During the existence of the property tax, various changes occurred with it. Mostly they concerned objects and the tax base. For example, since 2015, the tax base began to be determined on the basis of the cadastral value, and organizations using UTII and the simplified tax system were included in the payment of tax. And in 2021, movable property returned to the object of taxation; it was again excluded from the list of objects of taxation. Let us recall the main aspects relating to the corporate property tax, which relates to regional taxes, and also inform you of the main changes in 2021.
Object of taxation
The objects of taxation are:
1) for Russian organizations - real estate , recorded on the balance sheet as fixed assets (Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
2) real estate located on the territory of the Russian Federation and owned by organizations on the right of ownership or right of economic management, as well as received under a concession agreement, if the tax base for such property is determined as their cadastral value entered into the Unified State Register of Real Estate ( Article 375 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation);
Real estate criteria:
- the presence of a strong connection between the object and the ground (for example, the construction of the object on a monolithic reinforced concrete foundation, the functional or technological connection of this object with other objects by underground communications (cable power lines laid in underground trenches, etc.));
- moving an object is impossible without disproportionate damage to its purpose (including the ability of the object to act in civil circulation as a separate object of civil rights (as opposed to objects that perform an exclusively servicing (auxiliary) function in relation to real estate, including land plots, buildings , structures); the presence of independent useful properties of the object that can be used in economic activity regardless of the land plot on which it is located and other real estate objects located on the common land plot).
These can be buildings, structures, unfinished construction projects, premises, parking spaces, residential buildings, apartments, rooms, cottages and garages. In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, real rights to real estate are subject to state registration in the Unified State Register of Real Estate. At the same time, property for which such state registration has not been carried out can also be recognized as real estate. To reasonably classify property as real estate, it is necessary to take into account not only the presence/absence of a record about the object in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, but also the presence of grounds confirming the strong connection of the object with the land and the impossibility of moving it without disproportionate damage to its purpose. For example, for capital construction projects, such grounds may be documents that contain information about the relevant characteristics of the object (technical accounting or technical inventory documents, permits for construction and/or commissioning of the object, design documentation, etc.).
Foreign organizations operating in the Russian Federation through permanent representative offices keep records of taxable items in the manner established in the Russian Federation for accounting.
Movable property recorded on the balance sheet as fixed assets from January 1, 2021 is not subject to property tax.
The list of objects not subject to taxation for corporate property tax is specified in the Tax Code (clause 4 of Article 374 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- land plots and other environmental management facilities (water bodies and other natural resources);
- property owned by the right of operational management to federal executive bodies and federal state bodies in which the legislation of the Russian Federation provides for military and (or) equivalent service, used by these bodies for the needs of defense, civil defense, security and law enforcement in the Russian Federation ;
- objects recognized as objects of cultural heritage (historical and cultural monuments) of the peoples of the Russian Federation of federal significance in the manner established by the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- nuclear installations used for scientific purposes, storage facilities for nuclear materials and radioactive substances and radioactive waste storage facilities;
- icebreakers, ships with nuclear power plants and nuclear technology service ships;
- space objects;
- ships registered in the Russian International Register of Ships;
- vessels registered in the Russian Open Register of Vessels by persons who have received the status of a participant in a special administrative region in accordance with Federal Law of August 3, 2021 N 291-FZ “On Special Administrative Regions in the Territories of the Kaliningrad Region and Primorsky Territory”;
- aircraft registered in the State Register of Civil Aircraft by persons who have received the status of a participant in a special administrative region in accordance with Federal Law of August 3, 2021 N 291-FZ “On special administrative regions in the territories of the Kaliningrad Region and Primorsky Territory”.
Taxable and non-taxable objects
The question that worries entrepreneurs most is what kind of property will be considered a taxable item. According to the law, the tax applies to both movable and immovable property. This means that the objects of payment become:
- property transferred to the organization for temporary use;
- property that is the subject of joint activity;
- property received by the organization under a concession agreement.
Also subject to the tax is the organization’s property that is part of its fixed assets. This group of property may include any investments, including material ones.
As for the organization’s real estate, this includes the following objects:
- land;
- subsoil with minerals;
- buildings located on the site (including unfinished ones);
- various kinds of objects (for example, maritime or air transport objects) that have passed state registration.
All other objects that do not fall into the category of real estate belong to the group of movable property. For example, vehicles, securities, etc. are considered such objects.
