatically filled in with data from the fields According to document No. from , specified in the Receipt to current account . PDF
Find out more about VAT calculation when selling goods in wholesale trade
Other questions regarding prepayment (advance payment) in a check
In what cases is it necessary to make one check for all advances?
Companies and individual entrepreneurs that accept a large number of advances may not be able to cope with the flow of cash advance receipts that they are required by law to issue. Imagine how much time it takes for the conductor to count all the advance checks at the end of the trip and issue a check for payment?
For some companies there are concessions - they can issue one general check for the advance payment for the billing period, in which all cash receipts for the advance payment can be combined. Unfortunately, the list does not include trade organizations.
It is allowed to generate one (final) check that covers the advance:
- organizers of cultural events;
- carriers of various types;
- companies providing communication services;
- organizations in the field of electronic services (from Article 174.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- management companies and utilities (housing and communal services);
- private security companies and organizations in the field of security systems;
- companies from the educational sector.
Organizations on this list have 10 days after the service is provided to generate a check for the advance payment.
What to put in the name of a product (service) if it is impossible to accurately determine the model (list of services)?
We recommend writing “advance payment” in the name of the product (service) on the cash register receipt. Similarly, indicate the attribute of the calculation method -.
In the receipt for the advance payment, write down the name of the product (service) specifically.
Buying a wardrobe in a furniture showroom. The package has been agreed upon, but at the buyer’s request, we will negotiate with the supplier for a discount on components. The price may be lower in the end. What payment indicator should be on the check - advance or prepayment?
Insure yourself against potential problems and indicate that you received an advance from the client. However, write in the contract that the client gives you money in advance and that the final cost may change.
Is it possible to cancel a knocked out advance check? The client changed his mind and took the money an hour after the check was generated. Didn't receive the goods.
You need to cancel an advance check (including an erroneous one) using a refund. It is necessary to punch the return check (a special command at the online cash register), and indicate in the payment attribute that this is a refund of the advance payment.
How to indicate the amount in a check for an advance payment if the company is paid by a foreign client (payment in dollars)?
According to 54-FZ, it is necessary to indicate the price of the goods in the receipt only in rubles, that is, at the time of payment you will have to convert dollars into rubles (the exchange rate of the Central Bank or the bank in which you hold an account).
You can indicate the cost of a product (service) in dollars only in the form of additional details (in a free field).
When receiving payment for a trip, a travel agency is required to draw up a document indicating which method of payment? Closing time of the advance check: on the day of departure or on the last day of the tourist’s vacation?
Since at the time of payment the tourist and the agent know what the trip will be like (tickets, hotel, etc.), it is necessary to issue a check for prepayment. We recommend not to select the “100% prepayment” option, but to make a regular prepayment, since before the trip the tourist’s ideas may change and the payment will increase. It is allowed to make several checks for prepayment (regular).
A general, single check with all prepayments offset should be issued on the last day of the tourist’s vacation.
Link to full version:
https://www.business.ru/article/2497-chek-na-avans-zachet-i-vozvrat-avansa-nyuansy-i-pravila
Acceptance of VAT for deduction when offsetting the buyer's advance payment
Regulatory regulation
The organization has the right to deduct VAT from advances received from customers as of the date:
- shipment of goods (work, services) to the buyer (clause 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
- refund of the advance due to changes in conditions or termination of the contract (clause 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
Tax authorities believe that if an advance payment under a terminated contract was offset against payments under another contract with the same customer, then VAT deduction cannot be used at this moment (clause 5 of Article 171 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation).
At the same time, VAT calculated and paid by the seller from the amount of this advance payment can be deducted upon actual shipment under another agreement (Letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated July 18, 2016 N 03-07-11/41972, dated October 14, 2015 N 03-07-11/58845).
VAT is deducted in the amount of tax calculated from the cost of shipped goods (work, services), for which an advance payment was previously received (clause 6 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). This means that if you have charged VAT on advances at a rate of 18/118%, and goods are shipped at a rate of 10%, then only that part of the VAT that is calculated at a rate of 10/110% can be taken into account (Letter of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation dated November 28. 2014 N 03-07-11/60891).
In the 1C program, VAT is automatically deducted in the amount in which VAT was calculated on advances. The offset mechanism provided for by the current edition of clause 6 of Art. 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation, has not yet been implemented in the program. Be careful!
For the amount of VAT accepted for deduction:
- in the purchase book, a registration entry is made of the advance invoice, on which VAT was previously calculated, with the transaction type code “Advances received”;
- In accounting, the entry Dt 68.02 Kt 76.AV “VAT on advances and prepayments” is generated.