The list of tax-exempt objects in 2021 consists of the following items:
- areas related to environmental management;
- lands and objects related to military operations, civil defense needs, law and order, etc.;
- areas of historical and cultural value for the country;
- space objects;
- large sea vessels;
- icebreakers.
Please note that some types of property included in the first or second depreciation groups may also not be paid, but only if they were timely registered with the state.
Criteria for fixed assets
Fixed assets from an accounting point of view are assets that meet the following conditions:
- the object is intended for use in the production of products , performance of work, provision of services;
- the object is intended for use for a period exceeding 12 months ;
- subsequent resale of the object is not expected;
- the object is capable of generating economic benefits .
The criteria for fixed assets for tax purposes are somewhat different from those for accounting and are established by Chapter 25 of the Tax Code, namely, paragraph 1 of Article 256. In the Tax Code, fixed assets are classified as depreciable property. The following property is considered depreciable:
- Is owned or operated by the organization. Exception: fixed assets, the right to which is subject to mandatory state registration, are included in depreciable property from the moment the documents are submitted, clause 11 of Article 258 of the Tax Code;
- Used for the purpose of generating income;
- Intended for use over 12 months;
- Costing more than 40,000 rubles. From the beginning of 2021 For tax purposes, property with an original cost of 100 thousand rubles or more will be considered depreciable.
Please note: That property that meets all the criteria, but is less than the cost limit, is written off as material expenses.
The tax base
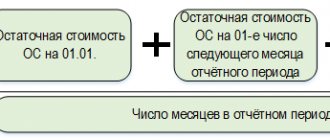
In general, the tax base for the property tax of legal entities is determined as the average annual value of property recognized as an object of taxation, and such property must be accounted for at its residual value.
Taking into account the changes of 2014, in relation to individual real estate objects, the tax base is now determined as their cadastral value. Since 01.01.2020, the Tax Code of the Russian Federation classifies not only fixed assets, but also any real estate owned by organizations under the right of ownership or right of economic management, as objects of taxation at cadastral value. Thus, it will not matter whether real estate is taken into account as a fixed asset or not - you will still have to charge and pay tax according to the cadastre. True, unless the region decides otherwise. Previously, if objects were not registered as fixed assets, tax, according to cadastral valuation, was not paid on them.
List of real estate taxed by legal entities at cadastral value (Article 378.2 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation):
- administrative and business centers and shopping centers (complexes) and premises in them;
- non-residential premises, the purpose, permitted use or name of which, in accordance with the information contained in the Unified State Register of Real Estate, or documents of technical registration (inventory) of real estate, provides for the placement of offices, retail facilities, public catering and consumer services, or which are actually used for placement offices, retail facilities, public catering and consumer services;
- objects of real estate of foreign organizations that do not carry out activities in the Russian Federation through permanent missions, as well as objects of real estate of foreign organizations not related to the activities of these organizations in the Russian Federation through permanent missions;
- residential premises, garages, parking spaces, unfinished construction projects, as well as residential buildings, garden houses, outbuildings or structures located on land plots provided for personal farming, vegetable gardening, horticulture or individual housing construction.
To pay tax at cadastral value, two conditions must be met:
- the cadastral value of the objects has been established;
- Regional laws indicate that objects are taxed at cadastral value.
If at least one of these requirements is not met, the tax on such objects must be calculated at the average annual cost, provided that they are taken into account in accounting as fixed assets. Exception: organizations on the simplified tax system and UTII. They do not pay tax on the average annual cost of new properties (clause 2 of article 346.11, clause 4 of article 346.26 of the Tax Code)
Data on cadastral value can be found:
- on the Rosreestr website;
- Public cadastral map;
- Government services.
Tax benefits
Preferences for calculating the total amount of the fee for Moscow and foreign organizations working in Moscow apply to movable and immovable property. Due to the abolition of the duty on movable property next year, tax rates apply to real estate, taking into account the added features:
- according to paragraph 7 of Art. 378.2 Tax Code of the Russian Federation Federal Law No. 117 dated 05.08.2000 (as amended on 27.11.2018), for objects whose tax base is the cadastral price, the fee is not paid if the buildings are included in the list corresponding to Order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia No. MMV-7-11/ 604 dated November 28, 2014. The register was introduced into the legislation of the Russian Federation in 2014 and is updated annually. If the organizational structure is not included in the published list, then a fee will have to be paid. The tax is calculated using a standard formula, taking into account the coefficient that applies to objects with a cadastral price;
- According to Letter of the Ministry of Finance No. 03-05-05-01/2969 dated January 26, 2016, residential buildings are exempt from paying the fee if the housing is not a fixed asset and is located on special land.