Accounting in 1C
Acceptance of VAT for deduction when offsetting advances received from the buyer is formalized by the document Formation of purchase ledger entries in the section Operations - Closing the period - Regular VAT operations.
To automatically fill out the Advances received , use the Fill .
Postings according to the document
The document generates transactions:
- Dt 68.02 Kt 76.AV – acceptance of VAT for deduction on offset advance payment.
The document generates movements in the VAT Purchases :
- record of an advance invoice with transaction type code 22 “Advances received” for the amount of accepted VAT for deduction.
Purchase Book report can be generated from the Reports – VAT – Purchase Book section. PDF
Let's check the calculation of the amount of VAT accepted for deduction when offsetting the buyer's advance using the following algorithm:
- Let's determine the amount of the credited advance payment, on which VAT was previously calculated - Dt 62.02 Kt 62.01 RUB 354,000.
- Let's carry out an arithmetic check of the VAT accepted for deduction from the credited advance payment using the formula:
VAT deductible = 354,000 * 18/118 = 54,000 rub.
To check the amount of VAT accepted for deduction, you can generate the report Turnover balance sheet for account 76.AB by counterparty.
The amount of VAT accepted for deduction under Kt 76.AB in 1C coincides with the verified amount. There is no balance on the invoice on which VAT was previously calculated. This means that VAT has been deducted correctly for the entire amount of the advance invoice.
VAT declaration
The VAT amount subject to recovery is reflected in the declaration:
In Section 3, page 170 “The amount of tax calculated by the seller from the amounts of payment, partial payment, subject to deduction from the seller from the date of shipment...”: PDF
- the amount of VAT subject to deduction.
In Section 8 “Information from the purchase book”:
- advance invoice issued, transaction type code "".
Accounting for advances issued.
Advances issued are an advance payment from the buyer to the supplier. Accounting for advances issued is kept in subaccount 60/02 - Advances issued. And accounting for settlements with suppliers if there were no advances is kept on subaccount (account) 60/01-Settlements with suppliers. Most likely, you can do without the subaccount 60/02-Advances, and keep everything on the subaccount 60/01-Calculations, and on the reporting date the advance payment if the payment exceeded the cost of goods and services, then just put it on the subaccount 60/02-Advance. In tax accounting (accounting for income tax and tax accounting), prepayment is not an expense.
Accounting for advances issued by transactions:
- Debit 60/02 Credit 51- 100,000 rubles. - Advance transferred to supplier. (No comment)
- Debit 41 Credit 60/01-100,000 rubles. - Goods received from the supplier. .(No comments)
- Debit 60/01 Credit 60/02-100,000 rubles. - Advance offset. (This entry is necessary because debit 60/02 has a balance of 100,000 rubles, and loan 60/01 has a balance of 100,000 rubles, i.e. at the same time we owe this supplier 100 tons of rubles and he owes us 100 tons of rubles, so that this does not happen, we close the amounts by subaccounts with one entry)
*In these transactions it is assumed that the supplier and buyer work without VAT
Accounting for advance VAT:
If the supplier has provided an invoice for the advance payment received, then VAT on the advance payment can be deducted. In order to deduct VAT from the listed prepayment, you need the following documents:
- Agreement.
- Invoice
- Payment order confirming the transfer of the advance.
How to take into account VAT on advances issued, exactly which account to use is not provided for by law, accordingly, according to the logic of the instructions for using the chart of accounts, you can use 76/VA for these purposes, in 1s this account is also used.
Postings for accounting for VAT on advances:
- Debit 60/02 Credit 51-120,000 rubles - Advance transferred to the supplier.
- Debit 68/VAT Credit 76/VA - 20,000 rubles. (120000/120*20) - Accepted for deduction of VAT on advance payment.
- Debit 41 Credit 60/01-100,000 rubles (120,000/120*100) - Goods received from the supplier.
- Debit 19 Credit 60/01-20,000 rubles (120,000/120*20) - VAT on purchased goods is reflected.
- Debit 68/VAT Credit 19-20,000 rubles. - VAT on purchased goods is accepted for deduction.
- Debit 60/01 Credit 60/02-120,000 rubles. Offsetting the advance. (This posting is necessary because there is a balance of 120,000 rubles on debit 60/02, and on loan 60/01 there is a balance of 120,000 rubles, that is, at the same time we owe this supplier 120 tons. Rubles and he owes us 120 so that this does not happen, we close the amounts by subaccounts with one entry)
- Debit 76/VA Credit 68/VAT-20,000 Set-off of VAT previously accepted for deduction (Since we debited account 68/02 twice for this trade transaction and was accepted for deduction twice, then one is extra, we restore this VAT).