Thus, according to Art. 4 of Moscow Law No. 64 of November 5, 2003 (as amended on May 17, 2018), in Moscow the following are exempt from paying duties on real estate:
- government institutions;
- buildings owned by government authorities, including garages for trucks for transporting government-important cargo;
- companies for passenger intracity transportation (except for taxis);
- warehouses of enterprises where liquid and solid anti-ice substances are stored;
- construction of enterprises providing work for people with disabilities;
- multi-storey parking lots and garages;
- buildings of housing and communal services;
- buildings where chemicals are manufactured (sodium hypochlorite, acids, technical soda, de-icing agents);
- religious companies, societies for the disabled;
- investment work organizations that have entered into a contract with the Moscow government;
- buildings of railway organizations, including depots;
- buildings of closed mutual investment communities;
- premises located on the territory of the medical cluster.
Preferential tariffs, the amount of which is determined as a percentage of the accrued fee at the standard rate:
CH x K x 0.75, where
- 10% applies to sports buildings (football fields, arenas, etc.), medical facilities;
- The fee for structures intended to display river and sea inhabitants is calculated according to the formula: Сн - the amount of the fee;
- K - the ratio of the area of the building, which is not subject to rent, to the total area of the territory;
- 0.75 - preferential coefficient.
Preferences do not apply to buildings that are rented out. The right to use benefits begins and ends on the 1st day of the reporting period - quarter.
To receive preferences for depositing tax funds, you must present an act from the State Inspectorate about the fact of operation of the structure, which is classified as preferential. Documentation is provided from the 1st day of the reporting period for the current tax period.
Procedure for calculation and payment
The amount of property tax for organizations is calculated based on the results of the tax period to which the calendar year relates.
From 01/01/2020 Tax calculations for advance payments based on the results of reporting periods (I quarter, I half of the year, 9 months) do not need to be submitted (clause 2 of Article 386 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation will no longer be in force). However, the obligation to make advance payments has not been cancelled. They must be transferred to the budget according to the old rules.
Also, based on the results of each reporting period (first quarter, half of the year and nine), it is necessary to calculate the amount of advance payments in the amount of 1/4 of the product of the tax base and the tax rate. Thus, the final amount of tax payable to the budget is determined as the difference between the amount of tax for the tax period and the amounts of advance payments .
What is the difference between paying property tax by Russian and foreign organizations? Property tax and advance payments are subject to payment by the taxpayer in the manner and within the time limits established by the constituent entities of the Russian Federation.
However, in relation to property located on the balance sheet of a Russian organization, tax and advance payments are subject to payment to the budget at the location of the specified organization. Foreign organizations operating in the Russian Federation through permanent representative offices pay taxes and advance payments to the budget at the place where these permanent representative offices are registered with the tax authorities.
How to calculate your contribution
To calculate the property tax contribution, two formulas are used:
1. NS (tax rate) = PP (percentage) × BN (tax base).
2. BN = BN × PP – AP (advance payments), which were made periodically.
Example of calculating the contribution amount
The tax base of the limited liability company "Kolibri" is 2,500,000 rubles. The regional interest rate is set at 1.5%. During the year, the LLC made three advance payments in the amount of 5,000, 6,000 and 8,000 rubles. The total amount of all advance payments was 19,000 rubles.
Using the above formula, we obtain the following indicators:
BN = 2,500,000 rubles × 1.5% - 19,000 rubles = 18,500 rubles.
Deadlines for submitting reports
From January 1, 2021, taxpayers will report property taxes only based on the results of the tax period. There is no longer a need to submit quarterly calculations of advance payments to the Federal Tax Service. The form of the declaration, as well as the procedure and format for its submission, were approved by Order of the Federal Tax Service of the Russian Federation dated August 14, 2019 No. SA-7-21/ [email protected]
If a taxpayer is registered with several tax authorities of one constituent entity of the Russian Federation at the location of real estate, the tax base for which is determined as the average annual cost, then the taxpayer is assigned the right to submit a single property tax return. Now the taxpayer can choose the tax authority to which he will submit the declaration, but is obliged annually before March 1 of the year, which is the tax period, to notify the tax authority of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation about this. The notification form was approved by order of the Federal Tax Service of Russia dated June 19, 2019 No. ММВ-7-21/ [email protected]
The deadline for submitting the declaration is no later than March 30 of the year following the tax period.
Calculation of property tax for legal entities
Currently, taxes are calculated in most cases using accounting software. I'll tell you how we will do this in 2021 using a short example.
LLC "A" is registered in the Smolensk region, applies the general taxation system, has equipment worth 1,200,000 rubles and a car worth 600,000 rubles on its balance sheet. The property was purchased for a fee. In the Smolensk region, the tax rate on real estate is 2.2%, on movable property - 1.1%. Let's consider the procedure based on the above conditions.
- We set property tax rates. To do this, open “Settings” - “Taxes and reports” - “Property tax”. We set the tax rates approved for the Smolensk region for movable and immovable property;
- In the directory “Nomenclature” and “Fixed Assets” we fill in the data on our property: name, financially responsible person (MRP), method of recording expenses, benefits, inventory card;
- We accept equipment for registration. In the section “OS and intangible assets” we fill out the document “Receipt of equipment”. Then, in the “OS and intangible assets” section, fill out the “Acceptance for accounting” document. We reflect the initial cost of the equipment, useful life, and method of calculating depreciation;
- We accept the car for accounting. In the section “Fixed assets and intangible assets” we fill out the document “Receipt of fixed assets”, we fill in the initial cost, car accounting and depreciation accounts, useful life (service life);
- We perform month closing every month. The program automatically calculates depreciation and writes it off to the organization's expenses;
- When closing the quarter, the program automatically calculates the tax. In the balance sheet, property tax will be reflected in account 68.08.
If you do not use an accounting program or need to calculate some special case, we recommend an online calculator to calculate the property tax of organizations.
Tax rate
According to Art. 380 ch. 30 Tax Code of the Russian Federation Federal Law No. 117 of 08/05/2000 (as amended on 11/27/2018), federal rates and benefits are determined at a minimum. Property tax is a regional tax, therefore Moscow has established individual city tariffs for real estate. In Art. 2 of Moscow Law No. 64 provides information: the standard tariff is 2.2%, and for the cadastral value - 1.5%.
When calculating the total amount of property duty at the cadastral price, an indicator of 0.1 is used relative to non-residential buildings. This condition applies if:
- for a structure located in a building, NB - cadastral price;
- buildings are used for catering, retail sales, household, tourism or banking services to individuals;
- buildings - museums, art galleries and the like;
- the structures are located in the basement, first, second floors or near the pedestrian area.
For the latter condition to function, the active pedestrian zone must be located on citywide major streets.
Payment of property tax by organizations under special regimes
We are talking about the entry into force of Federal Law No. 52-FZ of 04/02/2014, according to which the obligation of these taxpayers to pay property tax in respect of real estate is established, the tax base for which is determined as its cadastral value. Who does this innovation apply to? The new rule applies both to organizations using the simplified tax system and to organizations using UTII.
What is the difference between innovations for simplifiers and companies on UTII? For companies using UTII, the obligation to pay property tax arose on July 1, 2014, while organizations using the simplified tax system began on January 1, 2015.
Local authorities are obliged to approve, in accordance with the established procedure, the results of determining the cadastral value of objects. Moreover, they must conduct a cadastral valuation of real estate at least once every five years. A list of real estate objects in respect of which the new taxation procedure applies must also be determined. Thus, it is important to remember that now, in relation to individual fixed assets, the tax base for corporate property tax is calculated based on the cadastral value. And the tax on such property of organizations will now have to be paid by both simplified organizations and organizations under imputation.
Firmmaker, August 2014 (updated in January 2021) Alina Marina When using the material, a link is required
Who sets the tax rate?
The amount of this tax depends on its interest rate, which is determined by local governments. The specific interest rate depends on the types of activities dominant in the region, the number of entities, etc. The legislation has established rules establishing the maximum percentage, which applies to all regions of the country. In 2021, property tax in Russia should not exceed the limit of 2.2%. This means that local governments have the right to use the tax percentage at the same level or less, but not more.
In addition, the tax rate depends on the category of the taxable object.