So that the general picture is “drawn” in our head, let’s scatter these amounts among the main accounts and get:
Comments:
He.-The remainder is initial.
Ok.-Final balance.
Turnover - Turnover for the period.
After all the operations, we see that the budget owes us 20,000 rubles of VAT, 60/01 and 60/02 accounts are closed. 76/VA is also closed.
Reflection in the balance sheet of VAT on advances issued:
The author of this article has his own opinion on this matter, having read and understood the letter from the Ministry of Finance (the text of the letter will be below):
In the balance sheet, VAT on advances is deducted from Accounts Receivable. VAT on the advance payment is not reflected in the liability side of the balance sheet. Let’s say, according to the previous example, there were 2 transactions on the reporting date. 1 and 2. In the turnover there will be a debit of 120,000 rubles (60/02) and 20,000 rubles (76VA) Total 140,000 (120,000 + 20,000) receivables, in the balance sheet under the line Receivables we will reflect the amount of 120,000 rubles (140,000- 20000). This must be done because the listed advance includes 100,000 for the cost of the goods and 20,000 for the cost of VAT, which we set for reimbursement, i.e. the budget owes us this money.
Opinions of other authors:
On the balance sheet, the prepayment to the supplier is reflected minus VAT on the advance + VAT on account 76/VA. In our example, the calculation will be as follows if we only sent an advance but did not receive the goods. Prepayment minus VAT 100,000(120,000-20,000)+20,000 rubles=120,000 rubles. will be in the accounts payable line.
Here is what they say in the letter of the Ministry of Finance dated April 12, 2013 N 07-01-06/12203, think about this for yourself:
Regarding accounting issues, please note the following. In the case of an organization transferring payment or partial payment for upcoming deliveries of goods (performance of work, provision of services, transfer of property rights), the receivables are reflected in the balance sheet as assessed minus the amount of value added tax subject to deduction (accepted for deduction) in accordance with tax legislation, regardless of at what point the organization exercises its right to deduct value added tax granted to it by tax legislation.
Whatever method you use to calculate accounts payable, it will be the same in both the first and second cases.
The seller transfers the goods to the courier service for delivery to the buyer
Nowadays, a very popular method of trading is in which the client transfers an advance to the seller, after which the goods are delivered to the buyer by a third-party courier service. The prepayment receipt is obviously generated by the supplier. There are doubts regarding the shipment receipt: who is obliged to punch it - the seller or the courier?
Strictly speaking, issuing a cash receipt for the transfer of goods is the responsibility of the courier service. The justification is paragraph 1 of Article 4.3 of the Law on CCP. It says that cash register equipment is used by the person who makes payments to the buyer. Since transferring an order against an advance payment is a calculation, and the courier handles it, he must punch the cash register receipt.
But in life this option is extremely rare. Most often, a cash receipt is generated by the seller at the time of transfer of the goods to the courier. Next, the check is either sent to the client by email or transferred in paper form through a courier along with the order. Despite the fact that this approach is not entirely correct, problems with tax authorities, as a rule, do not arise.
Application of CVO for advances
All advances issued and received are formalized by an invoice, the details of which are recorded in the books of purchases and sales under the corresponding KVO transaction type codes.
In the sales book, the seller indicates the invoice data when issuing an advance to the contractor, and the buyer recovers VAT from the advance to the seller.
The seller makes an entry in the purchase book on the invoice from the advance payment issued to him in order to accept VAT for deduction, and the buyer makes an entry on the invoice from the advance payment issued to him in order to accept VAT from the seller for deduction.
At the same time, for the advance received, the seller records an invoice in the sales book according to KVO “02”, and the buyer with the same code in the purchase book indicates an invoice for the advance payment that he issued.
When the transaction has been completed, the buyer accepts VAT deduction from the received advance payment, which is possible only after the invoice for the advance payment is recorded by the seller in his purchase book with KVO “22”.
The seller, having shipped the goods, is obliged to restore the VAT deduction from the advance payment after the buyer indicates in his sales book an invoice from the advance payment with KVO “21”.
Upon shipment, the sales invoice is recorded by the seller and the buyer in the sales and purchases book, respectively, with the KVO “01”.
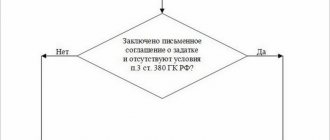
To avoid confusion about which QUOs to indicate when registering invoices, use the cheat sheet below. It clearly shows how the seller and buyer should act when recording transactions in the purchase and sales books.
How are prepayments, advances, and subsequent payments taken into account at the checkout?
Previously made prepayment or advance payment is taken into account in the cash receipt when calculating a separate form of payment ADVANCE PAYMENT. IMPORTANT The amount of the check by this form of payment is related to the previously made prepayment.
The provision of a loan is recorded in the cash receipt as a separate form of payment, SUBSEQUENT PAYMENT. IMPORTANT The amount of the check by this form of payment is linked to the subsequent payment towards the granted loan.
Each cash receipt indicates at least one of the forms of payment that are established by order of the Federal Tax Service dated March 21, 2021 N ММВ-7-20/ [email protected]
- CASH – indicates the amount of payment for the check in cash;
- NON-CASH - indicates the amount of payment for the check by any non-cash method;
- ADVANCE PAYMENT (ADVANCE) – indicates the offset amount from previously made payments. This line shows the amount of payment for the goods indicated in the receipt by a previously made payment;
- SUBSEQUENT PAYMENT (CREDIT) – indicates the amount of credit provided for the item specified in the receipt but not paid for;
- OTHER FORM OF PAYMENT or COUNTER PROVISION (EXCHANGE) - the amount of payment is indicated when correcting the cash receipt without changing the subject of payment and the amount of payment.
IMPORTANT When correcting an error made in a cash receipt, you must include the fiscal attribute of the corrected receipt in the new receipt. See Correcting errors on a check.
When should CCP be used for advance payments?
In the field of trade and services, situations often arise when it is convenient for the seller or buyer, and sometimes mutually beneficial, to space the moment of payment and the moment of receiving the goods or service. Federal Law No. 54-FZ of May 22, 2003 establishes that cash register equipment must be used for each calculation. Settlement, within the framework of 54-FZ, is considered to include, among other things, the acceptance and payment of funds in the form of prepayment and (or) advances, the offset and return of prepayment and (or) advances, the provision and repayment of loans.
Thus, CCP should be used both when receiving an advance payment or advance payment, and at the time of offsetting the advance payment or advance payment when transferring goods or providing services. And also when the seller ships the goods against future payments, i.e. sells in installments (provides credit). And also when the seller accepts money for previously sold goods to repay the loan provided. In each of these cases, which differ in payment methods, the seller is obliged to generate a cash receipt and transfer it to the buyer.
Samples of cash receipts for prepayment, advance payment, full or partial payment with offset of prepayment, as well as loan payment are presented on the pages:
How to punch a prepayment check
How to punch an advance check
How to punch a check to offset an advance or prepayment
How to pass a credit check
How to offset an advance on a loan check
Use cash register when crediting and returning an advance
From 07/01/2019, those who are required to use online cash registers must punch checks for offset and return of advances to cash registers.
Previously, the Federal Tax Service developed detailed guidelines for issuing checks for different forms of advance:
- generation of checks for prepayment for own goods, offset of prepayment, provision of a loan to pay for goods and when repaying a loan to pay for goods (letter of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated February 20, 2019 No. ED-4-20 / [email protected] );
- generation of receipts for the sale of goods using a gift card (letter of the Federal Tax Service 07/03/2018 No. ED-4-20 / [email protected] ).
In this material we will not dwell in detail on the general rules for making advances at the online cash register. Let's pay attention to technical aspects.
Let us only remind you that if the buyer did not receive the goods (service) at the time of payment, then both facts must be recorded: separate receipts must be issued for both the delivery of the goods (service) and for payment. This rule applies to any sales and forms of payment, including online.
Having received an advance payment from the buyer, do not forget to calculate and pay VAT. ConsultantPlus experts explained in detail how to do this correctly. Get trial access to the K+ system and upgrade to the Ready Solution for free.
The client buys a subscription for an unlimited number of visits to the gym (gallery, museum, etc.)
Many organizations offer clients to buy a subscription, which gives the right to an unlimited number of visits to any events: fitness classes, trips to the museum, etc. When paying for such a subscription, the seller generates a cash register receipt for the advance payment.
Then, each time the customer uses the subscription, the supplier must issue checks to offset the advance. But here difficulties arise, since it is impossible to calculate the cost of one visit in advance. Indeed, a person who paid, for example, 10,000 rubles for a subscription, can use it 5 times, or maybe 50 times. In the first case, the price of one visit will be 2,000 rubles (10,000 rubles / 5), in the second - 200 rubles (10,000 rubles / 50). Unfortunately, there is currently no complete clarity on how to correctly issue a cash receipt in such a situation. From our point of view, this situation can be viewed as if the seller is not selling services, but the right to use them. Then a cash receipt for shipment can be generated immediately after the subscription is delivered to the owner.